- Inmates who have undergone compulsory re-education programme to be moved to other parts of China under job placement scheme delayed by Covid-19 outbreak
- Critics have said the camps are a move to eradicate cultural and religious identity but Beijing has defended them as way of boosting job opportunities and combating Islamic radicalisation
The Chinese government has resumed a job placement scheme for tens of thousands of Uygur Muslims who have completed compulsory programmes at the “re-education” camps in the far-western region of Xinjiang, sources said.
The plan, which includes a quota for the numbers provinces must take, was finalised last year but disrupted by the outbreak of Covid-19.
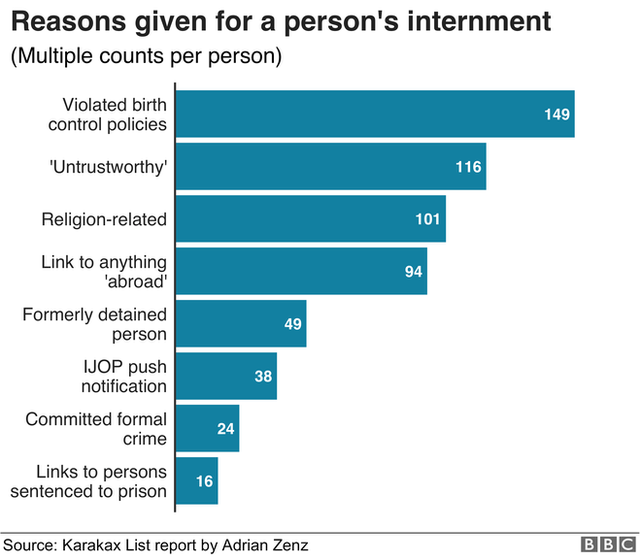
The delay threatens to undermine the Chinese government’s efforts to justify its use of internment camps in Xinjiang.
Critics have said these camps were part of the measures designed to eradicate the ethnic and cultural identity of Uygurs and other Muslim minorities and that participants had no choice but to undertake the re-education programme.

Now with the disease under control, the Chinese government has resumed the job placement deal for other provinces to absorb Xinjiang labourers, sources said.
, a source said.
“Excellent graduates were to be taken on as labourers by various inland governments, in particular, 19 provinces and municipalities,” said the source. It is unclear what constitutes “excellent graduates”.
Some sources earlier said that the programme may be scaled back in light of the new economic reality and uncertainties.
But a Beijing-based source said the overall targets would remain unchanged.
“The unemployment problem in Xinjiang must be resolved at all costs, despite the outbreak,” the source said.
The South China Morning Post has learned that at least 19 provinces and cities have been given quotas to hire Muslim minorities, mostly Uygurs, who have “graduated” from re-education camps.
As early as February, when the daily number of infections started to come down outside Hubei province, China already begun to send Uygur workers to their new jobs.
A photo taken in February showed thousands of young Uygurs, all wearing face masks and with huge red silk flowers pinned to their chests, being dispatched to work in factories outside their hometowns.
By the end of February, Xinjiang alone has created jobs for more than 60,000 Uygur graduates from the camps. A few thousand were also sent to work in other provinces.
Many have been employed in factories making toys and clothes.
Xinjiang’s new rules against domestic violence expand China’s ‘extremism’ front to the home

Sources told the Post that the southern city of Shenzhen – China’s hi-tech manufacturing centre – was given a target last year to eventually resettle 50,000 Uygurs. The city is allowed to do this in several batches, with 15,000 to 20,000 planned for the first stage.
He said the preparation work includes providing halal food to the workers as well as putting in place stronger security measures to “minimise the risks of mass incidents”. It is not known whether they will be given access to prayer rooms.
There are no official statistics of how many Uygurs will be resettled to other provinces and the matter is rarely reported by the mainland media.
But in March, Anhui Daily, the province’s official newspaper, reported that it had received 1,560 “organised labourers from Xinjiang”.
The Uygur workers on average could earn between 1,200 yuan (US$170) to 4,000 yuan (US$565) a month, with accommodation and meals provided by the local authorities, according to Chinese media reports.
However, they are not allowed to leave their dormitories without permission.
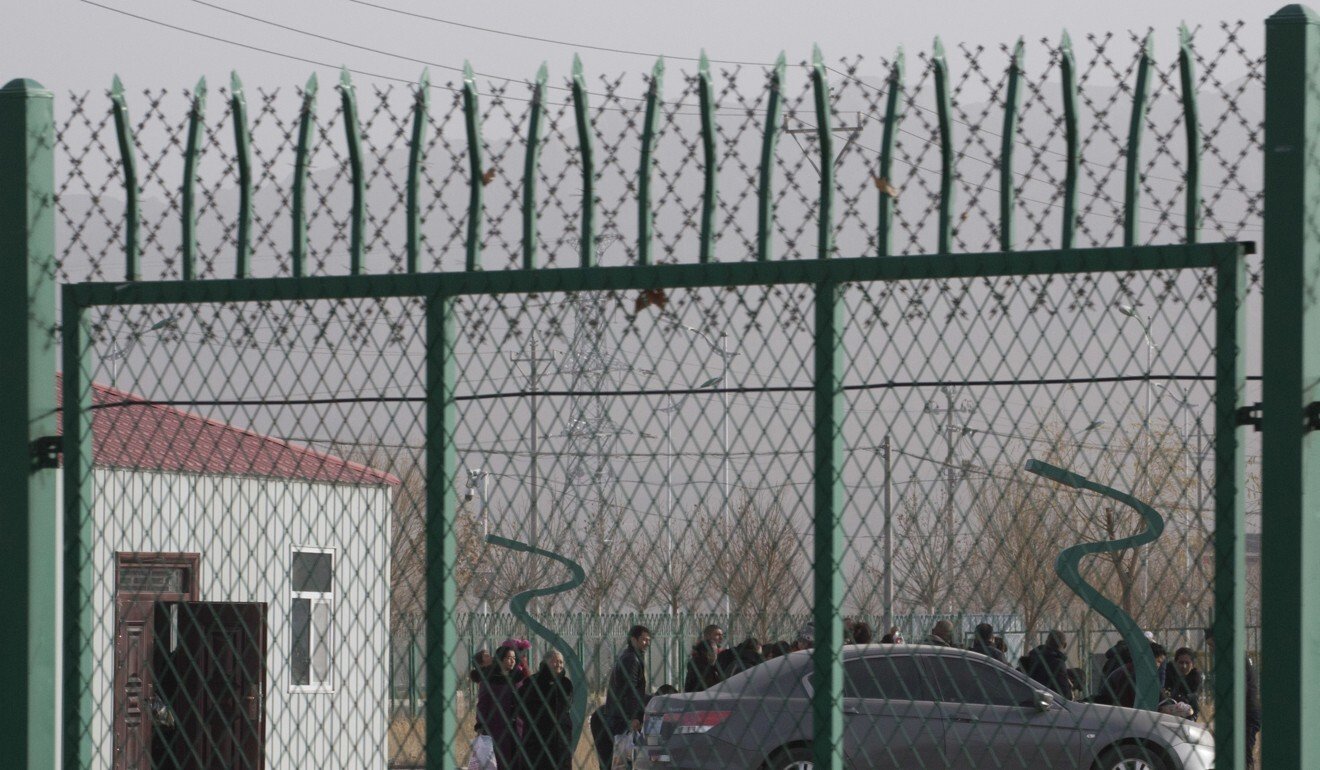


Such arrangements are not unique to Uygurs and local governments have made similar arrangements for ethnic Han workers in other parts of China.
After screening them for Covid-19, local governments have arranged for workers to be sent to their workplaces in batches. They are checked again on arrival, before being sent to work.
China is accelerating such placement deals on a massive scale to offset the impact of the economic slowdown after the outbreak.
Sources told the South China Morning Post that the job placement deal was first finalised by governments in Xinjiang and other provinces last year.
The aim is to guarantee jobs for Uygur Muslim who have “completed vocational training” at the re-education camps and meet poverty alleviation deals in the region, one of the poorest parts of China.
The training they receive in the camps includes vocational training for various job types such as factory work, mechanical maintenance and hotel room servicing. They also have to study Mandarin, Chinese law, core party values and patriotic education.
Xinjiang’s massive internment camps have drawn widespread international condemnation.
The United Nations has estimated that up to 1 million Uygur and other Muslim minority citizens are being arbitrarily detained in the camps, which Beijing insists are necessary to combat terrorism and Islamic radicalisation.
Late last year, Xinjiang’s officials announced that all the inmates of these so-called vocational training centres had “graduated” and taken up employment.
Before this labour placement scheme was introduced, it was extremely difficult for Uygurs to find jobs or live and work in inland regions.
The 2009 brawl at the factory in Shaoguan was one of the factors that triggered a deadly riot in Xinjiang’s capital Urumqi, that left 192 people dead and more than 1,000 wounded.
Muslim ethnic minorities, Uygurs in particular, have been subjected to blatant discrimination in China and the situation worsened after the 2009 clashes.
Earlier this month, the Australian Strategic Policy Institute released a report saying more than 80,000 Uygurs had been moved from Xinjiang to work in factories in nine Chinese regions and provinces.
It identified a total of 27 factories that supplied 83 brands, including household names such as Google, Apple, Microsoft, Mitsubishi, Siemens, Sony, Huawei, Samsung, Nike, Abercrombie and Fitch, Uniqlo, Adidas and Lacoste.
‘Psychological torture’: Uygurs abroad face mental health crisis over plight of relatives who remain in Xinjiang

The security think tank concluded that the Chinese government had transferred Uygur workers “under conditions that strongly suggest forced labour” between 2017 and 2019, sometimes drawing labourers directly from re-education camps.
The report also said the work programme represents a “new phase in China’s social re-engineering campaign targeting minority citizens”.
Workers were typically sent to live in segregated dormitories, underwent organised Mandarin lessons and ideological training outside working hours and were subject to constant surveillance, the researcher found.
They were also forbidden from taking part in religious observances, according to the report that is based on open-source documents, satellite pictures, academic research and on-the-ground reporting.
Chinese foreign ministry spokesman Zhao Lijian criticised the report saying it had “no factual basis”.
Source: SCMP