29/03/2020
- Virus may have jumped from animal to humans long before the first detection in Wuhan, according to research by an international team of scientists
- Findings significantly reduce the possibility of the virus having a laboratory origin, director of the US National Institute of Health says
An international team of scientists say the coronavirus may have jumped from animal to humans long before the first detection in China. Photo: AP
The
coronavirus that causes Covid-19 might have been quietly spreading among humans for years or even decades before the sudden outbreak that sparked a global health crisis, according to an investigation by some of the world’s top virus hunters.
Researchers from the United States, Britain and Australia looked at piles of data released by scientists around the world for clues about the virus’ evolutionary past, and found it might have made the jump from animal to humans long before the first detection in the central China city of Wuhan.
Though there could be other possibilities, the scientists said the coronavirus carried a unique mutation that was not found in suspected animal hosts, but was likely to occur during repeated, small-cluster infections in humans.
The study, conducted by Kristian Andersen from the Scripps Research Institute in California, Andrew Rambaut from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland, Ian Lipkin from Columbia University in New York, Edward Holmes from the University of Sydney, and Robert Garry from Tulane University in New Orleans, was published in the scientific journal Nature Medicine on March 17.
Dr Francis Collins, director of the US National Institute of Health, who was not involved in the research, said the study suggested a possible scenario in which the coronavirus crossed from animals into humans before it became capable of causing disease in people.
“Then, as a result of gradual evolutionary changes over years or perhaps decades, the virus eventually gained the ability to spread from human to human and cause serious, often life-threatening disease,” he said in an article published on the institute’s website on Thursday.
In December, doctors in Wuhan began noticing a surge in the number of people suffering from a mysterious pneumonia. Tests for flu and other pathogens returned negative. An unknown strain was isolated, and a team from the Wuhan Institute of Virology led by Shi Zhengli traced its origin to a bat virus found in a mountain cave close to the China-Myanmar border.
The two viruses shared more than 96 per cent of their genes, but the bat virus could not infect humans. It lacked a spike protein to bind with receptors in human cells.
Coronaviruses with a similar spike protein were later discovered in Malayan
pangolins
by separate teams from Guangzhou and Hong Kong, which led some researchers to believe that a recombination of genomes had occurred between the bat and pangolin viruses.
Doctors in Wuhan began noticing a surge in the number of people suffering from a mysterious pneumonia in December. Photo: Handout
But the new strain, or SARS-Cov-2, had a mutation in its genes known as a polybasic cleavage site that was unseen in any coronaviruses found in bats or pangolins, according to Andersen and his colleagues.
This mutation, according to separate studies by researchers from China, France and the US, could produce a unique structure in the virus’ spike protein to interact with furin, a widely distributed enzyme in the human body. That could then trigger a fusion of the viral envelope and human cell membrane when they came into contact with one another.
Some human viruses including HIV and Ebola have the same furin-like cleavage site, which makes them contagious.
It is possible that the mutation happened naturally to the virus on animal hosts. Sars (severe acute respiratory syndrome) and Mers (Middle East respiratory syndrome), for instance, were believed to have been direct descendants of species found in masked civets and camels, which had a 99 per cent genetic similarity.
There was, however, no such direct evidence for the novel coronavirus, according to the international team. The gap between human and animal types was too large, they said, so they proposed another alternative.
“It is possible that a progenitor of SARS-CoV-2 jumped into humans, acquiring the genomic features described above through adaptation during undetected human-to-human transmission,” they said in the paper.
“Once acquired, these adaptations would enable the pandemic to take off and produce a sufficiently large cluster of cases to trigger the surveillance system that detected it.”
They said also that the most powerful computer models based on current knowledge about the coronavirus could not generate such a strange but highly efficient spike protein structure to bind with host cells.
The study had significantly reduced, if not ruled out, the possibility of a laboratory origin, Collins said.
“In fact, any bioengineer trying to design a coronavirus that threatened human health probably would never have chosen this particular conformation for a spike protein,” he said.
The findings by Western scientists echoed the mainstream opinion among Chinese researchers.
Zhong Nanshan, who advises Beijing on outbreak containment policies, had said on numerous occasions that there was growing scientific evidence to suggest the origin of the virus might not have been in China.
“The occurrence of Covid-19 in Wuhan does not mean it originated in Wuhan,” he said last week.
A doctor working in a public hospital treating Covid-19 patients in Beijing said numerous cases of mysterious pneumonia outbreaks had been reported by health professionals in several countries last year.
Re-examining the records and samples of these patients could reveal more clues about the history of this worsening pandemic, said the doctor, who asked not to be named due to the political sensitivity of the issue.
“There will be a day when the whole thing comes to light.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in animal hosts, Australia, bat virus, Beijing, Britain, California, camels, China-Myanmar border, Columbia University, contagious, coronavirus, COVID-19, decades, Ebola, France, furin, Guangzhou, HIV, Hong Kong, humans, Malayan pangolins, masked civet, Mers (Middle East respiratory syndrome), mountain cave, Nature Medicine, New Orleans, New York, novel coronavirus, outbreak, pathogen, researchers, Sars (severe acute respiratory syndrome), Scotland, Scripps Research Institute, spreading, Tulane University, Uncategorized, United States, University of Edinburgh, University of Sydney, US, US National Institute of Health, Wuhan, Wuhan Institute of Virology |
Leave a Comment »
03/03/2020
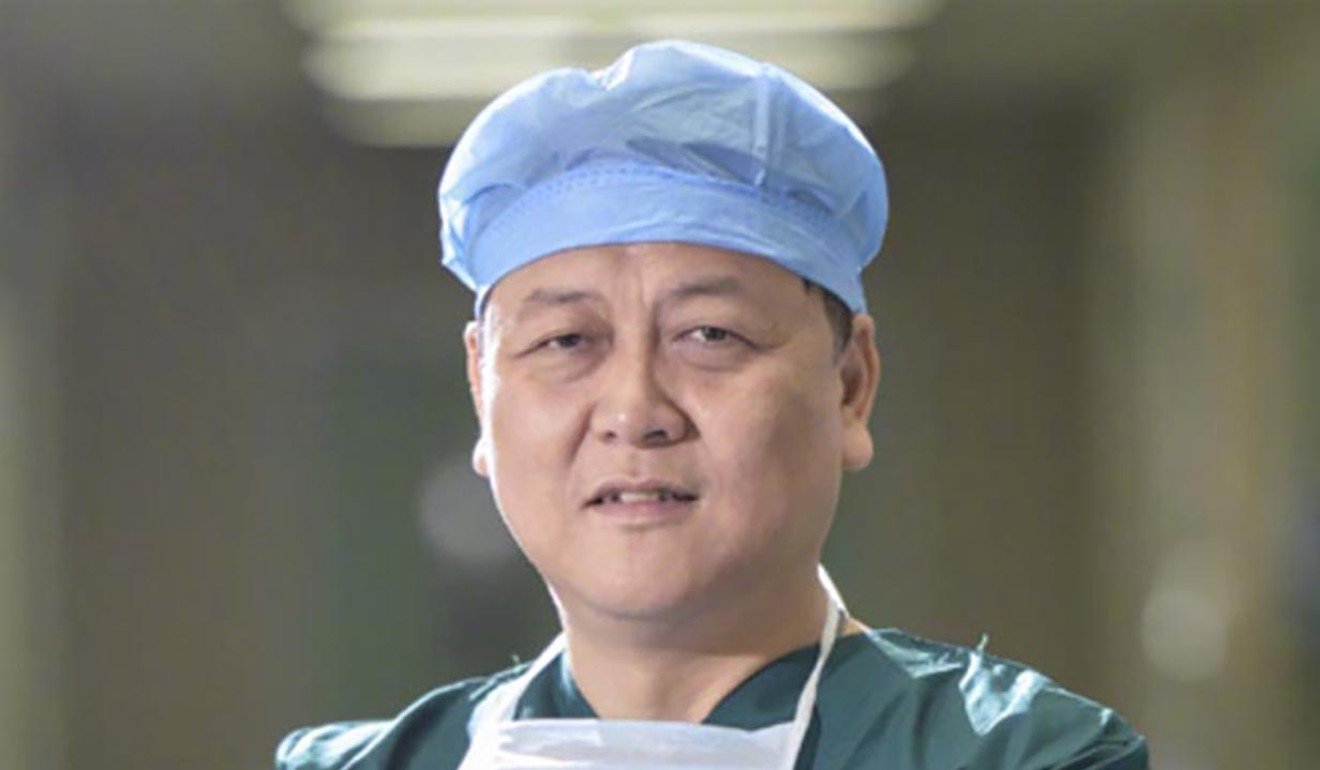
- Ophthalmologist Mei Zhongming, 57, said to have been infected after working long hours treating patients
- He is the third doctor from the hospital to die from Covid-19
Mei Zhongming died at the age of 57 after contracting the virus while he was working at the Wuhan Central Hospital. Photo: Weibo
An ophthalmologist who worked with whistle-blower doctor Li Wenliang on the coronavirus front line in Wuhan has also died from Covid-19, the disease caused by the virus.
Mei Zhongming, 57, contracted the virus while he was working at the Wuhan Central Hospital and died on Tuesday.
His 34-year-old colleague Li – who was silenced by police for sounding the alarm about the new virus strain – also died from the pneumonia-like illness last month, prompting an outpouring of grief and anger in China.
Mei is the third doctor from the hospital to die from Covid-19. Two days ago, Jiang Xueqing, head of thyroid and breast surgery, also died from the disease at the age of 55.
The hospital expressed condolences to Mei’s family and praised his 30 years of service in a brief announcement on social network WeChat.
Public mourning in China after death of coronavirus whistle-blower doctor Li Wenliang
According to the official numbers, 13 doctors and nurses have died from Covid-19 and more than 3,000 have been infected in China since the epidemic began in the central city of Wuhan in December. Hospitals in Wuhan and across the province of Hubei have been swamped with tens of thousands of patients, and health care workers treating them have also had to cope with a shortage of protective gear and medical supplies.
Part of the Wuhan Central Hospital is located just 2km (1.2 miles) from the Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market – the place the first coronavirus patients were linked to.
The hospital started treating patients who had been in close contact with the market in the middle of December, the director of its emergency department Ai Fen told China News Weekly last month.
Doctors reported the cases to management but no action was taken to protect medical staff at first, and they were warned not to talk publicly about the respiratory illness, the report said.
The Chinese medical workers on the front line of the coronavirus fight in Wuhan
posted a message to a closed group of medical school classmates on WeChat on December 30, warning them about an outbreak of a mysterious viral pneumonia at his hospital.
Two days later, Wuhan police announced that eight people had been punished for “spreading rumours”. It was later reported that they were all medical staff and one of them was Li.
The young doctor fell ill on January 10, later saying that he was probably infected by an 82-year-old glaucoma patient. “The patient did not have a fever, and I didn’t wear extra protection while taking care of her,” Li wrote in his blog. “I was careless.”
Li died from the illness on February 7, sparking widespread grief and fury over Beijing’s crackdown on “online rumours”, and calls for freedom of speech.
According to emergency department director Ai, staff on the front line at Wuhan Central Hospital began wearing N95 respirator masks and other protective gear in January as the number of virus cases jumped – but before authorities confirmed the virus was being transmitted between humans on January 20.
Despite the precautions, the first medical worker at the hospital was confirmed with the virus on January 10. More than 30 others from the emergency department alone have tested positive for Covid-19 since then, Ai told China News Weekly. The department has a staff of 200.
Jiang Xueqing, 55, head of thyroid and breast surgery at the hospital, died on Sunday. Photo: Weibo
The hospital did not give details of how Mei contracted the virus. But a report from the Wuhan Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference on February 18 said he had been infected after working long hours on the coronavirus front line.
Similarly, little information was released about Jiang’s death on Sunday. His colleague Li Hai told official newspaper People’s Daily that Jiang had been exhausted after working “non-stop” treating coronavirus patients.
Wuhan, China scrambles to handle massive amount of medical waste during the epidemic
Ian Lipkin, John Snow professor of epidemiology at the Mailman School of Public Health at Columbia University, said the risks faced by health care workers were high, even with protective gear, as they had a very intimate relationship with their patients.
“In addition, those individuals who are working in hospital settings may be immunosuppressed because, frankly, they’re exhausted … the viral load that they receive may be larger,” Lipkin said in a briefing last month after visiting China at the invitation of the government.
The coronavirus has claimed the lives of several young medical workers. Among the youngest was 29-year-old respiratory and critical care doctor Peng Yinhua, who worked at the Jiangxia district People’s No 1 Hospital in Wuhan and died last month from the disease. Peng had planned to get married over the Lunar New Year holiday but postponed his wedding to help treat coronavirus patients.
Another 29-year-old, gastroenterologist Xia Sisi, also died last month after she became infected while working at the Union Jiangbei Hospital in Wuhan.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Antarctica, China News Weekly, Columbia University, continent, contracting, coronavirus, COVID-19, dies, doctor, emergency department, epidemic, front line, gastroenterologist, head of thyroid and breast surgery, Hospital, Huanan Seafood Wholesale Market, hubei province, Jiangxia District's No. 1 people's hospital, Mailman School of Public Health, N95 respirator masks, professor of epidemiology, third, Uncategorized, Union Jiangbei Hospital, whistle-blower, worked, Wuhan, Wuhan Central Hospital, Wuhan Committee of the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference |
Leave a Comment »
02/12/2019
- World’s largest coal consumer shows little sign of ending its dependency even though it is also the biggest market for renewable energy sources
- UN climate summit is meeting to discuss ways to limit future warming, but hopes are fading that China will commit to further curbs on emissions
China now accounts for around 30 per cent of the world’s carbon emissions. Photo: AP
As world leaders gather in Spain to discuss how to slow the warming of the planet, the spotlight has fallen on China – the top emitter of greenhouse gases.
China burns about half the coal used globally each year. Between 2000 and 2018, its annual carbon emissions nearly tripled, and it now accounts for about 30 per cent of the world’s total.
Yet it is also the leading market for solar panels, wind turbines and electric vehicles, and it manufactures about two-thirds of solar cells installed worldwide.
“We are witnessing many contradictions in China’s energy development,” said Kevin Tu, a Beijing-based fellow with the Centre on Global Energy Policy at Columbia University. “It’s the largest coal market and the largest clean energy market in the world.”
That apparent paradox is possible because of the sheer scale of China’s energy demands.
Pollution alarm as tourism businesses contaminate home of China’s hairy crab
But as China’s economy slows to the lowest level in a quarter century – around 6 per cent growth, according to government statistics – policymakers are doubling down on support for coal and other heavy industries, the traditional backbones of China’s energy system and economy. At the same time, the country is reducing subsidies for renewable energy.
At the annual United Nations climate summit, this year in Madrid, government representatives will put the finishing touches on implementing the 2015 Paris Agreement, which set a goal to limit future warming to 1.5 to 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Nations may decide for themselves how to achieve it.
China had previously committed to shifting its energy mix to 20 per cent renewables, including nuclear and hydroelectric energy.
Climate experts generally agree that the initial targets pledged in Paris will not be enough to reach the goal, and next year nations are required to articulate more ambitious targets.
Hopes that China would offer to do much more are fading.
Recent media reports and satellite images suggest that China is building or planning to complete new coal power plants with total capacity of 148 gigawatts – nearly equal to the entire coal-power capacity of the European Union within the next few years, according to an analysis by Global Energy Monitor, a San Francisco-based non-profit.

China is the world’s leading market for wind turbines and other renewables – but is still a major source of emissions. Photo: Chinatopix via AP
Meanwhile, investment in China’s renewable energy dropped almost 40 per cent in the first half of 2019 compared with the same period last year, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, a research organisation. The government slashed subsidies for solar energy.
Last week in Beijing, China’s vice-minister of ecology and environment told reporters that non-fossil-fuel sources already account for 14.3 per cent of the country’s energy mix. He did not indicate that China would embrace more stringent targets soon.
“We are still faced with challenges of developing our economy, improving people’s livelihood,” Zhao Yingmin said.
As a fast-growing economy, it was always inevitable that China’s energy demands would climb steeply. The only question was whether the country could power a sufficiently large portion of its economy with renewables to curb emissions growth.
Many observers took hope from a brief dip in China’s carbon emissions between 2014 and 2016. Today the country’s renewed focus on coal comes as a disappointment.
“Now there’s a sense that rather than being a leader, China is the one that is out of step,” said Lauri Myllyvirta, lead analyst at the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air in Helsinki.
He notes that several developed countries – including Germany, South Korea and the United States – are rapidly reducing their reliance on coal power.
After climbing sharply for two decades, China’s emissions stalled around 2013 and then declined slightly in 2015 and 2016, according to Global Carbon Budget, which tracks emissions worldwide.
This dip came as Chinese leaders declared a “war on pollution” and suspended the construction of dozens of planned coal power plants, including some in Shanxi.
Pollution scandal near China nature reserve at Tengger desert’s edge
At the same time, the government required many existing coal operators to install new equipment in chimneys to remove sulphur dioxide, nitrous oxide and other hazardous substances. About 80 per cent of coal plants now have scrubbers, said Alvin Lin, Beijing-based China climate and energy policy director for the Natural Resources Defence Council, a non-profit.
As a result, the air quality in many Chinese cities, including Beijing, improved significantly between 2013 and 2017. Residents long accustomed to wearing face masks and running home air-filter machines enjoyed a reprieve of more “blue sky days,” as low-pollution days are known in China.
In the past three years, China’s carbon emissions have begun to rise again, according to Global Carbon Budget.
The coming winter in Beijing may see a return of prolonged smog, as authorities loosen environmental controls on heavy industry – in part to compensate for other slowing sectors in the economy.

The UN Climate Change Conference is taking place in Madrid this month. Photo: AFP
Permits for new coal plants proliferated after regulatory authority was briefly devolved from Beijing to provincial governments, which see construction projects and coal operations as boosts to local economies and tax bases, said Ted Nace, executive director of Global Energy Monitor.
“It’s as though a boa constrictor swallowed a giraffe, and now we’re watching that bulge move through the system,” said Nace. In China, it takes about three years to build a coal plant.
The world has already warmed by 1 degree Celsius. All scenarios envisioned by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change for holding planetary warming to around 1.5 degrees Celsius involve steep worldwide reductions in coal-power generation.
In that effort, other countries rely on Chinese manufacturing to hold down prices on solar panels. wind turbines and lithium-ion batteries.
“China has a really mixed record. On the one hand, it’s seen rapidly rising emissions over the past two decades,” said Jonas Nahm, an energy expert at Johns Hopkins University.
“On the other hand, it’s shown it’s able to innovate around manufacturing – and make new energy technologies available at scale, faster and cheaper.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in against, “blue sky days,, battle, Beijing, Bloomberg New Energy Finance, boa constrictor, boa constructor, Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air, Centre on Global Energy Policy, China’s, coal, coal plants, Coal Power, Columbia University, Construction, demands, electric vehicles, emissions, energy, European Union, Germany, giraffe, global, Global Carbon Budget, Global Energy Monitor, global warming, greenhouse gases, heavy industry, Helsinki, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Johns Hopkins University, leading market, Madrid, Natural Resources Defence Council, new, paradox, plans, plants, Reliance, renewables, Risk, Shanxi, Solar Energy, solar panels, source, South Korea, suspended, swallowed, Tengger desert, top emitter, UN Climate Change Conference, UN climate summit, Uncategorized, undermining, United States, war on pollution, warming, wind turbines |
Leave a Comment »