30/05/2020
- Chinese groups calling for more ‘fighting spirit’ are getting the upper hand on those who favour calm and cooperation, government adviser says
- From Hong Kong to Covid-19, trade to the South China Sea, Beijing and Washington are clashing on a growing number of fronts and in an increasingly aggressive way
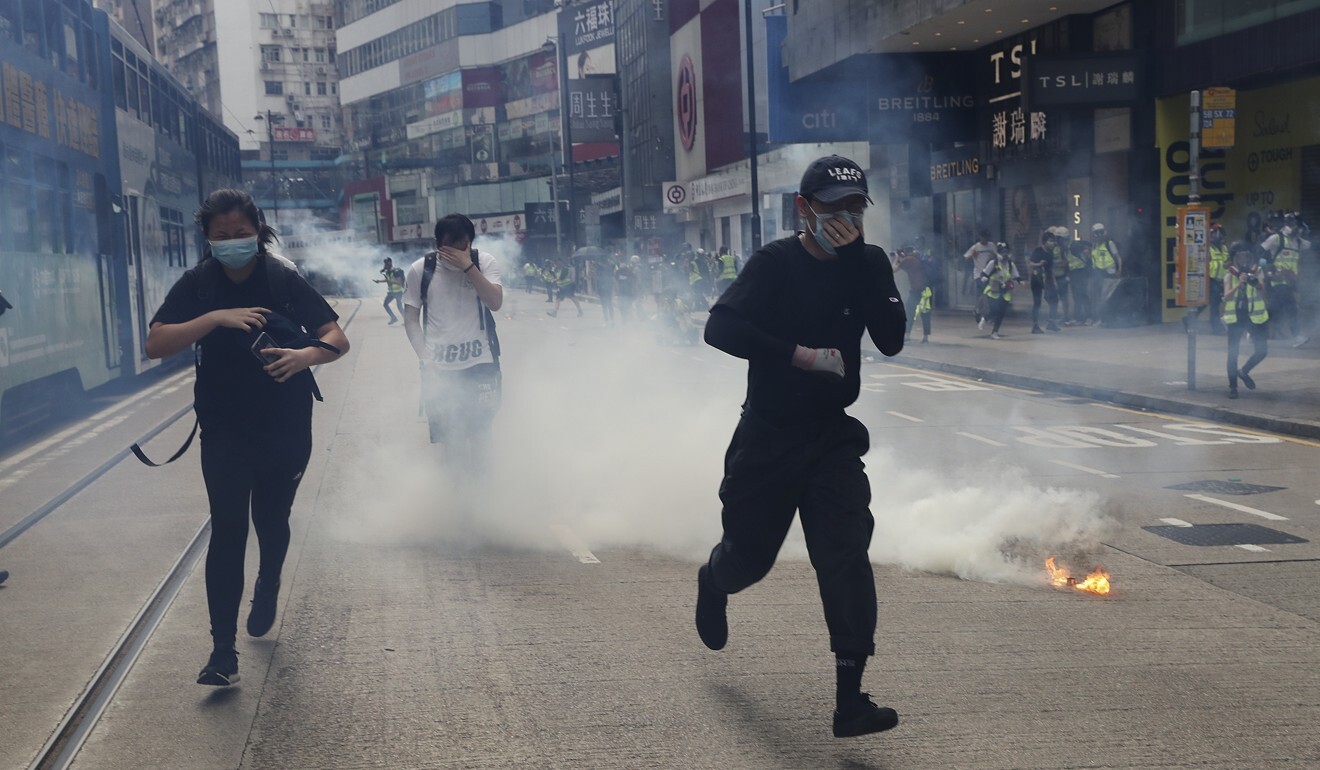
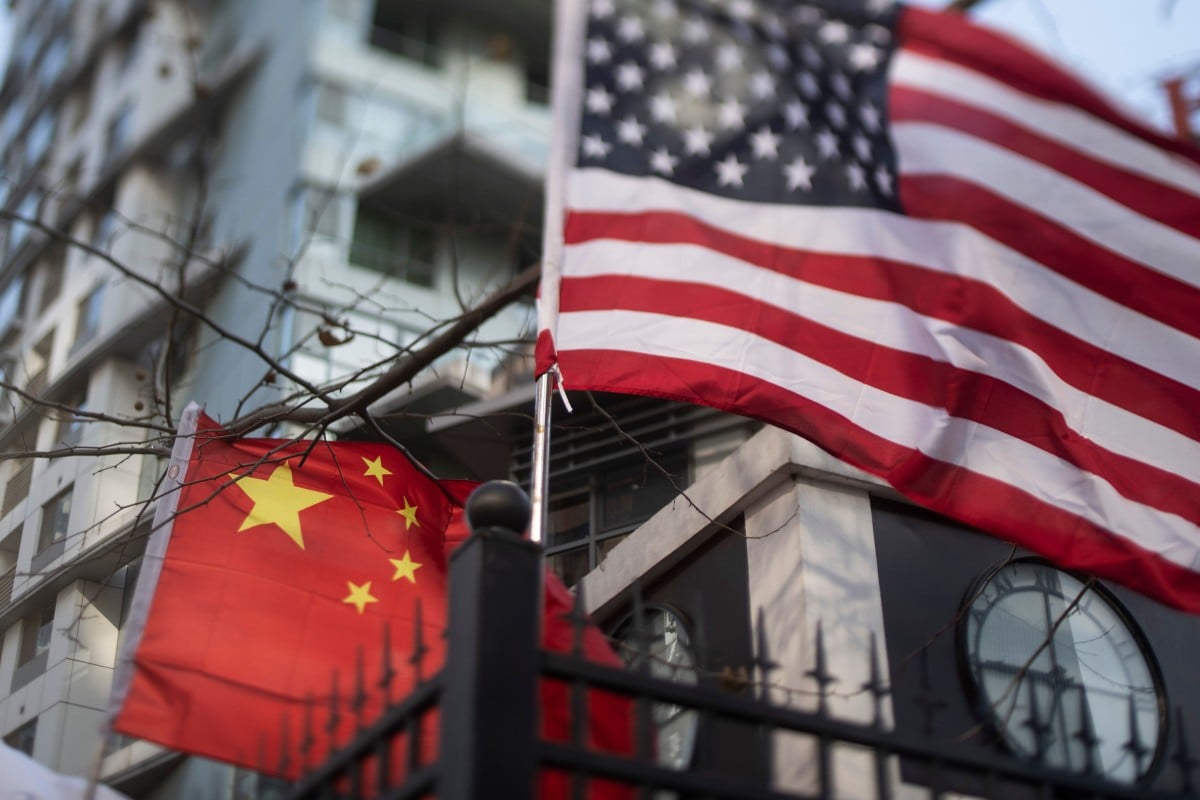
Efforts to promote dialogue and cooperation between the US and China are failing, observers say. Photo: AFP
Moderates who favour dialogue and cooperation as a way to resolve China’s disputes with the
United States are losing ground to hardline groups bent on taking the fight to Washington, according to political insiders and observers.
“There are two camps in China,” said a former state official who now serves as a government adviser and asked not to be named.
“One is stressing the combat spirit, the other is trying to relieve tensions. And the former has the upper hand.”
Relations between China and the US are under intense pressure. After Beijing moved to introduce a national security law for Hong Kong, US President Donald Trump said on Friday that Washington would begin eliminating the special policy exemptions it grants the city, as it no longer considers it autonomous from mainland China.
Beijing’s decision to enact a national security law for Hong Kong was met with anger from the US and other Western countries. Photo: Sam Tsang
The two nations have also clashed over trade, Xinjiang, Taiwan and the South China Sea, with the US passing several acts denouncing Beijing and sanctioning Chinese officials.
China has also experienced turbulence in its relations with other countries, including Australia and members of the European Union, mostly related to the Covid-19 pandemic
and Beijing’s efforts to position itself as a leader in the fight against the disease with its policy of “mask diplomacy”.
After Canberra appealed for an independent investigation to be carried out to determine the origins of the coronavirus, Beijing responded by imposing tariffs on imports of Australian barley, showing it is prepared to do more than just trade insults and accusations with its adversaries.
Pang Zhongying, a professor of international relations at Ocean University of China in Qingdao, said there was a worrying trend in China’s relations with other nations.
“We need political and diplomatic means to resolve the challenges we are facing, but … diplomatic methods have become undiplomatic,” he said.
“There are some who believe that problems can be solved through tough gestures, but this will never work. Without diplomacy, problems become confrontations.”
said during his annual press conference on the sidelines of the National People’s Congress last weekend that China and the United States must work together to prevent a new Cold War.
His words were echoed by
Chinese Premier Li Keqiang, who said during a press conference after the closure of the legislative session on Thursday that the many challenges facing the China-US relations could only be resolved through cooperation.
However, the government adviser said there was often quite a chasm between what China’s leaders said and what happened in reality.
“Even though we say we do not want a Cold War, what is happening at the working level seems to be different.” he said. “The implementation of policies is not properly coordinated and often chaotic.”
Tensions between China and the US have been in a poor state since the start of a trade war almost two years ago. After multiple rounds of negotiations, the sides in January signed a phase one deal, but the positivity that created was short-lived.
In February, Beijing expelled three reporters from The Wall Street Journal over an article it deemed racist, while Washington has ramped up its military activity in the South China Sea and Taiwan Strait, and threatened to revoke the visas of Chinese students studying science and technology in the US over concerns they might be engaged in espionage.
Beijing has also used its state media and army of “
Wolf Warrior” diplomats to promote its narrative, though many Chinese scholars and foreign policy advisers have said the latter’s nationalistic fervour has done more harm than good and appealed to Beijing to adopt a more conciliatory tone.
However, Hu Xijin, editor-in-chief of Chinese tabloid Global Times, said China had no option but to stare down the US, which regarded the world’s most populous nation as its main rival.
“Being contained by the US is too high a price for China to pay,” he said. “I think the best thing people can do is forget the old days of China-US ties”.
Jin Canrong, a professor of international relations at Renmin University in Beijing, wrote in a recent newspaper article that Beijing’s actions – notably enacting a national security law for Hong Kong – showed it was uncompromising and ready to stand its ground against the US.
Wu Xinbo, dean of international studies at Fudan University in Shanghai, agreed, saying relations between the two countries were likely to worsen in the run-up to the US presidential election in November and that Beijing should be prepared for a fight.
But Adam Ni, director of China Policy Centre, a think tank in Canberra, said the issue was not that the moderate camp had been sidelined, but rather Beijing’s perception of the US had changed.
“Beijing has woken up to the idea that America’s tough policy on China will continue and it is expecting an escalation of the tensions,” he said.
“The centre of gravity in terms of Beijing’s perception of the US has shifted, in the same way the US perception of China has shifted towards a more negative image”.
Beijing was simply responding in kind to the hardline, assertive manner of the US, he said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in aggressive way, annual, appealed, Australia, Australian, autonomous, ‘fighting spirit, “Wolf Warrior”, barley, Beijing, calm and cooperation, Canberra, chaotic, chasm, China-US relations, China-US ties, Chinese foreign minister Wang Yi, Chinese groups, Chinese premier Li Keqiang, Chinese scholars, Chinese students, Chinese tabloid, clashing, Cold War, conciliatory, confrontations, contained, cooperation, coordinated, coronavirus, COVID-19, Covid-19 pandemic, diplomacy, diplomats, editor-in-chief, Espionage, European Union, favour, foreign policy advisers, Fudan University, Global Times, growing, hardliners, Hong Kong, implementation, increasingly, independent investigation, lose out, main rival, Mainland China, moderate camp, moderates, more harm than good, narrative, National People’s Congress, national security law, November, number of fronts, observers, origins, policies, political insiders, presidential election, press conference, problems, promote, Qingdao, Renmin University, resolved, revoke, science and technology, Shanghai, sidelines, South China Sea, special policy exemptions, studying, Taiwan, Taiwan Strait, tariffs, The Wall Street Journal, think tank, threatened, tone, Trade, two camps, Uncategorized, uncompromising, undiplomatic, United States, upper hand, US President Donald Trump, US-China tensions, Visas, Washington, Western countries, world’s most populous nation, worsen, Xinjiang |
Leave a Comment »
25/03/2020

People enjoy sunset on a plank road at the East Lake in Wuhan, capital of central China’s Hubei Province, March 18, 2020. (Xinhua/Shen Bohan)
Arduous efforts have been made since Wuhan was locked down and the efforts have paid off, with the outbreak of the COVID-19 gradually brought under control in this once hardest-hit Chinese city. With sacrifices and persistence, a bright dawn is finally around the corner.
WUHAN, March 24 (Xinhua) — Xia Yongli starts a workday at dawn by having his temperature taken, disinfecting his bus and going through safety checks before hitting the road at 7:00 a.m. sharp.
Over the past eight weeks, the bus driver in the central Chinese city of Wuhan had not driven his familiar route, which is 14 km long and usually takes 40 minutes. Instead, he has been shuttling medics and delivering supplies to shops and supermarkets.
The city, with a population of over 10 million, pressed a “pause” button on Jan. 23 to contain the spread of the rampaging coronavirus behind the COVID-19 epidemic, with all public transport and outbound channels shut down and all residents staying indoors.
The streets of Wuhan are no longer bustling. Shopping blocks, pedestrian streets and other popular places where local people would stroll around are largely left to still figure sculptures.
Arduous efforts have been made since Wuhan was locked down and the efforts have paid off, with the outbreak of the COVID-19 gradually brought under control. Once hardest-hit, Wuhan only had one newly confirmed COVID-19 case reported for six consecutive days between March 18 and 23.
Wuhan had reported a total of 50,006 confirmed cases by March 23, and 43,214 patients had been cured and discharged from hospitals.
With sacrifices and persistence, a bright dawn is finally around the corner. People will be allowed to leave the city and the province from April 8, local authorities said Tuesday.

A staff member conducts disinfection at a subway station in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 23, 2020. (Xinhua/Shen Bohan)
To reduce the risk of imported cases, all personnel coming to Wuhan from overseas have to be brought under closed-loop management, with timely quarantine and epidemiological surveys conducted, said Ying Yong, secretary of Hubei Provincial Committee of the Communist Party of China.
“Wuhan had pressed the pause button and is currently in urgent need of restoring its urban functions with safe and ordered operations,” Ying said.
More than 110 bus routes citywide have conducted no-load test runs. Disinfection has been carried out at local metro and railway stations. Checkpoints for epidemic control, 27 on cross-river bridges and nearly 80 others in main urban areas, have been removed.
Infrared thermometers have been installed at subway entrances, with posters of QR codes for real-name registration inside the stations and carriages.

Staff members conduct disinfection on a subway train in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 23, 2020. (Xinhua/Xiao Yijiu)
“The traffic on the road is coming back,” said Hu Lijun, general manager of the Wuhan Zhengyuan Gaoli Optical Co., Ltd., a photoelectric encoder manufacturer, whose production capacity has been restored by 80 percent.
Traffic flow at highway exits is also increasing by about 10 percent per day due to a growing number of people returned as Wuhan speeds up resumption of work and production.
There were health staff, community workers and police in each lane at toll-gate checkpoints, scanning health codes and taking body temperatures of the returning workers, disinfecting their vehicles and making registrations.
“Drivers had to queue up at the highway exits in the past to spend five minutes filling a registration form,” said Dong Hongxiang, a police officer, noting that registration time has been cut short now by using PDA scanners.
On March 21, a special train arrived in Wuhan with 1,013 passengers on board, all of whom were employees of Dongfeng Honda, a local joint venture. They were picked up at the train station and sent directly to the factory or their residences.

Workers are busy on the production lines at the workshop of Dongfeng Passenger Vehicle Company in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 24, 2020. (Xinhua/Xiao Yijiu)
Wuhan-based enterprises that are important to the national and global industry chains and those closely related to people’s livelihood are allowed to continue operation or resume work, said Cao Guangjing, deputy governor of Hubei.
Hubei serves as one of China’s major auto producers and phosphate fertilizers. Cao said that relevant companies play significant role in the production chains. Their resumption of operation counts.
Preferential measures have been taken to support restart of engine in the city. The State Grid Wuhan electric power company has rolled out new policies to cut or exempt electricity bills for local enterprises, an estimated reduction of 389 million yuan (about 55 million U.S. dollars) by the end of June.
People have also started to venture out, although they cannot go as far or wherever they want.
Wang Tan, a Wuhan resident, stepped out of his home for the first time in two months to get some medicine for his father-in-law at a nearby pharmacy Monday morning.
With a health code on WeChat, Wang said he could visit convenience stores, green groceries and drug stores close to his home and have some free time outdoors inside his residential community, which has been clear of COVID-19 cases for 14 days in a row.
The Guoxinyuan community in Jiang’an District has been epidemic-free for 26 consecutive days. There were kids skipping ropes and the gray-haired doing exercises in open public areas. People observed social distancing while reclaiming a long-lost conversation.
“The public space in our community is quite small, thus no more than 80 people are allowed to have outdoor activities at one time,” said Wei Jilai, who heads the neighborhood committee.

A woman purchases daily necessities at a convenience store in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 19, 2020. (Xinhua/Shen Bohan)
As the epidemic recedes, more than 21,000 medical staff from across the country who had fought on the frontline in Wuhan and other places in Hubei are returning home. Before departure, some visited East Lake, one of the well-known tourist attractions in Wuhan, having group photos before cherry trees in blossom to mark the unforgettable days in the city.
Some are leaving, while others stand their ground. Ma Xin, vice president of the Huashan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University in Shanghai, stayed at Wuhan’s Tongji Hospital with his team, treating severe and critically ill patients.
“Most of them have underlying diseases and have to be treated for their complications,” Ma said, stressing that vigilance is still needed at present, especially against imported cases and relapse.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Arduous efforts, blossom, cherry trees, convenience store, COVID-19, COVID-19 cases, COVID-19 epidemic, delivering supplies, Dongfeng Honda, Dongfeng Passenger Vehicle Company, East Lake, epidemic-free, Factory, Fudan University, Huashan Hospital, Hubei, hubei province, indoors, kids, medical staff, outbound channels, pace of spring, pharmacy, Police officer, public transport, residences, residents, reviving, Shanghai, shops, shuttling medics, skipping ropes, supermarkets, Tongji Hospital, Train station, Uncategorized, WeChat, Wuhan, Wuhan Zhengyuan Gaoli Optical Co., Ltd., Xinhua Headlines |
Leave a Comment »
06/11/2019
- French leader calls for restraint and says he raised the topic ‘on several occasions’ during his visit
- Two sides find common ground on need to defend free trade and fight climate change as Donald Trump starts process of pulling US out of Paris Climate Agreement
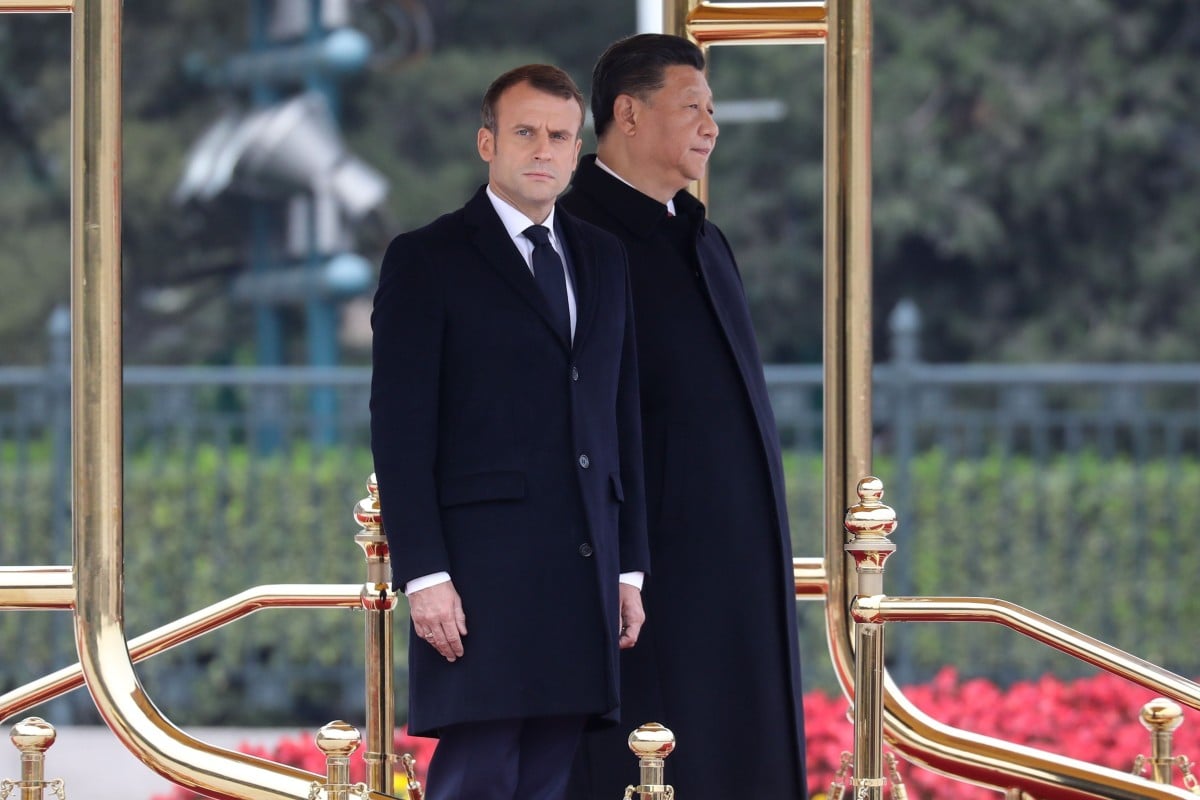
Xi Jinping and Emmanuel Macron at a welcome ceremony ahead of their talks in Beijing on Wednesday. Photo: AFP
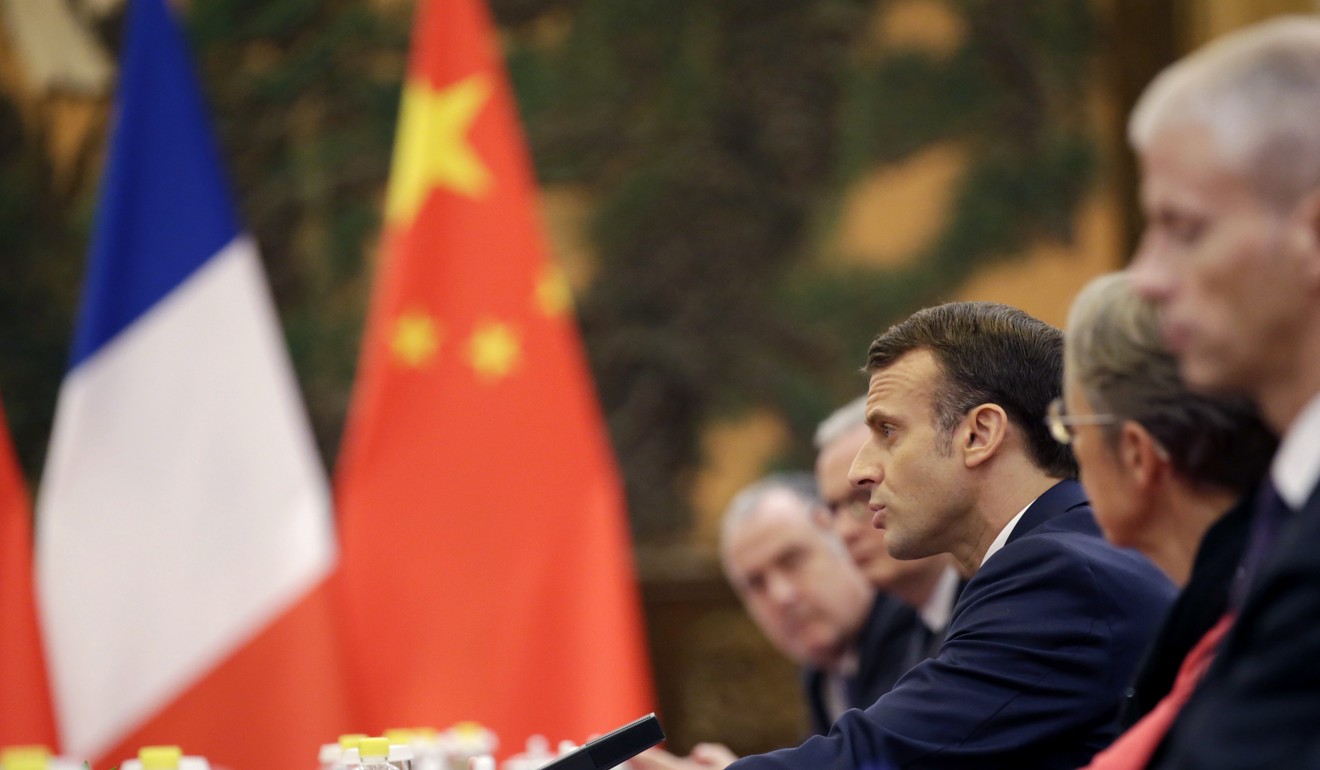
French President Emmanuel Macron said he raised human rights and the Hong Kong situation during his talks with his Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping on Wednesday.
Macron’s visit to China concluded with pledges to work together on climate change, but the French leader also said he also called for a de-escalation of the situation in the city through dialogue after months of protests.
Macron, who had promised to raise “taboo” topics during the visit, told a press conference: “I obviously raised this with President Xi Jinping on several occasions.
“We have repeatedly called on the parties involved to [engage in] dialogue, to show restraint, to de-escalate.”
The discussion followed Xi’s meeting with Hong Kong’s embattled Chief Executive Carrie Lam Cheng Yuet-ngor in Shanghai on Monday, where he expressed “high trust” in her and “fully affirmed” support for her response to the unrest that has gripped the city since June.
Earlier the French and Chinese leaders had restated their commitment to protect free trade and pledged their continued support for the Paris Agreement as the United States begins the process of formally withdrawing from the global climate deal.
Macron expressed “regret” over “some countries’ negative attitude” towards environmental protection and the fight against climate change and pledged to work with China to halt the loss of biodiversity.
The French president’s office also released a statement on Wednesday that reaffirmed France and China’s joint support for the “irreversible” Paris Agreement.
Macron points to common ground with China on tariffs and climate action
With the European Union, China and Russia backing the pact, he added, “the isolated choice of one or another is not enough to change the course of the world. It only leads to marginalisation.”
The two countries also agreed to work together to develop joint nuclear power projects and signed a series of contracts worth US$15 billion.
The deals covered aeronautics, energy and agriculture, including approval for 20 French companies to export poultry, beef and pork to China.
An additional action plan released after the talks said French utility giant EDF and China General Nuclear Power should be encouraged to cooperate on projects in China or third countries, citing the joint efforts by the two companies to build nuclear reactors at the Hinkley Point C station in Britain as an example.
The two sides also committed to signing a contract for the construction of a nuclear fuel recycling plant in China, which would involve French energy giant Orano, by January 31.
Xi took what appeared to be a veiled swipe at the United States, which is still embroiled in a protracted trade war and other confrontations with Beijing.
“We advocate for mutual respect and equal treatment, and are opposed to the law of the jungle and acts of intimidation,” Xi said.
“We advocate for openness, inclusion and for mutually beneficial cooperation, and are opposed to protectionism and a zero-sum game.”
Macron said China and the European Union should work in partnership as the world became more unstable, calling on the two sides to further open up market access.
“We call again for trade multilateralism to respond to distortions that have appeared in the global economy, which have led to a profound rise in inequalities and imbalances that explain the surge of challenges to the international systems,” he said.
“China and Europe also share the same views that the trade war only leads to loss.”
Macron kicks off China visit with deal to protect wine and cheese from counterfeiting
Chinese state news agency Xinhua said the two countries agreed to work together to push forward with plans to assemble Airbus’s A350 model in China.
Meanwhile, Beijing Gas Group and French utility firm Engie will collaborate on a liquefied natural gas terminal and storage in the northern city of Tianjin, while France’s Total will set up a joint venture with China’s Shenergy Group to distribute liquid nitrogen gas by truck in the Yangtze River Delta.
The two countries also agreed to reach an agreement by the end of January 2020 on the cost and location of a nuclear fuel reprocessing facility to be built by Orano, formerly known as Areva.
Wu Libo a professor and director of the Centre for Energy Economics and Strategies Studies at Fudan University, said there was “great potential” for further cooperation between the two countries on nuclear energy.
“France has many useful experiences in the operation and management of nuclear power plants and its plants have long-term safe and stable operation records,” she said.
The two sides agreed to work together on joint nuclear power projects. Photo: AP
Jiang Kejun, a senior researcher at the Energy Research Institute of China’s National Development and Reform Commission, said China’s cooperation with France would add credibility to potential third-country projects.
“China has advanced third-generation technology but it’s still a new member in the nuclear power market, while France has developed nuclear energy for a long time, and its EPR reactors – a technology designed and developed in France – are in business operation,” he said.
Jiang said possible markets for the joint projects included Argentina and India, while some Middle Eastern states – such as Saudi Arabia and Qatar – had expressed interest in nuclear energy.
China’s ambassador hits out at Macron’s team for backing ‘hypocritical’ EU stance on Hong Kong
Tong Jiadong, professor of international trade at Nankai University, said that the deals between the two sides helped show that France and China could work together to counteract US unilateralism.
“Objectively speaking, this will form, or at least imply, an opposition to US unilateralism,” Tong said. “China hopes the cooperation between these two countries produces demonstrable effects for other EU member states.”
Ding Chun, a professor of European Studies at Fudan University, said he did not think the EU wanted to “choose a side” between the US and China.
But Ding continued: “If we are talking about free trade and multilateralism, there’s no doubt that the EU and China share a common view and can balance Donald Trump’s unilateralism.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Airbus’s A350, Areva, Argentina, Beijing, Beijing Gas Group, calm, Carrie Lam Cheng Yuet-ngor, Centre for Energy Economics and Strategies Studies, Chief Executive, China alert, China’s Shenergy Group, Chinese leader Xi Jinping, Energy Research Institute, Engie, EPR reactors, EU, Europe, European Studies, European Union, French, French President Emmanuel Macron, Fudan University, Hong Kong, India, Liquefied natural gas, liquid nitrogen gas, Middle Eastern states, multilateralism, Nankai University, National Development and Reform Commission, National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), nuclear energy, nuclear fuel reprocessing facility, nuclear power projects, Orano, Paris climate agreement, President Donald Trump, Qatar, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Shanghai, situation, talks are needed, terminal and storage, Tianjin, Uncategorized, unilateralism, United States, utility firm, welcome ceremony, Yangtze River Delta, zero-sum game |
Leave a Comment »
14/08/2019
- Researchers at academy of science believe electromagnetic wave model is key that will herald new era in radar detection and avoidance for military ships and aircraft
China’s J-20 stealth fighter. Photo: AFP
Chinese scientists have achieved a series of breakthroughs in stealth materials technology that they claim can make fighter jets and other weaponry lighter, cheaper to build and less vulnerable to radar detection.
Professor Luo Xiangang and colleagues at the Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences in Chengdu, Sichuan province, said they had created the world’s first mathematical model to precisely describe the behaviour of electromagnetic waves when they strike a piece of metal engraved with microscopic patterns, according to a statement posted on the academy’s website on Monday.
With their new model and breakthroughs in materials fabrication, they developed a membrane, known as a meta surface, which can absorb radar waves in the widest spectrum yet reported.
At present, stealth aircraft mainly rely on special geometry – their body shape – to deflect radar signals, but those designs can affect aerodynamic performance. They also use radar absorbing paint, which has a high density but only works against a limited frequency spectrum.
In one test, the new technology cut the strength of a reflected radar signal – measured in decibels – by between 10 and nearly 30dB in a frequency range from 0.3 to 40 gigahertz.
A stealth technologist from Fudan University in Shanghai, who was not involved in the work, said a fighter jet or warship using the new technology could feasibly fool all military radar systems in operation today.
“This detection range is incredible,” the researcher said. “I have never heard of anyone even coming close to this performance. At present, absorbing technology with an effective range of between 4 and 18 GHz is considered very, very good.”
China’s new radar system could spot stealth aircraft from at long range
The lower the signal frequency, the longer a radar’s detection range. But detailed information about a moving target can only be obtained with higher frequency radio waves. Militaries typically use a combination of radars working at different frequencies to establish lines of defence.
The Medium Extended Air Defence System, Nato’s early warning radar, operates at a frequency range of 0.3 to 1 GHz. The American Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system, the missile defence radar that caught Beijing’s attention when it was deployed in South Korea in 2017, operates at frequencies around 10 GHz.
Some airports use extremely short-range, high-frequency radars running at 20 GHz or above to monitor vehicle and plane movements on the ground, but even they might not be able to see a jet with the new stealth technology until it is overhead.
“Materials with meta surface technology are already found on military hardware in China, although what they are and where they are used remains largely classified,” the Fudan researcher said.
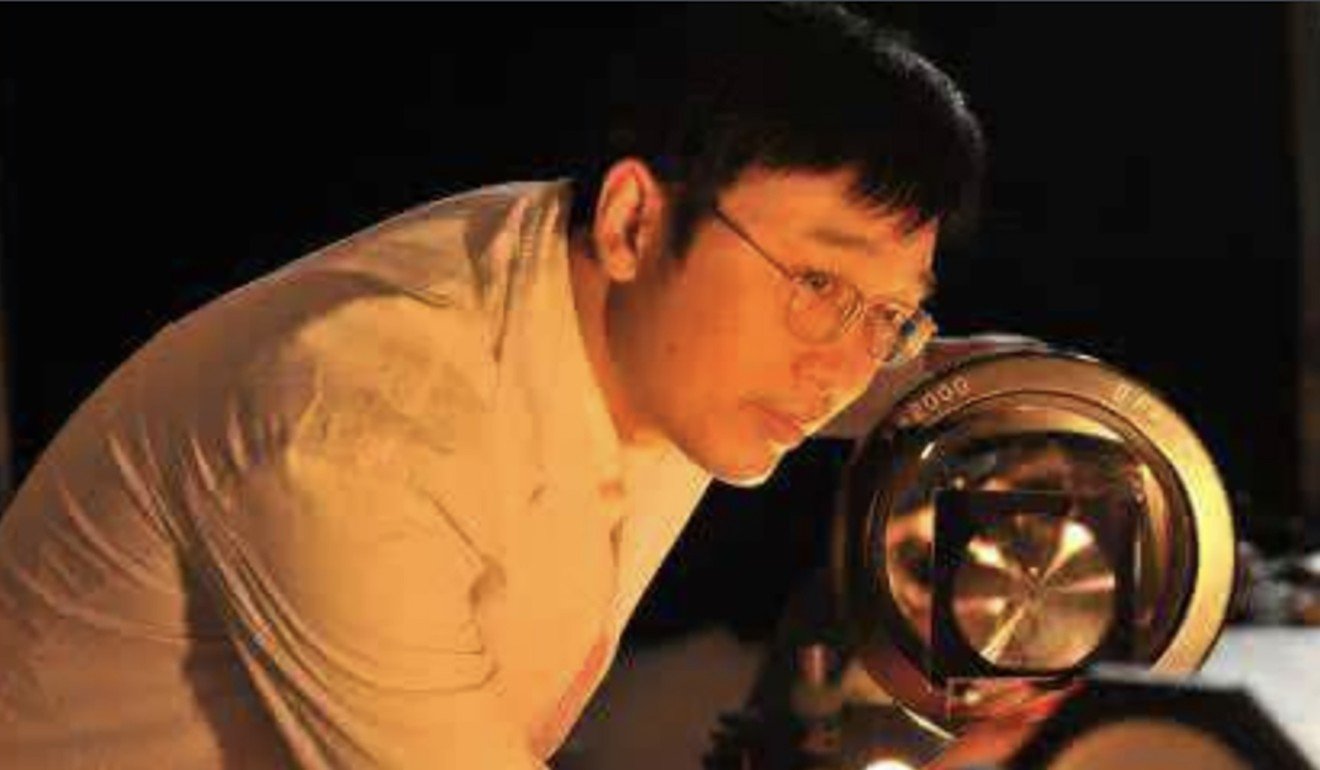
Professor Luo Xiangang. Photo: Baidu
Luo and his colleagues could not be reached for comment. But according to the academy’s statement and a paper the team published in the journal Advanced Science earlier this year, the stealth breakthroughs were based upon a discovery they made several years ago.
They found that the propagation pattern of radio waves – how they travelled – in extremely narrow metallic spaces was similar to a catenary curve, a shape similar to that assumed by chains suspended by two fixed points under their own weight.
China tests stealth ‘invisibility cloaks’ on regular fighter jets
Inspired by catenary electromagnetics, the team developed a mathematical model and designed meta surfaces suitable for nearly all kinds of wave manipulation.
These included energy-absorbing materials for stealth vehicles and antennas that can be used on satellites or military aircraft.
Zhu Shining, a professor of physics specialising in meta materials at Nanjing University, said the catenary model was a “novel idea”.
“The Institute of Optics and Electronics in Chengdu has conducted long-term research in this area which paved a solid foundation for their discoveries. They have done a good job,” Zhu said.
“Scientists are exploring new features of metal materials, some of them are already in real-life applications.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Advanced Science, aerodynamic, airports, American, blind, body shape, breakthroughs, catenary electromagnetics, Chengdu, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese scientists, discovery, early warning radar, fabrication, fighter jets, Fudan University, ground, hail, incredible, Institute of Optics and Electronics, invisibility cloaks, J-20 stealth fighter, materials, Medium Extended Air Defence System, membrane, meta surface, Military, Nanjing University, NATO, paint, performance, plane movements, radar absorbing, radar systems, Shanghai, sichuan province, South Korea, stealth breakthrough, Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system, Uncategorized, vehicle movements, warship |
Leave a Comment »
07/08/2019
BEIJING, Aug. 6 (Xinhua) — China on Tuesday announced the expanding of its Shanghai free trade zone (FTZ) in its latest major strategic move for further opening-up.
The addition of the Lingang area is a major strategic decision made by the Communist Party of China Central Committee to further opening up, Vice Commerce Minister Wang Shouwen told a press conference Tuesday.
It also demonstrates China’s clear stand to adhere to all-round opening up in the new era and an important measure taken to actively lead the healthy development of economic globalization, Wang said.
The new Lingang section will match the standard of the most competitive free trade zones worldwide and implement opening-up policies and systems with strong global market competitiveness, according to an overall plan for the new Lingang area of the China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone issued by the State Council, or the cabinet.
Lingang, with a start-up area of 119.5 square kilometers, will facilitate overseas investment and capital flows and realize the free flow of goods, according to the plan.
Aerial photo taken on June 27, 2019 shows the Lingang area in Shanghai, east China. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
“The new area is not just a simple expansion of the existing free trade zone and a copy of existing policies. It is comprehensive, profound and fundamental institutional innovation and reform,” Chen Yin, executive vice mayor of Shanghai, told the press briefing.
The Shanghai FTZ had an area of 28.78 square kilometers when it was established in September 2013 and expanded to 120.72 square kilometers in December 2014.
Over the past years, the Shanghai FTZ has made remarkable progress in its bold exploration in sectors like investment, trade and finance and contributed precious experience to the all-around deepening of reforms and high-level opening-up, said Wang.
SPECIAL ZONE
The area will be built into a special economic function zone with global influence and competitiveness, to better serve the country’s overall opening-up strategy, the plan says.
“The status as a special economic function zone means that it is not adding more facilitation but moving toward real investment and trade liberalization,” said Shen Yuliang, a researcher with the Institute of World Economics under the Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences.
By 2025, the Lingang area will have a relatively mature institutional system of investment and trade liberalization and facilitation. By 2035, it will be built into a special economic function zone with strong global market influence and competitiveness, becoming an important platform for the country to integrate into economic globalization.
The area, administered like a special economic zone, will establish an institutional system with its focus on investment and trade liberalization and set up an open industrial system with global competitiveness, according to the plan.

Aerial photo taken on June 27, 2019 shows new cars wating for shipment at a port in the Lingang area in Shanghai, east China. (Xinhua/Fang Zhe)
It will strive to become a business cluster for international business, cross-border financial services, frontier technology research and development and cross-border services trade, and speed up the industrial upgrading of existing companies.
The Yangshan comprehensive bonded area will be set up there, and the area will also pilot free capital inflows and outflows and free capital conversion.
Income tax shall be levied at a reduced rate of 15 percent within five years from its establishment for qualified enterprises engaged in manufacturing and R&D in key fields including integrated circuits, artificial intelligence, biomedicine and civil aviation, says the plan.
Shanghai will also set up a fund of 100 billion yuan (14.2 billion U.S. dollars) in five years to support the development of the new area, said Chen.
OPENING-UP, INNOVATION LEADER
The plan says the new area will be granted greater administration power for self-development, self-reform and self-innovation, and regularly promote its experience to spearhead a new round of reform and opening-up of the Yangtze River Delta.
Apart from serving the Belt and Road Initiative and the Yangtze River Economic Belt, the new area is also designed to promote the coordinated development, reform and opening-up of the Yangtze River Delta, said Wang.
The Lingang area, home to Tesla’s gigafactory, has become a cluster of high-end industries after more than a decade of development, and it now emphasizes the development of key industries like integrated circuits, AI, biomedicine and civil aviation.
Aerial photo taken on July 25, 2018 shows Phase IV of the Yangshan Deep Water Port of east China’s Shanghai. (Xinhua/Ding Ting)
China’s economy faces complicated external situations and to improve industrial competitiveness and move up the value chain, the boost of scientific and technological innovation capacity is the only way, said Yin Chen, secretary general of the Shanghai Free Trade Zone Comprehensive Research Institute with Fudan University.
With more openness, the new area can boost Shanghai’s high-end resources allocation ability and better represent the country to take part in global cooperation and competition, said Yin.
BOON FOR BUSINESSES
The addition of the new area to the FTZ is a boon for both domestic and foreign businesses.
“The new tax policy support will help speed up the commercialization of autonomous driving,”said Xue Jiancong, vice president of TuSimple, an AI company registered in Lingang that received the country’s first open road testing license for trucks.
“We hope that the new policies will help promote the free flow of auto parts,”said Song Feng, president of Caterpillar Remanufacturing Services (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., citing current restrictions on imports of old machinery parts.
Yu Bo, a tax partner at accounting firm PwC, said China has been rolling out institutional reforms over the past years to allow domestic institutions in alignment with international standards.
China, among the top three investment destinations with the biggest development potential for business executives worldwide in an PwC survey, should continue to improve the business environment for foreign investment and conduct more institutional reforms to promote the higher-level opening-up, said Yu.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in artificial intelligence (AI), Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), biomedicine, Caterpillar Remanufacturing Services (Shanghai) Co., Ltd., China (Shanghai) Pilot Free Trade Zone, China alert, Civil aviation, Communist Party of China Central Committee, economic globalization, expands, free trade zone (FTZ), Fudan University, healthy development, Institute of World Economics, integrated circuits, Lingang are, manufacturing and R&D, PwC, self-development, self-innovation, self-reform, Shanghai, Shanghai Academy of Social Sciences, special economic zone, State Council, trade liberalization, TuSimple, Uncategorized, Yangshan comprehensive bonded area, Yangtze River Delta, Yangtze River Economic Belt |
Leave a Comment »
07/07/2019
TOKYO, July 6 (Xinhua) — “When I wrote the letter, I didn’t expect to receive a reply from President Xi Jinping. I was surprised and honored,” said Daichi Nakashima with excitement.
The 27-year-old Japanese man said he had received the reply from Xi before the Chinese leader attended the Group of 20 summit in Osaka. “When my friend told me on WeChat, I was shocked!” Nakashima said in an exclusive interview with Xinhua.
Nakashima had several times been a winner in the Panda Cup Japan Youth Essay Contest. Founded in 2014, the competition is co-sponsored by People’s China magazine, the Chinese embassy in Japan and the Japan Science Society, aiming to help Japanese youths have a more comprehensive, objective and rational understanding of China.
Nakashima began learning Chinese in college and has participated in several short-term exchange programs in China.
When talking about his original intention of writing a letter to Xi, Nakashima said, “I wanted to convey the warmth and friendship of the Chinese people I felt during my visit to China and the importance of mutual understanding and exchanges between Japanese and Chinese youths.”
Xi, in his reply, said he was glad to see that Nakashima has been studying the Chinese language and literature for a long time and, by participating in essay contests and exchange activities in China, has learned more about China and strengthened his bonds with Chinese friends.
“It’s the best affirmation and recognition of my persistence for so many years. I’m very touched,” Nakashima said.
Born in 1992, Nakashima first learned about China through classics like “Romance of the Three Kingdoms” and “Outlaws of the Marsh,” but it was a two-week trip to Tianjin in 2011 that gave him a glimpse of a vibrant China.
After that, he visited Beijing, Sichuan, Guangdong and other places. Last year, he went to Fudan University in Shanghai and studied for half a year.
Nakashima found that Chinese youth are very familiar with Japanese anime, music and so on, while Japanese youngsters do not know much about China. Their impression of China is restricted to Chinese tourists, “not knowing about Chinese movies and popular music,” he said.
Nakashima said he believes that the friendship between the two peoples needs more bilateral youth exchanges, as President Xi said in the letter.
Noting that China and Japan are close neighbors separated by only a narrow strip of water, Xi said the friendship between the two countries is rooted in the people, and that the future of the friendship between the two peoples is in the hands of the young people.
Xi said he hopes that the youth of China and Japan will strengthen exchanges and mutual learning, enhance mutual understanding, develop long-lasting friendships, and contribute to creating an even brighter future for bilateral relations.
Xi also encouraged Nakashima to continue to promote the China-Japan friendship. Nakashima said this is an encouragement, a mission and also motivation for him to move forward.
Nakashima graduated with a master’s degree in April and has begun to work in a publishing house. He has been determined to introduce excellent works such as Chinese picture books and science fiction to Japan, so that Japanese teenagers can feel the affinity between the two countries.
“I have met many friendly Chinese people and made many friends that are very important to me. In the future, I will continue to make efforts to help Japanese and Chinese youth deepen mutual understanding,” he said.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Beijing, Chinese embassy in Japan, comprehensive, contributions, Daichi Nakashima, Fudan University, Group of 20 (G20), guangdong province, inspires, Japan Science Society, Japan-China friendship, Japanese youth, letter, master's degree, objective, Osaka, Outlaws of the Marsh, Panda Cup Japan Youth Essay Contest, People's China magazine, President Xi, publishing house, rational understanding, Romance of the Three Kingdoms, Shanghai, shocked, sichuan province, Tianjin, Uncategorized, WeChat |
Leave a Comment »
23/06/2019
- Stalled denuclearisation talks also expected to be on the agenda when Chinese president meets Kim Jong-un this week
- Analysts say Korean peninsula has become intense diplomatic battleground between Beijing and Washington
North Korean leader Kim Jong-un (right) attends a welcome ceremony in Beijing with Chinese President Xi Jinping in January. Xi will begin a visit to Pyongyang on Thursday. Photo: AP
Xi Jinping’s upcoming trip to
will be a state visit – a higher status than the last trip to the hermit kingdom by a Chinese president, highlighting the close bilateral ties between Beijing and Pyongyang.
Xi’s two-day trip, which
, is the first by a Chinese president to North Korea in 14 years and comes just a week before he is due to meet US President Donald Trump for talks on the sidelines of the Group of 20 summit in Japan.
“Leaders of the two countries will review the development of the bilateral relationship and carry out an in-depth exchange of opinions on the development of Sino-North Korean relations in the new era, and chart the future course of development,” state news agency Xinhua reported on Tuesday.
Xi’s predecessor, Hu Jintao, went to North Korea in October 2005 on a three-day trip described as an “official goodwill” visit.
Speaking at a regular press briefing in Beijing on Tuesday, foreign ministry spokesman Lu Kang said Xi’s visit aimed to “inject new impetus” into relations in the year the two countries marked the 70th anniversary of establishing diplomatic ties, and to give stalled denuclearisation talks a much needed push.
“Regarding the progress on denuclearisation, as I said, the result of the Hanoi leaders’ meeting in February was indeed a little unexpected. But after that, everyone actually looks forward to the resumption of dialogue in a good direction,” Lu said, referring to the failed talks between Trump and North Korean leader Kim Jong-un in the Vietnamese capital four months ago.
Trump hinted at the possibility of another meeting with Kim after receiving what he called “a beautiful letter” from the North Korean leader last week. On Tuesday, South Korea’s chief nuclear negotiator, Lee Do-hoon, said the US had been in contact with the North.
Life in North Korea the ‘admiration and envy’ of others, state media says
Washington will also send US Special Representative for North Korea Stephen Biegun to South Korea next week, days after Xi’s visit to Pyongyang, to fully align its position on North Korea with its ally.
Meanwhile, Trump confirmed he would meet Xi for talks in Osaka next week, saying in a tweet on Tuesday they had “a very good telephone conversation” and would hold “an extended meeting” at the G20 summit, where they are
over an almost year-long trade war.
Pyongyang has demanded the lifting of sanctions imposed on the regime following its nuclear and missile tests, while Beijing has said the livelihoods of North Koreans should not be affected. But Washington insists full sanctions should remain in place.
The US has also voiced scepticism about Chinese compliance with the sanctions. At a security summit in Singapore earlier this month, US acting Pentagon chief Patrick Shanahan – who on Wednesday stepped down from his role
– presented his Chinese counterpart Wei Fenghe with photographs and satellite images of North Korean ships transferring oil near China’s coast.
Analysts said Xi would seek to use the visit to boost China’s diplomatic leverage on the North Korean nuclear front, strengthening its hand in dealing with the US.
Exports from North Korea to China, which account for the bulk of its trade, plunged 87 per cent last year from 2017, and the country has faced other economic problems at a time when Kim has vowed to deliver on the economy.
A diplomatic source said China was expected to offer a large amount of humanitarian assistance, such as food and fertiliser, to North Korea, which could weaken the impact of sanctions.
China’s goal of denuclearisation on the Korean peninsula is unwavering and will not changeLu Chao, North Korean affairs expert at Liaoning Academy of Social Sciences
Communist Party mouthpiece People’s Daily on Tuesday said via its social media account that Xi would discuss economic and trade cooperation with Kim during the visit.
Quoting Zheng Jiyong, director of the Centre for Korean Studies at Fudan University in Shanghai, the newspaper said Pyongyang had taken steps to reform its economy and introduced China’s industrial manufacturing blueprint.
In September, Beijing proposed building a rail link from the city of Dandong, in China’s northeastern Liaoning province, to Pyongyang and then on to Seoul and Busan in the South, as well as a new road between Dandong and Pyongyang through Sinuiju.
Lu Chao, a North Korean affairs expert at the Liaoning Academy of Social Sciences, said large-scale economic cooperation between China and North Korea was unlikely because of the sanctions, but smaller moves were possible.
Chinese tourists flood North Korea as Beijing remains Pyongyang’s key ally
“For example, China may export daily necessities to North Korea. And if it’s needed, China is very likely to provide [food] assistance to North Korea,” Lu said. “I believe the UN sanctions on North Korea should change, because it has shown a more substantive approach to [achieving] denuclearisation.”
But analysts said Beijing remained firm on the need for Pyongyang to honour its pledges so that denuclearisation could be achieved.
“China’s goal of denuclearisation on the Korean peninsula is unwavering and will not change … China supports [North Korea] and the US continuing to hold talks,” Lu said.
Beijing also had an important part to play in the peace process, according to Boo Seung-chan, an adjunct professor at the Yonsei Institute for North Korean Studies in Seoul.
“China can have a positive role as a mediator to facilitate the peace process on the Korean peninsula,” Boo said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in aims, Asan Institute for Policy Studies, Beijing, Busan, Centre for Korean Studies, chinese tourists, Dandong, denuclearisation, diplomatic battleground, Fudan University, hermit kingdom, Hu Jintao, Kim Jong-un, Korean peninsula, Liaoning Academy of Social Sciences, Liaoning province, new impetus, North Korea, Patrick Shanahan, People’s Daily, President Donald Trump, President Xi Jinping, Pyongyang, Seoul, Shanghai, Singapore, Sino-North Korean relations, South Korea, State visit, ties, Uncategorized, US acting Pentagon chief, US Special Representative for North Korea, Washington, Wei Fenghe, Xinhua, Yonsei Institute for North Korean Studies |
Leave a Comment »
17/06/2019
- Washington has blamed Tehran for an attack on two oil tankers near the Strait of Hormuz, putting pressure on Iran’s allies like China
- Beijing usually backs its trade partner – but experts say the trade war with the US and problems with Huawei may have changed the equation
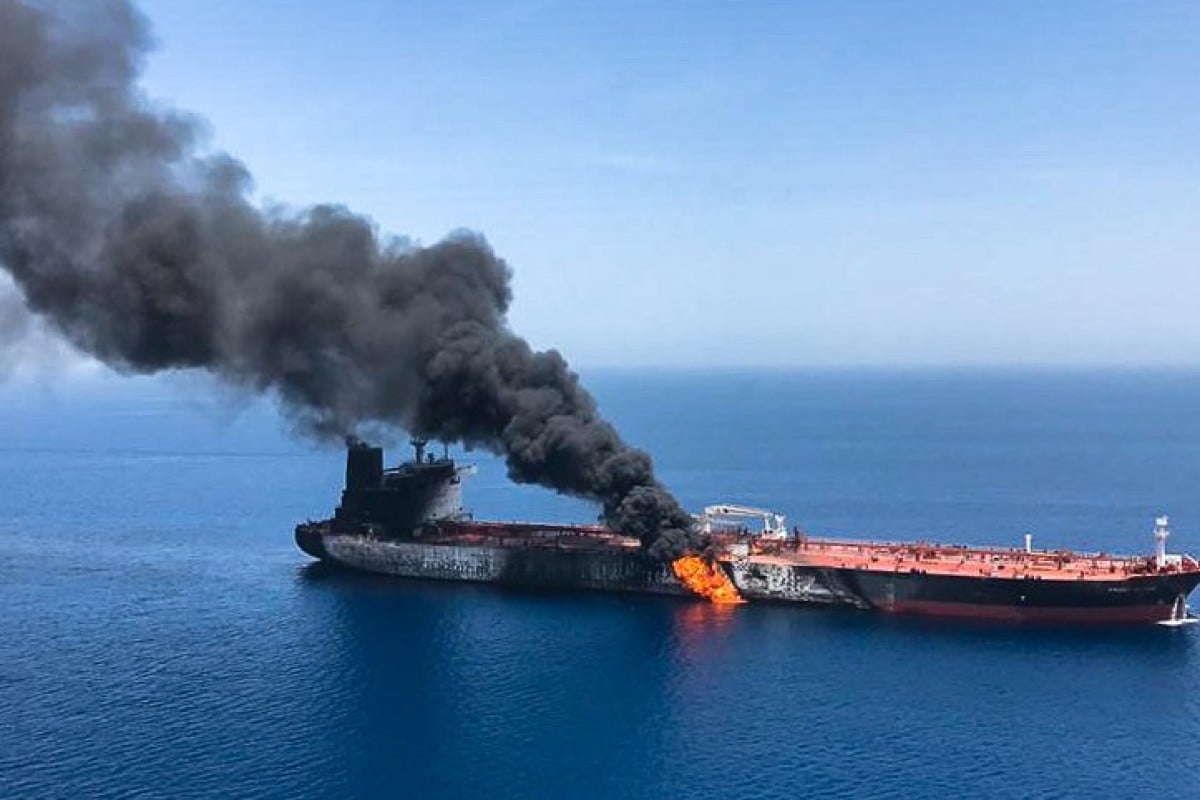
A tanker burns in the Gulf of Oman after a mystery attack that the United States has blamed on Iran. Photo: AFP
When
headed to Tehran this week for the first visit by a sitting Japanese prime minister in four decades, some in the diplomatic world imagined he could be the man to bring
back to the negotiating table with the
.
Those hopes were torpedoed on Thursday when, on the same day Abe was meeting Iran’s supreme leader Ayatollah Khamenei, explosions ripped through two oil tankers, one Japanese and one Norwegian, near the Strait of Hormuz, a strategically significant shipping lane.
The attack immediately overshadowed an earlier success for Abe, who had met President Hassan Rowhani a day before and was assured Iran would stick to the terms of a 2015 agreement limiting its nuclear activities.
Washington accused Iran of being behind the attack on the tankers, releasing a video on Friday that it said showed Iran’s revolutionary guard removing an unexploded mine from one of the ships, and warning that it would “defend its interests”.
Iranian President Hassan Rowhani and Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe meet Iran’s Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei in Tehran. Photo: Reuters
Tehran, for its part, claimed to have been set up, with its foreign minister Mohammad Javad Zarif saying “suspicious doesn’t begin to describe” the incident. So much, then, for hopes of mediation.
US President
, who had encouraged the Japanese leader’s visit, admitted on Twitter soon afterwards that when it came to negotiating, “they are not ready, and neither are we!”
Still, the incident exposed more than just the naivety of those hoping for an Abe-led breakthrough. In raising the stakes in Washington’s confrontation with Tehran, it also threw the spotlight on Iran’s dwindling number of allies – and perhaps most significantly on its largest trading partner, China – which face mounting pressure to rethink the relationship.
Tanker attacks: world divided over Iran role as Saudi prince breaks silence
The day after the attack, China’s President
said Beijing would promote its ties with Iran “however the situation changes” – a comment made during a meeting with Iranian President Hassan Rowhani on the sidelines of the Shanghai Cooperation Organisation summit in Kyrgyzstan – but diplomatic observers question just how far China can go in accommodating its controversial trading partner.
BEST FRIENDS FOREVER?
Iran has long been able to count on support from China, which accounts for 30 per cent of the Islamic republic’s exports and imports, and its willingness to defy US pressure is a gamble at least partly based on an assumption it can continue to count on Beijing’s support.
As Iran’s largest economic partner – Chinese direct investment in Iran hit a record high of nearly US$4 billion last year, according to data analysis project ChinaMed – Beijing already plays a key role in relieving US pressure on Iran, said Mohsen Shariatinia, assistant professor of regional studies at Shahid Beheshti University in Tehran.
But experts warn that reliance will come into question as China becomes increasingly hamstrung by its own problems.
China has enough problems of its own, starting with US pressure on Huawei. Photo: EPA
Chief among Beijing’s headaches are its
with Washington and the related assault on its
giant
– which, as analysts point out, originally ignited over allegations it was defying US sanctions on Iran. Beijing will also be well aware of the need to keep
, its second-biggest oil supplier and Tehran’s critic-in-chief, happy.
On the other hand, analysts say, China will be wary of being seen to abandon its old friend, as doing so would send a message to other nations at odds with Washington that they could no longer look to China as a diversification strategy.
“This could mean Chinese investment is vulnerable to US interference,” said Esfandyar Batmanghelidj, founder of Bourse Bazaar, a media company that supports business diplomacy between Europe and Iran.
Sanctions drive Iranian students away from US towards Asia
Doing so, Batmanghelidj said, would put a question mark over one of China’s most significant foreign policies of recent years – President Xi’s signature
to fund infrastructure across Eurasia.
THE BELT AND ROAD QUESTION
Tensions between Iran and the US have reached boiling point in recent weeks, after the Trump administration last month ended waivers on sanctions for nations importing Iranian oil – a move the US says is aimed at making the republic “radioactive to the international community” and which Rowhani has described as an “economic war against Iran”.
So far, China has largely stuck by the Islamic Republic, continuing to buy fuel from it despite the latest wave of US sanctions on Iranian oil that followed Trump’s decision last year to withdraw the US from the landmark 2015 agreement curbing Tehran’s nuclear development.
The deal had been widely lauded as a triumph of multilateralism and the dawning of a new economic era for Iran.
US releases video of ‘Iranian forces removing unexploded mine’ from ship
Part of its eagerness to support Iran has stemmed from the Islamic Republic’s key position in the Belt and Road plan. In 2017 alone, China signed deals for more than US$15 billion in Iranian infrastructure investment, according to the
mouthpiece China Daily.
Planned projects include high-speed rail lines, upgrades to the nation’s electrical grid, and natural gas pipelines. The two nations have also vowed to boost bilateral trade to US$600 billion in the next seven years.
“China sees Iran as its Western gateway, where not only is it a big market in itself, but it will also be the gateway to the rest of the
and ultimately to Europe for China,” said Anoush Ehteshami, professor of international relations at Durham University in Britain.
Nisha Mary Mathew, at the Middle East Institute in Singapore, said that China’s relationship with Iran was not just economic – but primarily strategic, with both nations envisioning an international order that was no longer dominated by the US and its Western allies.
DEFIANCE, FOR NOW
If the belt and road gives China good reason to stick with Iran, there are plenty of voices urging just that action. As Andrea Ghiselli at Shanghai’s Fudan University pointed out, US sanctions until now have only strengthened the hardline factions in Iran’s government.
The combination of the US withdrawal from the nuclear deal – which had the support of the international community – along with Europe’s tepid efforts to rescue it, may have emboldened those favouring resistance over negotiation.
Xi’s supportive comments in Kyrgyzstan were only the latest in a string of remarks from China that could encourage such factions.
If Trump kills off Huawei, do Asia’s 5G dreams die?
After China’s Foreign Minister Wang Yi met Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif in Beijing last month, the ministry’s spokesman Lu Kang said China’s economic relationship with Iran was “reasonable and lawful”.
Two months prior to that, China’s Minister of Commerce Zhong Shan, while hosting his Iranian counterpart Farhad Dejpasand, had claimed China’s “determination to maintain and develop the China-Iran comprehensive strategic partnership is unshakeable”.
Chinese President Xi Jinping with Iranian President Hassan Rowhani. Photo: AFP
Even so, the pressure is getting to some. In February, Foreign Minister Zarif temporarily resigned, in what Andrea Ghiselli at Fudan University in Shanghai called a clear sign of the “changing and precarious power balance with Iran’s foreign policy establishment”.
And nowhere is the pressure felt more keenly than the economy and China’s ability to serve as a lifeline.
“The real anxiety in Iran right now is about market share,” said Bourse and Bazaar’s Batmanghelidj. “If you’re exporting zero oil and your customers are buying oil elsewhere, you lose market share.
“The government wants to know if it agreed to go back to the negotiating table and the US promised sanctions relief, that there are people who are going to buy in significant volume.”
TURNING POINT: HUAWEI
For many analysts, the event most likely to have changed the equation in Beijing’s eyes is the arrest by the Canadian authorities of
, the chief financial officer of Chinese telecom giant Huawei.
Meng’s arrest came at the request of the US government, which claimed her company had violated sanctions by selling equipment to Iran.
Many observers saw the action as Washington’s way of signalling to Chinese companies that they would face repercussions if they eased the pressure on Iran by continuing to trade.
Huawei’s chief financial officer Meng Wanzhou. Photo: Reuters
“Going after Huawei was about going after Chinese enterprises – signalling that they can no longer trade with Iran with impunity,” Batmanghelidj said.
Since then, Chinese firms have shown increased skittishness towards trading with Iran. According to China’s General Customs Administration, Chinese exports to Iran declined by more than half between October 2018 and February 2019, from over US$1 billion to just under US$500 million.
Mohammad Ali Shabani, a researcher at the School of Oriental and African Studies in London, said other countries in the region were now watching to see if China would blink in the face of US pressure. “This could have dire consequences for China’s image as a reliable partner,” he said.
NOT JUST ABOUT AMERICA
There are reasons beyond US pressure that may factor into Beijing’s thinking. It has long stated its opposition to Iranian nuclear weapons development, and Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi has said that China is “ready” to take on “its due responsibilities and make a greater contribution to world peace and common development”.
Trade war: here are Beijing’s options – and none look any good
Zhao Hong, at the Research School of Southeast Asian Studies at Xiamen University, said that in stepping up as a responsible world power Beijing faced a dilemma over its approach to Iran.
“Chinese leaders have to painfully balance an impulse towards economic cooperation with Iran against other vital interests, including convincing Washington that China is a responsible stakeholder,” he wrote in the Journal of Contemporary China.
Saudi Aramco’s Ras Tanura oil refinery. The country is China’s second-largest oil supplier after Russia. Photo: Reuters
Then there is China’s relationship with Iran’s chief adversary, Saudi Arabia, to consider. Riyadh is China’s second-largest oil supplier, behind Russia, and it plays a central role in Beijing’s energy strategy.
According to International Trade Centre data, more than 12 per cent of China’s imported oil came from Saudi Arabia last year, compared with just 6 per cent from Iran. Last year, Saudi Arabia shipped 56.73 million tonnes of oil to China, or 1.135 million barrels per day.
Why would Kim Jong-un trust Trump, now that he’s ripped up Iran’s nuclear deal?
This April, China imported 6.3 million tonnes of oil from Saudi Arabia, nearly twice the 3.24 million tonnes it imported from Iran, according to China’s General Administration of Customs.
Iran’s comparatively small share of China’s oil imports market and its heavy reliance on China as a trading partner add up to a deeply uneven relationship, experts say, and it is this imbalance that will encourage the US that China may be open to rethinking its ties.
As Jon Alterman, director of the Middle East programme at Washington DC think tank the Centre for Strategic and International Studies, pointed out, while China was Iran’s largest trading partner, Iran represented less than 1 per cent of China’s international trade.
“Iran needs China,” Alterman said. “But to China, Iran is expendable.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Ayatollah Khamenei, Beijing, Belt and Road (B&R), Centre for Strategic and International Studies, Durham University in Britain, Farhad Dejpasand, Foreign Minister Wang Yi, Fudan University, General Administration of Customs, General Customs Administration, Gulf of Oman, high-speed rail lines, Huawei, iran, Iran’s ties with China, Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif, Iranian President Hassan Rowhani, Islamic Republic, Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, Journal of Contemporary China, Kyrgyzstan, Meng Wanzhou, Middle East, Middle East Institute in Singapore, Minister of Commerce Zhong Shan, Oil tanker attacks, oil tankers, President Xi Jinping, Research School of Southeast Asian Studies, Riyadh, Russia, Saudi Arabia, Saudi Aramco's Ras Tanura oil refinery, Strait of Hormuz, Tehran, torpedoed, Uncategorized, United States, US President Donald Trump, Washington, Xiamen University |
Leave a Comment »
29/05/2019
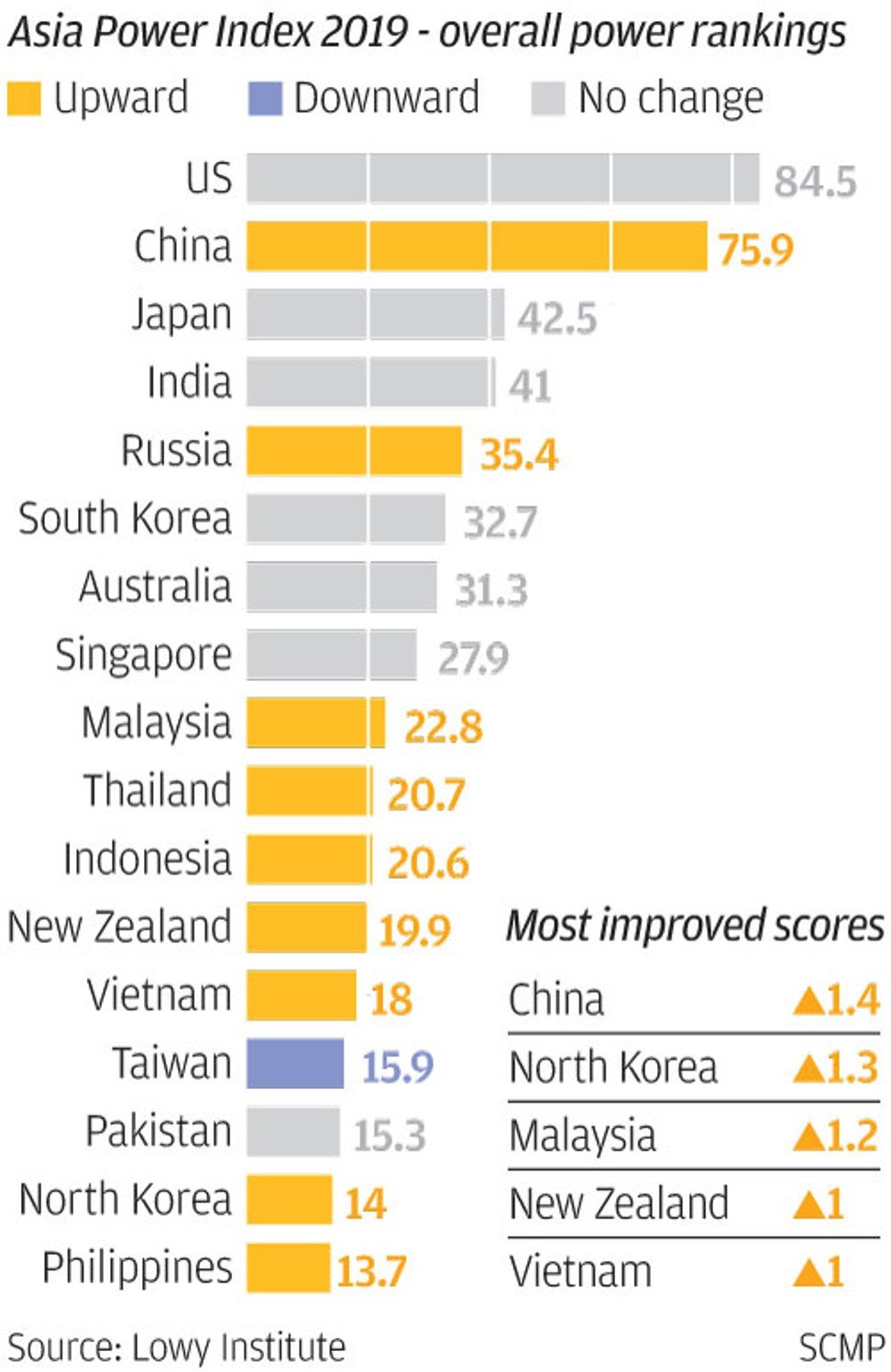
- Lowy Institute’s 2019 Asia Power Index puts Washington behind both Beijing and Tokyo for diplomatic influence
- Trump’s assault on trade has done little to stop Washington’s decline in regional influence, compared to Beijing, say experts
Chinese and US flags at an international school in Beijing. Photo: AFP
The
may be a dominant military force in Asia for now but short of going to war, it will be unable to stop its economic and diplomatic clout from declining relative to China’s power.
That’s the view of Australian think tank the Lowy Institute, which on Tuesday evening released its 2019 index on the distribution of power in Asia.
However, the institute also said China faced its own obstacles in the region, and that its ambitions would be constrained by a lack of trust from its neighbours.
The index scored China 75.9 out of 100, just behind the US, on 84.5. The gap was less than America’s 10 point lead last year, when the index was released for the first time.
“Current US foreign policy may be accelerating this trend,” said the institute, which contended that “under most scenarios, short of war, the United States is unlikely to halt the narrowing power differential between itself and China”.
The Lowy Institute’s Asia Power Index. Click to enlarge.
Share:
Since July, US President
has slapped tariffs on Chinese imports to reduce his country’s
. He most recently hiked a 10 per cent levy on US$200 billion worth of Chinese goods to 25 per cent and has also threatened to impose tariffs on other trading partners such as the European Union and Japan.
Herve Lemahieu, the director of the Lowy Institute’s Asian Power and Diplomacy programme, said: “The Trump administration’s focus on trade wars and balancing trade flows one country at a time has done little to reverse the relative decline of the United States, and carries significant collateral risk for third countries, including key allies of the United States.”
The index rates a nation’s power – which it defines as the ability to direct or influence choices of both state and non-state actors – using eight criteria. These include a country’s defence networks, economic relationships, future resources and military capability.
It ranked Washington behind both Beijing and Tokyo in terms of diplomatic influence in Asia, due in part to “contradictions” between its recent economic agenda and its traditional role of offering consensus-based leadership.
The spoils of trade war: Asia’s winners and losers in US-China clash
Toshihiro Nakayama, a fellow at the Wilson Centre in Washington, said the US had become its own enemy in terms of influence.
“I don’t see the US being overwhelmed by China in terms of sheer power,” said Nakayama. “It’s whether America is willing to maintain its internationalist outlook.”
But John Lee, a senior fellow at the Hudson Institute, said the Trump administration’s willingness to challenge the status quo on issues like trade could ultimately boost US standing in Asia.
“The current administration is disruptive but has earned respect for taking on difficult challenges which are of high regional concern but were largely ignored by the Obama administration –
illegal weapons and China’s predatory economic policies to name two,” said Lee.
“One’s diplomatic standing is not just about being ‘liked’ or ‘uncontroversial’ but being seen as a constructive presence.”
CHINA’S RISE
China’s move up the index overall – from 74.5 last year to 75.9 this year – was partly due to it overtaking the US on the criteria of “economic resources”, which encompasses GDP size, international leverage and technology.
China’s economy grew by more than the size of Australia’s GDP in 2018, the report noted, arguing that its growing base of upper-middle class consumers would blunt the impact of US efforts to restrict Chinese tech firms in Western markets.
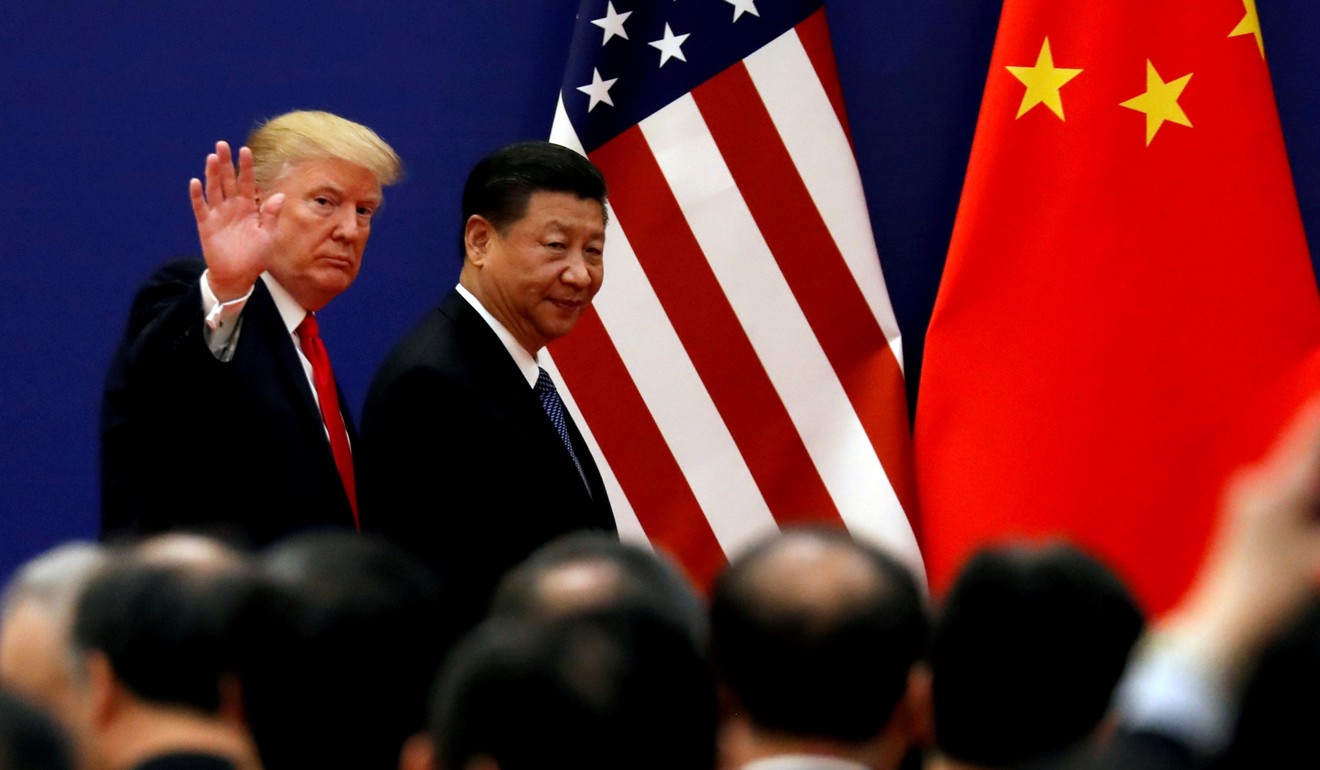
US President Donald Trump with Chinese counterpart Xi Jinping. Photo: Reuters
“In midstream products such as smartphones and with regard to developing country markets, Chinese tech companies can still be competitive and profitable due to their economies of scale and price competitiveness,” said Jingdong Yuan, an associate professor at the China Studies Centre at the University of Sydney.
“However, to become a true superpower in the tech sector and dominate the global market remains a steep climb for China, and the Trump administration is making it all the more difficult.”
The future competitiveness of Beijing’s military, currently a distant second to Washington’s, will depend on long-term political will, according to the report, which noted that China already spends over 50 per cent more on defence than the 10
stands in the way of its primacy in Asia, according to the index, which noted Beijing’s unresolved territorial and historical disputes with 11 neighbouring countries and “growing degrees of opposition” to its signature
.
Beijing is locked in disputes in the
with a raft of countries including Vietnam, the Philippines and Brunei, and has been forced to renegotiate infrastructure projects in
and Myanmar due to concerns over feasibility and cost.
If Trump kills off Huawei, do Asia’s 5G dreams die?
Xin Qiang, a professor at the Centre for American Studies at Fudan University in Shanghai, said Beijing still needed to persuade its neighbours it could be a “constructive, instead of a detrimental, force for the region”.
“There are still many challenges for [China to increase its] power and influence in the Asia-Pacific,” Xin said.
Wu Xinbo, also at Fudan University’s Centre for American Studies, said Beijing was having mixed success in terms of winning regional friends and allies.
“For China, the key challenge is how to manage the maritime disputes with its neighbours,” said Wu. “I don’t think there is growing opposition to the Belt and Road Initiative from the region, actually more and more countries are jumping aboard. It is the US that is intensifying its opposition to the project as Washington worries it may promote China’s geopolitical influence.”
Yuan said the rivalry between the
would persist and shape the global order into the distant future.
“They can still and do wish to cooperate where both find it mutually beneficial, but I think the more important task for now and for some time to come, is to manage their disputes in ways that do not escalate to a dangerous level,” Yuan said. “These differences probably cannot be resolved given their divergent interests, perspectives, etc, but they can and should be managed, simply because their issues are not confined to the bilateral [relationship] but have enormous regional and global implications.”
Elsewhere in Asia, the report spotlighted Japan, ranked third in the index, as the leader of the liberal order in Asia, and fourth-placed India as an “underachiever relative to both its size and potential”.
China’s wrong, the US can kill off Huawei. But here’s why it won’t
Lee said the index supported a growing perception that Tokyo had emerged as a “political and strategic leader among democracies in Asia” under
.
“This is important because Prime Minister Abe wants Japan to emerge as a constructive strategic player in the Indo-Pacific and high diplomatic standing is important to that end,” Lee said.
, South Korea, Australia,
, Malaysia and Thailand rounded out the top-10 most powerful countries, in that order. Among the pack, Russia, Malaysia and Thailand stood out as nations that improved their standing from the previous year.
, ranked 14th, was the only place to record an overall decline in score, reflecting its waning diplomatic influence
during the past year.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Asia, Asia Power Index, Asian Power and Diplomacy programme, Australia, Australia’s GDP, Beijing, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), Centre for American Studies, China alert, Chinese tech firms, European Union, Fudan University, geopolitical influence, Huawei, Hudson Institute, Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, Lowy Institute, Malaysia, North Korea, President Xi Jinping, rise, Russia, Short of war, Singapore, South Korea, Taiwan, Thailand, think tanks, Tokyo, Uncategorized, US, US President Donald Trump, Washington, Western markets, Wilson Centre in Washington |
Leave a Comment »
19/05/2019
- Experts win reprieve for two out of three heritage houses but fear their success is only temporary
- Authorities plan public cultural facilities for the site
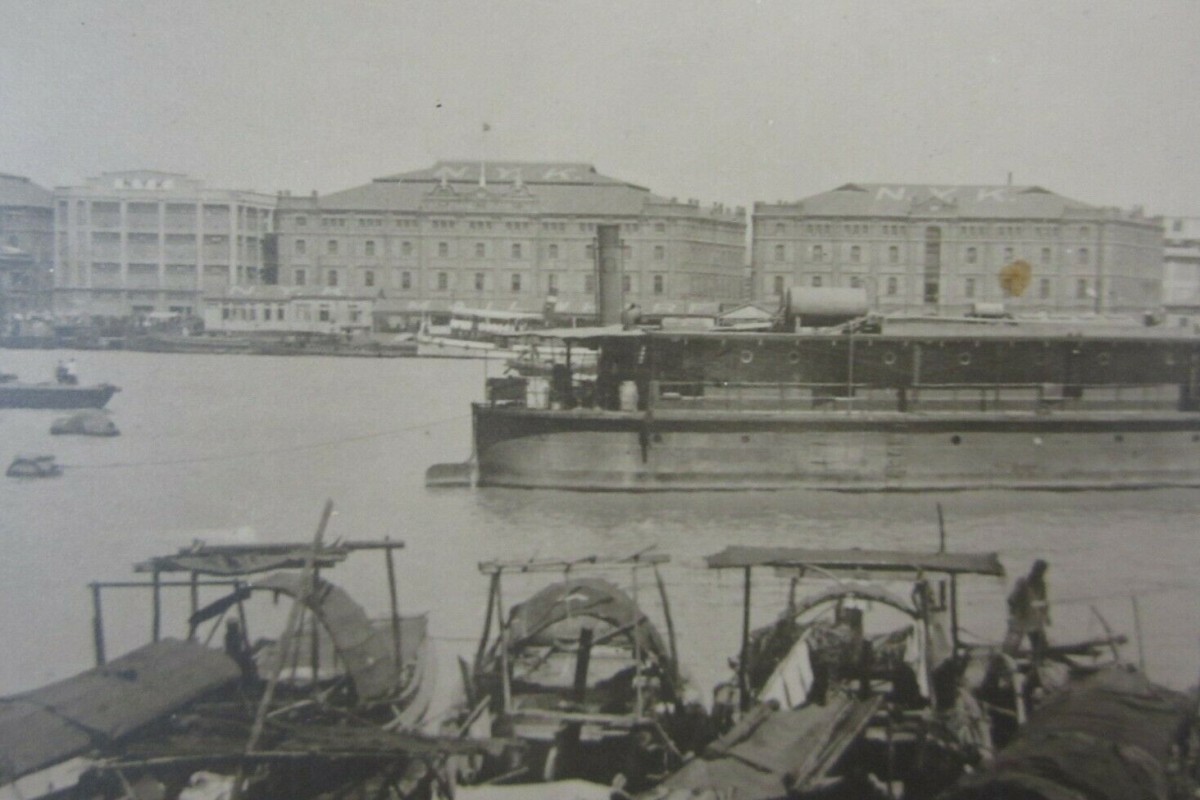
The historic buildings on Shanghai’s Bund in the 1930s. One of the three structures has already been demolished but authorities have temporarily suspended plans to knock down the other two. Photo: Handout
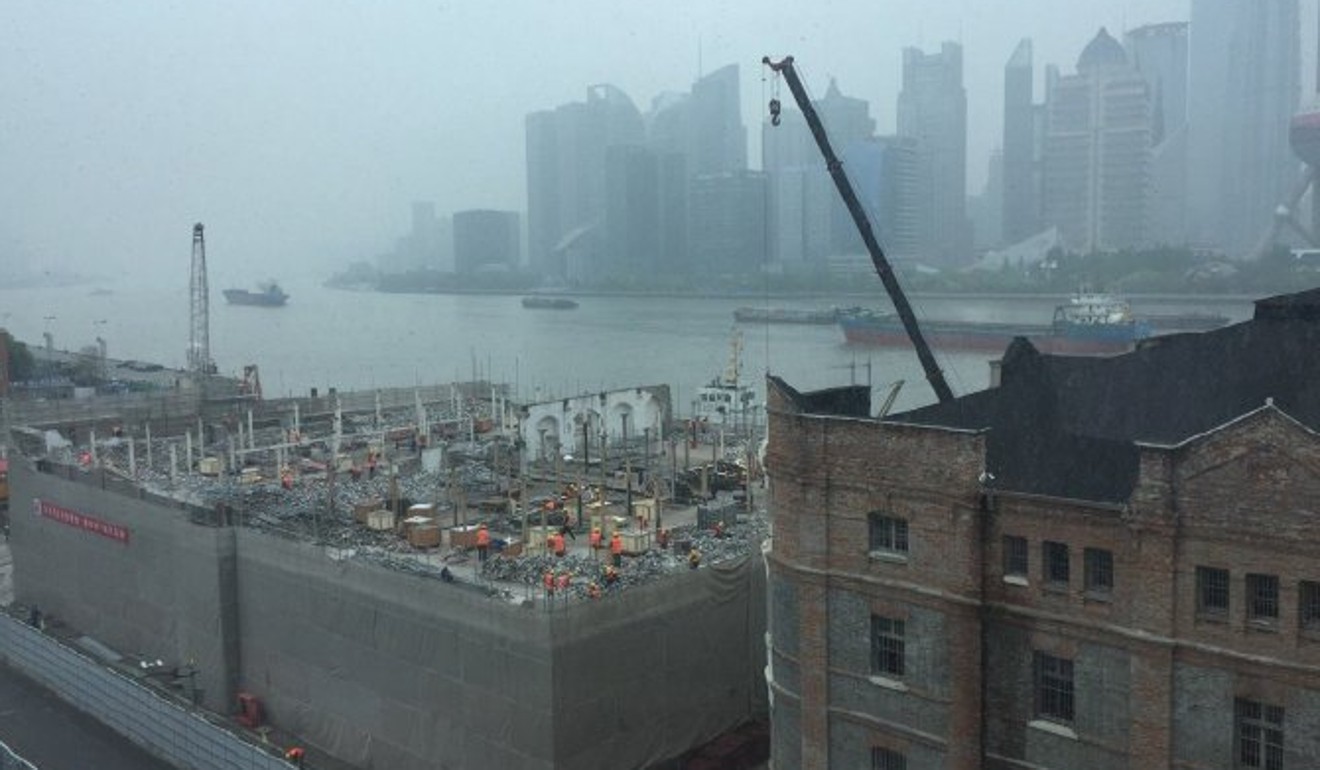
Two historic buildings on Shanghai’s famous Bund have temporarily escaped demolition after a group of experts appealed to the government to conserve the heritage sites, but the intervention was too late to save a third.
About 15 architecture, history and culture experts based in Shanghai banded together to write an article on social media app WeChat last month, calling on the city’s government to “protect the city’s memories” by preserving three houses on Huangpu Road.
A few days after the article was published one of the buildings was demolished as part of a plan to build public cultural facilities on the site. But authorities suspended work on the other two and are considering removing only the interior structure while preserving the external walls, according to the group.
The houses, which date back to 1902, witnessed the city’s boom in the first half of the 20th century when it became one of the world’s most important, and famous, ports, the experts said.
The demolition project on The Bund, Shanghai has been suspended, but not before one of the three historic buildings was demolished. Photo: Urban China magazine
All three of the properties originally belonged to Japanese shipping company Nippon Yusen Kaisha Group and were later used as storage facilities for Japan’s military forces during the second world war, according to Yu Hai, a sociologist from Shanghai’s Fudan University.
“These buildings, along with the nearby Yangzijiang port on the Huangpu River, represented Shanghai’s wharf culture and port culture,” Yu said. “They are historically significant as they witnessed Shanghai grow prosperous through shipping and trade industries about a century ago.”
Although the two remaining buildings are safe for now, the experts argue their interiors are also worth preserving.
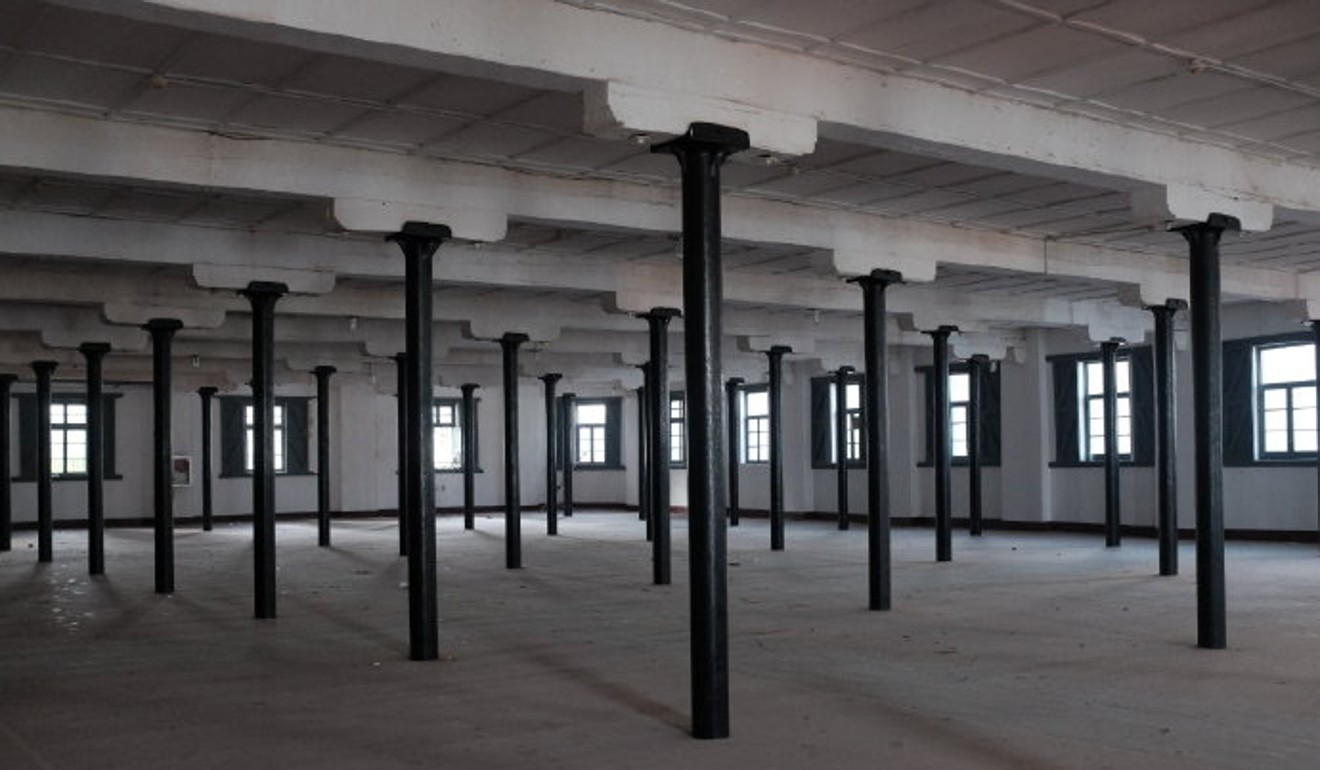
Liu Gang, an architecture professor at Shanghai’s Tongji University, said the properties featured big wooden beams supported by black iron pillars, which were prominent architectural features of industrial buildings dating back to the 19th century.
“We guess it was hard to move these giant beams with vehicles at the beginning of the 20th century. Quite possibly they were transported on the river. We guess that the wood was chopped down and processed in places across the Pacific [from North America] and shipped to Shanghai.”
In the WeChat article, Liu called for the protection of the interior structure of the buildings. “Without solid research, we cannot simply take them down to be replaced by new ones.”
Yu agreed, saying: “The building with a new inside structure would be a fake and this plan will destroy historical heritage.”
Experts say the interiors of the historic buildings are also worth preserving. Photo: Urban China magazine
Huangpu Road, where these houses sit, is rich with history. It features the Garden Bridge of Shanghai – the city’s first steel bridge, built in 1907 – and was once home to the consulates of the United States, Russia, Japan, Germany, Denmark and the Austro-Hungarian empire.
Other notable landmarks on the road include the Astor House Hotel, built in 1846, where Charlie Chaplin, Albert Einstein and George Bernard Shaw stayed in the 1920s and 1930s. The hotel is still there.
“History happened here,” Yu said. “But it’s a pity that most of the old buildings in this area no longer exist.”
Despite their success in winning a stay of execution for the two buildings, the experts are cautious in their expectations.
“The demolition work was suspended, but that does not mean they have accepted our proposals. We are not optimistic,” Yu said.
About two weeks ago as part of their effort to save the buildings, Yu and three other scholars approached officials from Shanghai’s Planning and Natural Resources Bureau, the government body behind the demolition project.
“Officials emphasised the difficulties of keeping the completeness of the old buildings and we just pointed out the damage to their historical values,” Yu said.
The Shanghai bureau did not immediately reply to a request for comment.
Shanghai nightclub king opens new art space – in disused oil tanks
Appeals by the public to conserve historical buildings have generally not been successful. Shenyuli, a typical Shanghai residential community built in the 1930s, was included in the city’s protected list of historical buildings in 2004.
The listing was not enough to prevent its demolition eight years later to make way for a public green land space.
Three years ago, the Shanghai government announced it was suspending the planned demolition of a former sex slavery station used by Japanese soldiers during the second world war, following media reports and a public outcry.
However, the building was later demolished, according to Su Zhiliang, history professor from Shanghai Normal University and a researcher on sex slavery, who predicts a similar outcome for this latest conservation effort.
“I think the government is just using the same tactic to postpone their plan. After the public’s attention is over, they will continue demolishing,” Su said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Albert Einstein, architecture professor, Astor House Hotel, Austro-Hungarian empire, big wooden beams, black iron pillars, Bund, century, Charlie Chaplin, consulates, demolition, Denmark, Fudan University, Garden Bridge, George Bernard Shaw, Germany, heritage houses, historic building, history professor, Huangpu Road, Japan, Japan’s military forces, Japanese shipping company, Liu Gang, Nippon Yusen Kaisha Group, North America, Pacific, Planning and Natural Resources Bureau, postpone, predicts, public cultural facilities, researcher, residential community, Russia, saved, second world war, sex slavery, Shanghai, Shanghai Normal University, Shenyuli, shipping, sociologist, storage facilities, Su Zhiliang, Tongji University, trade industries, Uncategorized, United States, WeChat, Yangzijiang port, Yu Hai |
Leave a Comment »