NEW YORK (Reuters) – The number of U.S. coronavirus infections climbed above 82,000 on Thursday, surpassing the national tallies of China and Italy, as New York, New Orleans and other hot spots faced a surge in hospitalizations and looming shortages of supplies, staff and sick beds.
With medical facilities running low on ventilators and protective masks and hampered by limited diagnostic testing capacity, the U.S. death toll from COVID-19, the respiratory disease caused by the virus, rose beyond 1,200.
“Any scenario that is realistic will overwhelm the capacity of the healthcare system,” New York Governor Andrew Cuomo told a news conference. He described the state’s projected shortfall in ventilators – machines that support the respiration of people have cannot breathe on their own – as “astronomical.”
“It’s not like they have them sitting in the warehouse,” Cuomo added. “There is no stockpile available.”
At least one New York City hospital, New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center in Manhattan, has begun a trial of sharing single ventilators between two patients.
While New York was the coronavirus epicenter in the United States this week, the next big wave of infections appeared headed for Louisiana, where demand for ventilators has already doubled. In New Orleans, the state’s biggest city, Mardi Gras celebrations late last month are believed to have fueled the outbreak.
Louisiana Governor John Bel Edwards said New Orleans would be out of ventilators by April 2 and potentially out of bed space by April 7 “if we don’t flatten the infection curve soon.”
“It’s not conjecture, it’s not some flimsy theory,” Edwards told a press conference. “This is what is going to happen.”
About 80% of Louisiana’s intensive care patients are now on breathing machines, up from the normal rate of 30-40%, said Warner Thomas, chief executive of Ochsner Health System, the state’s hospital group.
Scarcities of protective masks, gloves, gowns and eyewear for doctors and nurses – reports abound of healthcare workers recycling old face masks, making their own or even using trash bags to shield themselves – have emerged as a national problem.
“Our nurses across the country do not have the personal protective equipment that is necessary to care for COVID patients, or any of their patients,” Bonnie Castillo, head of the largest U.S. nurses union, National Nurses United, told MSNBC.
In an ominous milestone for the United States as a whole, at least 82,153 people nationwide were infected as of Thursday, according to a Reuters tally from state and local public health agencies. China, where the global pandemic emerged late last year, had the second highest number of cases, 81,285, followed by Italy with 80,539.
At least 1,204 Americans have died from COVID-19, which has proven especially dangerous to the elderly and people with underlying chronic health conditions, Reuters’ tally showed.
MORE BEDS NEEDED
For New York state, Cuomo said a key goal was rapidly to expand the number of available hospital beds from 53,000 to 140,000.
New York hospitals were racing to comply with Cuomo’s directive to increase capacity by at least 50%. At Mount Sinai Hospital’s Upper East Side location, rooms were being constructed within an atrium to open up more space for beds.
At Elmhurst Hospital in New York’s borough of Queens, about a hundred people, many wearing masks with their hoods pulled up, lined up behind barriers outside the emergency room entrance, waiting to enter a tent to be screened for the coronavirus.
The city coroner’s office has posted refrigerated trucks outside Elmhurst and Bellevue Hospital to temporarily store bodies of the deceased.
Deborah White, vice chair of emergency medicine at Jack D. Weiler Hospital in the city’s Bronx borough, said 80% of its emergency room visits were patients with coronavirus-like symptoms.
A ventilator shortfall and surge in hospitalizations has already raised the prospect of rationing healthcare.
Asked about guidelines being drafted on how to allocate ventilators to patients in case of a shortage, New Jersey Governor Phil Murphy told reporters such bioethical discussions “haunted him” but were unavoidable.
Outside New York and New Orleans, other hot spots appeared to be emerging around the country, including Detroit.
Brandon Allen, 48, was buying groceries in Detroit for his 72-year-old mother, who has tested positive and was self-quarantining at home.
“It’s surreal,” Allen said. “People around me I know are dying. I know of a couple people who have died. I know a couple of people who are fighting for their lives. Everyday you hear of another person who has it.”
RECORD UNEMPLOYMENT CLAIMS
Desperate to slow virus transmissions by limiting physical contact among people, state and local governments have issued stay-at-home orders covering about half the U.S. population. A major side effect has been the strangulation of the economy, and a wave of layoffs.
The U.S. Labor Department reported Thursday the number of Americans filing claims for unemployment benefits last week soared to a record of nearly 3.28 million – almost five times the previous weekly peak of 695,000 during the 1982 recession.
Dr. Anthony Fauci, director of the U.S. National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases, said warmer weather may help tamp down the U.S. outbreak as summer approaches, though the virus could re-emerge in the winter.
“We hope we get a respite as we get into April, May and June,” Fauci said on WNYC public radio.
Washington state Governor Jay Inslee said he may extend a stay-at-home order tentatively set to expire April 6, encouraged by what he called a “very modest improvement” in the Seattle area.
Washington experienced the first major U.S. outbreak of COVID-19 and has been among the hardest-hit states. As of Thursday the state reported about 3,200 cases and 147 deaths.
In California’s Coachella Valley, a region rife with retirees who are especially vulnerable, 25 members of the state’s National Guard helped a non-profit distribute food to people stuck in their homes, as most of the regular volunteers are senior citizens.
More than 10,000 troops have been deployed in 50 states to provide humanitarian aid during the pandemic.
Source: Reuters
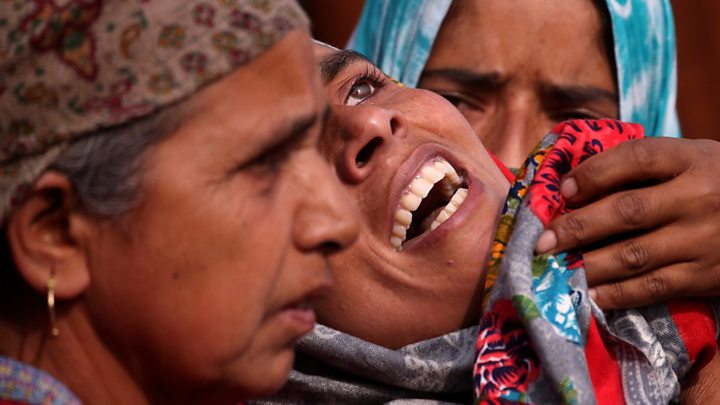



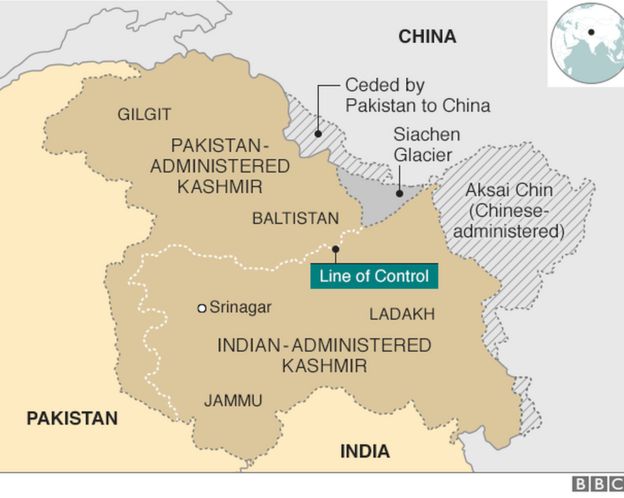



Indian, Chinese border troops in brief skirmish on northeast Indian border, India says
KOLKATA (Reuters) – Indian and Chinese troops on border patrol duties had a brief skirmish in Sikkim, a northeastern Indian state bordering China, the Indian Defence Ministry said on Sunday, blaming both sides for the incident.
“Aggressive behaviour by the two sides resulted in minor injuries to troops. The two sides disengaged after dialogue and interaction at the local level,” the ministry said in a statement.
The Indian daily Hindustan Times, citing a military source, said four Indian soldiers and seven Chinese troops were injured when some of the soldiers exchanged blows during the confrontation, which it said took place on Saturday and involved some 150 soldiers.
The Defence Ministry said the incident took place in the Nakula area but did not give details of how it started, or what caused the injuries.
China’s Ministry of Defense could not be immediately reached for comment on Sunday.
India and China have often accused each other of intrusions into each other’s territories, but clashes are rare.
There is still deep mistrust between the two countries over their festering border dispute, which triggered a brief war in 1962.
Hundreds of troops from both sides were deployed in 2017 on the Doklam plateau, near the borders of India, Bhutan, and China after India objected to Chinese construction of a road in the Himalayan area, in the most serious standoff in years.
Source: Reuters
Posted in 1962, 2017, accused, aggressive, behaviour, Bhutan, blaming, border, bordering, both, brief, China, China’s, Chinese, citing, clashes, comment, confrontations, Construction, countries, daily, deep, defence ministry, deployed, details, dialogue, disengaged, dispute, duties, festering, four, Himalayan, Hindustan Times, hundreds, immediately, incident, India, Indian, Indian soldiers, injured, injuries, interaction, intrusions, involved, Kolkata, level, local, Military, ministry, Ministry of Defense, minor, mistrust, Nakula, Northeast, Northeastern, patrol, rare, reached, resulted, roads, Saturday, serious, seven, sides, Sikkim, skirmish, source, standoff, state, statement, Sunday, territories, triggered, troops, two, Uncategorized, war, years | Leave a Comment »