29/05/2019
- China’s housing market showing signs of bubble similar to that seen in Japan in 1980s, says Asian Development Bank Institute dean and CEO Naoyuki Yoshino
- China’s loose policy following 2008 global financial crisis laid foundations for current housing bubble, with US-China trade war adding to concerns
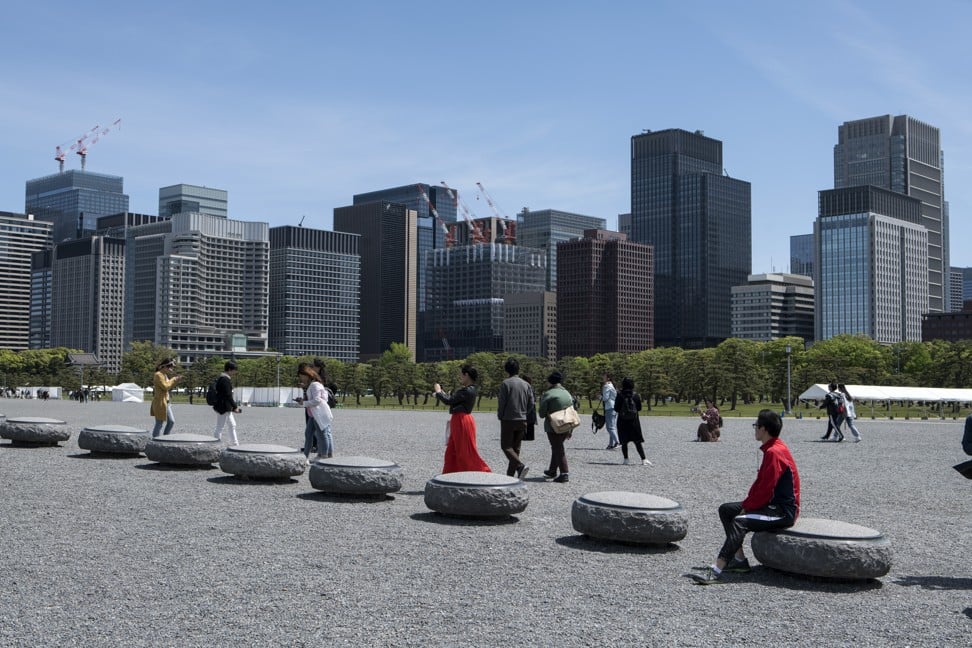
The average price of a home in Beijing has soared from around 380 yuan (US$55) per square feet in the early 2000s to the current level of well above 5,610 yuan (US$813) per square foot, according to property data provider creprice.cn. Photo: Bloomberg
China must exercise extreme caution in handling its housing sector because it is showing signs similar to those witnessed during Japan’s bubble period of the 1980s that contributed to the collapse of Japanese asset prices and its subsequent “lost decades” of weak economic growth and deflation, a Japanese financial system expert warned.
The parallels between China’s current landscape and Japan’s three decades ago are readily apparent, stemming from a loose monetary policy that laid the foundation for the expansion of a housing bubble, said Naoyuki Yoshino, dean and CEO of the Asian Development Bank Institute.
China flooded its economy with credit in response to the 2008 global financial crisis, fuelling rapid growth in mortgages, real estate borrowings and investments over the past decade.
In the same vein, the Japanese government’s relaxed monetary policy in the 1980s triggered an economic bubble that eventually burst and sank the economy into a recession that
with the Bank of Japan continuing to still keep interest rates at or below zero per cent to this day in an attempt to spur inflation.
The Japanese government’s relaxed monetary policy in the 1980s triggered an economic bubble that eventually burst and sank the economy into a recession that lasted almost 25 years. Photo: Bloomberg
Japan’s experience could serve as a lesson on how to avoid a housing market collapse that would be especially detrimental to China’s financial sector and real economy, according to Yoshino.
“I’m very much concerned that if land prices keep on rising and if the population starts to shrink along with aggregate demand, then China will experience a similar situation to that of Japan,” Yoshino said.
There are already several strong signs of a housing bubble in China, according to Yoshino, firstly the astronomical surge in property prices in recent years.
I’m very much concerned that if land prices keep on rising and if the population starts to shrink along with aggregate demand, then China will experience a similar situation to that of Japan Naoyuki Yoshino
Home ownership is one of the few ways for Chinese families to generate wealth because of limited investment opportunities. The average price of a home in Beijing has soared from around 4,000 yuan (US$578) per square metre, or 380 yuan (US$55) per square feet, in the early 2000s to the current level of well above 60,000 yuan (US$8,677) per square metre, or 5,610 yuan (US$813) per square foot, according to property data provider creprice.cn.
The increase has also lifted the housing price to income ratio sharply from 5.6 in 1996 to 7.6 in 2013, well above the Japanese rate of 3.0 at its peak in 1988. The price to income ratio is the basic affordability measure for housing.
According to the Global Times, a reasonable home price should be three to six times the median household income. That means a family with an average income can buy a house with three to six years’ annual income. The house price to income ratio in China is above 50 in the first-tier cities and 30 to 40 in the third- and fourth-tier cities, the newspaper said in October. There are four levels of cities in China, defined by a number of factors including gross domestic product (GDP) and population, with Beijing, Shanghai and Shenzhen considered tier-one cities.
Another worrying sign, according to Yoshino, is that China’s financial sector has lent more heavily to the real estate sector than did Japanese banks during their bubble period.
Thirdly, the ratio of Chinese housing loans to the nation’s GDP has consistently been higher than Japan’s by about three times more.
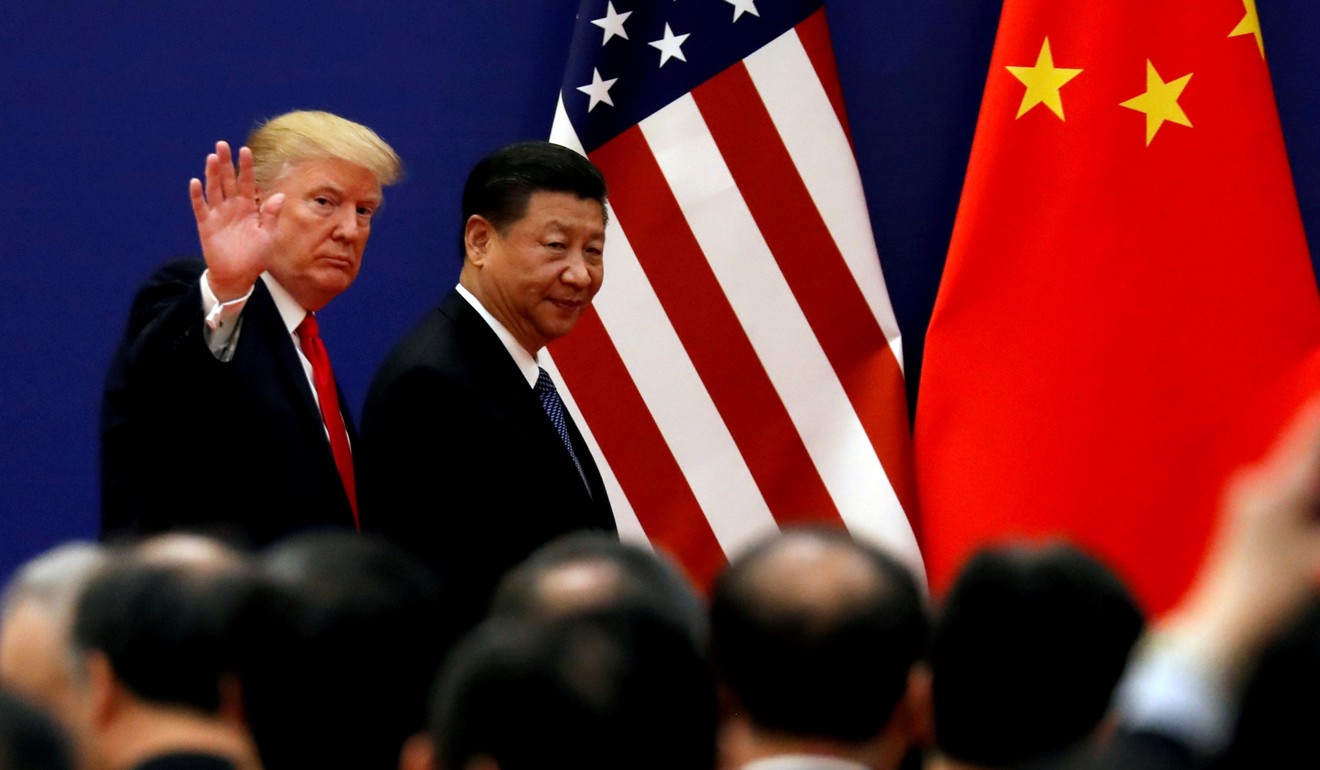
Ever since US President Donald Trump started imposing tariffs on Chinese imports in July, worries have been mounting that China’s property bubble and its record debt level would make the economy vulnerable to the impact of rising trade tensions, leading to a sharper-than-expected economic slowdown.
Despite a government crackdown on debt and risky lending over the last several years, housing prices and bank lending to the sector have continued to rise, pushing homes beyond what the vast majority of people can afford, as well as putting many property developers deeply into debt.
The Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, a top government think tank, said in a report last week that the growth in housing prices in China’s bigger cities, caused by a relatively short supply of new homes, is likely to push up costs across the country.
“The government should closely monitor these cities to avoid overheating,” said Wang Yeqiang, a researcher at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences who co-authored the report.
Property developers have begun a debt-fuelled land-buying spree just as urban housing demand is entering a long-running structural decline, said Julian Evans-Pritchard, senior China economist at Capital Economics. The potential supply of property that could be built on developers’ land reserves jumped last year to a record high, meaning the risk of a glut of new housing is real, Evans-Pritchard added, if developers were to convert all their land reserves into housing tracts.
“Since real estate drives around a fifth of GDP, a sharp downturn in this sector would be contagious, resulting in a jump in defaults across a wide swathe of the economy that could quickly erode bank capital buffers,” he warned.
China’s corporate debt stood at 155 per cent of GDP in the second quarter of 2018, much higher than other major economies, according to data from the Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development. In comparison, Japan’s corporate debt level is 100 per cent of GDP and is 74 per cent in the US. China’s corporate debt includes issuances by its
vehicles which by extension is mostly credit with an implicit guarantee from the central government.
Since real estate drives around a fifth of GDP, a sharp downturn in this sector would be contagious, resulting in a jump in defaults across a wide swathe of the economy that could quickly erode bank capital buffersJulian Evans-Pritchard
China’s imbalance between housing supply and demand may worsen because it faces a similar economic transition that is already well underway in Japan – a
and
that led to Japan’s long-term deflation problem, said Yoshino, who is also the chief adviser to the Japan Financial Services Agency’s Financial Research Centre.
Even if rising housing demand due to urbanisation were to push China’s housing prices higher over the near term, the country faces risks from an oversupply of housing in the longer term due to its increasingly unbalanced demographic structure, he said.
The government has proposed that China’s retirement ages of 45 to 50 years for females and 55 to 60 years for males introduced in the 1980s be gradually increased to 65 years for both by 2045 due to a rapidly ageing population.
The rising population of retirees will consume fewer goods and services compared to younger families with children, and in turn, could dampen business investment given lower expected rates of return.
At the same time, more retirees means a bigger burden on the younger generation of taxpayers, which would reduce their wealth and change patterns of consumption. This is especially worrying on the back of China’s high debt level and pension funding gap, similar to the situation in Japan, Yoshino said.
In Japan, benefits from government pension schemes account for an increasing share of the country’s accumulated debt as spending on social protection programmes now represents more than a third of the government’s total budget.
China’s national pension fund is forecast to peak at 6.99 trillion yuan (US$1 trillion) in 2027 before it gradually runs out by 2035, according to the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences. Photo: AFP
The strain is also evident in China with the
forecast to peak at 6.99 trillion yuan (US$1 trillion) in 2027 before it gradually runs out by 2035, according to the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, forcing the government to start to transfer assets from state-owned companies to fill the funding gap.
Against the broader economic slowdown, compounded by the trade war with the US, policymakers are also expected to carve out a highly expansionary fiscal budget for this year, with the broad deficit surging to 6.6 per cent of China’s GDP, up from 4.7 per cent last year, according to Larry Hu, head of China economics at Macquarie Capital.
Alicia Garcia Herrero, Asia-Pacific chief economist at Natixis, noted that the US criticisms of China’s unfair trade practises and currency manipulation were reminiscent of the US-Japan disputes in the 1980s and 1990s.
Because Japan was politically and economically dependent on the US at that time, it inevitably implemented economic policies to reduce its current account surplus. Subsequently, Japan suffered from the bursting of its asset price bubble, which led to deflation and the lost decades.
However, Herrero said that the modern China is less dependent on the US and so is in a better position to resist pressure to adjust its economic policies to create demand for American products.
Wang Yang, one of the seven members of China’s elite Politburo Standing Committee, said the US-China trade war could slash one percentage point off Beijing’s economic growth this year. Last year, growth expanded at its slowest pace since 1990, while corporate bond defaults hit a record high and banks’ non-performing loan ratio hit a 10-year high.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Ageing population, Asian Development Bank Institute, ‘lost decades’, Bank of Japan, Beijing, Central government, China alert, China’s housing market, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, Chinese imports, demographic structure, Financial Research Centre, financial sector, Financial Services Agency, Global Times, government think tank, gross domestic product (GDP), Home, housing loans, implicit guarantee, Japanese banks, Japanese housing bubble, national pension fund, Organisation for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), Population, real economy, real estate sector, Shanghai, Shenzhen, showing signs, similar to, Supply and demand, tariffs, Uncategorized, urbanisation, US President Donald Trump |
Leave a Comment »
29/05/2019
- Lowy Institute’s 2019 Asia Power Index puts Washington behind both Beijing and Tokyo for diplomatic influence
- Trump’s assault on trade has done little to stop Washington’s decline in regional influence, compared to Beijing, say experts
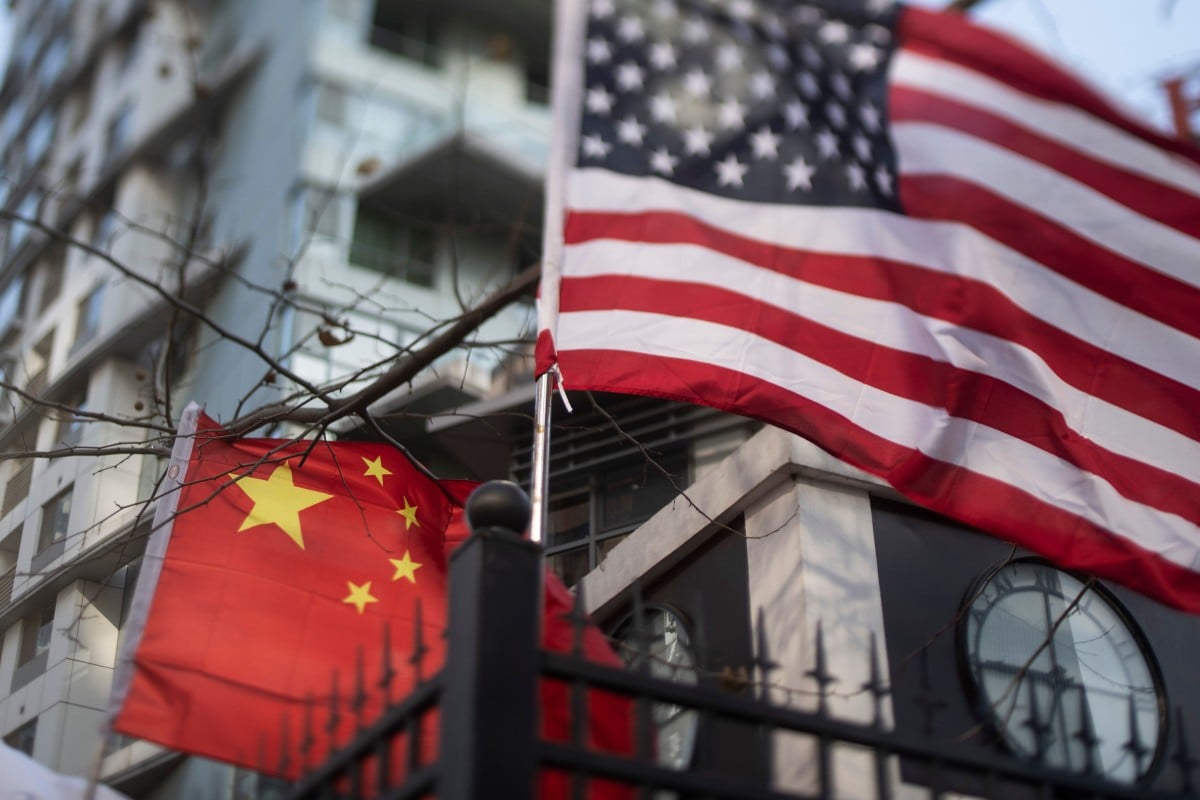
Chinese and US flags at an international school in Beijing. Photo: AFP
The
may be a dominant military force in Asia for now but short of going to war, it will be unable to stop its economic and diplomatic clout from declining relative to China’s power.
That’s the view of Australian think tank the Lowy Institute, which on Tuesday evening released its 2019 index on the distribution of power in Asia.
However, the institute also said China faced its own obstacles in the region, and that its ambitions would be constrained by a lack of trust from its neighbours.
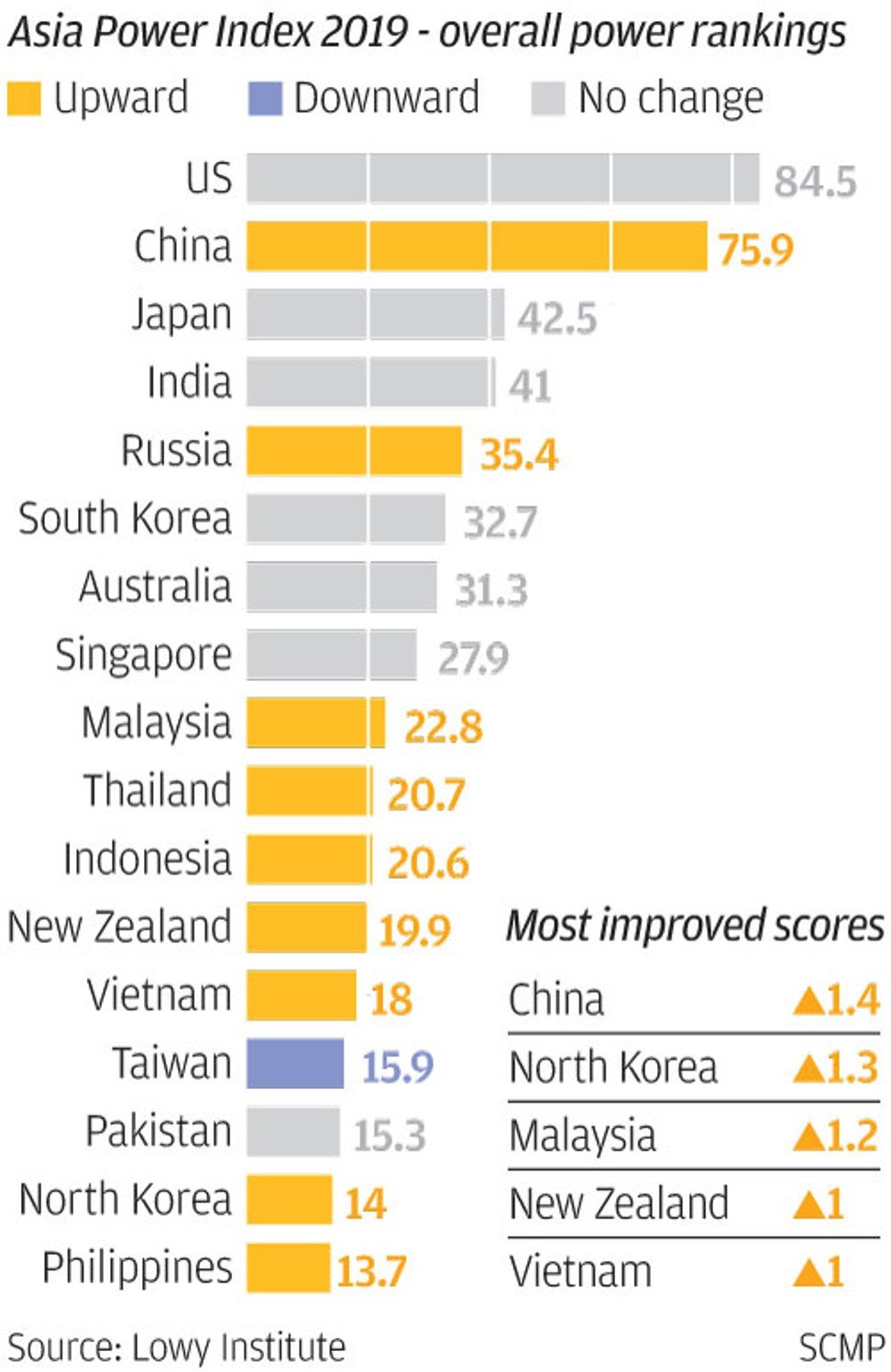
The index scored China 75.9 out of 100, just behind the US, on 84.5. The gap was less than America’s 10 point lead last year, when the index was released for the first time.
“Current US foreign policy may be accelerating this trend,” said the institute, which contended that “under most scenarios, short of war, the United States is unlikely to halt the narrowing power differential between itself and China”.
The Lowy Institute’s Asia Power Index. Click to enlarge.
Share:
Since July, US President
has slapped tariffs on Chinese imports to reduce his country’s
. He most recently hiked a 10 per cent levy on US$200 billion worth of Chinese goods to 25 per cent and has also threatened to impose tariffs on other trading partners such as the European Union and Japan.
Herve Lemahieu, the director of the Lowy Institute’s Asian Power and Diplomacy programme, said: “The Trump administration’s focus on trade wars and balancing trade flows one country at a time has done little to reverse the relative decline of the United States, and carries significant collateral risk for third countries, including key allies of the United States.”
The index rates a nation’s power – which it defines as the ability to direct or influence choices of both state and non-state actors – using eight criteria. These include a country’s defence networks, economic relationships, future resources and military capability.
It ranked Washington behind both Beijing and Tokyo in terms of diplomatic influence in Asia, due in part to “contradictions” between its recent economic agenda and its traditional role of offering consensus-based leadership.
The spoils of trade war: Asia’s winners and losers in US-China clash
Toshihiro Nakayama, a fellow at the Wilson Centre in Washington, said the US had become its own enemy in terms of influence.
“I don’t see the US being overwhelmed by China in terms of sheer power,” said Nakayama. “It’s whether America is willing to maintain its internationalist outlook.”
But John Lee, a senior fellow at the Hudson Institute, said the Trump administration’s willingness to challenge the status quo on issues like trade could ultimately boost US standing in Asia.
“The current administration is disruptive but has earned respect for taking on difficult challenges which are of high regional concern but were largely ignored by the Obama administration –
illegal weapons and China’s predatory economic policies to name two,” said Lee.
“One’s diplomatic standing is not just about being ‘liked’ or ‘uncontroversial’ but being seen as a constructive presence.”
CHINA’S RISE
China’s move up the index overall – from 74.5 last year to 75.9 this year – was partly due to it overtaking the US on the criteria of “economic resources”, which encompasses GDP size, international leverage and technology.
China’s economy grew by more than the size of Australia’s GDP in 2018, the report noted, arguing that its growing base of upper-middle class consumers would blunt the impact of US efforts to restrict Chinese tech firms in Western markets.
US President Donald Trump with Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping. Photo: Reuters
“In midstream products such as smartphones and with regard to developing country markets, Chinese tech companies can still be competitive and profitable due to their economies of scale and price competitiveness,” said Jingdong Yuan, an associate professor at the China Studies Centre at the University of Sydney.
“However, to become a true superpower in the tech sector and dominate the global market remains a steep climb for China, and the Trump administration is making it all the more difficult.”
The future competitiveness of Beijing’s military, currently a distant second to Washington’s, will depend on long-term political will, according to the report, which noted that China already spends over 50 per cent more on defence than the 10
stands in the way of its primacy in Asia, according to the index, which noted Beijing’s unresolved territorial and historical disputes with 11 neighbouring countries and “growing degrees of opposition” to its signature
.
Beijing is locked in disputes in the
with a raft of countries including Vietnam, the Philippines and Brunei, and has been forced to renegotiate infrastructure projects in
and Myanmar due to concerns over feasibility and cost.
If Trump kills off Huawei, do Asia’s 5G dreams die?
Xin Qiang, a professor at the Centre for American Studies at Fudan University in Shanghai, said Beijing still needed to persuade its neighbours it could be a “constructive, instead of a detrimental, force for the region”.
“There are still many challenges for [China to increase its] power and influence in the Asia-Pacific,” Xin said.
Wu Xinbo, also at Fudan University’s Centre for American Studies, said Beijing was having mixed success in terms of winning regional friends and allies.
“For China, the key challenge is how to manage the maritime disputes with its neighbours,” said Wu. “I don’t think there is growing opposition to the Belt and Road Initiative from the region, actually more and more countries are jumping aboard. It is the US that is intensifying its opposition to the project as Washington worries it may promote China’s geopolitical influence.”
Yuan said the rivalry between the
would persist and shape the global order into the distant future.
“They can still and do wish to cooperate where both find it mutually beneficial, but I think the more important task for now and for some time to come, is to manage their disputes in ways that do not escalate to a dangerous level,” Yuan said. “These differences probably cannot be resolved given their divergent interests, perspectives, etc, but they can and should be managed, simply because their issues are not confined to the bilateral [relationship] but have enormous regional and global implications.”
Elsewhere in Asia, the report spotlighted Japan, ranked third in the index, as the leader of the liberal order in Asia, and fourth-placed India as an “underachiever relative to both its size and potential”.
China’s wrong, the US can kill off Huawei. But here’s why it won’t
Lee said the index supported a growing perception that Tokyo had emerged as a “political and strategic leader among democracies in Asia” under
.
“This is important because Prime Minister Abe wants Japan to emerge as a constructive strategic player in the Indo-Pacific and high diplomatic standing is important to that end,” Lee said.
, South Korea, Australia,
, Malaysia and Thailand rounded out the top-10 most powerful countries, in that order. Among the pack, Russia, Malaysia and Thailand stood out as nations that improved their standing from the previous year.
, ranked 14th, was the only place to record an overall decline in score, reflecting its waning diplomatic influence
during the past year.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Asia, Asia Power Index, Asian Power and Diplomacy programme, Australia, Australia’s GDP, Beijing, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), Centre for American Studies, China alert, Chinese tech firms, European Union, Fudan University, geopolitical influence, Huawei, Hudson Institute, Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, Lowy Institute, Malaysia, North Korea, President Xi Jinping, rise, Russia, Short of war, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, think tanks, Tokyo, Uncategorized, US, US President Donald Trump, Washington, Western markets, Wilson Centre in Washington |
Leave a Comment »
29/05/2019
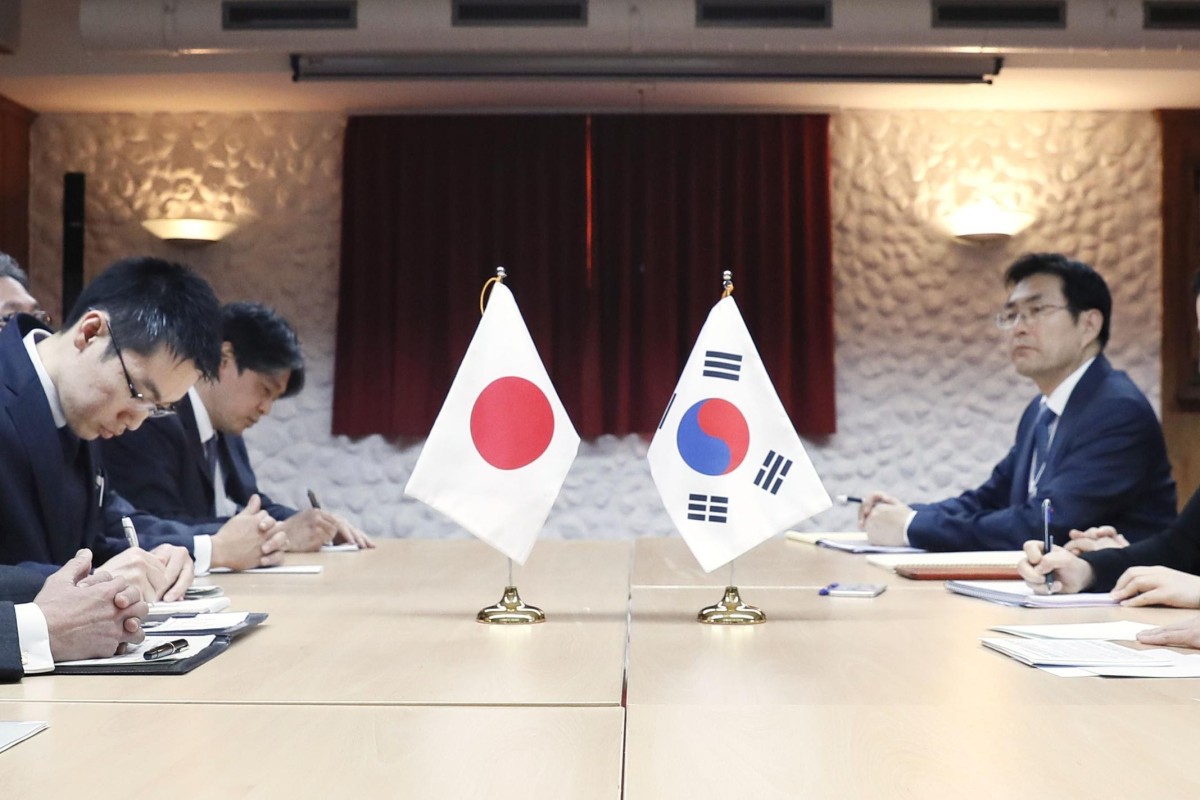
- The Asian security forum in Singapore had been seen as an ideal venue for a breakthrough in the growing diplomatic spat – but Tokyo has got cold feet
- That will ease the pressure on Beijing in the South China Sea, analysts say
Hopes are fading for a breakthrough in Japan-South Korea relations at the Shangri-La Dialogue in Singapore. Photo: Kyodo
Hopes that
and
could use the Shangri-La Dialogue in
to address their growing diplomatic spat are receding.
The three-day Asian security forum, which begins on Friday, had been seen as an ideal neutral venue for the two countries’ defence ministers to hold formal talks on issues including Tokyo’s claim that in January a
onto a Japanese reconnaissance aircraft.
The issue is one of the biggest deviling the bilateral relationship, alongside Japan’s perception that Seoul has backtracked on a promise to draw a line under Japan’s use of
– euphemistically known as “comfort women” – in military-run brothels during World War Two.
However, Tokyo appears to have concluded that formal talks on the sidelines of the Shangri-La Dialogue would be premature. The Yomiuri newspaper has reported that a formal meeting will no longer take place and that Takeshi Iwaya and Jeong Kyeong-doo, his South Korean opposite number, will now be restricted to a brief, stand-up exchange of their positions.
Despite the report, South Korean officials were guarded when asked whether the meeting had been shelved. “A detailed plan [on the bilateral talks] has yet to be fixed. Consultations are still underway between authorities of the two countries,” said the South Korean defence ministry spokesperson Choi Hyun-soo on Tuesday.
Analysts suggested Japan had run out of patience with South Korea and that the biggest winner in the stand off between two US allies would be China.
Japanese Defence Minister Takeshi Iwaya. Photo: Kyodo
“My sense is that Japan sees South Korea as not engaging in negotiations on a number of issues and not adhering in good faith to agreements that it has already signed,” said Stephen Nagy, a senior associate professor of international relations at Tokyo’s International Christian University.
Tokyo has been incensed that the administration of
has gone back on a 2015 agreement that was meant to draw a final line under the “comfort women” issue. Its anger deepened when Seoul said it would not intervene in a South Korean Supreme Court ruling, which ordered Japanese companies to pay up to 120 million won (US$100,000) to each of a dozen
of the Korean peninsula from 1910-1945.
Like its stance on “comfort women”, Japan believed a line had been drawn under the issue, this time in a 1965 pact that normalised relations between the two countries. Seoul argues that the 1965 treaty, which it signed after receiving US$800 million in grants and soft loans from Tokyo as compensation, does not cover individual victims of colonial-era atrocities.
As rift between Japan, South Korea deepens, how hard can Seoul afford to push?
“Japan is not ready to get into any more agreements because it fears that Seoul will not follow through or that they will become politicised in the future,” Nagy said.
“Tokyo wants binding, long-lasting agreements rather than having to renegotiate something each time a new Korean government comes in,” he said.
“The biggest winner in this stand-off between the US’ two most important allies in the region is, of course, China,” he added. “They must be delighted to see this playing out because it means the US is not able to exert nearly as much pressure in areas such as the
A long-standing strategic aim in US foreign policy circles has been to form a trilateral alliance with South Korea and Japan to present a united front against common security concerns, including China’s growing influence. However, the seeming inability of the two countries to get along has long thwarted this ambition.
“If Japan, South Korea and the US could find a way to cooperate, imagine the influence they could exert over the South China Sea or over
,” Nagy said. “If Japan and Korea could find a way to put their differences aside and with their security capacity, it would be a powerful deterrent to Beijing and Pyongyang.”
South Korean protesters demonstrate against Japan’s use of sex slaves – euphemistically termed ‘comfort women’ in World War II. Photo: AFP
Toshimitsu Shigemura, a professor of international relations at Tokyo’s Waseda University, agreed that the schism between Seoul and Tokyo would be of serious concern to Washington, but he believed that US pressure had already been brought to bear on the two neighbours.
“By avoiding talks in Singapore, Japan is doing its best to avoid public problems between the two sides and I believe that talks are already taking place between the two governments on these issues,” he said.
US wants Japan and South Korea to tag team China. But history is in the way
“The US will have told Tokyo and Seoul that it does not want to see more disagreements and that it is very important that they cooperate and calm things down a bit,” he said.
“I am sure that Washington knows exactly what happened when the Korean warship locked onto the Japanese aircraft in January, but they’re not publicly taking sides and instead they’re telling both governments to put the dispute behind them and to move on,” he added.
Other analysts were more pessimistic.
“The dynamics in domestic politics in both countries are currently overwhelming any diplomatic motives to improve bilateral ties,” said Bong Young-sik, a researcher at the Asan Institute for Policy Studies in Seoul.
Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe. Photo: AFP
“For President Moon Jae-in, Japan-bashing is a useful political card to appeal to his supporters while for
, giving the impression that South Korea is going too far in pressing Japan is also beneficial for his own political gains.”
Professor Ha Jong-moon at Hansin University said there were “no solutions in sight” to resolve the differences over forced labour and wartime sex slavery, but said there would be a chance to “smooth ruffled feathers” at the G20 summit in Osaka, which takes place at the end of June.
The last time the defence ministers of the two countries met was in October last year, when they held talks on the sidelines of the Asean Defence Ministers’ Meeting in Singapore.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Asian security forum, associate professor of international relations, ‘win for China’, “comfort women”, Beijing, China alert, cold feet, fire control radar, hopes fade, Japan-South Korea talks, Japan’s colonial rul, Japan’s colonial rule, Japanese, Jeong Kyeong-doo, Korean sex slaves, military-run brothels, President Moon Jae-in, professor of international relations, Pyongyang, reconnaissance aircraft, Seoul, Shangri-La Dialogue, Singapore, South China Sea, South Korea, South Korean Supreme Court, South Korean warship, Stephen Nagy, Takeshi Iwaya, Tokyo, Tokyo’s International Christian University., Tokyo’s Waseda University, Toshimitsu Shigemura, Uncategorized, US allies, World War Two, Yomiuri |
Leave a Comment »
29/05/2019
Chinese Vice President Wang Qishan meets with Pakistani President Arif Alvi in Islamabad, Pakistan, May 26, 2019. Wang Qishan visited Pakistan from Sunday to Tuesday and held meetings with Pakistani President Arif Alvi and Prime Minister Imran Khan respectively on further strengthening bilateral relations. (Xinhua/Yan Yan)
ISLAMABAD, May 28 (Xinhua) — Chinese Vice President Wang Qishan visited Pakistan from Sunday to Tuesday and held meetings with Pakistani President Arif Alvi and Prime Minister Imran Khan respectively on further strengthening bilateral relations.
When meeting with the Pakistani president, Wang said China and Pakistan are “iron friends.” Throughout the past 68 years since the establishment of diplomatic ties, the two countries have always respected and supported each other on issues concerning each others’ core interests, forging the sincerest friendship.
In recent years, the development of China-Pakistan relations has kept a good momentum, with mutual political trust further enhanced, pragmatic cooperation continuously deepened and people-to-people exchanges growing more vigorous, Wang said.
He said the development of the China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC) has made concrete achievements and has become an important hallmark for China-Pakistan friendly cooperation in the new era, adding that his visit was meant for sending out a signal once more to peoples of the two countries and the world that China and Pakistan are all-weather strategic cooperative partners.
Wang said China is willing to strengthen the all-around cooperation with Pakistan in various sectors and at various levels, so as to make the friendship better benefit the two sides and forge a closer China-Pakistan community of shared future in the new era.
For his part, President Arif Alvi extended congratulations to the upcoming 70th anniversary of the founding of the People’s Republic of China. He said Pakistan-China cooperation has become more important in current times. Pakistan is firmly committed to the one-China policy, firmly supports China in safeguarding the country’s core and major interests, he said.
Pakistan wishes to deepen cooperation with China in such areas including agriculture, tourism and trade, with a bid to promote the all-weather strategic cooperative partnership further ahead, said the president, who also expressed appreciation for China’s support to Pakistan and wished China to play a bigger role in international and regional affairs.
After their meeting, the Pakistani president conferred on Wang the Nishan-e-Pakistan, the country’s highest award for foreign leaders.
While meeting with Pakistani Prime Minister Imran Khan, Wang said the prime minister has visited China twice since taking office and reached important consensus with Chinese leaders on further pushing forward the development of bilateral relations.
China is ready to join hands with Pakistan to deepen high-level exchanges, boost strategic communication and pragmatic cooperation as well as closely coordinate in international and regional affairs between the two sides, Wang said.
Wang called on the two sides to work for high-quality CPEC development in the next phase, and make concrete progress in industrial park building and agricultural cooperation.
China will speed up the implementation of social and people’s livelihood projects of early harvest, and discuss the third-party cooperation in the CPEC development, he added.
The Chinese vice president called for strengthened people-to-people and cultural exchanges and collaboration so as to expand the public foundation for the China-Pakistan friendship.
Wang hoped that Pakistan will take effective measures to provide security guarantees for the cooperation and exchanges between the two countries.
Imran Khan, for his part, said that Pakistan adheres to the friendly policy towards China, admires the achievements of China’s reform and opening-up and stands ready to consolidate the traditional friendship with China.
Pakistan also hopes to learn from China in terms of state governance, and enhance exchanges and cooperation in the sectors of agricultural technology, special economic zone development, talent training and anti-corruption.
Noting that fruitful results have been reaped in the CPEC development, the Pakistani prime minister said that the CPEC has played an important role in promoting Pakistan’s economic development and improving people’s livelihood.
He said Pakistan has established a special committee to take charge of inter-department and inter-sector coordination and ensure personnel safety of Chinese institutions in Pakistan.
Pakistan will continue to enhance coordination with China in international and regional affairs so as to enrich bilateral all-weather strategic cooperative partnership.
After the meeting, Wang Qishan and Imran Khan jointly witnessed the signing of bilateral cooperation agreements concerning agriculture, customs and disaster relief.
During his stay in Pakistan, the Chinese vice president also met with local leaders of the Punjab province, addressed the Friends of Silk Road Forum and visited Haier-Ruba Economic Zone.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Arif Alvi, bilateral relations, China alert, China-Pakistan community, China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), Chinese vice president, cooperation, Friends of Silk Road Forum, Haier-Ruba Economic Zone, Imran Khan, Nishan-e-Pakistan, Pakistan, Pakistani President, People's Republic of China (PRC), Prime minister, Punjab, strengthen ties, strengthening, Uncategorized, vows, Wang Qishan |
Leave a Comment »
28/05/2019
Li Zhanshu, chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress (NPC), meets with Veroljub Arsic, deputy speaker of the National Assembly of Serbia, at the Great Hall of the People in Beijing, capital of China, May 27, 2019. (Xinhua/Shen Hong)
BEIJING, May 27 (Xinhua) — China’s top legislator Li Zhanshu Monday met with Veroljub Arsic, deputy speaker of the National Assembly of Serbia, here Monday, calling for closer bilateral ties.
Calling China and Serbia “sincere friends of each other,” Li, chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People’s Congress (NPC), said the bilateral comprehensive strategic partnership has been lifted to a new high under the guidance of the two heads of state.
Bilateral pragmatic cooperation has been at the forefront of the Belt and Road cooperation, Li added.
He called on both countries to consolidate traditional friendship, continue to firmly support each other on core interests and issues of major concern, set examples of political mutual trust, common development and people-to-people exchanges so as to build a closer community with shared interests and a shared future.
Li also called on the two legislatures to enhance cooperation in areas including legislation, supervision and governance in order to better implement the consensus of the two heads of state.
Arsic said the National Assembly of Serbia stands ready to intensify exchanges with the NPC and give full play to the cooperation committee between the legislatures of Serbia and China, to make new contributions to boosting practical cooperation between the two countries and friendship between the two peoples.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Belt and Road Cooperation, bilateral ties, chairman of the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress (NPC), China alert, China's top legislator, closer, comprehensive strategic partnership, deputy speaker, Li Zhanshu, National Assembly of Serbia, Serbia, Uncategorized, Veroljub Arsic |
Leave a Comment »
28/05/2019
- Asia has a rich but largely forgotten history of acceptance of queer relationships
- It was not until the colonial era that sexual and gender diversity came to be seen as a sin
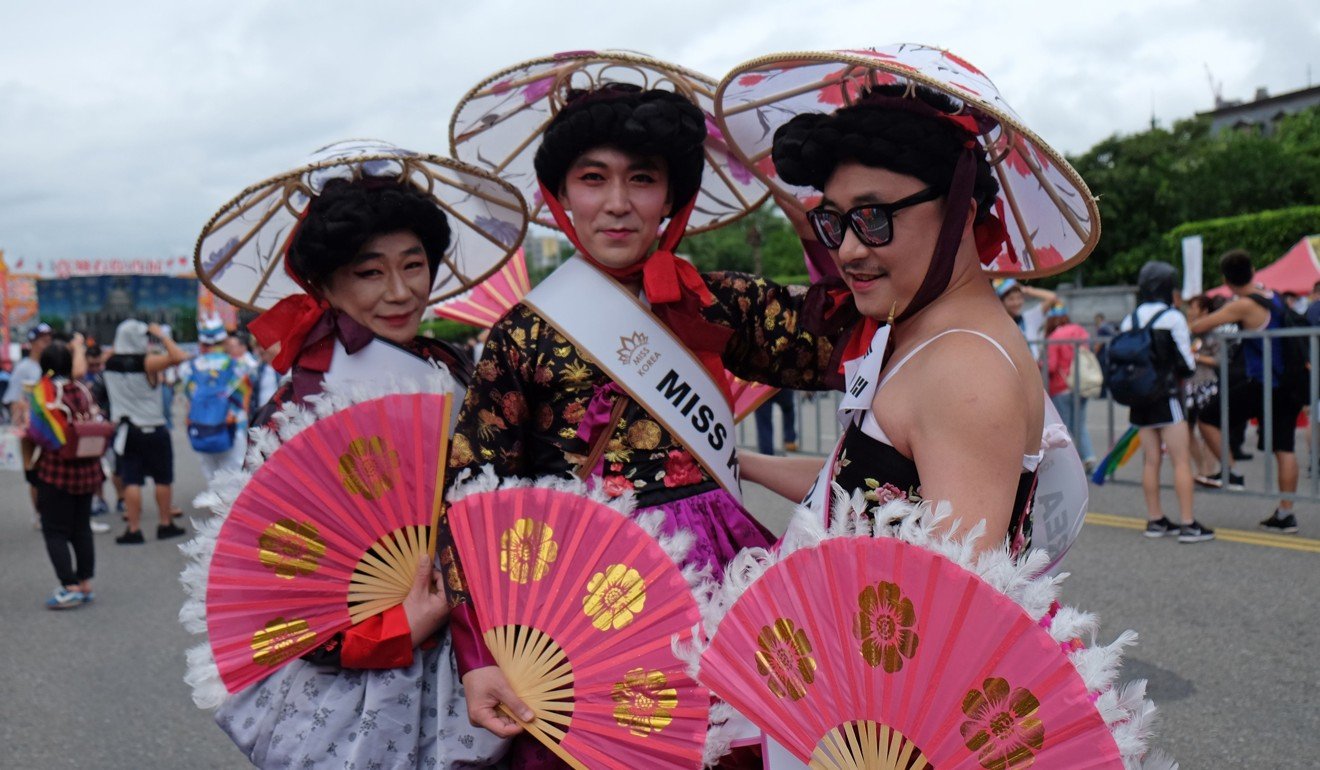
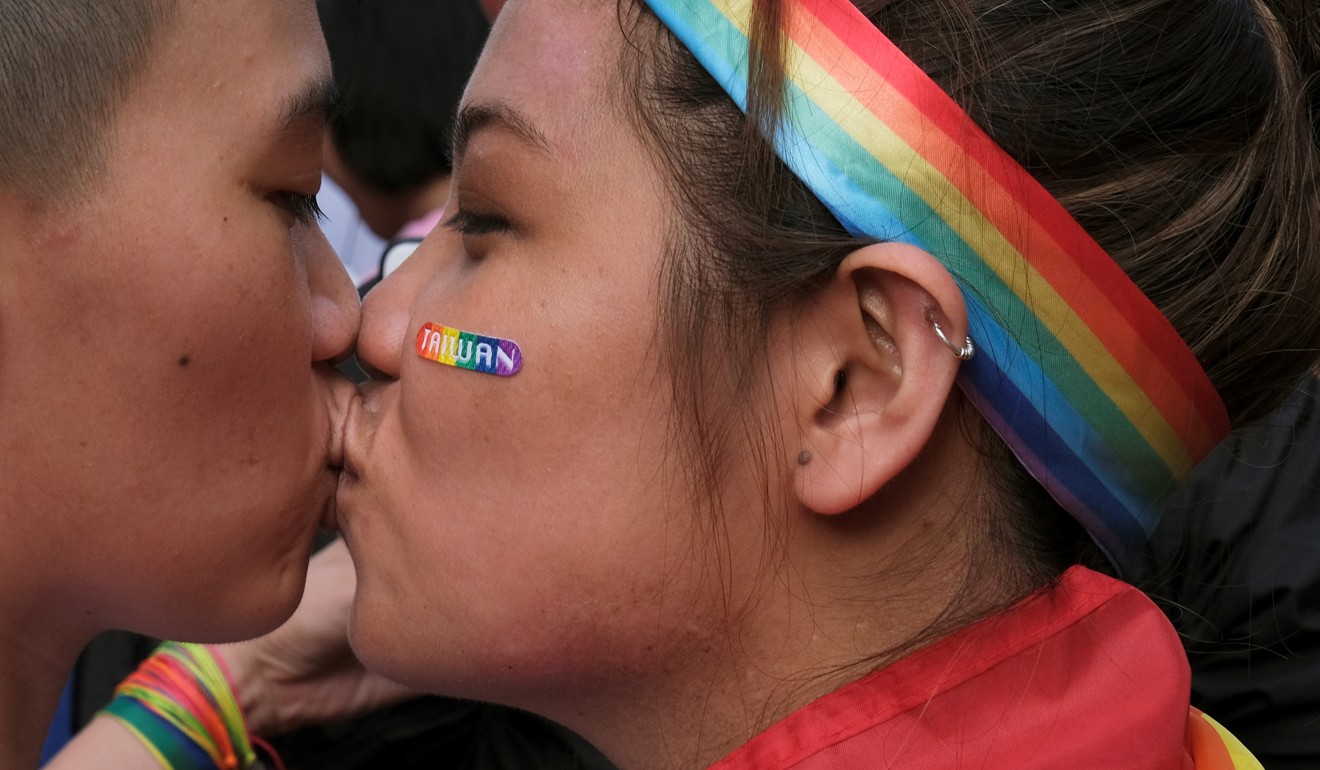
An LGBT pride parade in support of Taiwan’s same-sex marriage law. Photo: Reuters
A
nyone reading the headlines about
legalisation of same-sex marriage
would get the impression this was Asia’s first taste of marriage equality. They would be quite wrong.
While Taiwan may be the first jurisdiction in Asia to legalise the modern form of same-sex marriage, such unions have been recognised across the region in various guises for centuries.
It may be true that Asia does not have a great reputation among the
community, but it does have a rich history of acceptance of sexual and gender diversity – one that has largely been forgotten.
When Europeans first encountered Chinese society, they praised many aspects of it, from its efficient government to the sophisticated lifestyles of the upper-class. But they were shocked and repulsed about one aspect of Chinese society: the “abominable vice of sodomy”.
Opinion: Three lessons for Hong Kong from Taiwan’s LGBT journey
One Portuguese Dominican friar, Gaspar da Cruz, even wrote an apocalyptic tract which portrayed China as the new Sodom – beset by earthquakes, floods, and other natural disasters due to their acceptance of that “filthy abomination, which is that they are so given to the accursed sin of unnatural vice”, that is, sodomy.
Southern China, in particular, was known for a widespread acceptance of homosexual relationships. Shen Defu, a Chinese writer during the Ming dynasty, wrote that it was common for men of all social classes in Fujian province to take male lovers. While men generally took on these lovers while maintaining respectable marriages to women, there were some men who took their lover-relationships to a quasi-marriage level. The older man would be considered qixiong (adoptive older brother) and the younger qidi(adoptive younger brother).
South Korean men take part in Taiwan’s annual LGBT pride parade in Taipei. Photo: AFP
Bret Hinsch, a professor of history in Taiwan, describes the ceremony based on the narration of a Chinese playwright, Li Yu (1610-1680): “Two men sacrifice a carp, a rooster, and a duck. They then exchange their exact times of birth, smear each other’s mothers with the blood of their sacrifices, and then swear eternal loyalty to one another.
The ceremony concludes with feasting on the sacrificial victims …. The younger qidi would move into the qixiong’s household. There he would be treated as a son-in-law by his husband’s parents. Throughout the marriage, many of which lasted for 20 years, the qixiong would be completely responsible for his younger husband’s upkeep.
The marriage would typically dissolve after a number of years so that the younger man could find a bride to marry to procreate and further the family lineage. The elder man was expected to pay the bride a price for the younger man.
These forms of gay “marriage” were prevalent enough in Fujian that there was even a patron deity of homosexuality, the rabbit. Many Han people from Fujian migrated to Taiwan starting in the 17th century; they now make up 80 per cent of the population.
Explained: gay rights, LGBTQ and same-sex marriage in Asia
Most literary accounts of homosexual relationships in China involve men, and there is a lively debate among scholars as to whether women enjoyed the same freedom.
Nevertheless, the most documented of female “quasi-marriages” are the “Golden Orchid Associations” in Guangdong. (Around 15 per cent of Taiwan’s population is Hakka, which historians trace specifically to Han migrants from Guangdong and surrounding areas.) The Golden Orchid Society was a movement based in Guangdong that lasted from the late Qing dynasty until the early 1900s. It provided a “sisterhood” alternative to women who did not want to get married for various reasons.
To announce her intentions, one woman would offer another gifts of peanut candy, dates and other goods. If the recipient accepted the gift, it was a signal she had accepted the proposal. They would swear an oath to one another, where sometimes one woman was designated “husband” and the other “wife”.
A couple kiss as they celebrate Taiwan’s legalisation of same-sex marriage. Photo: Reuters
Hinsch describes the ceremony in this way: “After an exchange of ritual gifts, the foundation of the Chinese marriage ceremony, a feast attended by female companions served to witness the marriage. These married lesbian couples could even adopt female children, who in turn could inherit family property from the couple’s parents.”
While these “marriages” are not equivalent to the same-sex marriages of today, they nevertheless are historical precedents for what is now happening in Taiwan.
And China is far from being the only country in Asia with a queer history – Southeast Asia’s LGBTQ history is even richer.
Why some members of Singapore’s LGBT community prefer life in the shadows
In the early modern period, marriages between two people of the same assigned sex but who identified as different genders, were fairly normal in many parts of Southeast Asia. We know this primarily from the records Europeans kept when they landed on Asian shores.
For instance, here is a letter by a Portuguese missionary, Antonio de Paiva, to his Catholic bishop in 1544 about his observations of the Bugis people in what is now
: “Your lordship will know that the priests of these kings are generally called bissus. They grow no hair on their beards, dress in a womanly fashion, and grow their hair long and braided; they imitate [women’s] speech because they adopt all of the female gestures and inclinations. They marry and are received, according to the custom of the land, with other common men, and they live indoors, uniting carnally in their secret places with the men whom they have for husbands …”
After this scandalised description, the author concludes with amazement that the Christian god, who had destroyed “three cities of Sodom for the same sin”, had not yet destroyed such “wanton people” who were “encircled by evil”.
Drag queens at a gay nightclub in Beijing. Despite its reputation, Asia has a long history of accepting diversity. Photo: EPA
Dating as far back as the 13th century, bissu have traditionally served as council to kings and guarded sacred manuscripts. They are considered a fifth gender within the Bugis’ gender-system: oroané (male men), makkunrai (female women), calabai (male women), calalai (female men), and bissu, who were neither male nor female (or both).
Brunei’s LGBT residents face up to new death by stoning law against gay sex
Today, their ranks have thinned – in one area, the population has dwindled to just six people – but the tradition remains, and they still perform important blessings. Contemporary bissu are typically male-bodied individuals who adopt feminine and masculine elements in their appearance. Although in the past bissu were married men, today they are required to be celibate.
In pre-Islamic Bugis culture, bissu were accorded priestly honours and tasked with mediating between the gods and people precisely because of, not in spite of, their gender. According to professor Halilintar Lathier, an Indonesian anthropologist, Bugis culture “perceived the upper world as male and this world as female, and therefore only a meta-gender would be able to become an intermediary”.
This pattern of a “gender-expansive” priest able to marry others of the same sex recurs throughout Southeast Asia.
A transgender beauty contest in Pattaya, Thailand. Despite its reputation, Asia has a long history of accepting diversity. Photo: Handout
To the west of South Sulawesi is Borneo, a large island that contains all of Brunei and parts of Indonesia and
. Borneo is home to many indigenous communities, including the Iban. The Iban historically respected manang bali, who were typically male-bodied shamans who adopted feminine dress and demeanour, and who took men as their husbands. Manang bali were mediators and held roles of great ritual importance; they were typically wealthy village chiefs known for their healing arts.
West of Borneo is the Malay Peninsula, where there are records from the Malay Annals and Misa Melayu dating as far back as the 15th century about priests, called sida-sida, who served in the palaces of the Malay sultans. They were responsible for safeguarding women in the palace as well as the food and clothing of royalty, and overseeing ritual protocol. The sida-sida undertook “androgynous behaviour” such as wearing women’s clothing and doing women’s tasks. A Malay anthropologist in the 1950s, Shamsul A.B., recalls seeing male-bodied sida-sida in the royal palace in his childhood, who were believed by the population to either be celibate and asexual, or attracted to men. Michael Peletz, an anthropologist and author of Gender Pluralism in Southeast Asia, notes that based on the evidence, it is “highly likely” that sida-sida involved both male- and female-bodied people who were involved in transgender practices, and who engaged in sexual relationships with people of the same and opposite sex.
How a gay student’s suicide is helping Japan’s LGBT community speak up
Northeast of Malaysia is the
, where pre-colonial communities were religiously led by babylan: women healers and shamans who were responsible for mediating between the gods and people. Male-bodied people (asog, bayog), sometimes considered a third sex, could also hold these roles so long as they comported themselves like women. A 16th century Spanish Catholic manuscript records asog in the following manner:
“Ordinarily they dress as women, act like prudes and are so effeminate that one who does not know them would believe they are women … they marry other males and sleep with them as man and wife and have carnal knowledge.”
Dancers perform at the Shanghai PRIDE opening party. Despite its reputation, Asia has a long history of accepting diversity. Photo: AFP
The Spanish priests saw these asog as “devil-possessed”, particularly because they habitually practised “sodomy” among one another. Due to the Chinese reputation for homosexuality and various Sinophobic attitudes, some even attributed the prevalence of sodomy to the Chinese, whom they said had “infected the natives” and introduced the curse to the “Indians”, although there is no evidence of this.
COLONIAL CURVEBALL
Although these examples relate to the religious arena, anthropologists believe the respect accorded to these ritual specialists were an indicator of a wider societal acceptance of gender and sexual diversity in Southeast Asia – an acceptance that began to be eroded through the introduction of world religions (particularly Christianity), modernity, and colonialism. For example, in Malaysia, Brunei,
, Myanmar and throughout the commonwealth, the British enforced a penal code that legislated against sodomy. More than half of the countries that currently legally prohibit sodomy do so based on laws created by the British.
On gay sex, India has assumed an ancient position. Read the kama sutra
Similarly, after the Chinese were defeated by Western and Japanese imperialists, many Chinese progressives in the early 20th century sought to modernise China, which meant adopting “modern” Western ideas of dress, relationships, science and sexuality.
Concubinage was outlawed, prostitution was frowned upon, and women’s feet were unbound. It also meant importing European scientific understandings of homosexuality as an inverted or perverted pathology. These “scientific ideas” were debunked in the 1960s in the West, but lived on in China, frozen in time, and have only recently begun to thaw with the rise of LGBTQ activists in Asia.
A recent headline on the news from Taiwan read: “First in Asia: marriage equality comes to Taiwan”, as if the recent bill was an unprecedented “first” for Asia and that marriage equality – which, presumably, the headline writer associates with the West – has finally reached Asian shores.
But when we zoom out historically, it is evident that what happened in Taiwan is not so much a novel “breakthrough” for Asia. It is more a reconnection to its queer Chinese and Asian heritage, as well as a rejection of outdated Western ideas that it once adopted.
There is still much more work to be done to advance LGBT rights in Taiwan and the rest of Asia, but perhaps looking backwards in time can help us move forward.
Source: SCMP
Posted in adoptive older brother), adoptive younger brother, anthropologist, Antonio de Paiva, Asia, “Golden Orchid Associations”, “sisterhood” alternative, babylan, Beijing, bissu, Borneo, Bret Hinsch, Brunei, Bugis people, Bugis’ gender-system, calabai (male women), calalai (female men), carnal knowledge, carp, celibate, China alert, Chinese playwright, Chinese progressives, Chinese Society, colonial era, Concubinage, Drag queen, duck, embraced, encountered, Europeans, female “quasi-marriages”, Fujian Province, gay ‘marriage’, gay nightclub, gender diversity, Gender Pluralism in Southeast Asia, Guangdong, Hakka, Han, History, homosexual relationships, Iban, imperialists, Indians, Indonesia, Japanese, jurisdiction, Li Yu (1610-1680), makkunrai (female women), Malay Annals, Malay Peninsula, Malaysia, male lovers, Michael Peletz, Ming Dynasty, Misa Melayu, Myanmar, neither male nor female (or both), oroané (male men), patron deity of homosexuality, Pattaya, perverted, Portuguese missionary, professor of history, Prostitution, qidi, qixiong, queer relationships, rabbit, rooster, sexual and gender diversity, sin, Singapore, Sinophobic attitudes, Sodom, South Korean men, South Sulawesi, southern China, Spanish priests, Taiwan, Taiwan’s law, Thailand, times of birth, transgender beauty contest, Uncategorized, West, Western |
Leave a Comment »
26/05/2019
Infrared camera image taken on April 20, 2019 shows an all-white giant panda in the Wolong National Nature Reserve in southwest China’s Sichuan Province. A rare all-white panda has been captured on cameras in the Wolong National Nature Reserve in southwest China’s Sichuan Province, the reserve management authorities said on Saturday. (Xinhua)
CHENGDU, May 25 (Xinhua) — A rare all-white panda has been captured on camera in the Wolong National Nature Reserve in southwest China’s Sichuan Province, the reserve management authorities said on Saturday.
The panda was captured in mid-April by an infrared camera about 2,000 meters above sea level in the wild, the authorities said.
The panda has no spots on its body and its eyes look red. It was crossing the forest at the time.
“Judging from pictures, the panda is an albino, one to two years old,” said Li Sheng, a researcher with Peking University and a specialist in bears, who studied the pictures.
The panda is a rare all-white individual in wild pandas, which showed that the albinism genes exist in the wild population of giant pandas in Wolong, he said.
“The panda looked strong and its steps were steady, a sign that the genetic mutation may not have quite impeded its life,” Li said, adding that the gender of the panda cannot be decided based on current data.
Albinism exists in different vertebrate species. The albino mutation inhibits melanin synthesis in animal’s body. Albino usually does not affect animal’s physical makeup and functions. It could make them easier to be discovered and more sensitive to direct sunlight, Li said.
The albino mutation is a recessive gene. Only when the parent pandas both carry such gene, can the baby show the albino traits.
If this white panda would mate with a normal panda, their first generation babies will still be black and white. But their babies, carrying the albino gene, will possibly give birth to all-white pandas if their partners also carry such genes, Li said.
In order to better protect the ecosystems, the Wolong nature reserve has been using infrared cameras to monitor the distribution and activities of wild animals in its seven demonstration areas.
Previously, some rare brown giant pandas were found in China’s Qinling Mountains. The cause of the brown fur color was also considered as genetic mutation by some researchers.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in albino, brown fur color, China alert, Peking University, Qinling Mountains, Rare all-white panda, sichuan province, spotted, Uncategorized, Wolong National Nature Reserve |
Leave a Comment »
26/05/2019
BEIJING (Reuters) – It’s the most sensitive day of the year for China’s internet, the anniversary of the bloody June 4 crackdown on pro-democracy protests at Tiananmen Square, and with under two weeks to go, China’s robot censors are working overtime.
Censors at Chinese internet companies say tools to detect and block content related to the 1989 crackdown have reached unprecedented levels of accuracy, aided by machine learning and voice and image recognition.
“We sometimes say that the artificial intelligence is a scalpel, and a human is a machete,” said one content screening employee at Beijing Bytedance Co Ltd, who asked not to be identified because they are not authorised to speak to media.
Two employees at the firm said censorship of the Tiananmen crackdown, along with other highly sensitive issues including Taiwan and Tibet, is now largely automated.
Posts that allude to dates, images and names associated with the protests are automatically rejected.
“When I first began this kind of work four years ago there was opportunity to remove the images of Tiananmen, but now the artificial intelligence is very accurate,” one of the people said.
Four censors, working across Bytedance, Weibo Corp and Baidu Inc apps said they censor between 5,000-10,000 pieces of information a day, or five to seven pieces a minute, most of which they said were pornographic or violent content.
Despite advances in AI censorship, current-day tourist snaps in the square are sometimes unintentionally blocked, one of the censors said.
Bytedance declined to comment, while Weibo and Baidu did not respond to requests for comment.
SENSITIVE PERIOD
The Tiananmen crackdown is a taboo subject in China 30 years after the government sent tanks to quell student-led protests calling for democratic reforms. Beijing has never released a death toll but estimates from human rights groups and witnesses range from several hundred to several thousand.
June 4th itself is marked by a cat-and-mouse game as people use more and more obscure references on social media sites, with obvious allusions blocked immediately. In some years, even the word “today” has been scrubbed.
In 2012, China’s most-watched stock index fell 64.89 points on the anniversary day here, echoing the date of the original event in what analysts said was likely a strange coincidence rather than a deliberate reference.
Still, censors blocked access to the term “Shanghai stock market” and to the index numbers themselves on microblogs, along with other obscure references to sensitive issues.
While companies censorship tools are becoming more refined, analysts, academics and users say heavy-handed policies mean sensitive periods before anniversaries and political events have become catch-alls for a wide range of sensitive content.
In the lead-up to this year’s Tiananmen Square anniversary, censorship on social media has targeted LGBT groups, labour and environment activists and NGOs, they say.
Upgrades to censorship tech have been urged on by new policies introduced by the Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC). The group was set up – and officially led – by President Xi Jinping, whose tenure has been defined by increasingly strict ideological control of the internet.
The CAC did not respond to a request for comment.
Last November, the CAC introduced new rules aimed at quashing dissent online in China, where “falsifying the history of the Communist Party” on the internet is a punishable offence for both platforms and individuals.
The new rules require assessment reports and site visits for any internet platform that could be used to “socially mobilise” or lead to “major changes in public opinion”, including access to real names, network addresses, times of use, chat logs and call logs.
One official who works for CAC told Reuters the recent boost in online censorship is “very likely” linked to the upcoming anniversary.
“There is constant communication with the companies during this time,” said the official, who declined to directly talk about the Tiananmen, instead referring to the “the sensitive period in June”.
Companies, which are largely responsible for their own censorship, receive little in the way of directives from the CAC, but are responsible for creating guidelines in their own “internal ethical and party units”, the official said.
SECRET FACTS
With Xi’s tightening grip on the internet, the flow of information has been centralised under the Communist Party’s Propaganda Department and state media network. Censors and company staff say this reduces the pressure of censoring some events, including major political news, natural disasters and diplomatic visits.
“When it comes to news, the rule is simple… If it is not from state media first, it is not authorised, especially regarding the leaders and political items,” said one Baidu staffer.
“We have a basic list of keywords which include the 1989 details, but (AI) can more easily select those.”
Punishment for failing to properly censor content can be severe.
In the past six weeks, popular services including a Netease Inc news app, Tencent Holdings Ltd’s news app TianTian, and Sina Corp have all been hit with suspensions ranging from days to weeks, according to the CAC, meaning services are made temporarily unavailable on apps stores and online.
For internet users and activists, penalties can range from fines to jail time for spreading information about sensitive events online.
In China, social media accounts are linked to real names and national ID numbers by law, and companies are legally compelled to offer user information to authorities when requested.
“It has become normal to know things and also understand that they can’t be shared,” said one user, Andrew Hu. “They’re secret facts.”
In 2015, Hu spent three days in detention in his home region of Inner Mongolia after posting a comment about air pollution onto an unrelated image that alluded to the Tiananmen crackdown on Twitter-like social media site Weibo.
Hu, who declined to use his full Chinese name to avoid further run-ins with the law, said when police officers came to his parents house while he was on leave from his job in Beijing he was surprised, but not frightened.
“The responsible authorities and the internet users are equally confused,” said Hu. “Even if the enforcement is irregular, they know the simple option is to increase pressure.”
Source: Reuters
Posted in anniversary, artificial intelligence (AI), Baidu, Baidu Inc, Bytedance, cat-and-mouse game, China alert, Communist Party’s Propaganda Department, crank up, Cyberspace Administration of China (CAC), diplomatic visits, Human, Inner Mongolia, LGBT groups, machete, major political news, natural disasters, Netease Inc, President Xi Jinping, pro-democracy protests, robot censors, scalpel, Shanghai stock market, Sina Corp, taboo subject, Taiwan, Tencent Holdings Ltd, Tiananmen Square, TianTian, Tibet, Uncategorized, Weibo, Weibo Corp |
Leave a Comment »
25/05/2019
TASHKENT, May 24 (Xinhua) — Uzbek and Chinese experts discussed innovative approaches to the education of preschool children at a forum held here on Friday.
The one-day forum opens a new direction in cooperation between the two countries, said Agrippina Shin, minister of preschool education of Uzbekistan.
It has become an effective platform for comparing notes, she said in her opening speech.
The forum was held as the two sides are implementing the consensus reached by the leaders of the two countries and are advancing cooperation in people-to-people exchanges and education, said Jiang Yan, Chinese ambassador to Uzbekistan.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Agrippina Shin, China alert, Chinese ambassador to Uzbekistan, cooperate, innovative approaches, Jiang Yan, minister of preschool education, preschool education, Uncategorized, Uzbek, Uzbekistan |
Leave a Comment »
25/05/2019
BEIJING, May 25 (Xinhua) — China’s service trade with countries and regions along the Belt and Road (B&R) reached over 120 billion U.S. dollars last year, according to the Ministry of Commerce (MOC).
In 2018, the import-export volume of the service trade between China and Belt and Road countries and regions amounted to 121.7 billion U.S. dollars, accounting for 15.4 percent of China’s service trade, said Wang Bingnan, vice minister of the MOC.
China has been the world’s second-largest country in service trade for five consecutive years, with the total volume reaching 5.24 trillion yuan (759 billion U.S. dollars) in 2018, up 11.5 percent year on year, MOC data showed.
The share of service trade in China’s total foreign trade went up from 11.1 percent in 2012 to 14.7 percent in 2018, according to the MOC.
China has established bilateral cooperation mechanisms on service trade with 14 countries, endowing the country with a more diversified service trade market, said Wang.
The 2019 China International Fair for Trade in Services will open on May 28 in Beijing and last for five days, attracting 130 countries and regions and 21 international organizations.
Among the delegations, 98 come from the Belt and Road Initiative partner countries. A series of themed activities will be held during the fair, including forums on service trade cooperation.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Beijing, China alert, China International Fair for Trade in Services, Ministry of Commerce (MOC)., service trade, Uncategorized, vice minister of the MOC, Wang Bingnan |
Leave a Comment »