01/04/2020
- The coronavirus has fuelled explosive growth of the app, which now has 800 million users, few of whom will know it is owned by China’s ByteDance
- While videos of dancing teens may seem benign, there are growing fears in America it could be a Trojan Horse for mass surveillance by Beijing
TikTok is seen by some as the latest front in the US-China tech war. Photo: Shutterstock
Y
our average, not-so-hip adult would have probably drawn a blank at the mention of
not long ago – unless they have a child addicted to the wildly popular app, on which users make and share short, amusing videos.
It has grown explosively since its 2016 launch, with 800 million monthly active users now – 300 million of them outside China in places such as India (120 million) and the
(37 million). And many have no idea it is owned by a Chinese company, ByteDance.
The first Chinese app to mount a real global challenge to Facebook and Instagram, it is seen as one of the shiniest new weapons in the US-China technology war. And a boost, perhaps, to Chinese soft power.
TikTok, the missing link between Hong Kong and Indian protesters?
9 Feb 2020
It experienced a growth spurt in 2019 that analysts predicted would slow a little this year. That, however, was before the
coronavirus, which seems to be giving the app a bump, especially beyond its core teenage fan base.
As pandemic fears rise and millions are stuck indoors, major Hollywood celebrities such as Jennifer Lopez, 50, have taken to posting their own all-singing, all-dancing videos, which then go viral on other media platforms.
Even the
World Health Organisation has jumped on the bandwagon, joining the app in late February to share public health advice.
The TikTok logo on a smartphone. Photo: Getty Images
But to some, the growth of TikTok is far from benign.
Privacy advocates and several US congressmen want to rein in the app over concerns it may censor and monitor content for the Chinese government, and be used for misinformation and election interference. This despite the fact that TikTok keeps its servers outside China and swears it will not hand over user data.
Are these fears justified – or fuelled by political and anticompetitive motives?
Thinkers such as Yuval Noah Harari warn that the
coronavirus pandemic could be a watershed in the history of mass surveillance.
But Eric Harwit, a professor of Asian studies at the University of Hawaii, does not buy such arguments against TikTok, especially given that 60 per cent of its US users are aged 16 to 24.
“ByteDance has done a pretty good job of having a firewall between TikTok and the Chinese version of it, Douyin.
TikTok, iPhone: all you need to escape Mumbai’s slums – for 15 seconds
“Also, many users in the US are teens and they’re not a particularly useful source of national security information.
“So I’d say the concerns are motivated more by a general fear of any kind of Chinese telecommunication application rather than actual attempts to siphon off valuable US intelligence information.
“And Facebook and other American companies have similar products,” Harwit points out. “US government officials will always want to protect American commercial interests.”
Sarah Cook, a China analyst for Freedom House – the US government-funded think tank – disagrees.
“We have concerns about how Facebook and Twitter deal with information affecting electoral politics, and that’s magnified if you’re talking about a Chinese company that now has a user base that rivals theirs.”
Chinese officials, she argues, have shown a willingness to censor and manipulate information well beyond their country’s borders – for instance, regarding the scale of the initial outbreak in Wuhan, an obfuscation that may have exacerbated its impact abroad.
“For those who think Chinese government censorship is only Chinese people’s problem, this pandemic shows how much that’s not the case.
“And even if it’s not happening right now with TikTok, the concern is that Chinese companies are beholden to their government, whether they want to be or not.
“I’m not saying block TikTok entirely,” she says. “It’s a question of looking at it in a democratic system and deciding on reasonable oversight and safeguards to protect users and information flows when that time comes.”
When it comes to expanding China’s cultural influence, though, neither Cook nor Harwit believes the app is especially effective.
Most people are oblivious to its Chinese origins, which the user experience does not reflect in any way. So there is no goodwill-generating soft power of the sort wielded by, say,
through the K-pop industry.
If anything, TikTok often promotes the increasingly homogenous, Western-leaning culture seen on many globally popular social media apps.
So says Morten Bay, a lecturer in digital and social media at the University of Southern California’s Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism.
“A semi-Western culture, with small variations of local culture, is becoming the norm on social media. And Chinese soft power is difficult to assert because there’s no value difference.”
And even if Chinese tech companies keep taking bigger bites of the Western market, he is sceptical of China’s “ability to leverage that for soft power in a geopolitical sense”.
“Because there is a very big apparatus pushing against China in that regard. As soon as TikTok started gaining traction in the US, people came out against it, trying to make everyone aware of the privacy and geopolitical issues.
The #KaunsiBadiBaatHai campaign on TikTok aims to raise awareness about women’s safety issues in India. Image: TikTok
“So China faces a lot of resistance,” Bay concludes. “And I’m not sure a social media platform on its own can do much about that.”
Still, if you had to back a horse in this race, TikTok would be it, says Zhang Mengmeng.
When she and her colleagues from global industry analysis firm Counterpoint Research visited the company, they were impressed by its research and development capabilities.
“Because they’re a very young company, their pace for incubating new projects is a lot faster, especially compared to successful but older internet companies in China which have been around for 15 to 20 years.
Indian invasion of Chinese social media apps sparks fear and loathing in New Delhi
“They have lots of little start-up projects within the company and their organisational structure is very flat – it doesn’t matter what your age is, if you have a good idea, you get promoted very quickly.”
TikTok’s rise is also emblematic of a broader role reversal in the US-China tech war, she believes.
“Before, the US was more advanced in terms of internet development and China seemed to just copy its new ideas. Now, this is reversing. There are so many people in China using the internet that start-ups there can test ideas very easily.
“So now it seems like a lot of US companies are trying to see what ideas are coming out of China.” ■
Source: SCMP
Posted in addicted, Annenberg School for Communication and Journalism, APP, bandwagon, Beijing, benign, Bytedance, censorship, China, Chinese, chinese government, coronavirus, Coronavirus pandemic, Culture, explosive growth, Facebook, firewall, fuelled, geopolitical issues, homogenous, Hong Kong, India, Indian, industry, Instagram, intelligence information, IPhone, Jennifer Lopez, jumped, K-pop, living rooms, mass surveillance, Mumbai's, pandemic, protesters, public health advice, semi-Western culture, siphon off, slums, soft power, South Korea, telecommunication application, TikTok, time bomb, Trojan Horse, Twitter, Uncategorized, United States, University of Hawaii, University of Southern California’s, US-China technology war, watershed, women's safety issues, World Health Organisation, Wuhan |
Leave a Comment »
27/12/2019
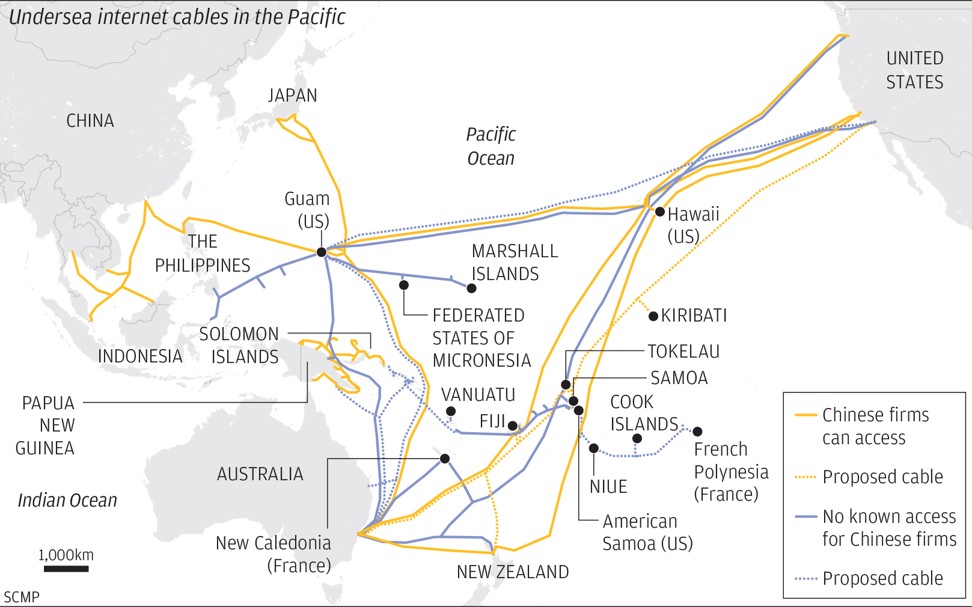
- A push to connect Pacific nations highlights a submarine struggle for dominance over the world’s technology infrastructure
- The ambitions of Chinese tech giants like Huawei, which have laid thousands of kilometres of cable, are of increasing concern to Washington
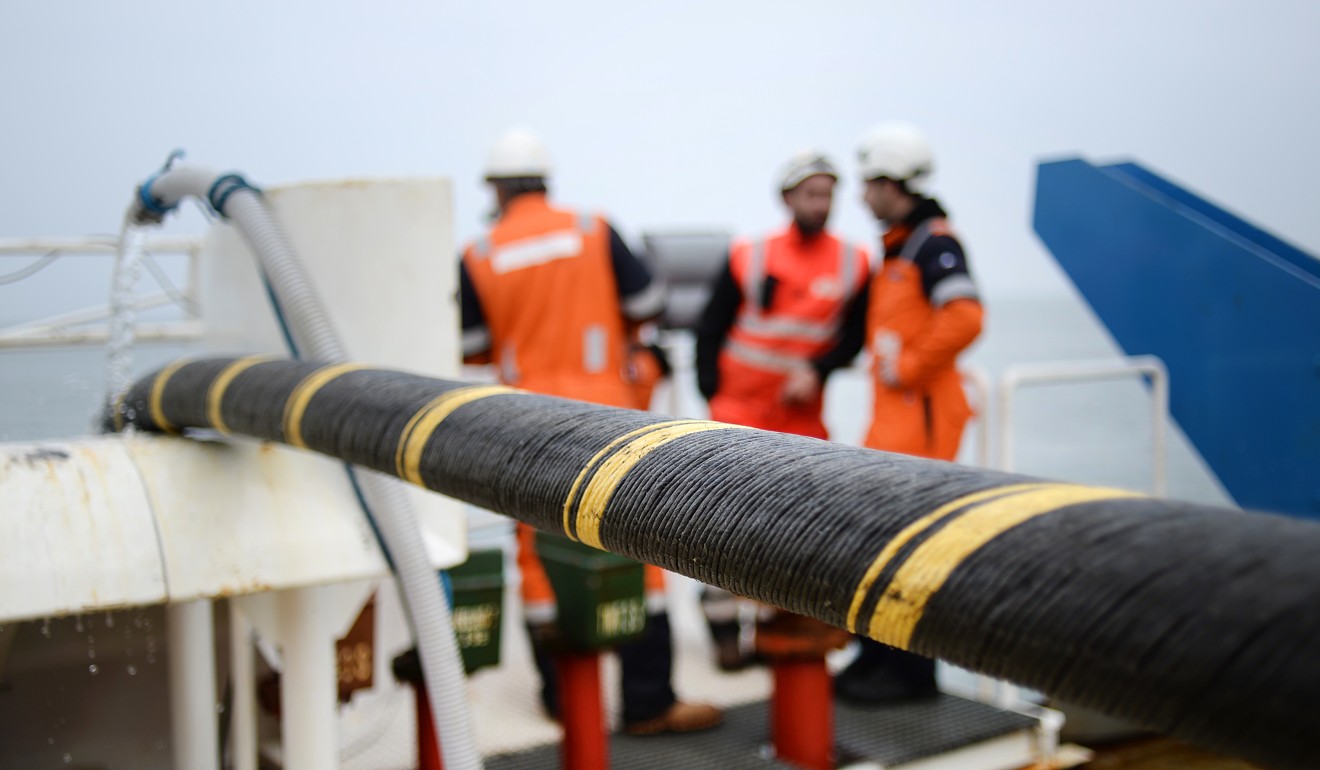
The ambitions of Chinese tech giants like Huawei, which have laid thousands of kilometres of cable, are of increasing concern to Washington. Photo: Reuters
I
n the contest between the
US and China for dominance over the world’s technology
infrastructure, the latest battle is taking place under the Pacific Ocean.
While the US has been upping the pressure on its allies not to include equipment made by Chinese telecom giants like Huawei and ZTE in their 5G systems, Chinese companies have gained a foothold in some of the world’s most essential communications infrastructure – undersea internet cables.
Smart telecom cables: climate change hope or submarine spying tech?
Almost all global data communications flow through cables under the ocean – just one per cent travels by satellite – and Chinese companies have quietly been eroding US, European and Japanese dominance over the backbone of the internet, the undersea cable market. Now, they have trained their sights on connecting one of the most virtually remote parts of the globe, the
Pacific Island countries.
Of the 378 cables currently operating worldwide, 23 are under the Pacific. But many of these cables run right by Pacific Island nations on their paths between hubs in Los Angeles, Tokyo and Singapore.
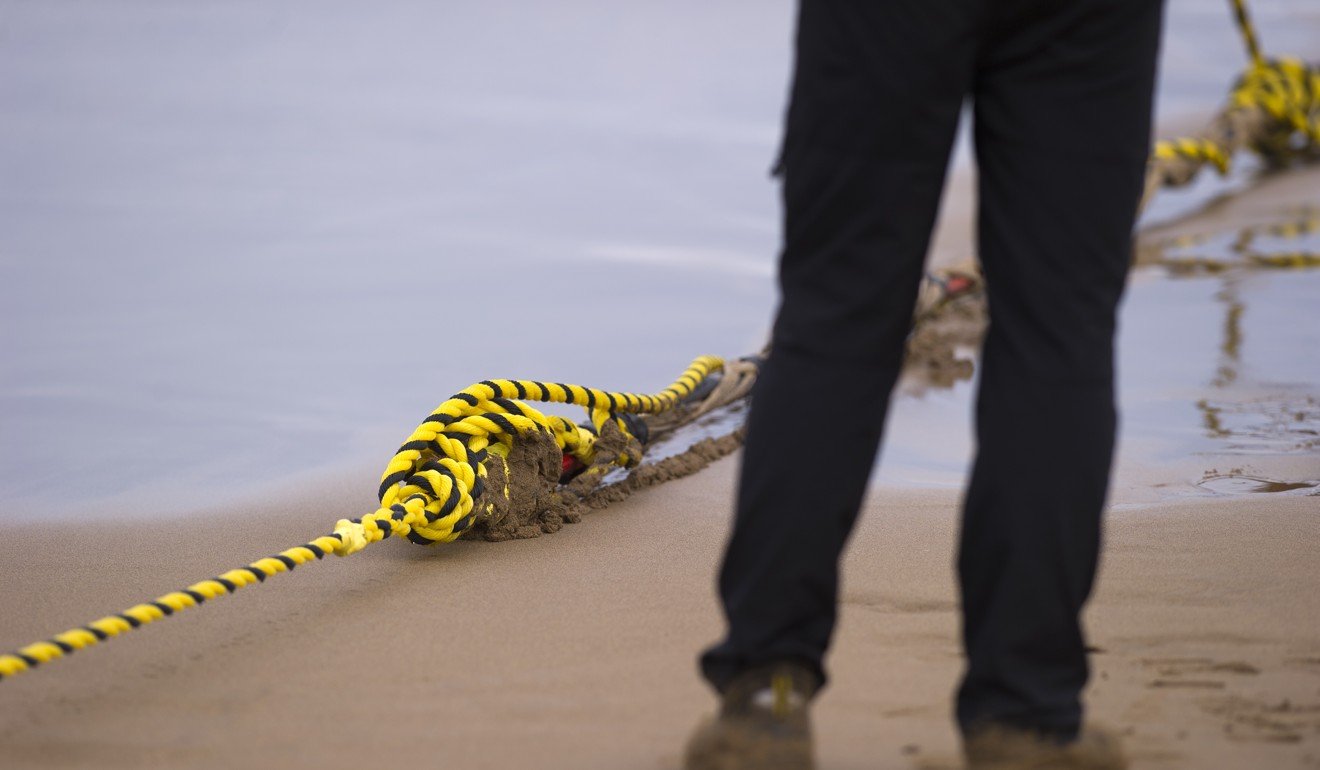
An electric submarine cable and optical fibre. File photo
Despite the volume of data flowing under the Pacific Ocean, just half a million of the 11 million people living in Pacific Island countries and Papua New Guinea – less than five per cent – have access to a wired internet connection and only 1.5 million to a mobile connection, according to the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for the Asia Pacific (UNESCAP), compared with 53 per cent of people in Thailand and 60 per cent in the Philippines.
More than US$4 billion worth of cables are to come into service by 2021, continuing a trend in which US$2 billion worth of cables have come online every year since 2016, and six of these cables will connect Pacific Island countries.
The push to connect Pacific Island nations to the latest generation of internet infrastructure has received extra scrutiny from the US and its allies like
Australia
over the involvement of Chinese tech companies.
Choose Beijing over Taipei, Solomon Islands task force recommends
While the US has moved to block Huawei from supplying equipment to its allies’ 5G networks, experts say Chinese tech companies could contest the US, EU and
long-standing dominance over global data traffic through investments in subsea cables.
Chinese tech giants like Huawei have entire divisions devoted to undersea connectivity that have laid thousands of kilometres of cable, and Chinese state telecommunication companies such as China Unicom have access to many of the existing trans-Pacific cables.
But a panel led by the US Department of Justice has held up a nearly complete trans-Pacific cable project over concerns about its Chinese investor, Beijing-based Dr Peng Telecom & Media Group.
The project, the Pacific Light Cable Network, could be the first cable rejected by the panel on the grounds of national security – despite being backed by American tech giants
Google and
Facebook – setting a precedent for a tougher US stance on Chinese involvement in subsea cables.
Chinese tech giants like Huawei have entire divisions devoted to undersea connectivity that have laid thousands of kilometres of cable. Photo: AP
Craige Sloots, director of sales at Southern Cross Cable Network, which operates the largest existing sets of trans-Pacific cables, said for any new cable, regulators were likely to scrutinise the ownership of the companies involved and the maker of the project’s equipment.
These two factors, said Sloots, “pragmatically limit some of the providers you can use if you want to connect through the US”.
Experts say that Hong Kong, where the stalled Pacific Light Cable would land, was previously considered a more secure shore landing point than mainland China. But people close to the project say the recent unrest in the city has made this distinction less relevant, according to The Wall Street Journal.
If these nations want to be part of the international economy, they need reliable communications: Bruce Howe, University of Hawaii
Similar concerns caused a proposed Huawei-backed cable linking Vanuatu with Papua New Guinea to be called off last year after Australia stepped in to fund its own cable instead.
Just months after the government-owned Solomon Islands Submarine Cable Company agreed to the project with Huawei in mid-2017, Canberra put up US$67 million to connect Sydney with the Solomon Islands and Papua New Guinea with cables laid under the Coral Sea by Nokia’s Alcatel Submarine Networks.
Simon Fletcher, CEO of Vanuatu company Interchange, which had been planning another cable in the neighbourhood connecting Vanuatu with the Solomon Islands, said the Coral Sea project undercut the viability for small private businesses to operate in the fledgling market, where services had historically been provided by international organisations like development banks. His company’s cable has been on pause since the announcement of the Coral Sea project, though Fletcher said it would go forward next year.
US-China battle for dominance extends across Pacific, above and below the sea
22 Jul 2019
VIRTUALLY REMOTE
For years, as Japan, Hong Kong and Singapore became global hubs of high-speed internet data traffic, the cables criss-crossing the ocean floor passed by just off the shores of Pacific Island countries en route between hubs on either side of the ocean.
Tiziana Bonapace, director of UNESCAP’s information technology and disaster risk-reduction division, said the Pacific Islands remain one of the most disconnected areas in the world, where “a vast proportion of the population has no access to the internet”.
Over the past five years, international organisations like UNESCAP, the Asia Development Bank and the World Bank have been pushing for better connectivity in the region. The World Bank’s Pacific Regional Connectivity Programme has invested more than US$90 million into broadband infrastructure for Fiji, the Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, Palau, Samoa and Tuvalu.
Internet cables in the Pacific Ocean.
But the business case had never been good, said Bonapace.
“A cable has to travel thousands of kilometres just to connect a population smaller than one of Asia’s megacities,” she said. “As everything we do is somehow connected to the internet, the prospects for the Pacific to become virtually more remote are even higher.”
Even nations which are connected have tenuous infrastructure. In January, Tonga experienced a total internet blackout for two weeks after damage to its single cable. Most parts of the world were linked by multiple cables to prevent this type of outage, said Bruce Howe, professor of ocean and resources engineering at University of Hawaii.
“If these nations want to be part of the international economy, they need reliable communications,” Howe said.
Is Chinese support for Pacific nations shaping their stance on West Papua?
26 Aug 2019
DRAWING NEW LINES
In Papua New Guinea, where mobile internet currently reaches less than a third of the population, a partnership between local telecoms company GoPNG and the Export-Import Bank of China funded the new Huawei-built Kumul Domestic cable system, which came online this year.
The Southern Cross Next system, owned by Spark, Verizon, Singtel Optus and Telstra – the same group of shareholders which operates the massive 30,500km (19,000 mile) set of twin cables connecting the US with Australia and New Zealand known as Southern Cross – is planned to come online in 2022, and will connect directly to Fiji, Samoa, Kiribati and Tokelau.
Chinese telecoms company China Unicom counts the existing Southern Cross cables among its network capabilities – meaning it is likely to have access to the cable through a leasing agreement with one of the other companies that uses the cable, according to Canberra think tank the Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI).
An undersea fibre optic cable. Photo: AFP
China Unicom and China Telecom also list the Asia America Gateway Cable System as one of their network capabilities, according to ASPI. The 20,000km (12,400-mile) cable came online in 2009 and connects the US, Guam, Hong Kong, Brunei, the Philippines, Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam and Thailand.
It is owned by a consortium of carriers including AT&T, Telekom Malaysia, Telstra and Spark.
A cable backed by Google and the Australian Academic and Research Network connecting Japan and Australia through Guam is to come online early next year.
China: the real reason Australia’s pumping cash into the Pacific?
28 Jul 2018
WHAT’S NEXT
Natasha Beschorner, senior digital development specialist at the World Bank, said that while there were challenges ahead in terms of broadband access and affordability, increased connectivity was starting to bring new opportunities to the Pacific.
“Digital technologies can contribute to economic diversification, income generation and service delivery in the Pacific,” Beschorner said. “E-commerce and financial technologies are emerging and governments are considering how to roll out selected services online.”
Experts say the industry has recently seen a switch from cables being mostly funded by telecommunication carriers to being funded by content providers, like Google and Facebook. Members of the private cable industry say content companies can afford to invest in cable infrastructure to ensure the supply chain for their customers, but that the competition puts the squeeze on the research-and-development budgets of other types of companies.
Sloots at Southern Cross predicted that the nations which connected directly to the massive next-generation cable – Samoa, Kiribati and Tokelau – would be able to function as connecting points for intra-Pacific cables.
“There’s a blossoming effect in capability once certain islands are connected,” Sloots said.
There is also the push to locate an exchange point within the Pacific so that internet data no longer has to travel to a hub in Tokyo or Los Angeles and back to Pacific nations when processing – a move that could ultimately lower the cost of broadband internet service for consumers in the Pacific.
Perhaps the most effective outcome could be for Pacific nations to cut the cord and receive their internet by satellite.
The Asian Development Bank has agreed to give a US$50 million loan to Singapore’s Kacific Broadband Satellites International to provide up to two billion people across the Asia-Pacific region with affordable satellite-based internet.
The project is to be launched into orbit by SpaceX next week and aims to begin providing service by early next year.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Alcatel Submarine Networks, Asia America Gateway Cable System, Asia Development Bank, Asian Development Bank, Australia, Australian Academic and Research Network, Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI), Beijing, broadband internet service, Brunei, cables, Canberra, China Telecom, China Unicom, Dr Peng Telecom & Media Group, Export-Import Bank of China, Facebook, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, Google, GoPNG, Guam, Hong Kong, Huawei, Internet, Japan, Kiribati, Kumul Domestic cable system, Los Angeles, Malaysia, new battleground, New Zealand, Nokia, Pacific island countries, Pacific Light Cable Network, Pacific Regional Connectivity Programme, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Singapore, Singtel Optus, Solomon Islands, Solomon Islands Submarine Cable Company, Southern Cross Cable Network, Southern Cross Next system, SpaceX, Spark, Taipei, Telekom Malaysia, Telstra, Thailand, the Coral Sea, the Philippines, The Wall Street Journal, think tank, Tokelau, Tokyo, Tonga, Uncategorized, undersea, United Nations Economic and Social Commission for the Asia Pacific (UNESCAP), University of Hawaii, US, US-China tech war, Vanuatu, Vanuatu company Interchange, Verizon, Vietnam, Washington, West Papua, World Bank, ZTE |
Leave a Comment »