Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
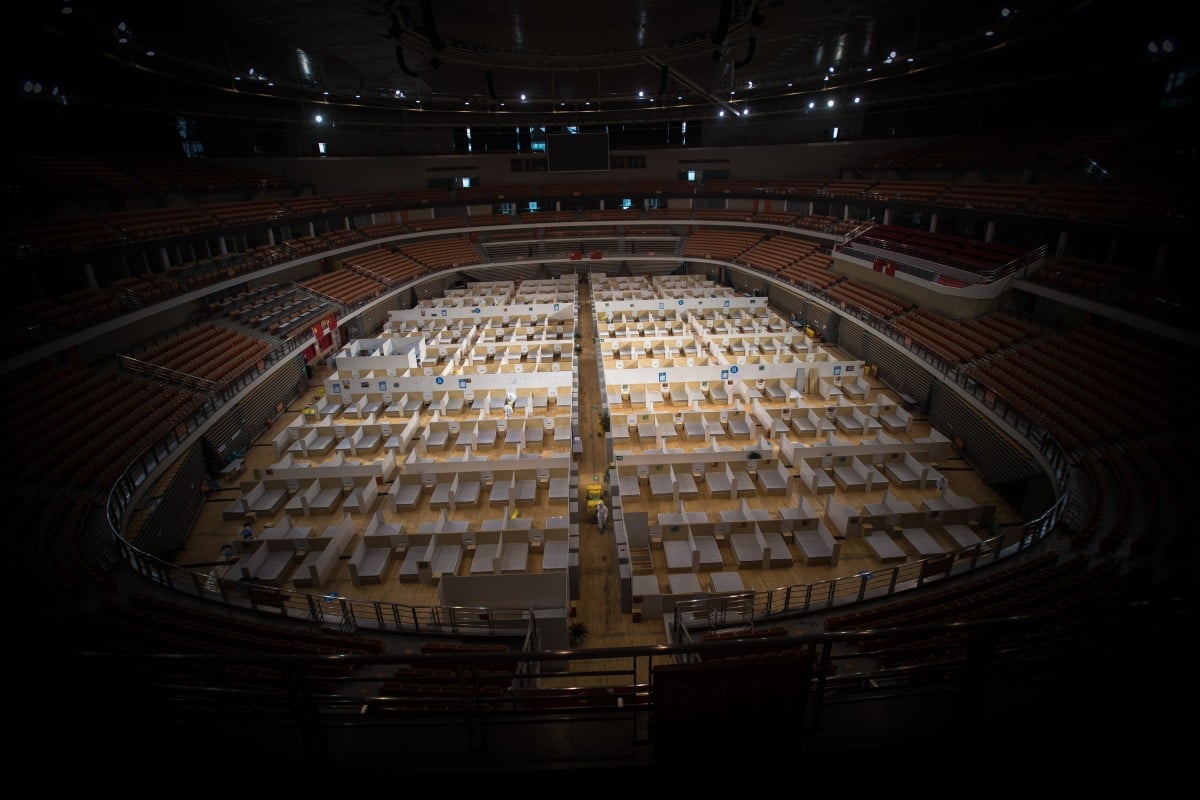
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESThe Chinese city of Wuhan, where the coronavirus originated last year, has raised its official Covid-19 death toll by 50%, adding 1,290 fatalities.
Wuhan officials attributed the new figure to updated reporting and deaths outside hospitals. China has insisted there was no cover-up.
It has been accused of downplaying the severity of its virus outbreak.
Wuhan’s 11 million residents spent months in strict lockdown conditions, which have only recently been eased.
The latest official figures bring the death toll in the city in China’s central Hubei province to 3,869, increasing the national total to more than 4,600.
China has confirmed nearly 84,000 coronavirus infections, the seventh-highest globally, according to Johns Hopkins University data.
The virus has had a huge impact on the Chinese economy, which shrank for the first time in decades in the first quarter of the year.
What’s China’s explanation for the rise in deaths?
In a statement released on Friday, officials in Wuhan said the revised figures were the result of new data received from multiple sources, including records kept by funeral homes and prisons.
Deaths linked to the virus outside hospitals, such as people who died at home, had not previously been recorded.

The “statistical verification” followed efforts by authorities to “ensure that information on the city’s Covid-19 epidemic is open, transparent and the data [is] accurate”, the statement said.
It added that health systems were initially overwhelmed and cases were “mistakenly reported” – in some instances counted more than once and in others missed entirely.
A shortage of testing capacity in the early stages meant that many infected patients were not accounted for, it said.
A spokesman for China’s National Health Commission, Mi Feng, said the new death count came from a “comprehensive review” of epidemic data.
In its daily news conference, the foreign ministry said accusations of a cover-up, which have been made most stridently on the world stage by US President Donald Trump, were unsubstantiated. “We’ll never allow any concealment,” a spokesman said.
Why are there concerns over China’s figures?
Friday’s revised figures come amid growing international concern that deaths in China have been under-reported. Questions have also been raised about Beijing’s handling of the epidemic, particularly in its early stages.
In December 2019, Chinese authorities launched an investigation into a mysterious viral pneumonia after cases began circulating in Wuhan.

- A SIMPLE GUIDE: How do I protect myself?
- AVOIDING CONTACT: The rules on self-isolation and exercise
- HOPE AND LOSS: Your coronavirus stories
- VIDEO: The 20-second hand wash
- STRESS: How to look after your mental health

China reported the cases to the World Health Organization (WHO), the UN’s global health agency, on 31 December.
But WHO experts were only allowed to visit China and investigate the outbreak on 10 February, by which time the country had more than 40,000 cases.
The mayor of Wuhan has previously admitted there was a lack of action between the start of January – when about 100 cases had been confirmed – and 23 January, when city-wide restrictions were enacted.
Around that time, a doctor who tried to warn his colleagues about an outbreak of a Sars-like virus was silenced by the authorities. Dr Li Wenliang later died from Covid-19.

Wuhan’s death toll increase of almost exactly 50% has left some analysts wondering if this is all a bit too neat.
For months questions have been asked about the veracity of China’s official coronavirus statistics.
The inference has been that some Chinese officials may have deliberately under-reported deaths and infections to give the impression that cities and towns were successfully managing the emergency.
If that was the case, Chinese officials were not to know just how bad this crisis would get in other countries, making its own figures now seem implausibly small.
The authorities in Wuhan, where the first cluster of this disease was reported, said there had been no deliberate misrepresentation of data, rather that a stabilisation in the emergency had allowed them time to revisit the reported cases and to add any previously missed.
That the new death toll was released at the same time as a press conference announcing a total collapse in China’s economic growth figures has led some to wonder whether this was a deliberate attempt to bury one or other of these stories.
Then again, it could also be a complete coincidence.
China has been pushing back against US suggestions that the coronavirus came from a laboratory studying infectious diseases in Wuhan, the BBC’s Barbara Plett Usher in Washington DC reports.
US President Donald Trump and some of his officials have been flirting with the outlier theory in the midst of a propaganda war with China over the origin and handling of the pandemic, our correspondent says.
Mr Trump this week halted funding for the World Health Organization (WHO), accusing it of making deadly mistakes and overly trusting China.
“Do you really believe those numbers in this vast country called China, and that they have a certain number of cases and a certain number of deaths; does anybody really believe that?” Mr Trump said at the White House on Wednesday.
French President Emmanuel Macron has also questioned China’s handling of the coronavirus outbreak, saying it was “naive” to suggest the country had dealt better with the crisis, adding things “happened that we don’t know about”.
On Thursday, UK Foreign Secretary Dominic Raab said: “We’ll have to ask the hard questions about how [coronavirus] came about and how it couldn’t have been stopped earlier.”
But China has also been praised for its handling of the crisis and the unprecedented restrictions that it instituted to slow the spread of the virus.
WHO Director General Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus has hailed China for the “speed with which [it] detected the outbreak” and its “commitment to transparency”.
Source: The BBC