
A farmer picks apples at a fruit and vegetables specialized cooperative in Nanhai New Area of Weihai, east China’s Shandong Province, Oct. 23, 2019. (Xinhua/Guo Xulei)
Source: Xinhua
continuously updated blog about China & India

A farmer picks apples at a fruit and vegetables specialized cooperative in Nanhai New Area of Weihai, east China’s Shandong Province, Oct. 23, 2019. (Xinhua/Guo Xulei)
Source: Xinhua
NEW DELHI (Reuters) – Tens of thousands of runners have signed up for the Indian capital’s half marathon and other races on Sunday, officials said, despite the air quality hitting dangerous levels in one of the most heavily polluted cities in the world.
New Delhi’s air quality index was around 300 on Thursday, classified as very poor and meaning prolonged exposure can cause respiratory illness.
Delhi Chief Minister Arvind Kejriwal, who has described the city as a “gas chamber” in winter, has ordered emergency measures, including restricting the number of private vehicles on the roads under an “odd-even” scheme based on number plates.
Race organisers said pollution was a worry but they would take steps to reduce the impact on runners. Hours ahead of and throughout the race, the course will be sprayed with water.
“The air quality is a concern and will remain a concern, there is no question about it,” said Vivek Singh, joint managing director of Procam International that conducts the race sponsored by telecom operator Bharti Airtel.
“The measures that we take for those few hours to give our runners a good experience have worked in the past.”
The race has been moved this year to avoid a sharp rise in pollutants during Diwali, the Hindu festival of lights, when hundreds of thousands of firecrackers are lit.
But farmers burning crop stubble in the states north of Delhi have turned the air over Delhi toxic. The forecast for the next few days and into Sunday is “very poor”.
A record 40,633 people have signed up for the 21-km, 10-km and a 5-km races. Last year there were 34,916 runners, many of whom wore masks.
A former Olympic gold medallist, Carmelita Jeter of the United States, is the international event ambassador.
Doctors have advised citizens to restrict their outdoor activities and said runners must be made aware of the risks they are taking.
“Just two weeks before the odd-even scheme comes into play, how have the civic authorities allowed more than 30,000 people to expose themselves to toxic air?” asked said Desh Deepak, senior chest physician at the city’s Ram Manohar Lohia Hospital.
Source: Reuters
BEIJING, Sept. 23 (Xinhua) — Chinese President Xi Jinping extended greetings to farmers and people working in agriculture and rural areas as Monday marked the second Chinese farmers’ harvest festival.
Xi, also general secretary of the Communist Party of China (CPC) Central Committee and chairman of the Central Military Commission, sent his greetings via the China Central Television’s newly-launched channel dedicated to agriculture and rural affairs.
“With a solid foundation laid by agriculture, we have full confidence in development,” Xi said.
The achievements that China has made in the fields related to agriculture, rural areas and farmers are not only the outcomes of concerted efforts of the whole CPC and the country but also the results of hard work of all farmers and people working in agriculture and rural areas, he said.
Xi also congratulated on the launch of the new channel, expecting the channel to publicize agricultural policies, plans as well as new looks of farmers and rural areas in-depth.
Xi also expected the channel to lead the audience to pay attention to agriculture, care for the countryside and farmers, and contribute to poverty alleviation, reform and development in agriculture and the countryside, and the realization of rural revitalization.
The Chinese farmers’ harvest festival is the first national festival created specifically for the country’s farmers. Starting in 2018, the festival coincides with the Autumnal Equinox each year, which is one of the 24 solar terms of the Chinese lunisolar calendar and usually falls between Sept. 22 and 24 during the country’s agricultural harvest season.
The new channel is the first national all-media channel dedicated to agriculture and rural affairs. With daily 18-hour programs, the channel officially began broadcasting on Monday.
Source: Xnhua
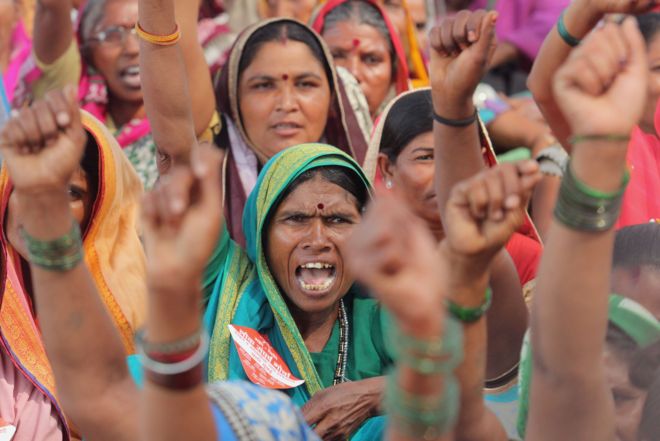 Image copyrightGETTY IMAGES
Image copyrightGETTY IMAGESThe plight of India’s farmers has been a major theme in the campaigns ahead of national elections, which get under way on 11 April.
Angry farmers have regularly taken to the streets demanding a better financial deal.
Many find themselves in debt and burdened by other liabilities they’ve taken on to buy seed, fertilisers and equipment.
Thousands of farmers commit suicide every year in India, although the reasons are often complex.

Pledge: Speaking in 2016, India’s Prime Minister, Narendra Modi, said farmers’ incomes would double by 2022.
Verdict: Official data shows farmers’ incomes were rising between 2013 and 2016. Income data for the past two years is not available but there are signs the rural economy is depressed. Unless there is a significant upturn, the doubling of farm incomes by 2022 is unlikely.


The government has now pledged to pay 6,000 Indian rupees (£64) a year to help farmers with holdings of less than two hectares (20,000 sq m), in a bid to reach that goal.
These moves have been criticised by opposition parties as vote-buying ahead of the elections.
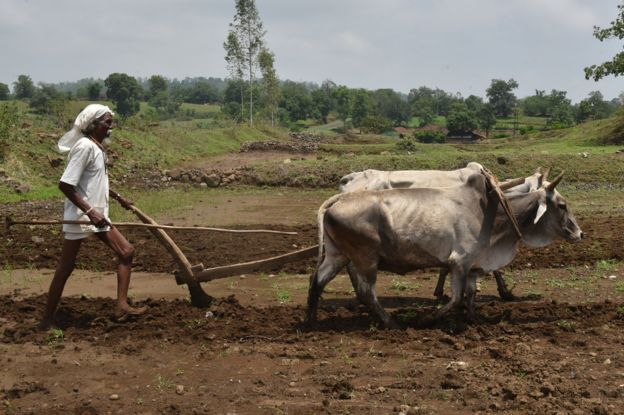
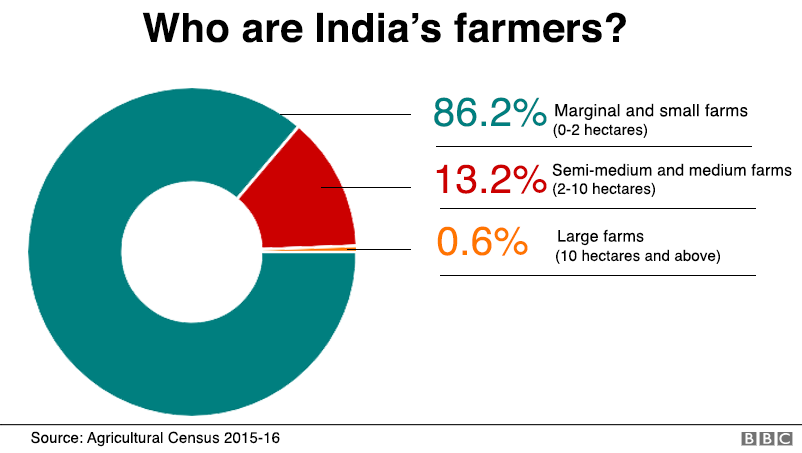
The agricultural sector employs more than 40% of the workforce in India, despite its shrinking contribution to the country’s gross domestic product (GDP), the total value of goods and services produced.

In 2016, the average monthly income of a farming household was about 9,000 Indian rupees (£100), according to a survey conducted by the National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development.
This report also found that farmers’ income had increased by 40% in the three years up to 2016, the latest year for which data is available.
However, there is evidence of a more recent slowdown in the rural economy.
According to one estimate, farm income, which had grown by more than 14% in the year to 2017, slumped to just over a 2% growth rate between 2017 and 2018.
And in several state elections in December 2018, the ruling BJP fared poorly – something put down to growing discontent in rural areas.
Droughts, bad weather and a lack of modern equipment have plagued Indian agriculture for decades.
In addition, many of India’s farmers work on vulnerable small or marginal holdings.
The current administration has introduced pro-farming policies that include:
But it’s also faced criticism for other policies that have negatively affected farmers – such as the sudden decision to 2016 withdraw the 500 and 1,000 rupee notes from circulation in a bid to tackle the black economy.
 Image copyrightGETTY IMAGES
Image copyrightGETTY IMAGESA very good harvest in any year will result in a sharp fall in the price of a commodity.
This helps keep food prices in check for urban consumers but is not so good for rural producers.
To counter this, the government sets a minimum purchase price for major agricultural products each year.
However, a recent official report pointed out serious shortcomings of these price controls.
It cited a lack of awareness among farmers, delays in payments and insufficient facilities to enable farmers to store produce at government-controlled warehouses.
At various times over the years, national and state governments have also announced loan waivers for farmers to write off their debts.
These schemes are expensive and not everyone qualifies for help.
Source: The BBC
BEIJING, March 14 (Xinhua) — Farmer Zhao Huijie, spiced with humor when speaking at panel discussions at the second session of the 13th National People’s Congress (NPC), China’s national legislature, has a clearer vision for the development of her village.
The 48-year-old woman from north China’s Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region has fought for fortune for her fellow villagers after she became the village Party chief in 2009, and now for the interest of more people in rural China now that she is a deputy to the NPC.
At the ongoing second session of the 13th NPC, Zhao submitted a suggestion on pollution control in animal husbandry and farming in rural areas.
“Random disposal of livestock waste has not only damaged the rural environment, but also polluted groundwater,” she said, advising the government to fund major livestock farms in harmless waste treatment.
She also suggested the government to subsidize farmers to use degradable plastic films to protect the environment.
Unlike legislators in the West who make a career of politics, NPC deputies are from all walks of life and work part-time. Of the nearly 3,000 national lawmakers, more than 15 percent are workers and farmers.
Zhao, an ethnic Manchu, is also one of the 400-plus ethnic minority deputies.
URBAN WOMAN’S RURAL LIFE
Born into a worker’s family, Zhao worked at a gold mine in the city of Chifeng, Inner Mongolia, where she got married in 1991.
“He was four years older than me. I think it was a perfect match considering I am talkative, while he is quiet,” Zhao said of her husband.
Their daughter was born in 1992. In the same year, the gold mine went bankrupt, forcing the couple back to her husband’s home in Xiaomiaozi Village.
Located between two mountains with a river traversing through, Xiaomiaozi was known for its poverty back then. Shabby houses, bumpy roads and barren farmland formed the major landscape, and the only crop villagers grew was corn.
To make ends meet, Zhao’s husband found a job in town, and she rented a small plot of farmland at home.
She had to learn how to farm from scratch, including driving a horse to plow in the field. When she was farming, she had to place her baby on the field ridge.
“I didn’t want to depend on my parents after getting married. If the other villagers could get used to the country life here, how could I not?” she said.
In 1995, she started teaching at the village elementary school. Four years later, she was assigned to take charge of family planning and women’s work in the village.
“I was familiar with every household — newborn babies, young brides marrying into our village, and the elderly,” Zhao said.
In 2009, she was elected unanimously as the village Party chief.
As soon as she took office, Zhao was asked to attend “a meeting” in the township.
“It turned out to be a training for Party chiefs of backward villages. That was shameful,” she said, determined to change the situation.
NEW ROAD, NEW LIFE
The first thing she decided to work on was to build a concrete road, as she found corn buyers were reluctant to come due to the bumpy roads. Higher transport costs even dragged down corn prices in the village.
For more than a year, Zhao visited door to door to persuade villagers to relocate to give way to the road. She talked so much that she was diagnosed with sphagitis, and had to undergo a surgery.
“I liked singing in the past, but after the surgery, I could never hold a high note,” she said.
After the road project was completed, Zhao had a bridge built, ending the days when villagers had to trek in waters to cross the river.
In 2013, when Zhao engaged herself in the bridge project, she broke her left arm and knee in a road accident.
“After work, I was riding my motorcycle in the dark when a donkey rushed on to the road. I was thrown away along with the vehicle,” she said.
Instead of lying in bed, Zhao insisted going to the construction site on crutches, touching the villagers and drawing more and more followers.
Li Yongbo, a villager who used to work in Beijing, was persuaded home and led the farmers to grow traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) such as balloon flower root, which secures three times the income of corn.
According to Li, the sandy soil, big day-and-night temperature difference and easy access to irrigation made the village an ideal place for TCM plantation.
The village has expanded the TCM plantation areas to more than 200 hectares now, producing more than 4,000 tonnes of TCM every year. A TCM processing workshop has been established, further doubling the income from mere TCM plantation.
The per capita income of the village reached 14,000 yuan (2,087 U.S. dollars) in 2018, 10,000 yuan more than the levels of 2010.
“As villagers get rich and spend more, my tiny store now can bring me more than 100,000 yuan of profit every year,” grocery runner You Junguang said.
Last year, Zhao was elected as a deputy to the 13th NPC. She suggested utilizing private investment in rural development.
“To my delight, the Ministry of Finance replied to me, accepting my suggestion and pledging to encourage private investors to contribute to revitalizing the rural areas.”
Zhao said they had registered “Xiaomiaozi Village” as a brand, and were talking to a tourism company on cooperation to entice tourists with the village’s Manchu and Mongolian ethnic cultures, as well as its beautiful landscape.
After graduating from college, Zhao’s daughter found a teaching job in Changsha City in central China in 2014. Her son is studying in a senior high school in Chifeng City. Zhao is too busy to visit them.
“I feel guilty because I have rarely taken care of my kids. But I hope I can set an example for them by trying my best to do everything, be it vital or trivial, and making positive contribution to the society,” she said.
Source: Xinhua
LHASA, March 6 (Xinhua) — To conserve the ecosystem while eradicating poverty, southwest China’s Tibet Autonomous Region hired 309,000 farmers and herders as forest rangers in 2018, bringing the total number of people engaged in environmental protection to 667,000.
Average annual subsidies in the jobs increased to 3,500 yuan (522 U.S. dollars), according to the regional department of ecology and environment.
Last year, Tibet invested 10.7 billion yuan in environmental protection funds, with 74,133 hectares of trees planted and forest coverage rising to 12.14 percent.
The region also invested 100 million yuan in enhancing the ecology along the upper reaches of the Yangtze, China’s longest river.
“Protecting the forests is equal to protecting our homeland,” said a local Tibetan forest ranger.
The implementation of a series of measures contributed to environmental protection, making Tibet one of the areas with the best ecological environment in the world, authorities said.
Source: Xinhua
continuously updated blog about China & India
continuously updated blog about China & India
continuously updated blog about China & India