 Image copyright EPA
Image copyright EPAThe head of the religious sect that has been at the centre of the coronavirus outbreak in South Korea has apologised to the nation for the disease’s spread.
Lee Man-hee, the leader of the Shincheonji Church of Jesus, got on his knees and bowed at a news conference.
About 60% of the country’s more than 4,000 confirmed cases are sect members.
On Monday, South Korea – the biggest hotspot outside China – reported 476 new cases, bringing the total number to 4,212. It has recorded 26 deaths.
Prosecutors have been asked to investigate Mr Lee on possible charges of gross negligence.
“Although it was not intentional, many people have been infected,” said the 88-year-old leader. “We put our utmost efforts, but were unable to prevent it all.”

Of the confirmed cases, 3,081 are from the southern city of Daegu and 73% of these cases have been linked to the Shincheonji Church near there.
In the capital Seoul, the mayor urged the city’s 10 million residents to work from home and to avoid crowded places.
Why is the Shincheonji Church of Jesus in the spotlight?
Members of the fringe Christian group are believed to have infected one another and then travelled around the country, apparently undetected.
The group has been accused of keeping its members’ names secret, making it harder to track the outbreak.
But church spokesman Kim Shin-chang told the BBC they had provided a list of members, students, and buildings to authorities.
“We were worried about releasing this information because of the safety of our members,” Mr Kim said.
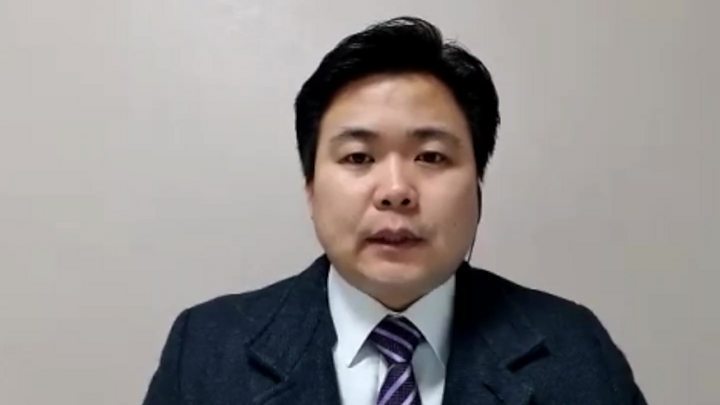

Mr Lee claims he is the second coming of Jesus Christ and identifies as “the promised pastor” mentioned in the Bible who will take 144,000 people to heaven with him.
The Shincheonji Church is labelled as a cult within South Korea and also in the Christian community, which results in the group often being discriminated against, persecuted or criticised, Mr Kim told the BBC.
What’s the global situation?
The number of people killed worldwide by the coronavirus has exceeded 3,000, as China reported 42 more deaths. More than 90% of the total deaths are in Hubei, the Chinese province where the virus emerged late last year.
But there have also been deaths in 10 other countries, including more than 50 in Iran and more than 30 in Italy.
Worldwide, there have been almost 90,000 confirmed cases, with the numbers outside China now growing faster than inside China.
In other developments:
- In the UK, where there are 36 confirmed cases, Prime Minister Boris Johnson has called a meeting of the emergency Cobra committee on Monday
- Indonesia – one of the world’s most populous countries – has announced its first confirmed cases of coronavirus, a 64-year-old woman and her 31-year-old daughter, currently being treated at a Jakarta hospital
- Iceland and Andorra also reported their first confirmed cases on Monday
- Share prices in Asia and in Europe rose after central banks pledged to intervene to help protect markets from the impact of the coronavirus. Concerns about the outbreak last week wiped more than $5tn (£3.9tn) from global stocks
- US sportswear giant Nike has closed its European headquarters in Hilversum city in the Netherlands after an employee tested positive for the virus
In the European hotspot of Italy, the number of infections doubled in 48 hours, the head of the country’s civil protection body said on Sunday.
There have been at least 34 deaths and 1,694 confirmed cases. Amazon said two of its employees in Italy have the virus and are under quarantine.
Countries including Qatar, Ecuador, Luxembourg and Ireland all confirmed their first cases over the weekend. On Monday, Ecuador reported five new cases of the disease, bringing the total number of infected patients in the country to six.
The US state of New York has also confirmed its first case. The patient is a woman in her 30s who contracted the virus during a recent trip to Iran. Two people have died in the US, both in the state of Washington.

What do I need to know about the coronavirus?
- WHAT ARE THE SYMPTOMS? A simple guide
- WAYS TO PREVENT CATCHING IT: How to wash your hands
- WHERE ARE WE WITH A VACCINE? Progress so far
- A VISUAL GUIDE TO THE OUTBREAK: Virus maps and charts
- WHAT DOES IT MEAN FOR MY HOLIDAY? Your rights as a traveller

What’s the situation in China?
China on Monday reported 42 more deaths, all in Hubei. There were also 202 confirmed new cases – only six of which were outside Hubei.
A total of 2,912 people have died inside China, with more than 80,000 confirmed cases of the virus.
- Diary of a life in locked-down Wuhan
- China pollution clears amid coronavirus slowdown
- How deadly is the coronavirus?
A spokesman from China’s National Health Commission said the next stop would be to “focus on the risks brought by the resumption of work”.
China’s economy has taken a hit – with factory activity falling at a record rate.
On Monday, a man was sentenced to death by a Chinese court for fatally stabbing two officials at a virus checkpoint, news agency AFP reported.
Ma Jianguo, 23, refused to co-operate with officials – though it is not clear what he was told to do – and stabbed two checkpoint officials.
 What has the WHO said?
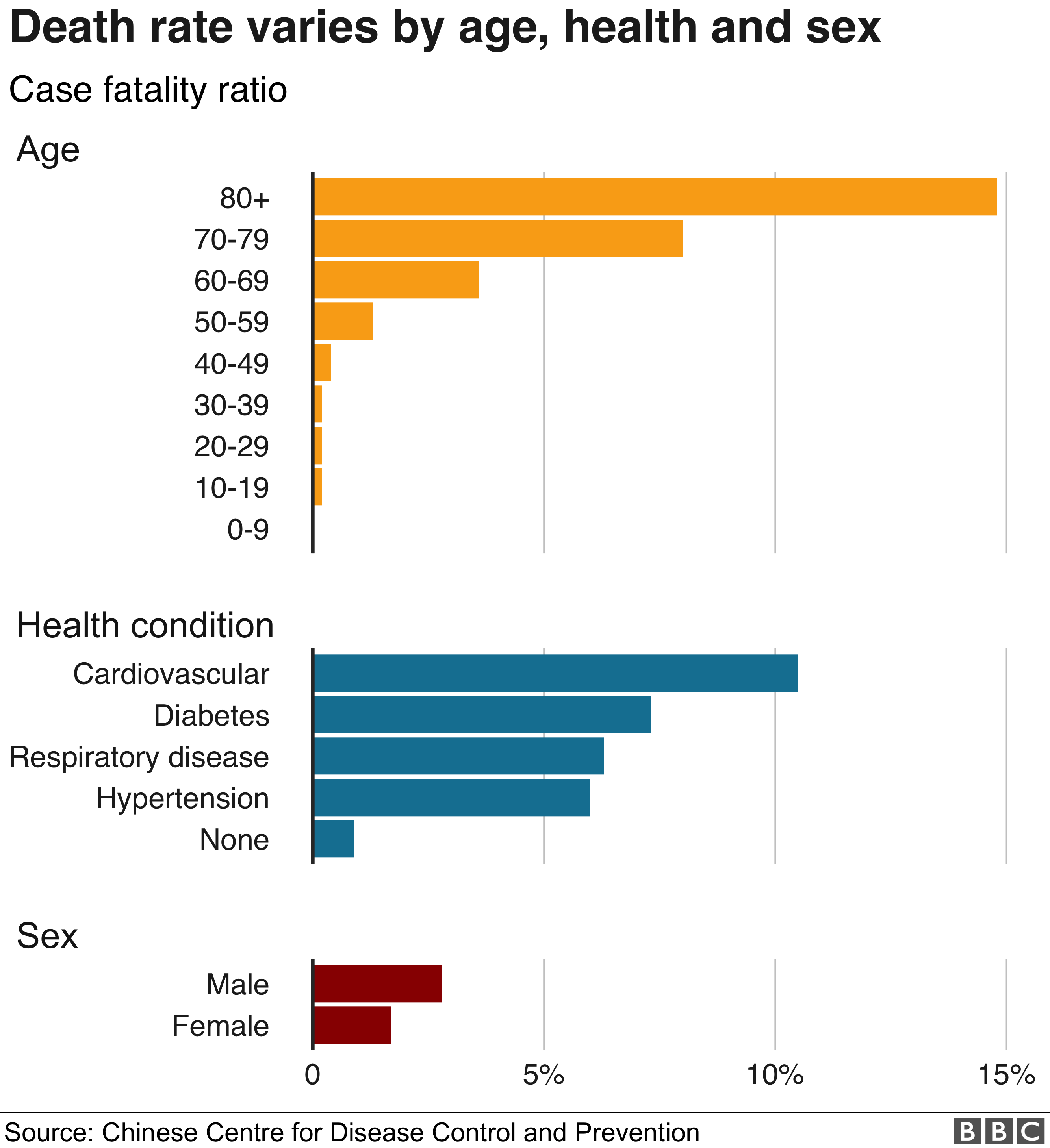
What has the WHO said?On Sunday, the World Health Organization (WHO) said the virus appears to particularly affect those over 60, and people already ill.
It urged countries to stock up on ventilators, saying “oxygen therapy is a major treatment intervention for patients with severe Covid-19”.
In the first large analysis of more than 44,000 cases from China, the death rate was 10 times higher in the very elderly compared to the middle-aged.
But most patients have only mild symptoms and the death rate appears to be between 2% and 5%, the WHO said.
By comparison, the seasonal flu has an average mortality rate of about 0.1%, but is highly infectious – with up to 400,000 people dying from it each year.
Other strains of coronavirus, such as Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome (Sars) and Middle East Respiratory Syndrome (Mers), have much higher death rates than Covid-19.
Source: The BBC




