Iranian President Hassan Rowhani and Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe meet Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei in Tehran. Photo: Reuters
Tehran, for its part, claimed to have been set up, with its foreign minister Mohammad Javad Zarif saying “suspicious doesn’t begin to describe” the incident. So much, then, for hopes of mediation.
US President
, who had encouraged the Japanese leader’s visit, admitted on Twitter soon afterwards that when it came to negotiating, “they are not ready, and neither are we!”
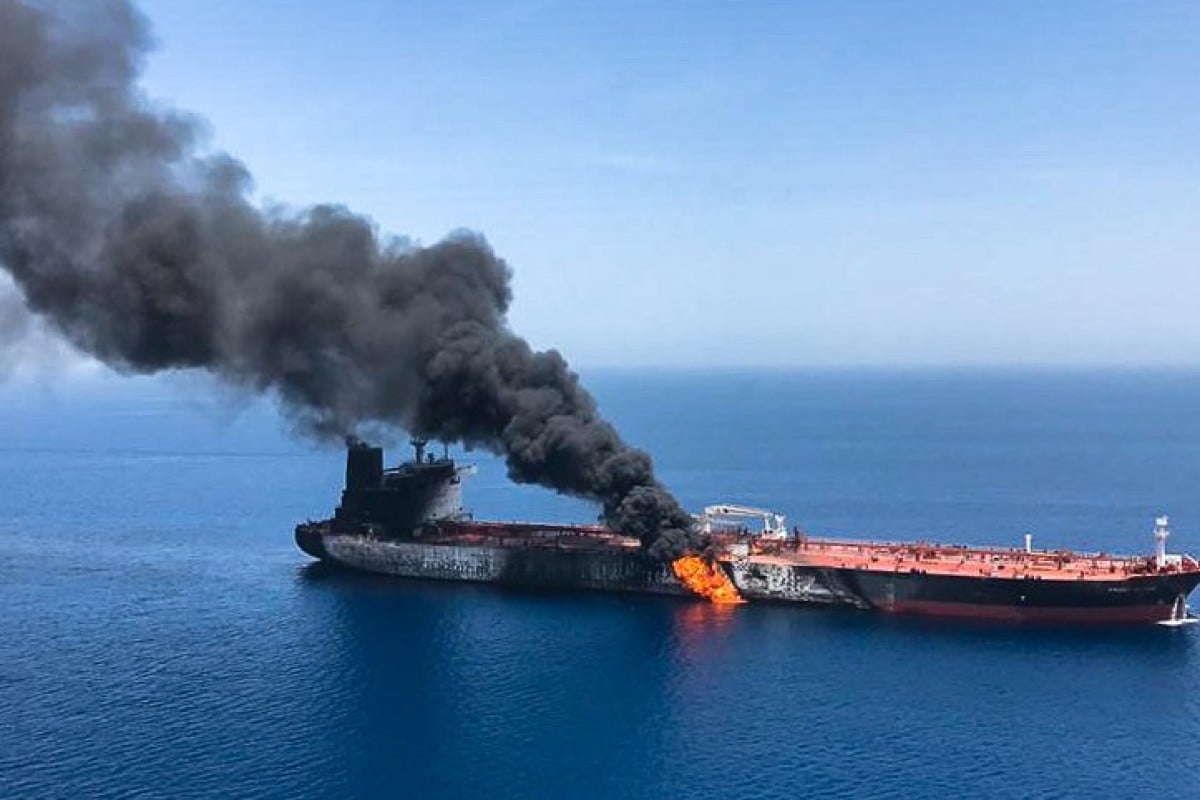
Still, the incident exposed more than just the naivety of those hoping for an Abe-led breakthrough. In raising the stakes in Washington’s confrontation with Tehran, it also threw the spotlight on Iran’s dwindling number of allies – and perhaps most significantly on its largest trading partner, China – which face mounting pressure to rethink the relationship.
Tanker attacks: world divided over Iran role as Saudi prince breaks silence
The day after the attack, China’s President
said Beijing would promote its ties with Iran “however the situation changes” – a comment made during a meeting with Iranian President Hassan Rowhani on the sidelines of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation summit in Kyrgyzstan – but diplomatic observers question just how far China can go in accommodating its controversial trading partner.
BEST FRIENDS FOREVER?
Iran has long been able to count on support from China, which accounts for 30 per cent of the Islamic republic’s exports and imports, and its willingness to defy US pressure is a gamble at least partly based on an assumption it can continue to count on Beijing’s support.
As Iran’s largest economic partner – Chinese direct investment in Iran hit a record high of nearly US$4 billion last year, according to data analysis project ChinaMed – Beijing already plays a key role in relieving US pressure on Iran, said Mohsen Shariatinia, assistant professor of regional studies at Shahid Beheshti University in Tehran.
But experts warn that reliance will come into question as China becomes increasingly hamstrung by its own problems.
China has enough problems of its own, starting with US pressure on Huawei. Photo: EPA
Chief among Beijing’s headaches are its
with Washington and the related assault on its
giant
– which, as analysts point out, originally ignited over allegations it was defying US sanctions on Iran. Beijing will also be well aware of the need to keep
, its second-biggest oil supplier and Tehran’s critic-in-chief, happy.
On the other hand, analysts say, China will be wary of being seen to abandon its old friend, as doing so would send a message to other nations at odds with Washington that they could no longer look to China as a diversification strategy.
“This could mean Chinese investment is vulnerable to US interference,” said Esfandyar Batmanghelidj, founder of Bourse Bazaar, a media company that supports business diplomacy between Europe and Iran.
Sanctions drive Iranian students away from US towards Asia
Doing so, Batmanghelidj said, would put a question mark over one of China’s most significant foreign policies of recent years – President Xi’s signature
to fund infrastructure across Eurasia.
THE BELT AND ROAD QUESTION
Tensions between Iran and the US have reached boiling point in recent weeks, after the Trump administration last month ended waivers on sanctions for nations importing Iranian oil – a move the US says is aimed at making the republic “radioactive to the international community” and which Rowhani has described as an “economic war against Iran”.
So far, China has largely stuck by the Islamic Republic, continuing to buy fuel from it despite the latest wave of US sanctions on Iranian oil that followed Trump’s decision last year to withdraw the US from the landmark 2015 agreement curbing Tehran’s nuclear development.
The deal had been widely lauded as a triumph of multilateralism and the dawning of a new economic era for Iran.
US releases video of ‘Iranian forces removing unexploded mine’ from ship
Part of its eagerness to support Iran has stemmed from the Islamic Republic’s key position in the Belt and Road plan. In 2017 alone, China signed deals for more than US$15 billion in Iranian infrastructure investment, according to the
mouthpiece China Daily.
Planned projects include high-speed rail lines, upgrades to the nation’s electrical grid, and natural gas pipelines. The two nations have also vowed to boost bilateral trade to US$600 billion in the next seven years.
“China sees Iran as its Western gateway, where not only is it a big market in itself, but it will also be the gateway to the rest of the
and ultimately to Europe for China,” said Anoush Ehteshami, professor of international relations at Durham University in Britain.
Nisha Mary Mathew, at the Middle East Institute in Singapore, said that China’s relationship with Iran was not just economic – but primarily strategic, with both nations envisioning an international order that was no longer dominated by the US and its Western allies.
DEFIANCE, FOR NOW
If the belt and road gives China good reason to stick with Iran, there are plenty of voices urging just that action. As Andrea Ghiselli at Shanghai’s Fudan University pointed out, US sanctions until now have only strengthened the hardline factions in Iran’s government.
The combination of the US withdrawal from the nuclear deal – which had the support of the international community – along with Europe’s tepid efforts to rescue it, may have emboldened those favouring resistance over negotiation.
Xi’s supportive comments in Kyrgyzstan were only the latest in a string of remarks from China that could encourage such factions.
If Trump kills off Huawei, do Asia’s 5G dreams die?
After China’s Foreign Minister Wang Yi met Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif in Beijing last month, the ministry’s spokesman Lu Kang said China’s economic relationship with Iran was “reasonable and lawful”.
Two months prior to that, China’s Minister of Commerce Zhong Shan, while hosting his Iranian counterpart Farhad Dejpasand, had claimed China’s “determination to maintain and develop the China-Iran comprehensive strategic partnership is unshakeable”.
Chinese President Xi Jinping with Iranian President Hassan Rowhani. Photo: AFP
Even so, the pressure is getting to some. In February, Foreign Minister Zarif temporarily resigned, in what Andrea Ghiselli at Fudan University in Shanghai called a clear sign of the “changing and precarious power balance with Iran’s foreign policy establishment”.
And nowhere is the pressure felt more keenly than the economy and China’s ability to serve as a lifeline.
“The real anxiety in Iran right now is about market share,” said Bourse and Bazaar’s Batmanghelidj. “If you’re exporting zero oil and your customers are buying oil elsewhere, you lose market share.
“The government wants to know if it agreed to go back to the negotiating table and the US promised sanctions relief, that there are people who are going to buy in significant volume.”
TURNING POINT: HUAWEI
For many analysts, the event most likely to have changed the equation in Beijing’s eyes is the arrest by the Canadian authorities of
, the chief financial officer of Chinese telecom giant Huawei.
Meng’s arrest came at the request of the US government, which claimed her company had violated sanctions by selling equipment to Iran.
Many observers saw the action as Washington’s way of signalling to Chinese companies that they would face repercussions if they eased the pressure on Iran by continuing to trade.
Huawei’s chief financial officer Meng Wanzhou. Photo: Reuters
“Going after Huawei was about going after Chinese enterprises – signalling that they can no longer trade with Iran with impunity,” Batmanghelidj said.
Since then, Chinese firms have shown increased skittishness towards trading with Iran. According to China’s General Customs Administration, Chinese exports to Iran declined by more than half between October 2018 and February 2019, from over US$1 billion to just under US$500 million.
Mohammad Ali Shabani, a researcher at the School of Oriental and African Studies in London, said other countries in the region were now watching to see if China would blink in the face of US pressure. “This could have dire consequences for China’s image as a reliable partner,” he said.
NOT JUST ABOUT AMERICA
There are reasons beyond US pressure that may factor into Beijing’s thinking. It has long stated its opposition to Iranian nuclear weapons development, and Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi has said that China is “ready” to take on “its due responsibilities and make a greater contribution to world peace and common development”.
Trade war: here are Beijing’s options – and none look any good
Zhao Hong, at the Research School of Southeast Asian Studies at Xiamen University, said that in stepping up as a responsible world power Beijing faced a dilemma over its approach to Iran.
“Chinese leaders have to painfully balance an impulse towards economic cooperation with Iran against other vital interests, including convincing Washington that China is a responsible stakeholder,” he wrote in the Journal of Contemporary China.
Saudi Aramco’s Ras Tanura oil refinery. The country is China’s second-largest oil supplier after Russia. Photo: Reuters
Then there is China’s relationship with Iran’s chief adversary, Saudi Arabia, to consider. Riyadh is China’s second-largest oil supplier, behind Russia, and it plays a central role in Beijing’s energy strategy.
According to International Trade Centre data, more than 12 per cent of China’s imported oil came from Saudi Arabia last year, compared with just 6 per cent from Iran. Last year, Saudi Arabia shipped 56.73 million tonnes of oil to China, or 1.135 million barrels per day.
Why would Kim Jong-un trust Trump, now that he’s ripped up Iran’s nuclear deal?
This April, China imported 6.3 million tonnes of oil from Saudi Arabia, nearly twice the 3.24 million tonnes it imported from Iran, according to China’s General Administration of Customs.
Iran’s comparatively small share of China’s oil imports market and its heavy reliance on China as a trading partner add up to a deeply uneven relationship, experts say, and it is this imbalance that will encourage the US that China may be open to rethinking its ties.
As Jon Alterman, director of the Middle East programme at Washington DC think tank the Centre for Strategic and International Studies, pointed out, while China was Iran’s largest trading partner, Iran represented less than 1 per cent of China’s international trade.
“Iran needs China,” Alterman said. “But to China, Iran is expendable.”
Source: SCMP