22/05/2020
- The tech investment push is part of a fiscal package waiting to be signed off by the National People’s Congress, which convenes this week
- This initiative will reduce China’s dependence on foreign technology, echoing objectives set forth previously in the ‘Made in China 2025’ programme
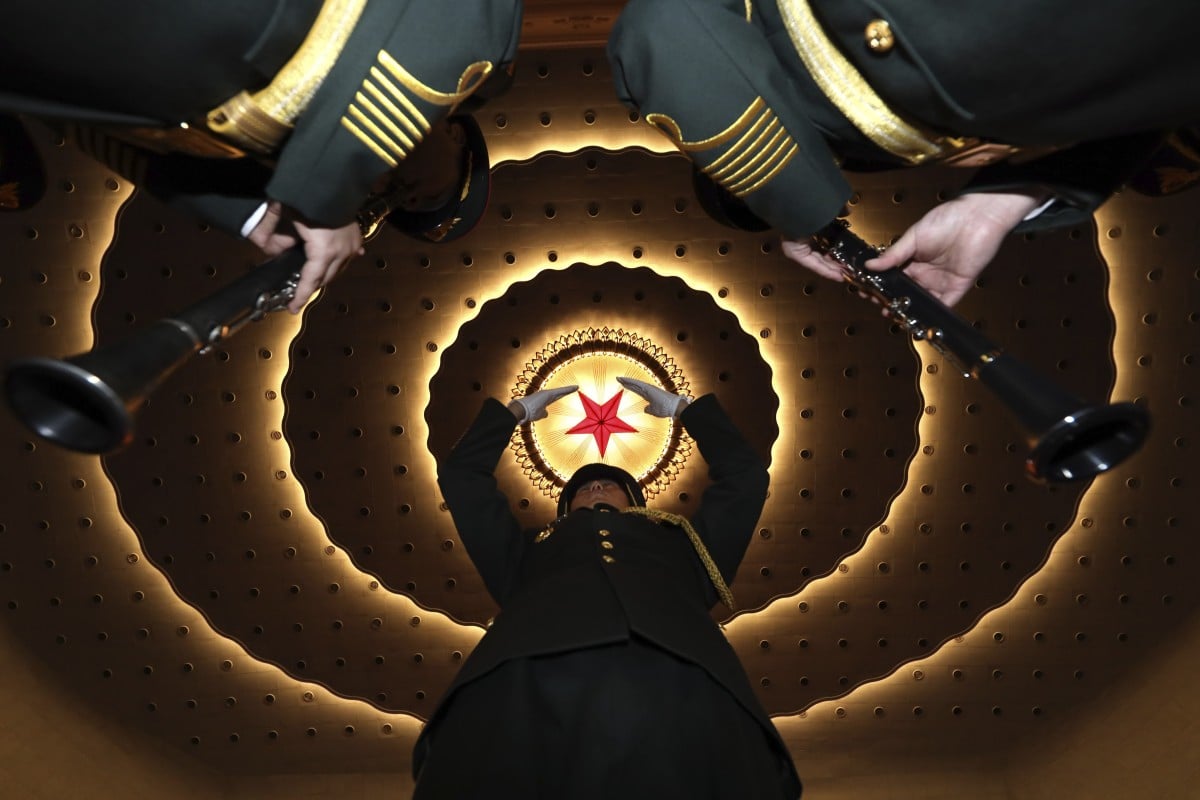
A conductor rehearses the military band on the sidelines of the National People’s Congress in Beijing’s Great Hall of the People in March of last year. China’s legislature is expected to sign off on a massive tech-led stimulus plan. Photo: AP
Beijing is accelerating its bid for global leadership in key technologies, planning to pump more than a trillion dollars into the economy through the roll-out of everything from next-generation wireless networks to artificial intelligence (AI).
In the master plan backed by President Xi Jinping himself, China will invest an estimated 10 trillion yuan (US$1.4 trillion) over six years to 2025, calling on urban governments and private hi-tech giants like Huawei Technologies to help lay 5G wireless networks, install cameras and sensors, and develop AI software that will underpin
to automated factories and mass surveillance.
The new infrastructure initiative is expected to drive mainly local giants, from
and Huawei to SenseTime Group at the expense of US companies.
As tech nationalism mounts, the investment drive will reduce China’s dependence on foreign technology, echoing objectives set forth previously in the “Made in China 2025”
programme. Such initiatives have already drawn fierce criticism from the Trump administration, resulting in moves to block the rise of Chinese tech companies such as Huawei.
How will China’s annual legislative meetings affect the stock investor? Five key industries to watch
“Nothing like this has happened before, this is China’s gambit to win the global tech race,” said Digital China Holdings chief operating officer Maria Kwok, as she sat in a Hong Kong office surrounded by facial recognition cameras and sensors. “Starting this year, we are really beginning to see the money flow through.”
The tech investment push is part of a fiscal package waiting to be signed off by China’s legislature, the
National People’s Congress, which convenes this week. The government is expected to announce infrastructure funding of as much as US$563 billion this year, against the backdrop of the country’s worst economic performance since the Mao era.
The nation’s biggest purveyors of cloud computing and data analysis Alibaba, the parent company of the
South China Morning Post, and
Tencent Holding will be linchpins of the upcoming endeavour. China has already entrusted Huawei, the world’s largest telecommunications equipment supplier, to help galvanise 5G. Tech leaders including Pony Ma Huateng and
Jack Ma are espousing the programme.
Maria Kwok’s company is a government-backed information technology systems integration provider, among many that are jumping at the chance. In the southern city of Guangzhou, Digital China is bringing half a million units of project housing online, including a complex three quarters the size of Central Park in New York City. To find a home, a user just has to log on to an app, scan their face and verify their identity. Leases can be signed digitally via smartphone and the renting authority is automatically flagged if a tenant’s payment is late.
China is no stranger to far-reaching plans with massive price tags that appear to achieve little. There is no guarantee this programme will deliver the economic rejuvenation its proponents promise. Unlike previous efforts to resuscitate the economy with “dumb” bridges and highways, this newly laid digital infrastructure will help national champions develop cutting-edge technologies.
“China’s new stimulus plan will likely lead to a consolidation of
industrial internet
providers, and could lead to the emergence of some larger companies able to compete with global leaders, such as GE and Siemens,” said Nannan Kou, head of research at BloombergNEF, in a report. “One bet is on industrial
internet-of-things (IoT) platforms, as China aims to cultivate three world leading companies in this area by 2025.”
China is not alone in pumping money into the technology sector as a way to get out of the post-coronavirus economic slump. Earlier this month, South Korea said AI and wireless communications would be at the core of it its “New Deal” to create jobs and boost growth.
Nothing like this has happened before, this is China’s gambit to win the global tech raceMaria Kwok, COO at Digital China Holdings
The 10 trillion yuan that China is estimated to spend from now until 2025 encompasses areas typically considered leading edge, such as AI and IoT, as well as items such as ultra-high voltage lines and high-speed rail, according to the government-backed China Centre for Information Industry Development. More than 20 of mainland China’s 31 provinces and regions have announced projects totaling over 1 trillion yuan with active participation from private capital, a state-backed newspaper reported on Wednesday.
Separate estimates by Morgan Stanley put new infrastructure at around US$180 billion each year for the next 11 years – or US$1.98 trillion in total. Those calculations also include power and rail lines. That annual figure would be almost double the past three-year average, the investment bank said in a March report that listed key stock beneficiaries including companies such as China Tower Corp, Alibaba, GDS Holdings, Quanta Computer and Advantech Co.
Beijing’s half-formed vision is already stirring a plethora of stocks, a big reason why five of China’s 10 best-performing stocks this year are tech plays like networking gear maker Dawning Information Industry and Apple supplier GoerTek. The bare outlines of the master plan were enough to drive pundits toward everything from satellite operators to broadband providers.
China’s telecoms carriers push to complete ‘political task’ of 5G network roll-out amid coronavirus crisis
It is unlikely that US companies will benefit much from the tech-led stimulus and in some cases they stand to lose existing business. Earlier this year, when the country’s largest telecoms carrier China Mobile awarded contracts worth 37 billion yuan for 5G base stations, the lion’s share went to Huawei and other Chinese companies. Sweden’s Ericsson got only a little over 10 per cent of the business in the first four months. In one of its projects, Digital China will help the northeastern city of Changchun swap out American cloud computing staples IBM, Oracle and EMC with home-grown technology.
It is in data centres that a considerable chunk of the new infrastructure development will take place. Over 20 provinces have launched policies to support enterprises using cloud computing services, according to a March research note from UBS Group.
Tony Yu, chief executive of Chinese server maker H3C, said that his company was seeing a significant increase in demand for data centre services from some of the country’s top internet companies. “Rapid growth in up-and-coming sectors will bring a new force to China’s economy after the pandemic passes,” he told Bloomberg News.
From there, more investment should flow. Bain Capital-backed data centre operator ChinData Group estimated that for every one dollar spent on data centres another US$5 to US$10 in investment in related sectors would take place, including in networking, power grid and advanced equipment manufacturing. “A whole host of
supply chain companies will benefit,” the company said in a statement.
There is concern about whether this long-term strategy provides much in the way of stimulus now, and where the money will come from. “It’s impossible to prop up China’s economy with new infrastructure alone,” said Zhu Tian, professor of economics at China Europe International Business School in Shanghai. “If you are worried about the government’s added debt levels and their debt servicing abilities right now, of course you wouldn’t do it. But it’s a necessary thing to do at a time of crisis.”
Digital China is confident that follow-up projects from its housing initiative in Guangzhou could generate 30 million yuan in revenue for the company. It is also hoping to replicate those efforts with local governments in the northeastern province of Jilin, where it has 3.3 billion yuan worth of projects approved. These include building a so-called city brain that will for the first time connect databases including traffic, schools and civil matters such as marriage registry. “The concept of smart cities has been touted for years but now we are finally seeing the investment,” said Kwok.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 5G network roll-out, 5G wireless networks, accelerating, Advantech Co, Alibaba Group Holding, American cloud computing, Apple, artificial intelligence (AI), automated factories, autonomous driving, ‘political task’, Bain Capital, Beijing, BloombergNEF, broadband providers, cameras and sensors, Central Park, Changchun, China, China Centre for Information Industry Development, China Europe International Business School, China Mobile, China Tower Corp, civil matters, conductor, coronavirus crisis, cutting-edge technologies, data centres, Dawning Information Industry, dependence, Digital China, Digital China Holdings, digital infrastructure, economic rejuvenation, EMC, Ericsson, everything, facial recognition cameras and sensors, foreign, GDS Holdings, GE, global leadership, GoerTek, Great Hall of the People, Guangzhou, H3C, High-speed rail, Huawei, huawei technologies, IBM, industrial internet, Infrastructure, install, internet-of-things (IoT), Jack Ma, Jilin, key technologies, linchpins, local governments, Made in China 2025, marriage registry, mass surveillance, master plan, military band, national champions, National People’s Congress, networking gear maker, New York City, next-generation wireless networks, northeastern province, Oracle, plan, planning, Pony Ma Huateng, President Xi Jinping, private hi-tech giants, pundits, Quanta Computer, rehearses, roll out, satellite operators, schools, SenseTime Group, Shanghai, Siemens, south china morning post, South Korea, tech crown, Technology, telecommunications equipment supplier, telecoms carriers, Tencent Holding, to pump, to seize, traffic, trillion dollars, UBS Group, ultra-high voltage lines, Uncategorized, urban governments, wireless communications, world’s |
Leave a Comment »
01/04/2020
- The coronavirus has fuelled explosive growth of the app, which now has 800 million users, few of whom will know it is owned by China’s ByteDance
- While videos of dancing teens may seem benign, there are growing fears in America it could be a Trojan Horse for mass surveillance by Beijing
TikTok is seen by some as the latest front in the US-China tech war. Photo: Shutterstock
Y
our average, not-so-hip adult would have probably drawn a blank at the mention of
not long ago – unless they have a child addicted to the wildly popular app, on which users make and share short, amusing videos.
It has grown explosively since its 2016 launch, with 800 million monthly active users now – 300 million of them outside China in places such as India (120 million) and the
(37 million). And many have no idea it is owned by a Chinese company, ByteDance.
The first Chinese app to mount a real global challenge to Facebook and Instagram, it is seen as one of the shiniest new weapons in the US-China technology war. And a boost, perhaps, to Chinese soft power.
TikTok, the missing link between Hong Kong and Indian protesters?
9 Feb 2020
It experienced a growth spurt in 2019 that analysts predicted would slow a little this year. That, however, was before the
coronavirus, which seems to be giving the app a bump, especially beyond its core teenage fan base.
As pandemic fears rise and millions are stuck indoors, major Hollywood celebrities such as Jennifer Lopez, 50, have taken to posting their own all-singing, all-dancing videos, which then go viral on other media platforms.
Even the
World Health Organisation has jumped on the bandwagon, joining the app in late February to share public health advice.
The TikTok logo on a smartphone. Photo: Getty Images
But to some, the growth of TikTok is far from benign.
Privacy advocates and several US congressmen want to rein in the app over concerns it may censor and monitor content for the Chinese government, and be used for misinformation and election interference. This despite the fact that TikTok keeps its servers outside China and swears it will not hand over user data.
Are these fears justified – or fuelled by political and anticompetitive motives?
Thinkers such as Yuval Noah Harari warn that the
coronavirus pandemic could be a watershed in the history of mass surveillance.
But Eric Harwit, a professor of Asian studies at the University of Hawaii, does not buy such arguments against TikTok, especially given that 60 per cent of its US users are aged 16 to 24.
“ByteDance has done a pretty good job of having a firewall between TikTok and the Chinese version of it, Douyin.
TikTok, iPhone: all you need to escape Mumbai’s slums – for 15 seconds
“Also, many users in the US are teens and they’re not a particularly useful source of national security information.
“So I’d say the concerns are motivated more by a general fear of any kind of Chinese telecommunication application rather than actual attempts to siphon off valuable US intelligence information.
“And Facebook and other American companies have similar products,” Harwit points out. “US government officials will always want to protect American commercial interests.”
Sarah Cook, a China analyst for Freedom House – the US government-funded think tank – disagrees.
“We have concerns about how Facebook and Twitter deal with information affecting electoral politics, and that’s magnified if you’re talking about a Chinese company that now has a user base that rivals theirs.”
Chinese officials, she argues, have shown a willingness to censor and manipulate information well beyond their country’s borders – for instance, regarding the scale of the initial outbreak in Wuhan, an obfuscation that may have exacerbated its impact abroad.
“For those who think Chinese government censorship is only Chinese people’s problem, this pandemic shows how much that’s not the case.
“And even if it’s not happening right now with TikTok, the concern is that Chinese companies are beholden to their government, whether they want to be or not.
“I’m not saying block TikTok entirely,” she says. “It’s a question of looking at it in a democratic system and deciding on reasonable oversight and safeguards to protect users and information flows when that time comes.”
When it comes to expanding China’s cultural influence, though, neither Cook nor Harwit believes the app is especially effective.
Most people are oblivious to its Chinese origins, which the user experience does not reflect in any way. So there is no goodwill-generating soft power of the sort wielded by, say,
through the K-pop industry.
If anything, TikTok often promotes the increasingly homogenous, Western-leaning culture seen on many globally popular social media apps.
So says Morten Bay, a lecturer in digital and social media at the University of Southern California’s Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism.
“A semi-Western culture, with small variations of local culture, is becoming the norm on social media. And Chinese soft power is difficult to assert because there’s no value difference.”
And even if Chinese tech companies keep taking bigger bites of the Western market, he is sceptical of China’s “ability to leverage that for soft power in a geopolitical sense”.
“Because there is a very big apparatus pushing against China in that regard. As soon as TikTok started gaining traction in the US, people came out against it, trying to make everyone aware of the privacy and geopolitical issues.
The #KaunsiBadiBaatHai campaign on TikTok aims to raise awareness about women’s safety issues in India. Image: TikTok
“So China faces a lot of resistance,” Bay concludes. “And I’m not sure a social media platform on its own can do much about that.”
Still, if you had to back a horse in this race, TikTok would be it, says Zhang Mengmeng.
When she and her colleagues from global industry analysis firm Counterpoint Research visited the company, they were impressed by its research and development capabilities.
“Because they’re a very young company, their pace for incubating new projects is a lot faster, especially compared to successful but older internet companies in China which have been around for 15 to 20 years.
Indian invasion of Chinese social media apps sparks fear and loathing in New Delhi
“They have lots of little start-up projects within the company and their organisational structure is very flat – it doesn’t matter what your age is, if you have a good idea, you get promoted very quickly.”
TikTok’s rise is also emblematic of a broader role reversal in the US-China tech war, she believes.
“Before, the US was more advanced in terms of internet development and China seemed to just copy its new ideas. Now, this is reversing. There are so many people in China using the internet that start-ups there can test ideas very easily.
“So now it seems like a lot of US companies are trying to see what ideas are coming out of China.” ■
Source: SCMP
Posted in addicted, Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism, APP, bandwagon, Beijing, benign, Bytedance, censorship, China, Chinese, chinese government, coronavirus, Coronavirus pandemic, Culture, explosive growth, Facebook, firewall, fuelled, geopolitical issues, homogenous, Hong Kong, India, Indian, industry, Instagram, intelligence information, IPhone, Jennifer Lopez, jumped, K-pop, living rooms, mass surveillance, Mumbai's, pandemic, protesters, public health advice, semi-Western culture, siphon off, slums, soft power, South Korea, telecommunication application, TikTok, time bomb, Trojan Horse, Twitter, Uncategorized, United States, University of Hawaii, University of Southern California’s, US-China technology war, watershed, women's safety issues, World Health Organisation, Wuhan |
Leave a Comment »