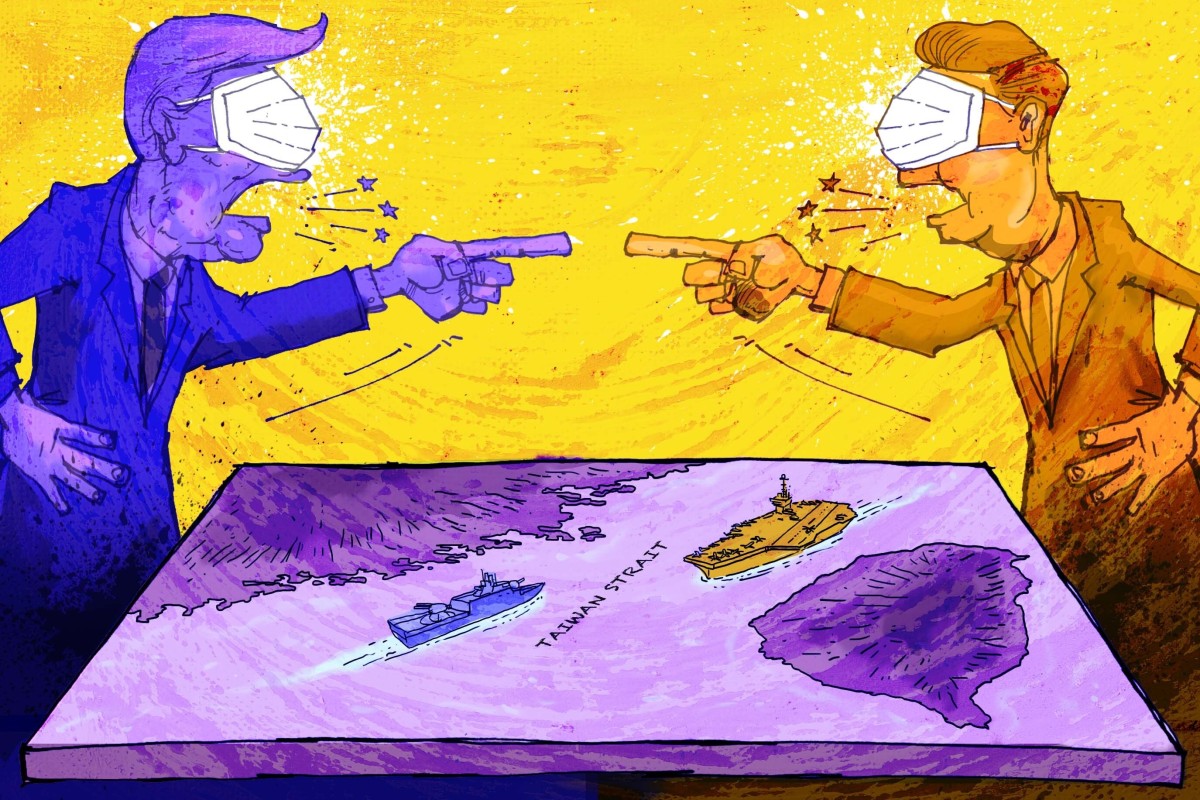
- Taiwan Strait and South China Sea are settings for China and the US to assert influence and defiance
- Analysts warn costly missteps and miscalculations are possible amid rift
This is the fourth in a series exploring the global backlash that China may face as a result of its actions and rhetoric during the coronavirus pandemic. This story examines the outlook from a military viewpoint, including relations in the South China Sea, with China’s neighbours and with the United States.
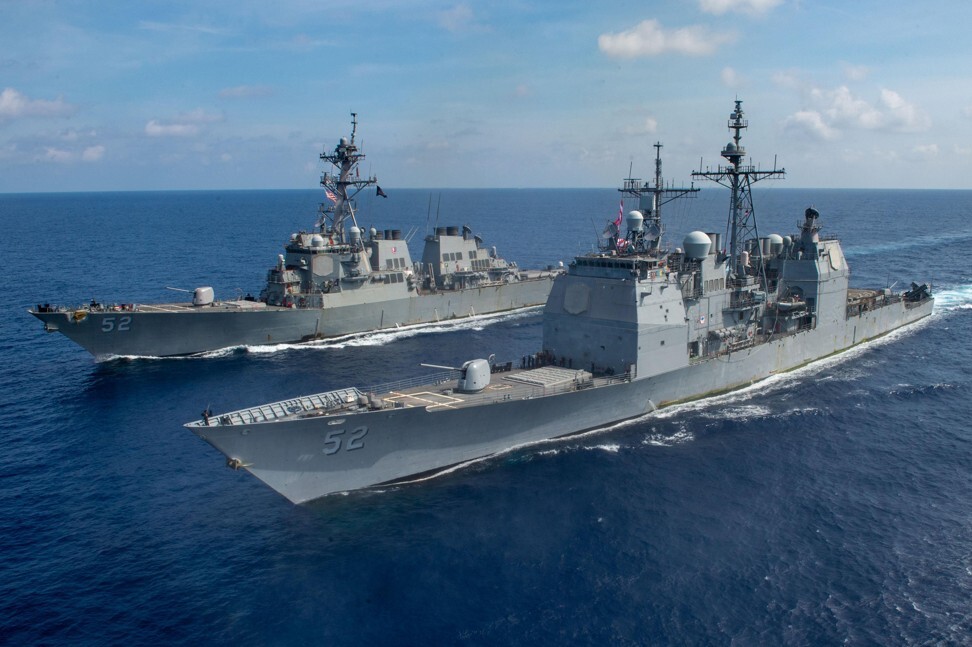
As the USS Barry, one of the US’ most advanced destroyers, sailed through the Taiwan Strait last Thursday, an officer on board posted a message on Facebook: “They don’t call us the Finest Forward Deployed Destroyer for nothing! Your Bulldogs always have the watch – together, we ensure a free and open Indo-Pacific!”
Based in Yokosuka, Japan, the guided-missile destroyer was no stranger to the sensitive channel separating Taiwan and mainland China. In fact, this was its second passage through the 180km [112-mile]-wide waterway – defined as part of the South China Sea under international protocol – this month.
As the Covid-19 global health crisis continues to rage around the world, infecting more than 3 million people and causing more than 210,000 deaths, military manoeuvres are being analysed to see if the pandemic has changed the balance of force in the region.
“These provocative acts by the US side … seriously violated China’s sovereignty and security interests, deliberately increased regional security risks and they could easily trigger unexpected incidents,” a spokesman of the command said.
The frequency of such tours has raised concerns among military observers and analysts that these exercises could lead to miscalculation as different countries use their militaries to jostle for greater influence or rattle the sabre amid the pandemic.
“Adversaries who think now is the time to challenge the #USA: you’re dangerously wrong,” United States Secretary of Defence Mark Esper tweeted in mid-April.
And on Wednesday last week he tweeted: “Do not test our resolve. Our service members continue to demonstrate why the American people call on the US military during the most trying times.”
into a deepening rift as officials from both sides engage in a blame game about delays that have allowed the contagious disease to spread.
Experts are now looking at how the pandemic will affect other aspects of China’s international relations.
Zhu Feng, a professor of international relations at Nanjing University in eastern China, expressed worry that Beijing and Washington had grown even further apart because of the pandemic.
“China and the US are supposed to work together to battle this world-sweeping deadly contagion, but what worries me most is that the geopolitical strategic competition and differences between the two countries have widened because of the pandemic,” he said.
Zhu said Washington’s growing cosiness with Taipei had also alarmed Beijing.
as they are called in Japanese.
On Tuesday last week, another US amphibious assault ship and a guided-missile cruiser joined with an Australian frigate.
They entered the contested waters off Malaysia, where a Chinese government survey vessel, the Haiyang Dizhi 8, has been operating close to a drill ship under contract to the Malaysian state oil company, Petronas, according to a report from Reuters citing regional security sources.
“The show of force of the US and Australian warships in the South China Sea was aimed at warning China: ‘The pandemic will not give you any opportunity to change the current balance of power [in the region]’,” Zhu said.
“And [it also means to] tell Malaysia and other Southeast Asian countries that no matter how the pandemic develops, the US is still Big Brother in the region,” he added.

“[Chinese President] Xi Jinping has said that the vast Pacific Ocean is big enough to accommodate both the PRC [People’s Republic of China] and the US. However the PRC’s build-up in the South China Sea and training exercises have, in the eyes of Americans, threatened the freedom of navigation and challenged the US predominance in maritime Asia.”
Drew Thompson, a former US defence official and now a senior research fellow at National University of Singapore’s Lee Kuan Yew School of Public Policy, wrote in a recent paper that China under Xi’s leadership has taken a more aggressive stance in dealing with its neighbours.
“Xi Jinping’s rise to power has heralded a new foreign policy that is more assertive and uncompromising toward China’s neighbours, the US and the rest of the world,” he wrote.
He warned that Xi’s assertiveness would put China’s diplomatic and defence policies at higher risk, especially given Beijing’s determination to resolve the Taiwan problem.
“The pandemic does not fundamentally change the military or strategic balance across the Taiwan Strait but it potentially increases the possibility of miscalculation if Beijing thinks its handling of the pandemic gives it a military advantage,” Thompson told the South China Morning Post.
But Collin Koh, a research fellow of the S Rajaratnam School of International Studies at Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University, cautioned that such an assumption was risky.
“It’s unwise to underestimate the resolve of the Trump administration, given that in recent times it’s been putting more focus on enhancing strategic ties with Taiwan, having seen the island as a crucial element to its Indo-Pacific strategy,” Koh said.
“US credibility is at stake if it’s shown to be unwilling to defend its allies.”
Michael Jones, former chief of staff of US Central Command, was quoted by the Military Times, a US-based military news website, saying it had become imperative for US diplomats to reach out abroad and explain Washington’s intention to avoid mistakes and misunderstandings.
“Covid-19 merely is a factor that can lead to miscalculation,” Jones was quoted as saying. “If they [US adversaries] were to assume this is one more distraction that would keep the US from responding to an attack or challenge, it could add to the possibility of miscalculation.”
Source: SCMP