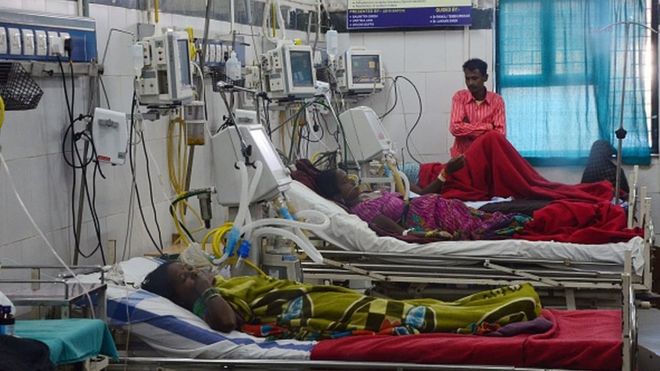
Staff members pose for a group photo to celebrate the timely finding of the return capsule of the trial version of China’s new-generation manned spaceship that successfully returned to the Dongfeng landing site in north China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region, May 8, 2020. The return capsule successfully returned to the Dongfeng landing site at 1:49 p.m. (Beijing Time) Friday, according to the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA). (Photo by Wang Jiangbo/Xinhua)
by Xinhua writers Quan Xiaoshu, Yu Fei and Li Guoli
JIUQUAN, May 8 (Xinhua) — The return capsule of the trial version of China’s new-generation manned spaceship successfully returned to the Dongfeng landing site in north China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region at 1:49 p.m. (Beijing Time) Friday, according to the China Manned Space Agency (CMSA).
The test was a complete success, the agency said.
Following the instructions from the Beijing Aerospace Control Center, the experimental spaceship applied the brake and entered the return orbit at 12:21 p.m., and its return capsule separated with its service capsule at 1:33 p.m.
After it re-entered the atmosphere and reached the designated altitude, the two deceleration parachutes and three main parachutes on the return capsule opened, slowing the flight speed of the spacecraft to the driving speed of an urban vehicle. Before touching down, its six airbags were deployed and inflated to help it land softly, according to the China Aerospace Science and Technology Corporation (CASC).
At 1:49 p.m., the return capsule landed safely. The search team found it in a timely manner and confirmed that the capsule structure was intact.
China launched the trial version of the new spaceship without a crew by the Long March-5B carrier rocket from the Wenchang Space Launch Center in southern China’s island province of Hainan on Tuesday.
The experimental spaceship flew in orbit for two days and 19 hours, during which it carried out a series of space science and technology experiments, including space 3D printing, said CMSA.
It also tested key technologies including the heat shielding and control during its re-entry into the atmosphere, as well as multi-parachute recovery and partial reuse, CMSA said.
The new-generation manned spaceship is an advanced space transport vehicle adapted to multiple tasks. It can be used not only in low-Earth orbit missions to support the construction of China’s space station but also for deep-space exploration, such as manned lunar exploration, CMSA said.
INNOVATIVE DESIGN
Developed by the China Academy of Space Technology (CAST) under the CASC, the test spaceship is nearly 9 meters tall and about 4.5 meters at its widest point. It weighs more than 20 tonnes.
Different from the three-capsule structure of Shenzhou spaceships currently in use, the new spacecraft comprises a return capsule, which is the command center and the living place for astronauts, and a service capsule, which provides power and energy, according to the CAST.
In Shenzhou spaceships, astronauts have to go back and forth between two smaller capsules for life and work. The return capsule of the new ship has a larger sealed space. In the future, it can be partitioned to set up a work area, entertainment area, dining area and bathroom, so as to provide a more comfortable living environment for astronauts.
The capsule can also be equipped with large screens for entertainment and display instruments connected with wearable devices so that astronauts can enjoy colorful space travel and be kept informed of the ship’s conditions.
The new design can also shorten the spaceship development cycle and cut the development costs, which will show a significant advantage in the future with space exploration activities more and more frequent, said Yang Qing, a designer of the experimental spaceship with the CAST.
Researchers have integrated the power supply, propulsion, fuel resources and other subsystems all into the service capsule, so that the same return capsule can be paired with different service capsules to meet variant needs of multiple tasks, including the space station operation and subsequent manned space missions.
The return capsule is designed to be reusable. Star sensors, computers and other high-value equipment have been moved from the service capsule to the return capsule so that they can be recycled after returning to Earth.
The return capsule is wrapped in two items of “clothing.” The inner layer is made of new metal materials and acts as a “wall” around the “driving cab.” The outer layer is made of a new type of light heat-resistant material, which can withstand ablation of thousands of degrees Celsius in the process of re-entry and return, according to Guo Bin, a member of the development team of the experimental spaceship with the CAST.
The new heat-resistant materials, adopted for the first time, are lighter than the traditional materials by 30 percent but have a greater heat-shielding capacity. They are also replaceable to improve the reusable rate of the capsule, Guo said.
The return capsule also uses a non-toxic propulsion system, consisting of 12 monopropellant-powered engines with the largest thrust in the world, which are applied for the first time in China to make the capsule safer and reusable, Guo said.
NEW DREAM SHIP
China started its manned space program in 1992 and has so far witnessed 11 astronauts enter space and return safely.
However, when the country eyes on the moon and the deeper space, Shenzhou spaceships and Tianzhou cargo spacecraft are no longer enough to meet its greater dreams.
Engineers started to create the new test spaceship from January 2017 and completed it in just three years after making many technological breakthroughs.
It can transport both people and goods, greatly expanding the capability and application of China’s manned spacecraft, Yang said.
It can be called a “space bus” as it is able to send six to seven astronauts at a time into low-Earth orbit. It can also be converted into a “space truck” according to new mission requirements, delivering a large number of supplies to the space station or bringing back space engineers’ test samples to Earth, Yang said.
The reliability, safety, comfort, economy and intelligence of the new spaceship have been greatly improved.
When in orbit, the ship’s “brain” — the guidance, navigation and control systems — can control the flight independently without relying on instructions from the ground. Through the combination of high-performance computers and sensors, the ship can fulfill emergency orbit entry, orbit raising and lift control autonomously, enabling it to cope with various emergencies quickly and calmly.
If a “health problem” occurs, the new spaceship can make a diagnosis itself through its intelligent system to locate the lesion and remove it temporarily or permanently. It will then share the work of the malfunctioning part by optimizing and recombining the functions of other parts, which can greatly simplify the ground control and support work.
In addition to the non-toxic monopropellant-powered engines, the new spacecraft adopts a series of advanced technologies, including the distributed integrated electronic system, solar cells with high conversion efficiency and multi-terminal human-computer interaction system, which improve its overall performance by leaps and bounds.
The engineers also installed a data acquisition system in the test spaceship, which will help provide scientific reference for the development and optimization of the follow-on versions of the new spaceship.
“The new and old spaceships will compliment each other. Just as trucks, buses and vans are all available on the road, there should be more transport means between space and Earth, and the new ship will enrich the selections,” Yang said.
Source: Xinhua