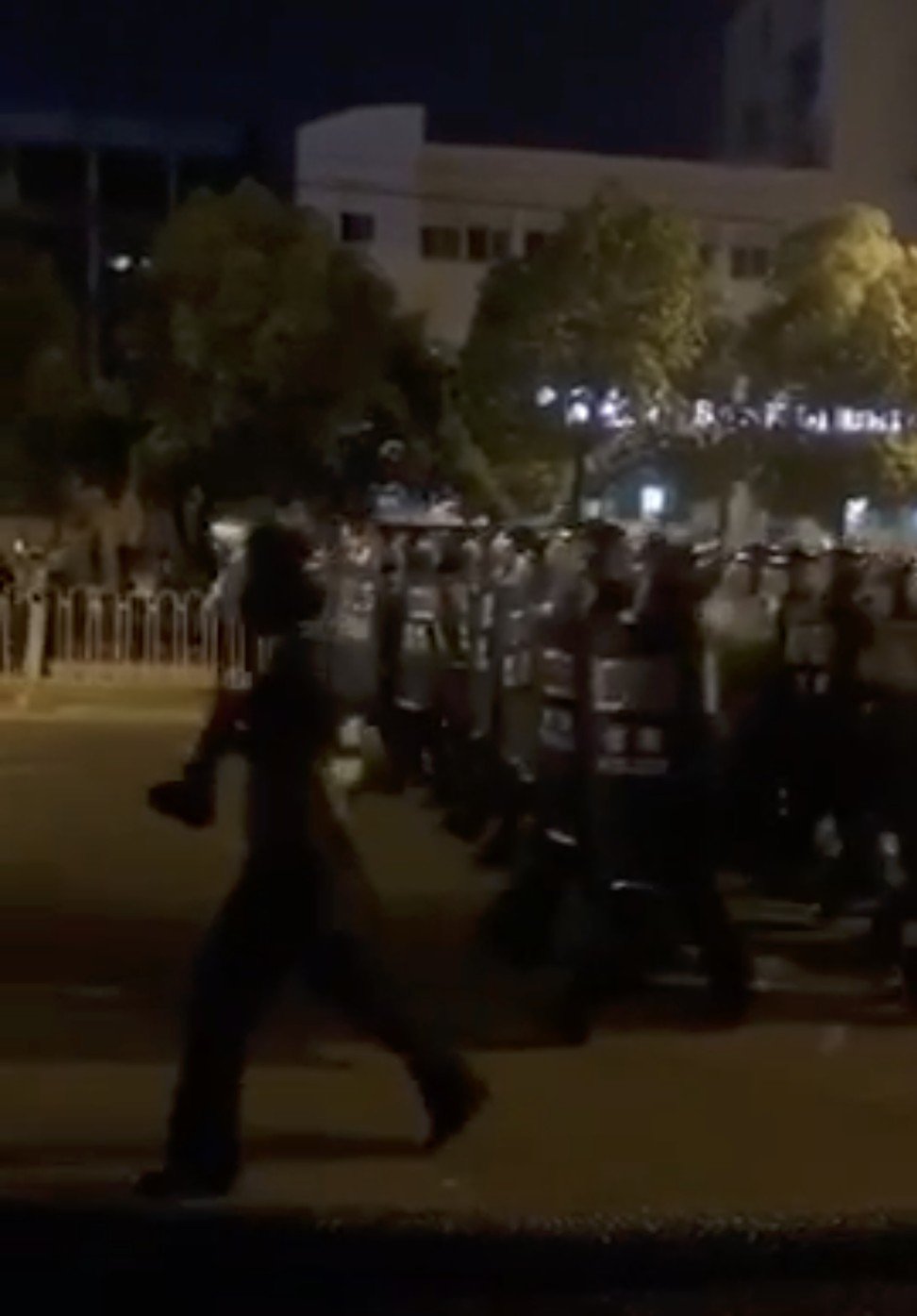30/04/2020
– The last nine poverty-stricken county-level regions in east China’s Anhui Province have been removed from the country’s list of impoverished counties.
– This marks that all county-level regions in the Yangtze River Delta, consisting of Shanghai and the provinces of Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Anhui, have been officially lifted out of poverty for the first time in history.
HEFEI, April 29 (Xinhua) — Sitting in front of his smartphone, Zhang Chuanfeng touts dried sweet potatoes to viewers on China’s popular video-sharing app Douyin, also known as TikTok.
“These are made from sweet potatoes I grew myself. They are sweet and have an excellent texture,” said Zhang while livestreaming in Tangjiahui Township of Jinzhai County in east China’s Anhui Province. Tucked away in the boundless Dabie Mountains, the township used to have the biggest poor population in the county.

Aerial photo taken on April 16, 2020 shows residential buildings in Dawan Village of Jinzhai County, east China’s Anhui Province. (Xinhua/Liu Junxi)
Jinzhai County is among the last nine county-level regions in Anhui that have been removed from the country’s list of impoverished counties, according to an announcement issued by the provincial government Wednesday. They are also the last group of county-level regions that bid farewell to poverty in the Yangtze River Delta.
E-COMMERCE
Zhang might seem like a typical e-commerce businessman reaping success in China’s booming livestreaming industry. But his road to success has been a lot bumpier: he suffers from dwarfism.
A little more than 1.4 meters tall, Zhang has a babyface, making him “look like a junior school student,” he said. But the man, 38, is the father of a nine-year-old boy.
For Zhang, life was tough before 2014. “Nobody wanted me because of my ‘disabilities’ when I went out to look for jobs,” he said. “I was turned down again and again.”
Zhang was put on the government’s poverty list in 2014 as China implemented targeted poverty-relief measures. With the help of local officials, he got a bank loan of 10,000 yuan (about 1,400 U.S. dollars) and bought 22 lambs. He tended the animals whole-heartedly and seized every opportunity to learn how to raise them more professionally.

Zhang Chuanfeng feeds his lambs in Zhufan Village of Jinzhai County, east China’s Anhui Province, April 26, 2017. (Xinhua/Zhang Duan)
Within a year, the number of his lambs expanded to hundreds. In 2016, Zhang’s earnings exceeded 100,000 yuan, more than enough for him to cast off poverty.
Riding on this success, Zhang began to seek new opportunities. He rented a shop and started selling products online to embrace an e-commerce strategy the local government introduced in 2017.
More than 100 online shops, including Zhang’s, in the county have helped more than 7,000 poverty-stricken households sell about 73 million yuan worth of local specialties since 2018. Zhang alone earned 500,000 yuan from a sales revenue of 5 million yuan last year.

A villager arranges local specialties for sale at Dawan Village of Jinzhai County, east China’s Anhui Province, April 17, 2020. (Xinhua/Liu Junxi)
WICKERWORK SUCCESS
About 100 km north of Jinzhai lies Funan, a place that used to be vulnerable to constant floods.
Zhang Chaoling, who lives by the Huaihe River in Funan County, had to flee her hometown at a young age due to floods, but has flourished on a willow plantation along the river later.
“The land is largely covered by silt following continual flooding in the past. It is an ideal place to plant willows and make wickerwork,” Zhang said.
Zhang left her hometown for Guangzhou in 1993 and found a job in a garment factory. A few years later, she founded a trading company with her husband in Guangzhou, selling wickerwork products from her hometown to other countries.
Zhang returned to her hometown and set up a wickerwork production base in 2011. Funan is famous for its delicate wickerwork. Skilled craftsmen traditionally use local willow as a raw material to weave products such as baskets, furniture and home decorations.

A villager arranges wickerwork products in Funan County, east China’s Anhui Province, April 15, 2020. (Photo by Zhou Mu/Xinhua)
“The flood is well controlled now. I remember the last huge flood came in 2007,” Zhang said.
Taking advantage of the fertile land along the Huaihe River, she plants over 130 hectares of willow trees and employs hundreds of locals mostly in their 50s and 60s.
“I can process 100 to 150 kg of willow twigs per day, from which I make around 80 yuan,” said Geng Shifen, who peels willow twigs with a clamp next to the plantation.
A total of 130,000 people are engaged in the wickerwork industry in Funan, creating an output of nearly 9 billion yuan in 2019, and helping 15,000 locals shake off poverty, local statistics showed.
POVERTY REDUCTION FEAT
The Anhui provincial government Wednesday announced that its last nine county-level regions including Jinzhai and Funan are removed from the country’s list of impoverished counties.
This marks that all 31 impoverished county-level regions in Anhui have shaken off poverty, echoing China’s efforts to eradicate absolute poverty by the end of 2020.
With the announcement, all county-level regions in the Yangtze River Delta have been officially lifted out of poverty for the first time in history.

A bus runs on a rural road in Jinzhai County, east China’s Anhui Province, April 17, 2020. (Xinhua/Liu Junxi)
Covering a 358,000-square-km expanse, the Yangtze River Delta, consisting of Shanghai and the provinces of Jiangsu, Zhejiang and Anhui, is one of the most populated and economically dynamic areas in China, contributing one-fourth of the country’s GDP.
Anhui had a population of 63.65 million as of 2019, official data showed. The poor population in the province had decreased from 4.84 million in 2014 to 87,000 in 2019, and the poverty headcount ratio had been reduced from 9.1 percent to 0.16 percent during the period, according to the provincial poverty relief office.
A county can be removed from the list if its impoverished population drops to less than 2 percent, according to a national mechanism established in April 2016 to eliminate poverty in affected regions. The ratio can be loosened to 3 percent in the western region.
By the end of 2019, 5.51 million people in China were still living in poverty.
“We will continue our work to prevent people from returning to poverty, and help the remaining poor population shake off poverty by all means,” said Jiang Hong, director of the Anhui provincial poverty relief office.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in 100, 100,000, 1993, 2014, 2016, 2017, 2018, 7,000, also known as, Anhui, Anhui province, animals, announcement, £500,000, babyface, bank loan, baskets, began, bid farewell, biggest, booming, bought, boundless, boy, bumpier, businessman, cast off, China's, constant, continual, counties, country's, county, county-level, covered, Dabie Mountains, decorations, disabilities, dried sweet potatoes, dwarfism, E-commerce, e-commerce strategy, earnings, east China's, embrace, enough, exceeded, expanded, father, first time, flee, flooding, floods, flourished, following, Funan, Funan County, furniture, garment factory, Guangzhou, helped, History, hometown, households, Huaihe River, hundreds, ideal, impoverished, in front, including, industry, introduced, Jiangsu, Jinzhai County, jobs, lambs, land, last nine, last year, lifted out of poverty, list, livestreaming, Local government, local officials, local specialties, marks, more than, Nobody, officially, online, online shops, opportunity, out of poverty, past, place, Plant, plantation, poor population, popular, poverty, poverty-relief measures, poverty-stricken, products, professionally, provinces, provincial government, raise, reaping, regions, removed, rented, Revenue, Riding, River, road to success, seek, seized, selling, Shanghai, shop, silt, Sitting, Skilled craftsmen, smartphone, started, success, suffers, Tangjiahui Township, tended, TikTok, tough, touts, township, Tucked away, typically, Uncategorized, video-sharing app, viewers, vulnerable, Wednesday, whole-heartedly, WICKERWORK, willow, willows, worth, Xinhua Headlines, Yangtze River Delta, young age, yuan, Zhang, Zhang's, Zhejiang |
Leave a Comment »
30/03/2020
WUHAN, China (Reuters) – China reported a drop in new coronavirus infections for a fourth day as drastic curbs on international travellers reined in the number of imported cases, while policymakers turned their efforts to healing the world’s second-largest economy.
The city of Wuhan, at the centre of the outbreak, reported no new cases for a sixth day, as businesses reopened and residents set about reclaiming a more normal life after a lockdown for almost two months.
Smartly turned out staff waited in masks and gloves to greet customers at entrances to the newly-reopened Wuhan International Plaza, home to boutiques of luxury brands such as Cartier and Louis Vuitton.
“The Wuhan International Plaza is very representative (of the city),” said Zhang Yu, 29. “So its reopening really makes me feel this city is coming back to life.”
Sunday’s figure of 31 new cases, including one locally transmitted infection, was down from 45 the previous day, the National Health Commission said.
As infections fall, policymakers are scrambling to revitalise an economy nearly paralysed by months-long curbs to control the spread of the flu-like disease.
On Monday, the central bank unexpectedly cut the interest rate on reverse repurchase agreements by 20 basis points, the largest in nearly five years.
The government is pushing businesses and factories to reopen, as it rolls out fiscal and monetary stimulus to spur recovery from what is feared to be an outright economic contraction in the quarter to March.
China’s exports and imports could worsen as the pandemic spreads, depressing demand both at home and abroad, Xin Guobin, the vice minister of industry and information technology, said on Monday.
The country has extended loans of 200 billion yuan (22.75 billion pounds) to 5,000 businesses, from 300 billion allocated to help companies as they resume work, Xin said.
Authorities in Ningbo said they would encourage national banks to offer preferential credit of up to 100 billion yuan to the eastern port city’s larger export firms. The city government will subsidize such loans, it said in a notice.
VIRUS CONCERNS
While new infections have fallen sharply from February’s peak, authorities worry about a second wave triggered by returning Chinese, many of them students.
China cut international flights massively from Sunday for an indefinite period, after it began denying entry to almost all foreigners a day earlier.
Average daily arrivals at airports this week are expected to be about 4,000, down from 25,000 last week, an official of the Civil Aviation Administration of China told a news conference in Beijing on Monday.
The return to work has also prompted concern about potential domestic infections, especially over carriers who exhibit no, or very mild, symptoms of the highly contagious virus.
Northwestern Gansu province reported a new case of a traveller from the central province of Hubei, who drove back with a virus-free health code, national health authorities said.
Hubei authorities say 4.6 million people in the province returned to work by Saturday, with 2.8 million of them heading for other parts of China.
Most of the departing migrant workers went to the southern provinces of Guangdong and Fujian, the eastern provinces of Zhejiang and Jiangsu, and northeast China.
In Hubei’s capital of Wuhan, more retail complexes and shopping streets reopened.
Electric carmaker Tesla Inc has also reopened a showroom in Wuhan, a company executive said on Weibo.
Shoppers queued 1-1/2 metres (5 ft) apart for temperature checks at Wuhan International Plaza, while flashing “green” mobile telephone codes attesting to a clean bill of health.
To be cleared to resume work, Wuhan residents have been asked to take nucleic acid tests twice.
“Being able to be healthy and leave the house, and meet other colleagues who are also healthy is a very happy thing,” said Wang Xueman, a cosmetics sales representative.
Source: Reuters
Posted in airports, authorities, boutiques, businesses, Cartier, China's, Civil Aviation Administration of China, companies, company executive, concerns, contagious virus, control, coronavirus cases, Country, curbs, cut, daily arrivals, demand, denying entry, depressing, drop, economic contraction, economy, Electric carmaker, export firms, factories, fiscal and monetary stimulus, flu-like disease, Foreigners, Fujian, Gansu Province, gloves, Guangdong, healing, home and abroad, hubei province, indefinite period, infections, Interest rate, international flights, Jiangsu, lockdown, luxury brands, masks, national banks, National Health Commission, new, Ningbo, none, normal life, outbreak, outright, pandemic, paralysed, policymakers, preferential credit, reclaiming, reopen, reopened, residents, resume work, returning Chinese, revitalise, scrambling, second wave, second-largest economy, Showroom, spread, spreads, spur recovery, students, subsidize, Tesla Inc, the central bank, Uncategorized, unexpectedly, vice minister of industry and information technology, Virus, Weibo, world’s, worsen, Wuhan, Wuhan International Plaza, Zhejiang |
Leave a Comment »
19/03/2020
NANJING, March 19 (Xinhua) — Chinese cities are encouraging residents to dine out and shop with measures such as handing out e-vouchers to boost consumption sectors hit hard by the novel coronavirus outbreak.
Like many living in the eastern city of Nanjing, Wang Linlin was waked up by her alarm clock at midnight and with a few clicks on her cellphone, she was ready to meet her luck of the draw: getting a meal voucher worth 100 yuan (about 14.2 U.S. dollars).
“I’ve always been thinking about hanging out and having hotpot with my friends after the epidemic, so getting a voucher would be great,” Wang said.
Nanjing has been giving out vouchers worth 318 million yuan to its residents since Sunday. People are invited to participate in lotteries for e-vouchers which can be used in restaurants, gymnasiums, bookshops as well as tourist spots, helping the service sector bounce back.
The voucher bonus has been well received as more than 1.6 million local citizens have registered for the lotteries as of Monday, according to the Nanjing Big Data Administration Bureau.
Besides Nanjing, many other regions have also been taking similar actions.
Macao gives out vouchers totaling 2.2 billion patacas (about 275 million U.S. dollars) to its residents. The city of Ningbo in east China’s Zhejiang Province is issuing consumption vouchers worth 100 million yuan while the city of Jinan, east China’s Shandong Province, is handing out vouchers worth 20 million yuan to stimulate spending on tourism and culture.
Due to the coronavirus outbreak, Chinese customers have shied away from restaurants and shopping malls. China’s retail sales of consumer goods, a major indicator of consumption growth, declined 20.5 percent year on year in the first two months of this year, according to the National Bureau of Statistics.
“People are more willing to dine out with the vouchers, which can boost confidence in the catering sector and finally get the economy back on track,” said Shen Jiahua, chairman of a chain restaurant company in Nanjing.
After the coronavirus outbreak ends, people are eager to spend generously. According to a survey conducted by the Jiangsu consumers council, nearly 90 percent of the respondents expressed suppressed consumption desire.
Restaurants, shopping malls, movie theaters, gymnasiums and tourist spots are the top five destinations for consumers to unleash their spending spree after normal life resumes, the survey showed.
Local officials across China have been taking the lead in recent days in patronizing restaurants and shopping malls, hoping to use their appearances in public to persuade more residents to go outside.
In provinces such as Jiangsu, Anhui, and Jiangxi, government notices have urged officials to dine out and go shopping to help related businesses through the epidemic period.
“Government officials are using their actions to convey confidence and support work resumption and consumer spending,” commented a Chinese netizen.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Anhui province, bookshops, cellphone, China, consumers council, consumption, coronavirus outbreak, e-vouchers, gymnasiums, hands out, Jiangsu, jiangsu province, Jiangxi Province, Jinan, Macao, Nanjing, Nanjing Big Data Administration Bureau, national bureau of statistics, Ningbo, novel coronavirus outbreak, restaurants, shandong province, spur, tourist spots, Uncategorized, virus-hit, vouchers, zhejiang province |
Leave a Comment »
20/02/2020
- A government task force has estimated a US$5 billion loss if Chinese students – angered and frustrated by the ban – cannot enrol for university
- The tourism sector is also likely to be hit by restrictions on travel from the mainland as Chinese visitors spend about U$8 billion in Australia each year
Some 150,000 Chinese nationals are enrolled at Australian universities, making up around 11 per cent of the student population. Photo: Shutterstock
Abbey Shi knows first hand the anger and frustration felt by Chinese students left stranded by the Australian government’s decision to ban travel from the mainland in response to the
coronavirus outbreak.
Shi, general secretary of the Students’ Representative Council at the University of Sydney, is in contact with more than 2,000 Chinese students who went home for the Lunar New Year holiday and now cannot return to
Australia with just weeks to go until the start of the new academic year.
“There is a lot of confusion about the ban and anger towards the government,” said Shi, an international student from Shanghai. Currently in Australia, she is sharing information with the stranded students via WeChat.
How to beat the coronavirus? Re-creating it in Singapore, Australia is vital first step
“The
education sector in Australia is being commercialised and students are being treated like cash cows,” she said. “Universities don’t care about our affected career path, life, tenancy issues, our pets at home.”
Prime Minister Scott Morrison on Saturday announced that non-citizens – excluding permanent residents and their immediate family members – who arrived from or passed through mainland China within the previous 14 days would be denied entry to Australia as part of efforts to halt the spread of the coronavirus, which was first detected in December in the Chinese city of Wuhan.
Other countries including the
United States,
Singapore and the
Philippines have introduced similar travel restrictions in response to the outbreak, which has sickened more than 19,000 people in at least 26 countries and territories outside mainland China and claimed 425 lives.
The travel ban, which is due to be reviewed on February 15, has upended the plans of numerous Chinese students who were due to begin or return to their studies from late February following the summer break.
Tony Yan, a mathematics undergraduate at Australian National University (ANU), said he had been left out of pocket for several weeks’ rent after being stranded in his home province of Jiangsu, but hoped he could return before classes started on February 24.
“I think the Australian government should have given a few days earlier notice,” Yan said. “I haven’t paid the tuition yet, many others haven’t as well.”
About 150,000 Chinese nationals are enrolled at Australian universities, making up around 11 per cent of the student population – a far greater proportion than in Britain and the United States, which came in at 6 per cent and 2 per cent respectively, in a 2017 report from an Australian think tank.
Coronavirus: Australia evacuates 243 people from China as deaths mount
ANU Vice-Chancellor Brian Schmidt on Saturday described the travel ban as “disappointing”, pledging that the university would be “generous and flexible in supporting our students” through the coming weeks.
Monash University in Melbourne has delayed the start of its academic year, while other universities are exploring options such as online tuition and intensive summer courses.
Australian universities, some of which rely on Chinese students for nearly one-quarter of their revenue, are bracing to take a major financial hit due to the ban.
Phil Honeywood, the head of a government task force initially set up to manage the reputation of Australia’s international education sector in the wake of the country’s bush fires crisis, on Sunday warned the ban could cost universities A$8 billion (US$5.34 billion) if Chinese students could not enrol for the first semester of the year.
Coronavirus: what we know so far about the outbreak spreading in China and abroad
Education minister Dan Tehan on Monday met with peak body Universities Australia to discuss ways to minimise fallout for the sector.
“Australia will remain an attractive study destination for Chinese students, but it may take several years for Chinese student numbers to recover,” said Salvatore Babones, associate professor at the University of Sydney and adjunct scholar at the Centre for Independent Studies. “Students who are already in the middle of a degree are likely to return at the first possible opportunity, even at the cost of missing one semester, but students who have not yet started may make other plans.”
But ANU tertiary education expert Andrew Norton said there remained too many unknowns, including the number of Chinese students stranded abroad, to gauge the impact of the ban.
How the coronavirus spread anti-Chinese racism like a disease through Asia
“This travel ban is a short-term policy to minimise the risk of disease spreading, which would be a more serious problem than a disruption to university timetables,” he said. “One of Australia’s major [education] competitors – the US – has a similar policy, and due to travel restrictions within China and the cancelling of commercial flights to and from China Australia’s competitors are unlikely to be able to take advantage.”
Norton noted that the sector had weathered previous outbreaks such as the 2003 outbreak of severe acute respiratory syndrome (Sars), and “although there were sometimes short-term dips in numbers, none of them have changed the long-term trend towards growth”.
The ban has also sent jitters throughout the tourism industry, which relies on Chinese visitors for a quarter of international spending. Nearly 1.5 million
visited Australia in 2018-19, Australian Bureau of Statistics records show, accounting for about one in eight arrivals.
Nearly 1.5 million Chinese nationals visited Australia in 2018-19, according to Australian Bureau of Statistics records. Photo: SCMP / Alkira Reinfrank
With Chinese tourists spending about A$12 billion (US$8 billion) in Australia each year, according to Tourism Research Australia, every month the travel ban remains in place could amount to billion-dollar losses for the sector.
Tourism Tropical North Queensland on Monday said the outbreak had already cost operators for Cairns and the Great Barrier Reef 25,000 direct bookings worth A$10 million. Chief executive Mark Olsen said the situation constituted a crisis for the industry that called for “unprecedented action” by the government.
David Beirman, senior lecturer in tourism at the University of Technology Sydney, said the ban was especially damaging for the industry as it came on the heels of devastating bush fires that had kept visitors away.
Coronavirus: how Facebook clickbait fuels a perfect storm of fake news
“There is no doubt that the coronavirus outbreak following on so closely to the bush fires will combine to hit international tourism to Australia very hard,” Beirman said. “Later this month the Australian Bureau of Statistics will reveal the December 2019 tourism figures, which are expected to show at best a 25 per cent downturn in international visitor arrivals compared to December 2018. January 2020 is likely to be far worse as the impact of coronavirus will certainly be a factor.”
Others have raised concerns about the impact of the travel restrictions on public attitudes toward Chinese and Chinese-Australians, warning they could stoke latent prejudices.
“This is an overreaction from the Australian government, and in many ways it feels like it is a form of racial targeting,” said Erin Chew, national convenor of the Asian Australian Alliance. “When previous viruses happened such as mad cow disease or the swine flu, Australia didn’t ban non-citizens from Britain and the US. Nor was the blame placed on the people in [those countries].
“Since the coronavirus outbreak it has been coined that this virus is the fault of Chinese people, not just in mainland China, but really all over the world.”
Source:, SCMP
Posted in Academic year, Asian Australian Alliance, Australia, Australia’s, Australian Bureau of Statistics, Australian National University (ANU), ‘We’re like cash cows’, Britain, bush fires crisis,, Chinese, Chinese Australians, coronavirus, enrol, immediate family members, Jiangsu, Lunar New Year holiday, mainland, Mainland China, Monash University, non-citizens, permanent residents, Philippines, Prime minister, Scott Morrison, Shanghai, Singapore, stranded, students, Students’ Representative Council, Tourism Research Australia, tourism sector, Tourism Tropical North Queensland, travel ban, Uncategorized, United States, university, University of Sydney, University of Technology Sydney, upset, US, WeChat, Wuhan |
Leave a Comment »
15/09/2019
A waiter serves a dish named “sweet soup balls”, in the shape of riverstones, at the “Huaiyang Cuisine Week” in The Hague, the Netherlands, Sept. 13, 2019. A series of events including a tourism seminar, a photo exhibition and a Huaiyang Cuisine Week activity were held during the Jiangsu Cultural and Tourism Carnival. The carnival, held from Sept. 7 to 19 in the Netherlands, aims to encourage more foreign tourists to visit China’s eastern coastal province of Jiangsu. (Xinhua/Lin Liping)
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Cultural and Tourism Carnival, dish, foreign tourists, Huaiyang Cuisine Week, Jiangsu, jiangsu province, photo exhibition, riverstones, sweet soup balls, The Hague, the Netherlands, tourism seminar, Uncategorized, visit, waiter |
Leave a Comment »
15/09/2019
- Facial recognition technology helped officers narrow down search to building in Nantong, but they were unable to tell which room suspect was in
- Police went door-to-door hunting for the smell of hotpot after fugitive was spotted buying ingredients at market
Eating hotpot can be a hot and sweaty business. Photo: Shutterstock
China’s facial recognition technology is now so advanced that it can positively identify 98.1 per cent of human faces and within 0.8 seconds, according to China Daily.
But the latest case of unconventional detective work comes from the eastern province of Jiangsu, where local police used their faces, not their target’s, to locate their man – specifically their noses. Call it olfactory recognition.
Jiangsu police had been looking for a man named Guo Bing, who was suspected of gang crimes, fraud and extortion and had been on the run in the city of Nantong since police there cracked down on gang-related activity in late May, local media reported on Tuesday.
Police used facial recognition to figure out which Nantong building Guo was living in, but they did not know which flat.
So they put in 24-hour camera surveillance and spotted Guo going to a local market on Saturday afternoon and buying ingredients for hotpot.
“We saw him buying vegetables and hotpot soup base at a market one afternoon,” Ge said, “so we guessed he was going to have hotpot that day.”
Police narrowed down the search to the seventh floor of the building, then started sniffing at each door. When they registered the unmistakable aroma of hotpot, they knew they had their man.
Television footage of the bust showed police descending on the surprised and shirtless man – eating hotpot is a messy and sweaty business – and being hauled away.
Source: SCMP
Posted in case, China Daily, chinese police, detective work, extortion, facial recognition technology, fraud, Fugitive, gang crimes, hotpot, ingredients, Jiangsu, Jiangsu police, literally, market, Nantong, olfactory recognition, smell, sniff out, telltale hotpot, Uncategorized, unconventional |
Leave a Comment »
10/09/2019
- Suspects rounded up after people complain of being duped into making donations to support non-existent temples
- One woman says she handed over US$4,600 after being told that charitable gesture would help her live to be 400
One victim of the alleged scams said she was told she could live for 400 years if she handed over her money. Photo: Thepaper.cn
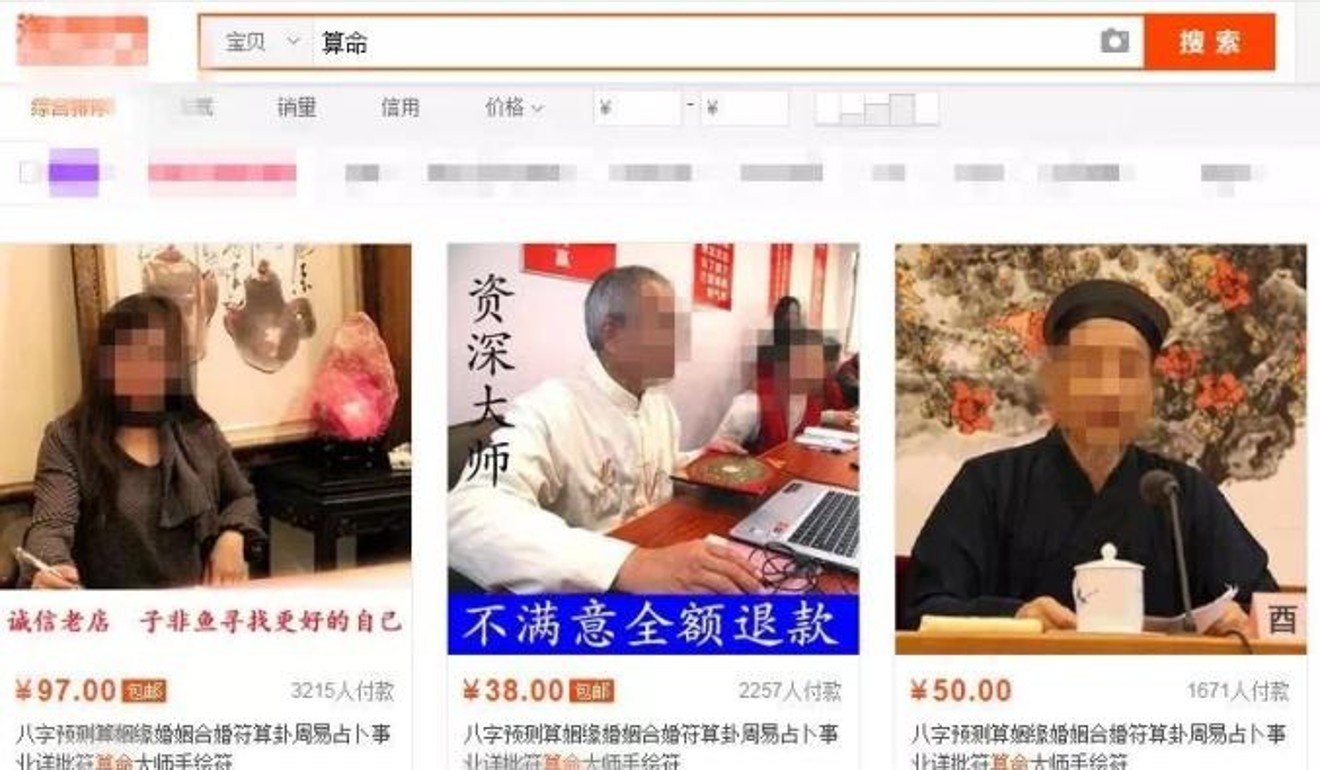
Police in southeast China have detained 100 people on suspicion of being part of a criminal network that cheated members of the public out of 50 million yuan (US$7 million) by preying on their superstitions and generosity.
Authorities in Ningguo, Anhui province launched an investigation in May after receiving a number of complaints about the activities of several groups posing as fortune-tellers on social media platforms like Weibo, financial news outlet Caijing reported on its website on Tuesday.
One of the groups, which operated on the Twitter-like service under the name “Kanxiang Zen Master”, was run by a local man surnamed Zhang and had 12 million followers, the report said.
Adverts for online fortune-telling services are common in China. Photo: Thepaper.cn
In one alleged scam, members of the group were told they would receive good luck if they made a donation to support a “famous temple”. But when a man who gifted 10,000 yuan via WeChat Pay checked on the address of the recipient, he found it was a residential address in the city of Xuancheng and not a place of worship, the report said.
When police investigated, they found Zhang had links to seven criminal groups in Anhui and neighbouring Jiangsu province, which between them operated about 60 fortune-telling accounts on Weibo, several of which had more than 10 million followers. The Kanxiang Zen Master account has since been removed from the platform.
Six Chinese wanted for internet scam arrested in Vanuatu
A number of the gangs were registered as media companies and operated as semi-professional organisations with formal recruiting procedures and regular conferences to plan their fraudulent activities, the report said, adding that they had been operating for at least two years.
Police in July staged a series of raids to round up the suspects and confiscated associated equipment, including computers, vehicles and mobile phones, the report said.
Authorities in Ningguo have appealed for more victims to come forward.
A separate report by Shanghai-based news outlet Thepaper.cn said that some of the suspects also used e-commerce sites such as Taobao and the messaging service WeChat to promote their fortune-telling services.
Taobao is owned by Alibaba Group, which also owns the South China Morning Post.
In one case, a woman from the city of Changshu in Jiangsu said she made multiple payments – totalling about 33,000 yuan – to a fortune-teller she met on WeChat who said the money would be used to buy incense for use in offerings to the gods.
She said she reported the alleged fraud after starting to doubt the fortune-teller’s claims, including one that said if she made the donations she could live for up to 400 years.
Alibaba, Weibo and Tencent, which owns WeChat, have been contacted for comment.
Posted in Adverts, Alibaba Group, Anhui, authorities, Caijing, Changshu, chinese police, complain, detain, duped, e-commerce sites, famous temple, financial news outlet, fortune-tellers, fortune-telling, generosity, gods, incense, Jiangsu, jiangsu province, Kanxiang Zen Master, making donations, messaging service, Ningguo, non-existent temples, offerings, place of worship, promote, residential address, scam, Services, Shanghai-based news outlet, social media platforms, south china morning post, superstitions, Taobao, TENCENT, Thepaper.cn, Uncategorized, Vanuatu, website, WeChat, WeChat Pay, Weibo, Xuancheng, Zhang |
Leave a Comment »
05/07/2019
- Riot police deployed after week of unrest over proposed plant next to residential areas – echoing recent years’ protests against incinerators elsewhere in the country
- District government urges people to ignore rumours and says plant’s location has yet to be finalised
People in Yangluo protest against the proposed incineration plant on Thursday night. Photo: Handout
Thousands of people took to the streets in central China on Thursday night in a seventh day of protests against the construction of a waste incineration plant.
Protesters carried banners and chanted as they marched against a waste-to-energy plant that could be built next to residential areas in Yangluo, near Wuhan, the capital of Hubei province.
Residents were angered by plans to build the plant on a garbage landfill site that had been expected to be turned into a public park.
They shouted slogans such as “Return us the green mountain and clear waters” and “Garbage burning plant get lost from Yangluo”.
Riot police move in as protests continue in Yangluo on Thursday. Photo: Handout
A letter to the public by the Xinzhou district government on Wednesday had urged people “not to listen to or spread rumours”, and said that a location had yet to be finalised for the plant.
“What is rumoured online to be the garbage burning project that has already started is in fact demolition work for a railway construction project,” the letter said.
Converting waste to energy by burning it has been adopted in China as an alternative to burying rubbish in landfill sites – which causes pollution and requires a lot of land – but it has been widely resisted because of fears that it is a health hazard. Large protests against incinerators have been held in recent years in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Hubei, Beijing and Guangdong.
“We understand the need to dispose of garbage in an environmentally friendly way, but does it have to be that close to our homes? Two universities and more than 10 residential areas are within a 3km (1.86 miles) radius,” said the man, referring to the Wuhan University of Bioengineering and Wuhan Engineering Institute.
Yangluo, designated as an economic and technology development area, is 30km northeast of downtown Wuhan and has a population of 300,000. The incineration plant would handle 2,000 tonnes of waste per day, the Wuhan urban management committee said last month.
Residents asked about the progress of the project in early June and were told that the authorities were still choosing a site.
Protests broke out last Friday after rumours spread that the project had already started – forcing the district government to say on Saturday that it would “not start without approval from the public”.
Nonetheless, thousands of protesters – about 10,000, according to one source – marched on Saturday and Sunday, leading to some arrests, although those detained at the weekend had since been released, protesters said.
After minor protests on Monday and Tuesday, residents gathered in greater numbers in Yangluo on Wednesday and Thursday nights, met by a heavy police presence.
Videos seen by the South China Morning Post show hundreds of riot police marching through the streets, equipped with helmets, shields and batons
The crowd dispersed at about 10pm as police began to round up some protesters. They were taken aboard a coach and two men were handled roughly, the videos showed.
Chinese town residents clash with riot police over incinerator
An official from the Xinzhou district government’s publicity department stressed to the Post that the project would not begin without public approval and its location had not yet been chosen.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Beijing, economic and technology development area, garbage landfill site, Guangdong, Hubei, hubei province, Jiangsu, public park, south china morning post, Thousands protest, Uncategorized, waste incineration plant, Wuhan, Wuhan Engineering Institute, Wuhan University of Bioengineering, Xinzhou, Yangluo, Zhejiang |
Leave a Comment »
25/02/2019
BEIJING, Feb. 24 (Xinhua) — China’s national observatory on Sunday forecast that some northern and eastern parts of the country would be shrouded in smog in the coming days while snow will hit western regions.
Thick smog will envelop northern and eastern areas including Hebei and Shandong provinces until Thursday, according to the National Meteorological Center (NMC).
From Sunday night to Monday morning, thick fog will be seen in the provinces of Henan, Anhui, Jiangsu, Shanghai and Hubei, reducing visibility in some areas to less than 200 meters, the NMC said.
From Sunday night to Tuesday, snow will hit west China’s Tibet, Qinghai and Gansu, while rain will soak the south from Tuesday to Wednesday.
Bad weather could disrupt traffic after the Spring Festival holiday when many people are returning to work after the break.
China’s Spring Festival travel rush started from Jan. 21 and will last till March 1.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Anhui, China alert, Gansu, Hebei, Henan, Hubei, Jiangsu, National Meteorological Center (NMC), national observatory, Qinghai, shandong province, Shanghai, Smog, snow, Spring Festival, Tibet, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
22/02/2019
- Firms in Jiangsu and Guangdong provinces top the list of new additions to blacklist in 2018
- Bogus advertising, illegal activities in property industry, substandard health care products and P2P lending fraud are typical cases
A real property agent checks a property advertising board in Beijing. According to a report by the Chinese government, property brokerages are among the country’s least scrupulous group of firms. Photo: Agence France-Presse
China’s wealthiest regions also have the largest number of untrustworthy businesses, according to the government’s social credit system, which rates citizens and companies based on their behaviour.
Jiangsu, the country’s second largest provincial economy – 9.26 trillion yuan (US$1.37 trillion) – accounted for 16.7 per cent of the discredited businesses that were added to the national blacklist last year, more than any other region.
According to a report compiled by the National Public Credit Information Centre that is backed by China’s state planner, the National Development and Reform Commission, Guangdong is next in line.
Guangdong is China’s most prosperous province, Guangdong, but is also home to 12.77 per cent of the total 3.59 million blacklisted firms. The southern province had a gross domestic product of 9.73 trillion yuan last year.
In third spot was Zhejiang, the prosperous province just south of Shanghai, while the capital city of Beijing was ranked fifth. These places together contributed slightly more than 30 per cent of China’s gross domestic product (GDP) last year.
By naming and shaming the millions of Chinese businesses and individuals on the annual blacklist, Beijing hopes to boost “trustworthiness” in Chinese society. Under the system, each of its 1.4 billion citizens is expected to receive a personal trustworthiness score.
“In more developed coastal provinces, businesses have long operated in the grey area between emerging China and established Hong Kong,” said Brock Silvers, managing director of Kaiyuan Capital, a Shanghai-based financial advisory firm.
Silvers said the situation evoked the Chinese saying: “Heaven is high and the Emperor is far away”, which alludes to local officials’ tendency to disregard central government’s directives.
While it was previously not such a faux pas to engage in “untrustworthy” behaviour in attaining economic development, things are now different.
China’s social credit system shows its teeth, banning millions from taking flights, trains
“The ability to cut corners in search of profit isn’t as prized in China’s modern economy, and many of those old traits can now lead companies to be added to Beijing’s blacklist,” Silvers said.
Among the firms named in the hall of shame is Chuangyue Energy Group, from northwest Xinjiang, which topped the list of new cases involving at least 500 million yuan in fraudulent activity.
Chuangyue and its legal representative Qin Yong were reprimanded by the Shenzhen Stock Exchange in 2016 for failing to disclose transactions on time. The transaction involved changes to the shareholding structure of a listed firm in which Chuangyue held interest in, state media reported.
Also on the list was property developer Zhonghong Holding, which was delisted from the Shenzhen exchange late-last year after its shares fell below the par value of 1 yuan for 20 consecutive days.
Zhonghong had posted massive losses, failed to repay loans and halted development projects during 2018.
A typical area of fraud cited in the report was bogus advertising, with the biggest number of discredited companies located Shanghai, China’s most commercial city.
Property brokerage was a hotbed industry for fraudsters. The report named and shamed two agents in Wuhan, An Yi Real Estate Brokerage and Hong Run De Real Estate Brokerage, which Chinese netizens described as “black brokers”.
In one case, Hong Run De subdivided one flat to lease without the owner’s knowledge and consent. To terminate the contract, the owner had to pay “compensation” of 30,000 yuan before they could reclaim the flat.
Other dodgy sectors were health care product makers and peer-to-peer (P2P) lending platforms.
Quanjian Group, a maker of herbal medicines, was accused of making false marketing claims about the benefits of a product that a four-year-old cancer patient drank.
Health care companies are among the worst performing in China, according to a report on the country’s social credit index. Photo: Agence France-Presse
Share:
Changsheng Bio-Technology, the major Chinese manufacturer of rabies vaccines, was fined US$1.3 billion in October after it was found to have fabricated records.
A total of 1,282 P2P operators, more than half located in Zhejiang, Guangdong and Shanghai, were placed on the blacklist because they could not repay investors, or were involved in illegal fundraising.
While more individuals and companies were added to the blacklist, others were also removed – 2.17 million. Those removed had paid taxes owed or fines imposed.
Source: SCMP
Posted in An Yi Real Estate Brokerage, Beijing, black broker, Brock Silvers, cancer patient, Changsheng Bio-Technology, China alert, Chinese manufacturer, Chuangyue Energy Group, dodgy firms, faux pas, Guangdong, Heaven is high and the Emperor is far away, herbal medicines, Hong Run De Real Estate Brokerage, Jiangsu, Kaiyuan Capital, National Public Credit Information Centre, netizens, Qin Yong, Quanjian Group, rabies vaccines, richest provinces, Shanghai, Shenzhen, social credit system, Stock exchange, Uncategorized, Wuhan, Xinjiang, Zhejiang, Zhonghong Holding |
Leave a Comment »