- Education ministry says they will be held a month later than planned – on July 7 and 8 – when there is ‘a lower risk’ for students and staff
- It will also give them more time to prepare after months of online learning due to school closures
Wang Hui, a ministry official who handles the university sector, said 10.71 million students were expected to sit the exams this summer.
He said the ministry decided to postpone this year’s gaokao to put students’ “health and fairness first”.
“[Disease control and] prevention experts suggest that if the gaokao is postponed for a month, there will be a lower risk from … the epidemic,” Wang said.
“We must adopt the most appropriate and the least risky plan in order to protect the safety and health of the students as well as the staff involved in the tests.”
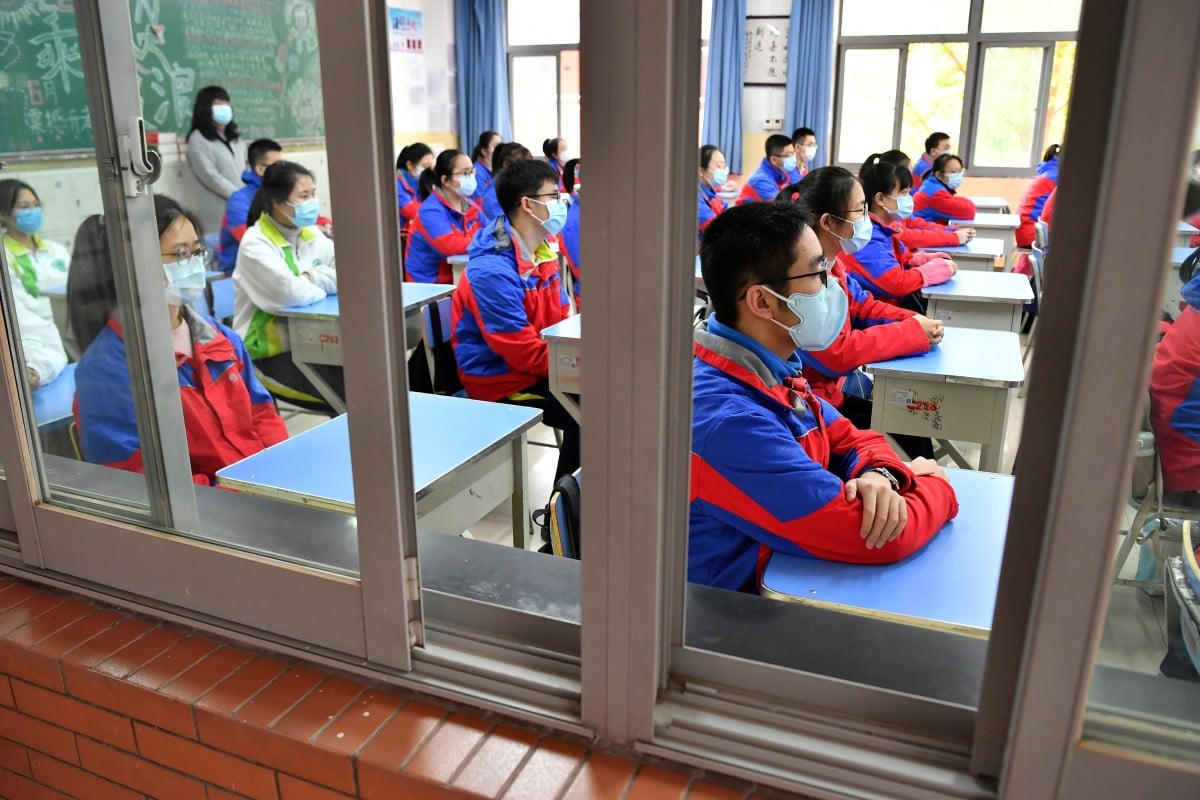
The ministry official said the delay was also about fairness, by giving students more time to study at school and prepare for the exams.
“We hope to reduce the impact of the epidemic on students, especially those from rural and poverty-stricken regions, as much as possible,” Wang said.
“Third-year high school students have had to stay home [because of the coronavirus outbreak] so their preparation for the gaokao has been affected,” he said. “The internet [access] divide between urban and rural areas means some students in rural and poorer regions have been more affected by this epidemic.”
With schools remaining closed during coronavirus outbreak, China launches national remote learning platforms

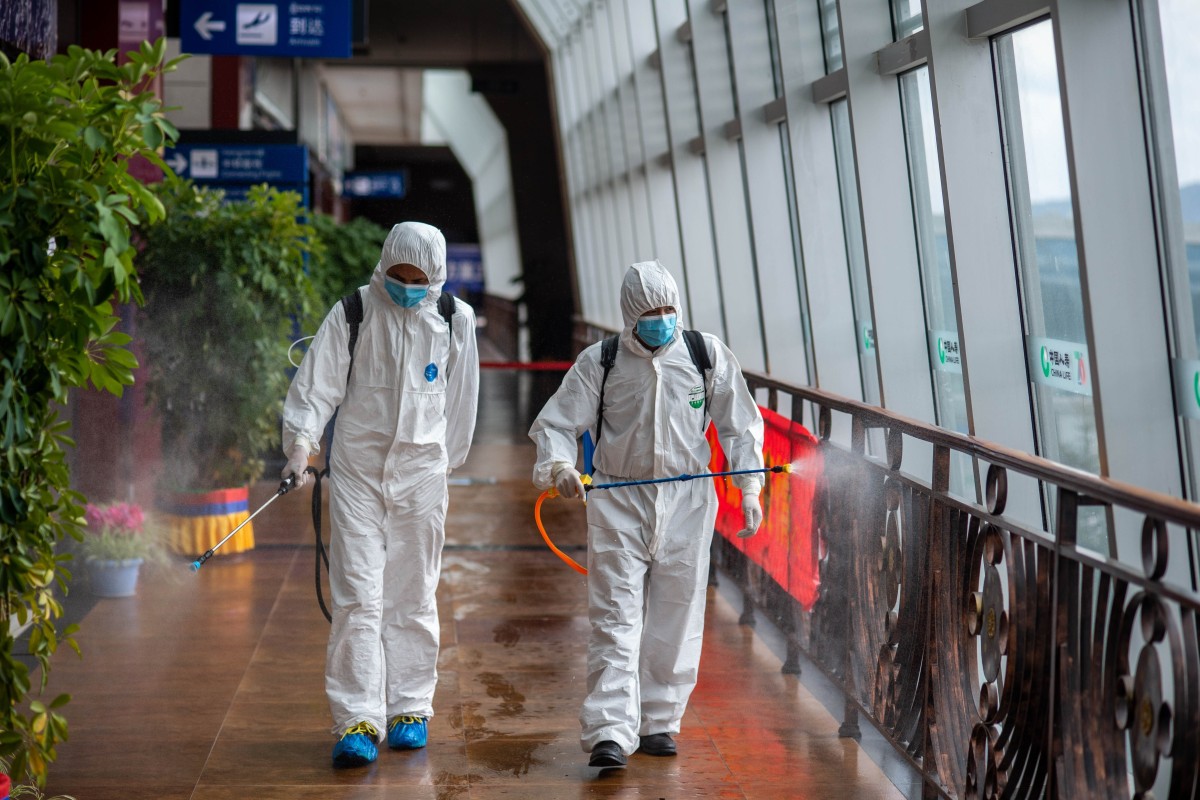
Beijing imposed a nationwide school closure after the Lunar New Year holiday in late January as the pneumonia-like illness rapidly spread. Schools were told to postpone the new term that was due to start in mid- or late February, meaning millions of students – from primary school to university – had to turn to online learning. Several provinces began reopening schools this month and more are set to follow in early to mid-April, but authorities in Beijing and Guangdong have yet to set a date for classes to resume.
The last time the gaokao was disrupted was during the Cultural Revolution, a decade of political and social turmoil that ended in 1976. It was cancelled during this time and since it resumed in 1979 until 2002 it has been held nearly every year from July 7 to 9. From 2003, the ministry moved the gaokao forward to June 7 and 8 to avoid hot weather and potential natural disasters. The severe acute respiratory syndrome outbreak (Sars) in 2002-03 did not delay the exams.
China’s university entry exam, gaokao: elliptical, obscure and confusing

According to an online survey conducted by microblogging website Sina Weibo on Tuesday, some 537,000 users said they were “shocked” by the ministry’s decision and were “experiencing history”.
About 282,000 people said it was a good thing for students since it gave them more time to prepare for the exams. But it was bad news for another 153,000 users, who said they would have to endure an extra month of exhausting preparation.
Source: SCMP