Image copyright NASA
Image copyright NASANasa says one of its satellites has found the debris of India’s Moon rover which crashed on the lunar surface in September.
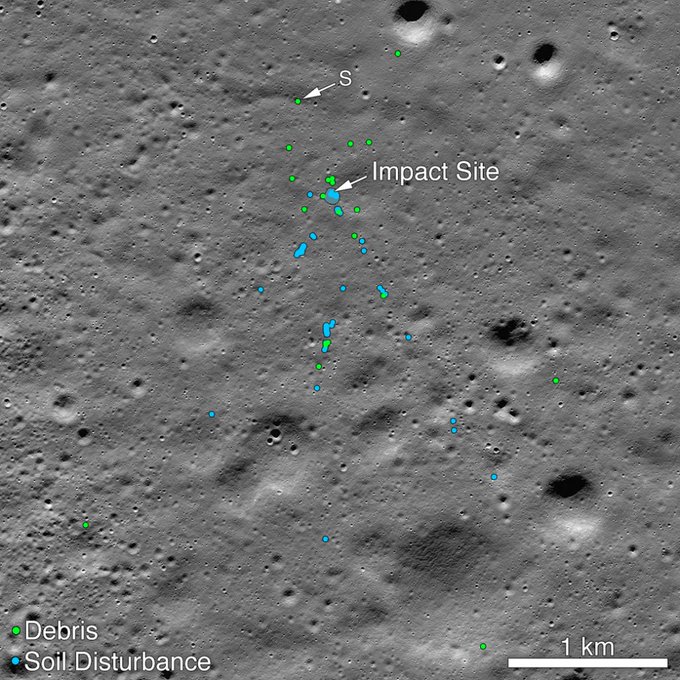
The space agency released a picture showing the site of the rover’s impact and the “associated debris field”.
Nasa has credited an Indian engineer, Shanmuga Subramanian, with helping locate the site of the debris.
Mr Subramanian examined a Nasa picture and located the first debris about 750m north-west of the crash site.
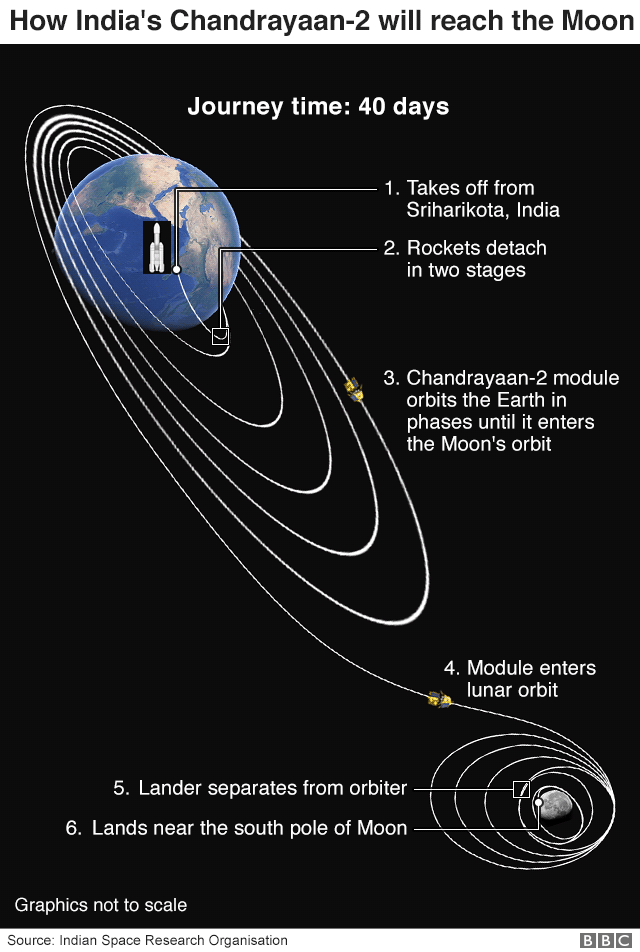
Chandrayaan-2 was due to touch down at the lunar South Pole on 7 September, over a month after it first took off.
It approached the Moon as normal until an error occurred about 2.1km (1.3 miles) from the surface, moments before it was to touch down.
The rover lost contact and had a “hard landing” about 600km (370 miles) from the South Pole in a “relatively ancient terrain”.
Announcing the discovery of the Vikram lander, Nasa tweeted a mosaic image of the site.
Many people had downloaded the image released by Nasa’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter Camera (LROC) team, a statement by the space agency said.
It said after receiving Mr Subramanian’s tip about the location of the debris, the LROC team “confirmed the identification by comparing before and after images”.
Mr Subramanian has tweeted an email sent to him by the space agency congratulating him for his effort.
Mr Subramanian said he had always “been interested in space” and had watched the July launch of the rocket.

What was this mission all about?
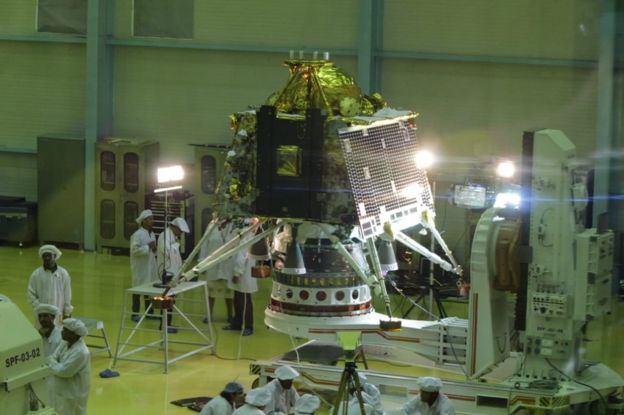
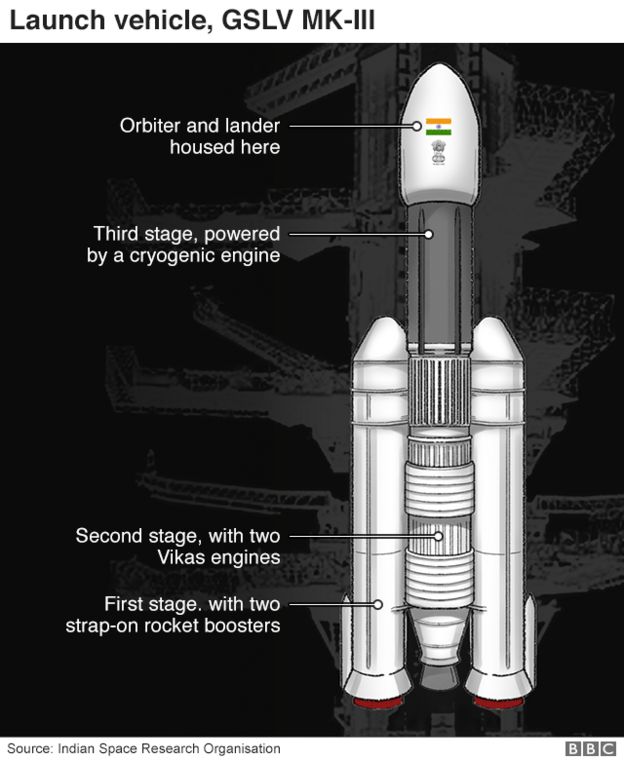
Chandrayaan-2 (Moon vehicle 2) was the most complex mission ever attempted by India’s space agency, Isro.
“It is the beginning of a historical journey,” Isro chief K Sivan said after launch in July.
The lander (named Vikram, after the founder of Isro) carried within its belly a 27kg (59lbs) Moon rover with instruments to analyse the lunar soil.
The rover (called Pragyan – wisdom in Sanskrit) had the capacity to travel 500m from the lander in its 14-day life span, and would have sent data and images back to Earth for analysis.
The mission would have focussed on the lunar surface, searching for water and minerals and measuring moonquakes, among other things.
Why would it have been significant?
A soft landing on another planetary body – a feat achieved by just three other countries so far – would have been a huge technological achievement for Isro and India’s space ambitions, says science writer Pallava Bagla.
He adds that it would also have paved the way for future Indian missions to land on Mars, and opened up the possibility of India sending astronauts into space.
For the first time in India’s space history, the interplanetary expedition was led by two women – project director Muthaya Vanitha and mission director Ritu Karidhal.

It was also a matter of national pride – the satellite’s lift-off in July was broadcast live on TV and Isro’s official social media accounts.
The mission also made global headlines because it was so cheap – the budget for Avengers: Endgame, for instance, was more than double at an estimated $356m. But this wasn’t the first time Isro has been hailed for its thrift. Its 2014 Mars mission cost $74m, a tenth of the budget for the American Maven orbiter.
Source: The BBC