Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESOne of the world’s busiest urban rail systems will be shut down for ordinary commuters from Monday morning to prevent the spread of coronavirus infection in Mumbai, one of India’s most populous cities. Only government workers in “essential services” will be allowed to travel on a truncated service.
This was waiting to happen.
Consider this. Eight million people take Mumbai’s crowded suburban train network every day. Packed to nearly three times its capacity, this is one of the busiest railway systems in the world.
The 459km (285-mile) network is the lifeline of India’s financial and entertainment capital, accounting for nearly 80% of all commuting trips in the populous western city. The suburban trains “cover almost the distance up to [the] moon in one week,” the network’s website says.
The 66-year-old network carries 60,000 passengers per km per day, the highest among all the leading commuter rail systems in the world, say officials. The coaches are sturdy enough to carry a “super dense crush load”, a phrase coined by the railways to describe the intense crowding on Mumbai’s trains. This means that a nine-car train designed for 1,800 standing passengers will often carry up to 7,000 passengers, according to Monisha Rajesh, author of Around India in 80 Trains. “Mumbai’s local trains were certainly not for the fainthearted,” she wrote.
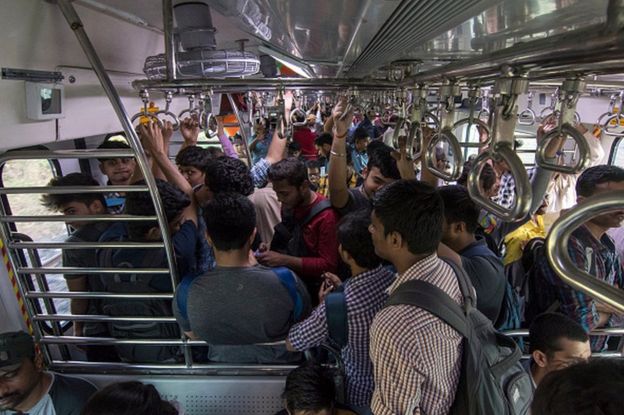 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESNow consider this. The western state of Maharashtra, of which Mumbai is the capital, has confirmed more than 60 coronavirus infections, the highest in India so far. Scores of long distance trains out of the city have been cancelled, but the suburban network has continued to rumble on, raising fears of the mass spread of the virus on these packed trains. The crowded service was an easy target of a terror attack in 2006 when serial blasts ripped though a number of trains. At least 180 people were killed and more than 800 injured – the high casualty figure was attributed to overcrowding.
- Indian cities go eerily quiet as virus cases rise
- What India can learn from 1918 flu to fight Covid-19
- Is India prepared for a coronavirus outbreak?
It is intuitively obvious that there’s a link between commuting with a lot of people and catching respiratory diseases. During the 1918 Spanish flu pandemic, which killed some 18 million Indians, the railways “played a prominent part [in aiding the spread of the disease] as was inevitable,” according to an official report.
“From ports and landing places the local transport networks, particularly the railways, carried the virus from large cities to the smallest, remotest settlements,” said a report on the spread of the flu in Britain in 1918-1919.
So should one of the world’s busiest rail networks be shut down to stop a possible spread of the virus in a city that many fear could turn into a coronavirus hotspot?
 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESEconomists like Shruti Rajagopalan believe so.
“India is conducting the fewest tests per million at the moment. If the virus is truly within the community, then given these two issues, the Mumbai outbreak cannot be contained and people will die without healthcare.
“Mumbai trains are the fastest and surest way to spread the virus (if it is within the community) to the densest parts of the city,” she told me.
There is enough precedent: China stopped trains, ferries, planes and buses from leaving the city of Wuhan; and on Thursday, London officials announced that up to 40 stations on the London Underground network are to be shut as the city attempts to contain the outbreak.
Others are not so sure about linking the spread of a pandemic to public transport systems. One study does not support the effectiveness of suspending mass urban transport systems to reduce or slow down a pandemic because, “whatever the relevance of public transport is to individual-level risk, household exposure most likely poses a greater threat”.
“I have not seen any data on the relative risk of public transportation compared with [dense places like] workplaces or schools,” Timothy Brewer, a professor of epidemiology at the University of California Los Angeles told Vox.com.
He said data from China suggested that “household contact was an important means of transmission outside of Wuhan, suggesting that prolonged contact [with a sick person] increases the risk of transmission”.
“If correct, then the time spent commuting and the density of people commuting could be important factors in assessing if public transportation is a risk factor for the disease’s transmission.”
 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESShivaji Sutar, a senior communications officer of the railways, told me that the network was running an aggressive campaign to ease the rush: awareness announcements, posters and videos containing virus information.
They were also monitoring crowds, scrubbing the trains, taking the temperature of willing passengers and embarking on a drive against public spitting, he said.
A combination of awareness and panic has already led to a 27% drop in traffic on the network. But millions of people continue to take the train to work and home every day.
“This is more because of fear than anything else. Most of us have to take the network because we have to come to work. There is still no government directive to all companies to work from home. And apart from passengers wearing masks, I haven’t seen any other precautions being taken,” Rekha Hodge, who has been using the network for three decades, told me. That is bad news.
Source: The BBC