Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESA number of European governments have rejected Chinese-made equipment designed to combat the coronavirus outbreak.
Thousands of testing kits and medical masks are below standard or defective, according to authorities in Spain, Turkey and the Netherlands.
Europe has reported hundreds of thousands of cases of coronavirus.
More than 10,000 people have died in Italy since the outbreak began.
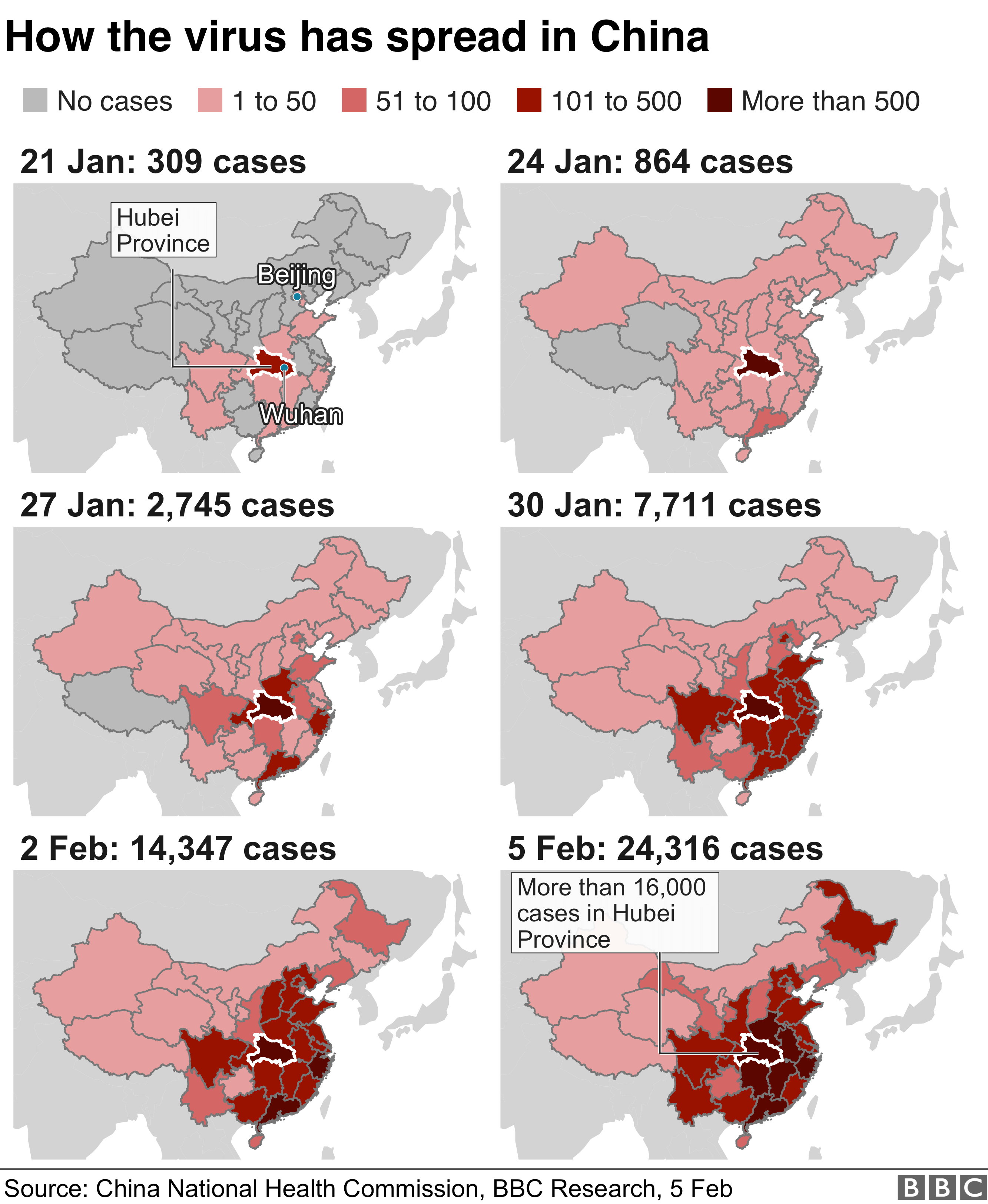
The virus was first detected in China at the end of 2019. The government implemented strict lockdown measures to bring it under control.
What’s wrong with the equipment?
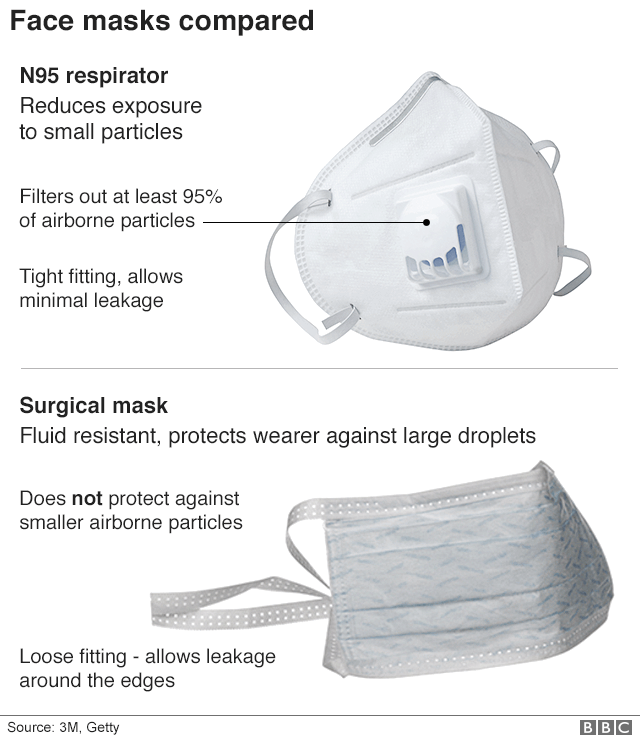
On Saturday, the Dutch health ministry announced it had recalled 600,000 face masks. The equipment had arrived from a Chinese manufacturer on 21 March, and had already been distributed to front-line medical teams.
Dutch officials said that the masks did not fit and that their filters did not work as intended, even though they had a quality certificate,

You may also be interested in:
- Mercedes F1 to make breathing aid
- Manufacturers cast doubt on ventilator target
- A visual guide to the pandemic

“The rest of the shipment was immediately put on hold and has not been distributed,” a statement read. “Now it has been decided not to use any of this shipment.”
Spain’s government encountered similar problems with testing kits ordered from a Chinese company.
It announced it had bought hundreds of thousands of tests to combat the virus, but revealed in the following days that nearly 60,000 could not accurately determine if a patient had the virus.
The Chinese embassy in Spain tweeted that the company behind the kits, Shenzhen Bioeasy Biotechnology, did not have an official license from Chinese medical authorities to sell its products.
It clarified that separate material donated by the Chinese government and technology and retail group Alibaba did not include products from Shenzhen Bioeasy.
Turkey also announced that it had found some testing kits ordered from Chinese companies were not sufficiently accurate, although it said that some 350,000 of the tests worked well.
Allegations of defective equipment come after critics warned China could be using the coronavirus outbreak to further its influence.
In a blog post last week, EU chief diplomat Josep Borrell warned that there is “a geo-political component including a struggle for influence through spinning and the ‘politics of generosity’.”
“China is aggressively pushing the message that, unlike the US, it is a responsible and reliable partner,” he wrote. “Armed with facts, we need to defend Europe against its detractors.”
What’s the situation in Europe?
On Monday, Spain reported 812 new deaths in the space of 24 hours – bringing its total death toll to 7,340. It now has more than 85,000 infections – surpassing the number of cases reported in China.
New measures have also come into force in Spain banning all non-essential workers from going to their jobs. The restrictions will be in place for at least two weeks.
Italy remains the worst affected country worldwide. More than 10,000 people have died from the virus there, and it has recorded nearly 100,000 infections. Only the US has more confirmed cases, although the death toll there is far lower.
Source: The BBC