- French leader calls for restraint and says he raised the topic ‘on several occasions’ during his visit
- Two sides find common ground on need to defend free trade and fight climate change as Donald Trump starts process of pulling US out of Paris Climate Agreement
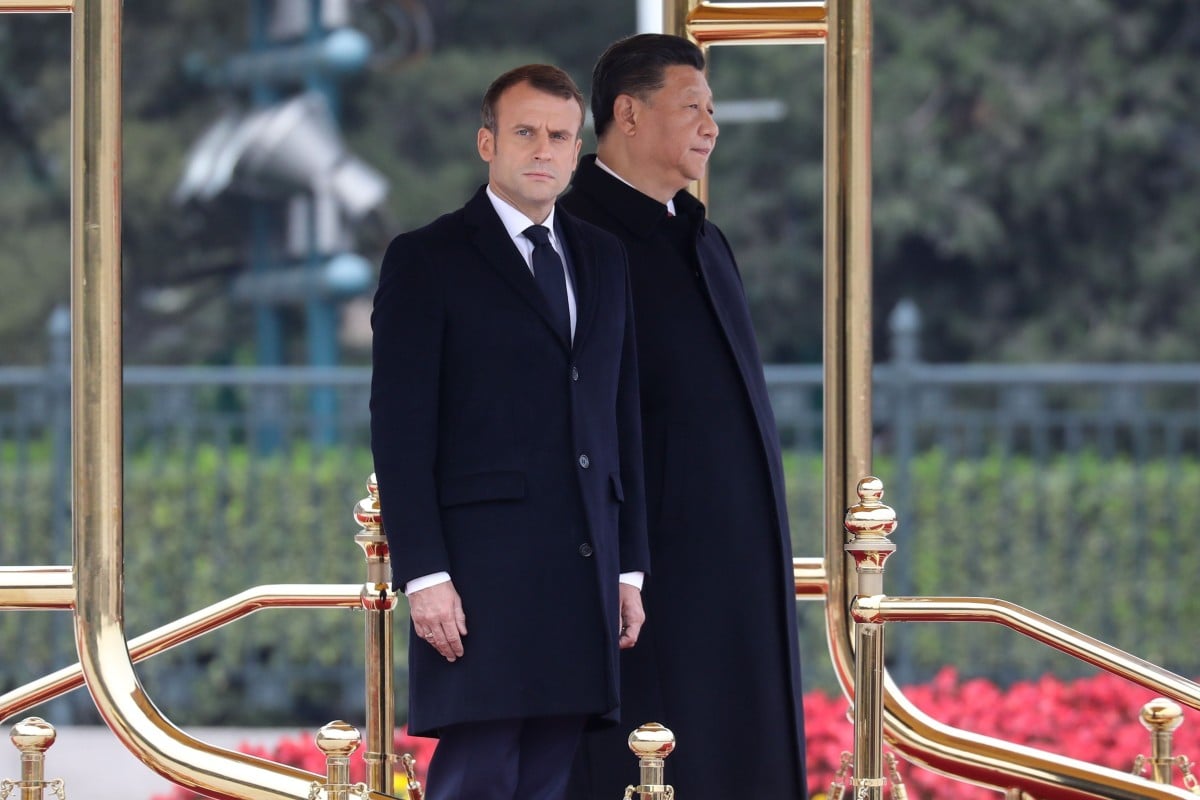
French President Emmanuel Macron said he raised human rights and the Hong Kong situation during his talks with his Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping on Wednesday.
Macron’s visit to China concluded with pledges to work together on climate change, but the French leader also said he also called for a de-escalation of the situation in the city through dialogue after months of protests.
Macron, who had promised to raise “taboo” topics during the visit, told a press conference: “I obviously raised this with President Xi Jinping on several occasions.
“We have repeatedly called on the parties involved to [engage in] dialogue, to show restraint, to de-escalate.”
Earlier the French and Chinese leaders had restated their commitment to protect free trade and pledged their continued support for the Paris Agreement as the United States begins the process of formally withdrawing from the global climate deal.
Macron expressed “regret” over “some countries’ negative attitude” towards environmental protection and the fight against climate change and pledged to work with China to halt the loss of biodiversity.
The French president’s office also released a statement on Wednesday that reaffirmed France and China’s joint support for the “irreversible” Paris Agreement.
With the European Union, China and Russia backing the pact, he added, “the isolated choice of one or another is not enough to change the course of the world. It only leads to marginalisation.”
The two countries also agreed to work together to develop joint nuclear power projects and signed a series of contracts worth US$15 billion.
The deals covered aeronautics, energy and agriculture, including approval for 20 French companies to export poultry, beef and pork to China.
An additional action plan released after the talks said French utility giant EDF and China General Nuclear Power should be encouraged to cooperate on projects in China or third countries, citing the joint efforts by the two companies to build nuclear reactors at the Hinkley Point C station in Britain as an example.
The two sides also committed to signing a contract for the construction of a nuclear fuel recycling plant in China, which would involve French energy giant Orano, by January 31.
Xi took what appeared to be a veiled swipe at the United States, which is still embroiled in a protracted trade war and other confrontations with Beijing.
“We advocate for mutual respect and equal treatment, and are opposed to the law of the jungle and acts of intimidation,” Xi said.
“We advocate for openness, inclusion and for mutually beneficial cooperation, and are opposed to protectionism and a zero-sum game.”
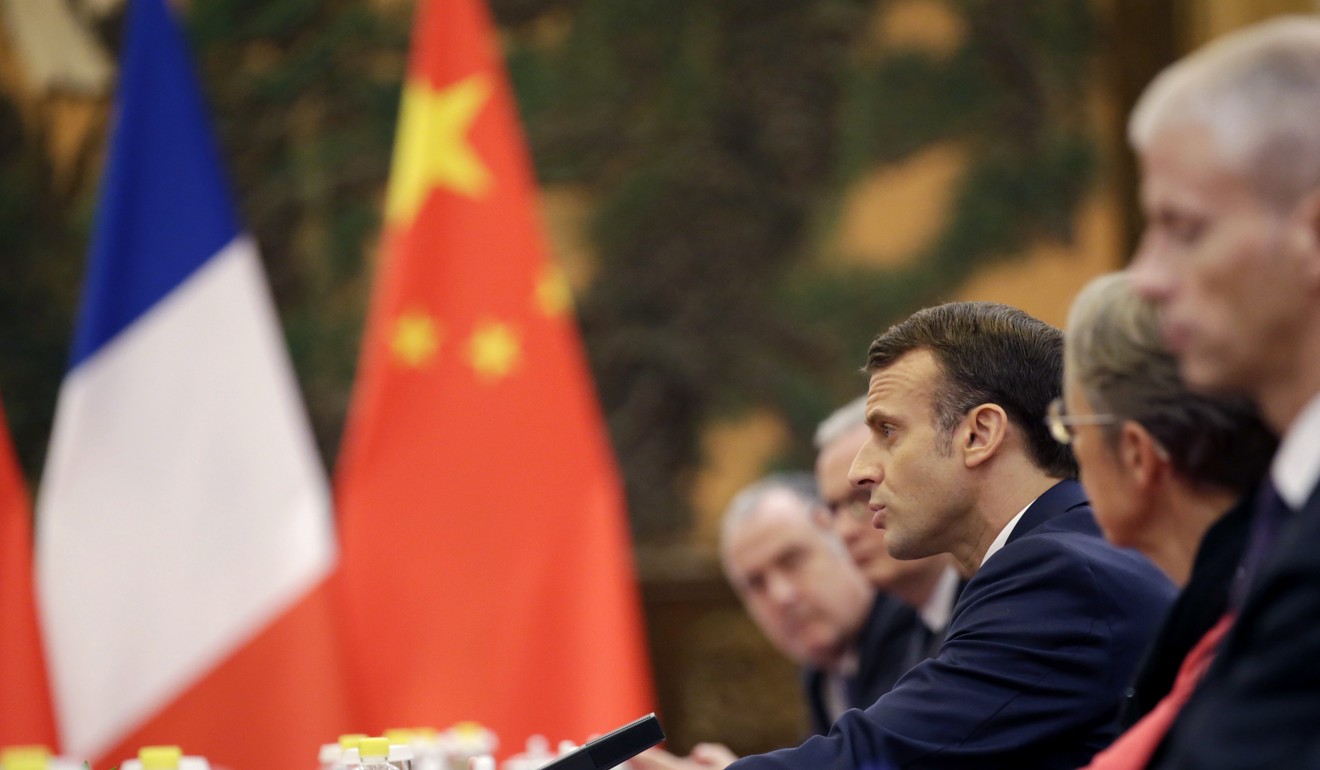
Macron said China and the European Union should work in partnership as the world became more unstable, calling on the two sides to further open up market access.
“We call again for trade multilateralism to respond to distortions that have appeared in the global economy, which have led to a profound rise in inequalities and imbalances that explain the surge of challenges to the international systems,” he said.
“China and Europe also share the same views that the trade war only leads to loss.”
Macron kicks off China visit with deal to protect wine and cheese from counterfeiting
Chinese state news agency Xinhua said the two countries agreed to work together to push forward with plans to assemble Airbus’s A350 model in China.
Meanwhile, Beijing Gas Group and French utility firm Engie will collaborate on a liquefied natural gas terminal and storage in the northern city of Tianjin, while France’s Total will set up a joint venture with China’s Shenergy Group to distribute liquid nitrogen gas by truck in the Yangtze River Delta.
The two countries also agreed to reach an agreement by the end of January 2020 on the cost and location of a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility to be built by Orano, formerly known as Areva.
Wu Libo a professor and director of the Centre for Energy Economics and Strategies Studies at Fudan University, said there was “great potential” for further cooperation between the two countries on nuclear energy.
“France has many useful experiences in the operation and management of nuclear power plants and its plants have long-term safe and stable operation records,” she said.

Jiang Kejun, a senior researcher at the Energy Research Institute of China’s National Development and Reform Commission, said China’s cooperation with France would add credibility to potential third-country projects.
“China has advanced third-generation technology but it’s still a new member in the nuclear power market, while France has developed nuclear energy for a long time, and its EPR reactors – a technology designed and developed in France – are in business operation,” he said.
Jiang said possible markets for the joint projects included Argentina and India, while some Middle Eastern states – such as Saudi Arabia and Qatar – had expressed interest in nuclear energy.
China’s ambassador hits out at Macron’s team for backing ‘hypocritical’ EU stance on Hong Kong
Tong Jiadong, professor of international trade at Nankai University, said that the deals between the two sides helped show that France and China could work together to counteract US unilateralism.
“Objectively speaking, this will form, or at least imply, an opposition to US unilateralism,” Tong said. “China hopes the cooperation between these two countries produces demonstrable effects for other EU member states.”
Ding Chun, a professor of European Studies at Fudan University, said he did not think the EU wanted to “choose a side” between the US and China.
But Ding continued: “If we are talking about free trade and multilateralism, there’s no doubt that the EU and China share a common view and can balance Donald Trump’s unilateralism.”
Source: SCMP