People enjoy sunset on a plank road at the East Lake in Wuhan, capital of central China’s Hubei Province, March 18, 2020. (Xinhua/Shen Bohan)
Arduous efforts have been made since Wuhan was locked down and the efforts have paid off, with the outbreak of the COVID-19 gradually brought under control in this once hardest-hit Chinese city. With sacrifices and persistence, a bright dawn is finally around the corner.
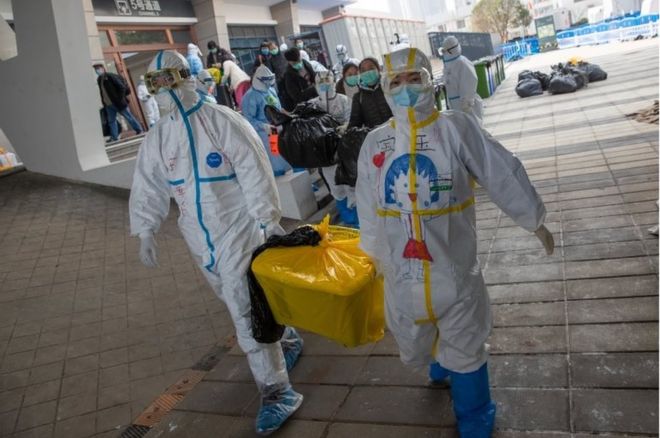
WUHAN, March 24 (Xinhua) — Xia Yongli starts a workday at dawn by having his temperature taken, disinfecting his bus and going through safety checks before hitting the road at 7:00 a.m. sharp.
Over the past eight weeks, the bus driver in the central Chinese city of Wuhan had not driven his familiar route, which is 14 km long and usually takes 40 minutes. Instead, he has been shuttling medics and delivering supplies to shops and supermarkets.
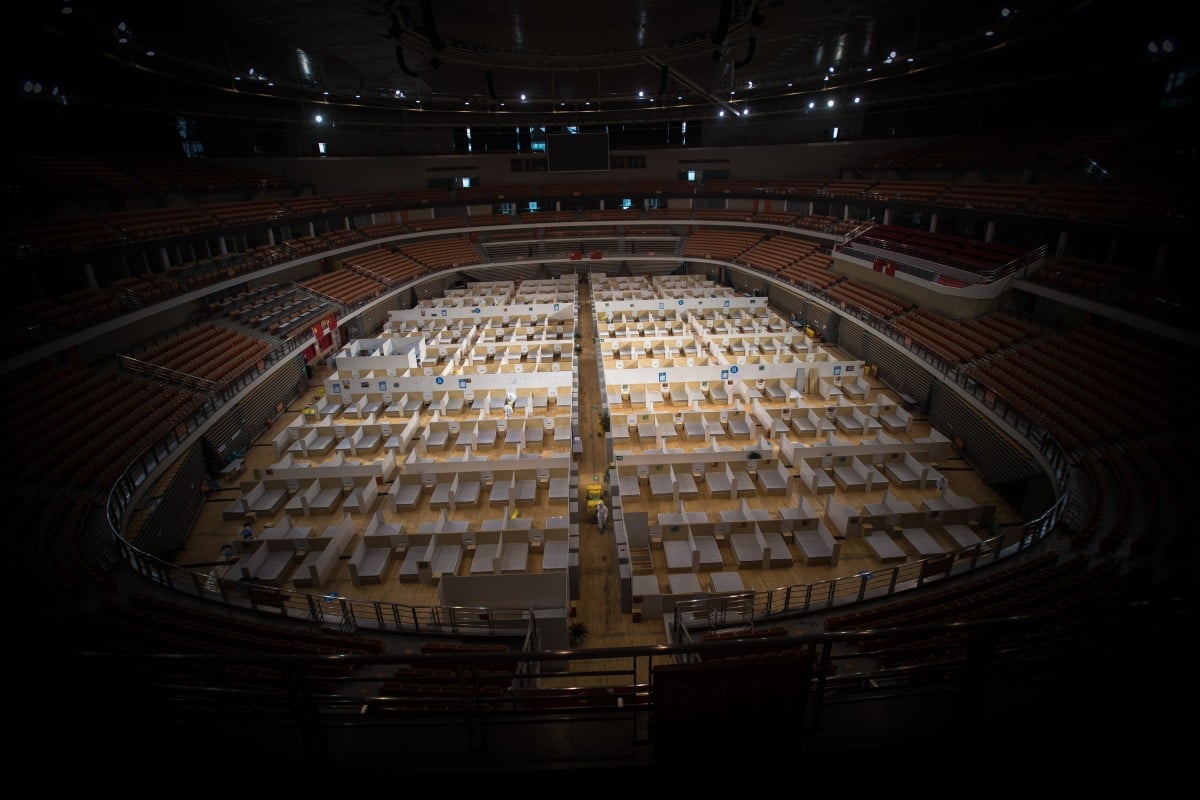
The city, with a population of over 10 million, pressed a “pause” button on Jan. 23 to contain the spread of the rampaging coronavirus behind the COVID-19 epidemic, with all public transport and outbound channels shut down and all residents staying indoors.
The streets of Wuhan are no longer bustling. Shopping blocks, pedestrian streets and other popular places where local people would stroll around are largely left to still figure sculptures.
Arduous efforts have been made since Wuhan was locked down and the efforts have paid off, with the outbreak of the COVID-19 gradually brought under control. Once hardest-hit, Wuhan only had one newly confirmed COVID-19 case reported for six consecutive days between March 18 and 23.
Wuhan had reported a total of 50,006 confirmed cases by March 23, and 43,214 patients had been cured and discharged from hospitals.
With sacrifices and persistence, a bright dawn is finally around the corner. People will be allowed to leave the city and the province from April 8, local authorities said Tuesday.

A staff member conducts disinfection at a subway station in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 23, 2020. (Xinhua/Shen Bohan)
To reduce the risk of imported cases, all personnel coming to Wuhan from overseas have to be brought under closed-loop management, with timely quarantine and epidemiological surveys conducted, said Ying Yong, secretary of Hubei Provincial Committee of the Communist Party of China.
“Wuhan had pressed the pause button and is currently in urgent need of restoring its urban functions with safe and ordered operations,” Ying said.
More than 110 bus routes citywide have conducted no-load test runs. Disinfection has been carried out at local metro and railway stations. Checkpoints for epidemic control, 27 on cross-river bridges and nearly 80 others in main urban areas, have been removed.
Infrared thermometers have been installed at subway entrances, with posters of QR codes for real-name registration inside the stations and carriages.

Staff members conduct disinfection on a subway train in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 23, 2020. (Xinhua/Xiao Yijiu)
“The traffic on the road is coming back,” said Hu Lijun, general manager of the Wuhan Zhengyuan Gaoli Optical Co., Ltd., a photoelectric encoder manufacturer, whose production capacity has been restored by 80 percent.
Traffic flow at highway exits is also increasing by about 10 percent per day due to a growing number of people returned as Wuhan speeds up resumption of work and production.
There were health staff, community workers and police in each lane at toll-gate checkpoints, scanning health codes and taking body temperatures of the returning workers, disinfecting their vehicles and making registrations.
“Drivers had to queue up at the highway exits in the past to spend five minutes filling a registration form,” said Dong Hongxiang, a police officer, noting that registration time has been cut short now by using PDA scanners.
On March 21, a special train arrived in Wuhan with 1,013 passengers on board, all of whom were employees of Dongfeng Honda, a local joint venture. They were picked up at the train station and sent directly to the factory or their residences.

Workers are busy on the production lines at the workshop of Dongfeng Passenger Vehicle Company in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 24, 2020. (Xinhua/Xiao Yijiu)
Wuhan-based enterprises that are important to the national and global industry chains and those closely related to people’s livelihood are allowed to continue operation or resume work, said Cao Guangjing, deputy governor of Hubei.
Hubei serves as one of China’s major auto producers and phosphate fertilizers. Cao said that relevant companies play significant role in the production chains. Their resumption of operation counts.
Preferential measures have been taken to support restart of engine in the city. The State Grid Wuhan electric power company has rolled out new policies to cut or exempt electricity bills for local enterprises, an estimated reduction of 389 million yuan (about 55 million U.S. dollars) by the end of June.
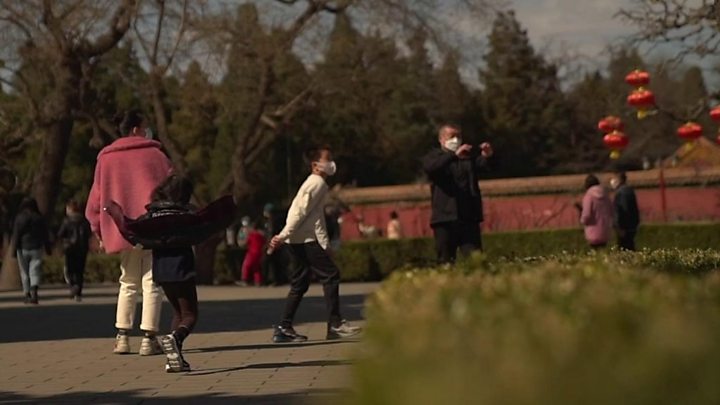
People have also started to venture out, although they cannot go as far or wherever they want.
Wang Tan, a Wuhan resident, stepped out of his home for the first time in two months to get some medicine for his father-in-law at a nearby pharmacy Monday morning.
With a health code on WeChat, Wang said he could visit convenience stores, green groceries and drug stores close to his home and have some free time outdoors inside his residential community, which has been clear of COVID-19 cases for 14 days in a row.
The Guoxinyuan community in Jiang’an District has been epidemic-free for 26 consecutive days. There were kids skipping ropes and the gray-haired doing exercises in open public areas. People observed social distancing while reclaiming a long-lost conversation.
“The public space in our community is quite small, thus no more than 80 people are allowed to have outdoor activities at one time,” said Wei Jilai, who heads the neighborhood committee.

A woman purchases daily necessities at a convenience store in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, March 19, 2020. (Xinhua/Shen Bohan)
As the epidemic recedes, more than 21,000 medical staff from across the country who had fought on the frontline in Wuhan and other places in Hubei are returning home. Before departure, some visited East Lake, one of the well-known tourist attractions in Wuhan, having group photos before cherry trees in blossom to mark the unforgettable days in the city.
Some are leaving, while others stand their ground. Ma Xin, vice president of the Huashan Hospital affiliated to Fudan University in Shanghai, stayed at Wuhan’s Tongji Hospital with his team, treating severe and critically ill patients.
“Most of them have underlying diseases and have to be treated for their complications,” Ma said, stressing that vigilance is still needed at present, especially against imported cases and relapse.
Source: Xinhua