- Inspired by early colour television, method can create thousands of alloys quickly
- Leader of Beijing team says a ‘revolution in material science’ is close to hand
In the conventional method, metals needed to be weighed, melted to an alloy and tested for performance. To find the right formula, researchers might need to test more than a thousand combinations and each test might take a day or two.
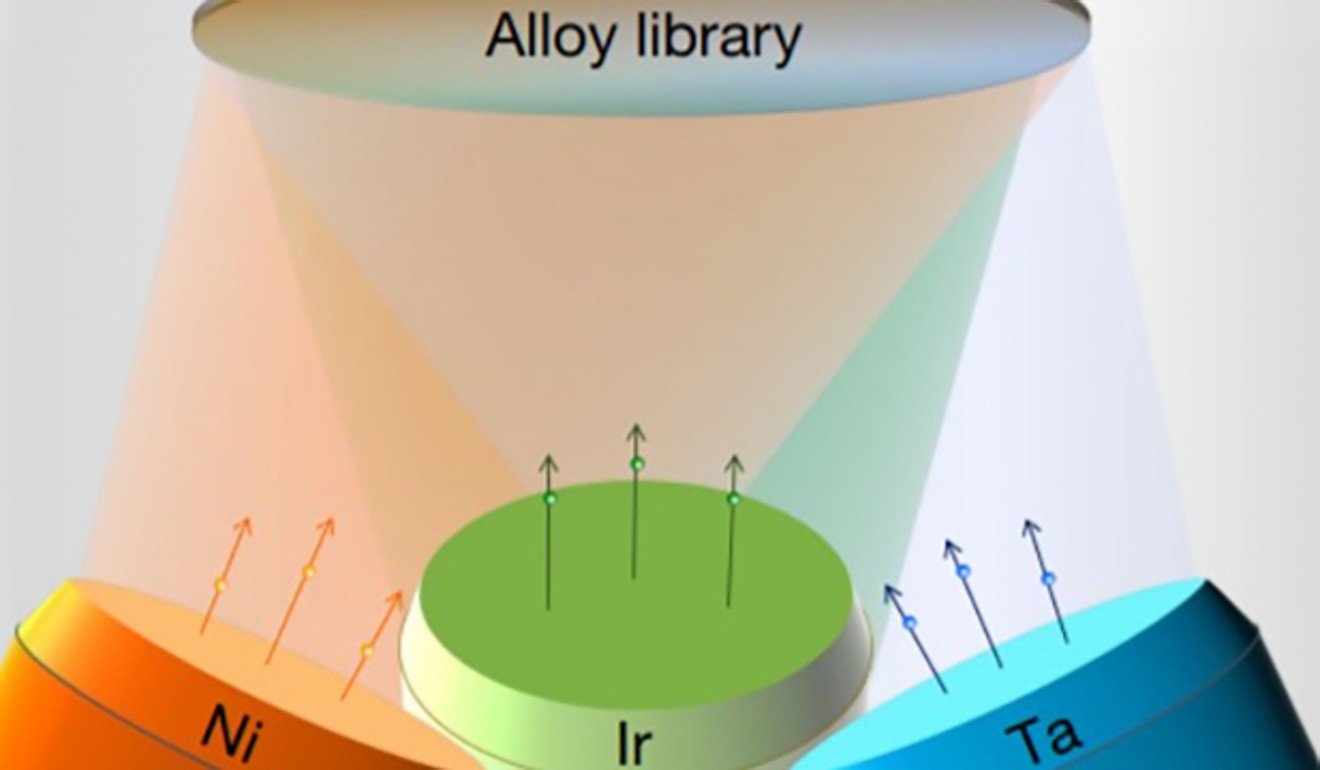
Professor Wang Weihua, researcher with the institute of physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing and lead scientist of the study, said his team’s research was inspired by early colour televisions, which used three electric devices known as guns that fired red, green and blue light onto the back of the screen to create real-world colours for the viewer.
Wang’s team’s alloy technology also involved three guns, but instead of electronic pulses they fired “bullets” made of different metals. These struck a silicon board simultaneously and fused to form alloys.
Sensors quickly measured the alloys’ properties and picked the most appropriate for the researchers.
This approach allowed scientists to create more than 1,000 samples, test their performance and select the most promising within a couple of hours.
“We proved it works,” Wang said. “It will increase people’s confidence. There will be a revolution in material science.”
The alloy reported in the Nature paper contained iridium, nickel and tantalum. It had a distorted atomic structure similar to that of glass. Metallic glasses can be extremely strong but they usually weaken by temperatures of 400 degrees Celsius or more.
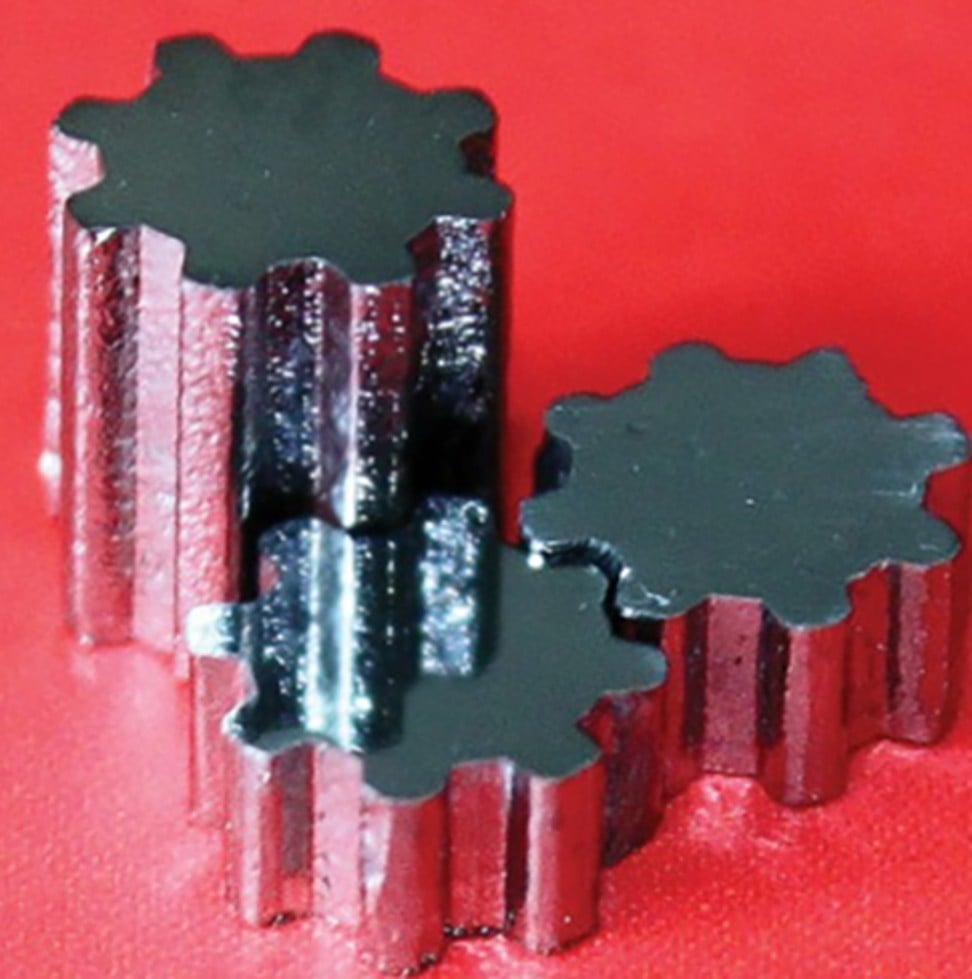

The new alloy can maintain a tensile strength nearly eight times that of steel at more than 700 degrees Celsius, researchers said.
It can also remain intact for months in aqua regia, the mixture of nitric acid and hydrochloric acid that can dissolve gold and platinum.
Such properties make the alloy an ideal candidate material for manufacturing critical components for use in harsh environments such as space, ocean depths and battlefields.
“We are introducing artificial intelligence into the design and search for new amorphous metals,” Wang said. “It can further increase the speed of discoveries. In the near future, we may even be able to create material on demand.
“The potential application is almost unlimited.”
Source: SCMP


