 Image copyright EPA
Image copyright EPAIndia is set to re-attempt the launch of its second lunar mission a week after it halted the scheduled blast-off due to a technical snag.
Chandrayaan-2 will be launched at 14:43 local time (09:13 GMT) on Monday, space agency Isro said.
It added the spacecraft was ready “to take a billion dreams to the Moon – now stronger than ever before”.
The space agency hopes the $150m (£120m) mission will be the first to land on the Moon’s south pole.
The countdown on 15 July was stopped 56 minutes before launch after a “technical snag was observed in [the] launch vehicle system”, according to Isro. Indian media have reported that a leak from a helium gas bottle in the cryogenic engine of the rocket was to blame.
The fuel from the rocket was drained and the scientists resolved the glitch.
“It was a simple to fix [but it was] a serious problem that could have resulted in total failure,” says a source at Isro.
Isro thanked people for supporting the mission despite the delay.
India’s first lunar mission in 2008 – Chandrayaan-1 – did not land on the lunar surface, but it carried out the first and most detailed search for water on the Moon using radars.
Chandrayaan-2 (Moon vehicle 2) will try to land near the little-explored south pole of the Moon.
The mission will focus on the lunar surface, searching for water and minerals and measuring moonquakes, among other things.
India is using its most powerful rocket, the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle Mark III (GSLV Mk-III), in this mission. It weighs 640 tonnes (almost 1.5 times the weight of a fully-loaded 747 jumbo jet) and at 44 metres (144ft) is as high as a 14-storey building.
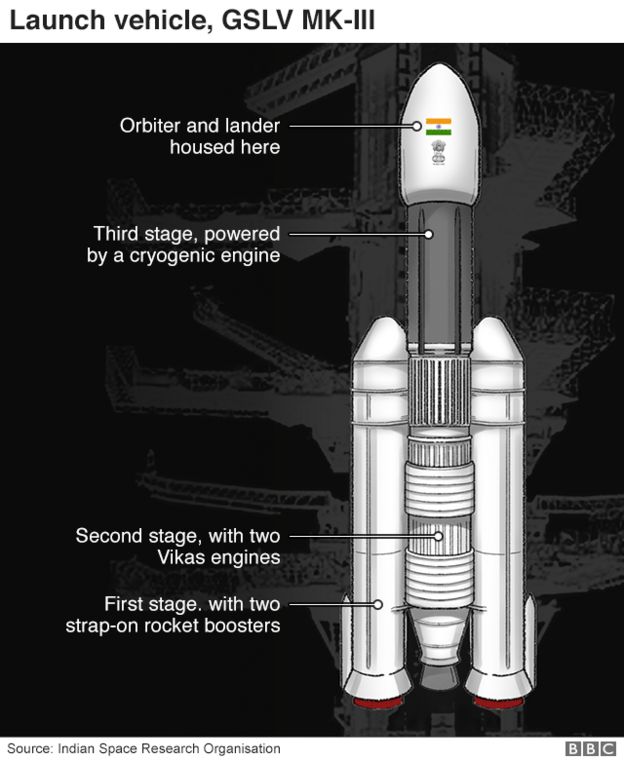
The orbiter, which has a mission life of a year, will take images of the lunar surface, and “sniff” the tenuous atmosphere.
- The women scientists who took India into space
- Israeli spacecraft crashes on Moon
- Is India ready to send someone to space?
The lander (named Vikram, after the founder of Isro) weighs about half as much, and carries within its belly a 27kg Moon rover with instruments to analyse the lunar soil. In its 14-day life, the rover (called Pragyan – wisdom in Sanskrit) can travel up to a half a kilometre from the lander and will send data and images back to Earth for analysis.
“India can hope to get the first selfies from the lunar surface once the rover gets on its job,” Dr K Sivan, the Isro chief, said before the first launch attempt.

How long is the journey to the Moon?
The launch is only the beginning of a 384,000km (239,000-mile) journey – Isro is still hoping the lander will touch down on the Moon on 6 or 7 September as planned, despite the week-long delay of the launch.
The journey of more than six weeks is a lot longer than the four days the Apollo 11 mission 50 years ago took to reach the Moon- and land humans on the lunar surface for the first time.
In order to save fuel, India’s space agency has chosen a circuitous route to take advantage of the Earth’s gravity, which will help slingshot the satellite towards the Moon. India does not have a rocket powerful enough to hurl Chandrayaan-2 on a direct path. In comparison, the Saturn V rocket used by the Apollo programme remains the largest and most powerful rocket ever built.
“There will be 15 terrifying minutes for scientists once the lander is released and is hurled towards the south pole of the Moon,” Dr Sivan said.

Earlier this year, Israel’s first Moon mission crash-landed while attempting to touch down.

Nearly 1,000 engineers and scientists have worked on this mission. But for the first time, Isro has chosen women to lead an interplanetary expedition.
Two women are steering India’s journey to the Moon. While programme director Muthaya Vanitha has nurtured Chandrayaan-2 over the years, it will be navigated by Ritu Karidhal.
Source: The BBC





