06/09/2019
- Material that generates heat from sunlight could provide self-maintaining water supply on remote islands
An international research team used solar power to generate a supply of drinking water. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences
A Chinese-led international research team has created a “tree” that can generate clean drinking water.
Drawing its energy entirely from the sun just like a real tree, the “water tree” has a root made of cotton fabric that can absorb water from its surroundings, such as from sand on a beach.
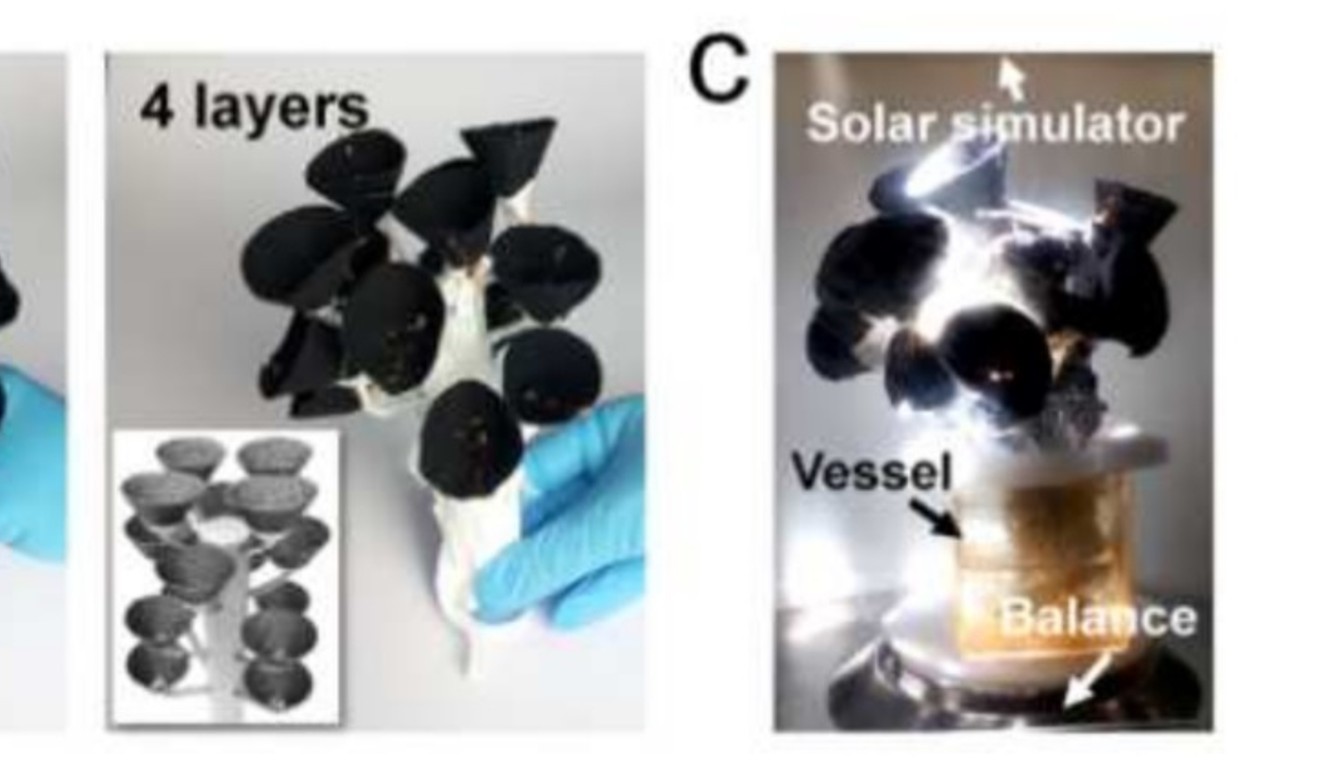
After water moves up the stem, it is vaporised by “leaves” made of black-carbon paper cones that convert light energy to heat, reaching nearly 50 degrees Celsius (122 Fahrenheit). The tree sits in a glass chamber with a relatively cool surface that collects the vapour.
Using standard cotton fabric and a new nanomaterial that can be cheaply mass-produced from charcoal, a paper cone with a surface area as large as 1 square metre would cost only US$2, according to the researchers.
The cones, which function like leaves, could be mass-produced cheaply, researchers say. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences
A cone that size can generate up to 3.4kg (7.5lbs) of condensed water per hour, faster than any other solar-powered desalination methods previously reported.
Even on a cloudy day, the total output in seven hours of sunlight can reach 5.4kg, or three times the amount the typical adult needs to stay hydrated.
One tree can have multiple layers of branches, each with several cones to increase the vapour-producing surface area.
The study, published this month in the journal Nano Energy, was led by Professor Chen Tao at the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering in Zhejiang province, and also involved researchers from Singapore and Taiwan.
World’s thirst for fresh water is causing a big toxic problem
One of the paper’s co-authors, Dr Ouyang Jianyong, associate professor at the National University of Singapore’s department of materials science and engineering, told the South China Morning Post that the technology could be applied in remote places such as on islands in the South China Sea.
“It is particularly useful for isles far away without a stable drinking water supply,” Ouyang said. “These ‘trees’ may not be able to quench the thirst of a large city, but they can meet the critical demand of a small community, especially in emergencies.
“We are already in contact with some companies [to commercialise the technology],” he added.
The material used to make the cone has several advantages, according to Ouyang. The cones can absorb a wide spectrum of sunlight, maximising the amount of energy they can collect, and their porous structure allows them to release vapour quickly.
Lawmakers endorse plan for HK$7.7 billion desalination plant
When used to desalinate a supply of seawater, the trees would be self-cleaning at night, by water washing away salt residue without being vaporised as it would during sunlight hours.
The vapour-producing fabric is as thin and lightweight as a few sheets of paper. It can be folded and sewn into almost any shape, or cleaned in a washing machine, and can operate effectively for several years in a harsh environment, the researchers say.
The condensed water meets stringent safety standards for direct drinking set by the World Health Organisation, according to the researchers.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Chinese Academy of Sciences, cleaned, department of materials science and engineering, desalinate, desalination plant, Drinking water, lawmakers, Nano Energy, National University of Singapore, night, Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering, paper, remote islands, sea, Seawater, self-cleaning, self-maintaining water supply, sewn, shape, sheets, Singapore, solar-powered ‘tree’, solar-powered desalination methods, south china morning post, South China Sea, Taiwan, turns, Uncategorized, vapour-producing fabric, washing machine, World Health Organisation, zhejiang province |
Leave a Comment »
26/08/2019
- Associate professor caused ‘vicious social impact’ in comments to student in social media chat room
- Ethics committee suspends him from teaching for two years
The four great inventions of ancient China: Paper, gunpowder, the compass and printing. Photo: Alamy
An associate professor has been suspended by his university in southwestern China for causing “vicious social impact” by belittling the four great ancient Chinese inventions of papermaking, printing, gunpowder and the compass.
Zheng Wenfeng was suspended from teaching for 24 months by the University of Electronic Science and Technology of China in Chengdu, Sichuan province, for his comments in June to a student in an online group discussion on Chinese social media platform WeChat.
Zheng told the student, who wanted to choose the four great inventions as a thesis topic on innovation, that “ancient China did not have any substantial innovations” and that the four great inventions were “not advanced in the world and did not generate any productivity or cooperation in reality”.
The four inventions are extolled in China as important contributions to the development of world civilisation.
The student’s boyfriend put a screenshot of the conversation on Zhihu.com, a Quora-style knowledge-sharing website, where it generated wide attention.
First day at university in China now means a face scan to enrol
In July, the university issued a statement saying that Zheng had expressed mistaken opinions in the online chat room which had “caused vicious social impact”. The university went on to say that its teachers’ ethics committee had determined Zheng had violated ethics regulations and he would be suspended from teaching, recruitment of master’s degree candidates, and promotion for the next 24 months.
Academics began speaking out in support of Zheng last week, with some university teachers alleging on social media that Zheng had been ambushed by his students. Others felt his punishment went too far.
Huang Shaoqin, an associate professor of the Antai School of Economics and Management at Shanghai Jiao Tong University, called for a boycott of Zheng’s university in response to his treatment and demanded a public apology from the students involved.
“Until you rectify your wrongdoings, I cannot have any academic communication with you,” Huang said. “I call on teachers at Chinese universities to boycott this university.”
College entrance exam boot camp accused of fake advertising
In an editorial on Saturday, GMW.cn – a news website targeting China’s intelligentsia – defended academic debate, saying people could provide their own evidence on the significance of the four great innovations, and this was how academic issues should be argued.
“Students ignored the basic rules of academic discussions and they exaggerated the teacher’s errors. They released the private chat record to the public, no doubt with an intention of making a fuss,” the editorial said. “Their meticulous thought is really horrible.”
Chinese state broadcaster CCTV addressed the issue in an editorial on Friday, saying schools should distinguish correctly between politics and academic issues, and should not magnify the seriousness of the teacher’s opinions.
“This kind of case involves how freely university teachers can talk and the boundary between academic freedom and political red lines,” it said. “The university should give a clear explanation about its punishment so that the public and the teacher involved will be convinced.”
The Ministry of Education promoted 10 principles for university teachers at the end of last year, with “sticking to correct political direction” at the top of the list.
Zheng said he accepted the university’s punishment and did not need to make any clarification or self-justification, according to online news portal Sohu.com last week.
“I will focus on scientific research. This incident is over, is my attitude,” he was quoted as saying.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Antai School of Economics and Management, Chengdu, compass, four great inventions of ancient China, GMW.cn – a news website, gunpowder, intelligentsia, paper, Printing, punishment, Quora-style knowledge-sharing website, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, sichuan province, Uncategorized, University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, WeChat, world civilisation, Zhihu.com |
Leave a Comment »
08/07/2019
- Settlements along the route linking Europe and Asia thrived by providing accommodation and services for countless traders
- Formally established during the Han dynasty, it was a 19th-century German geographer who coined the term Silk Road
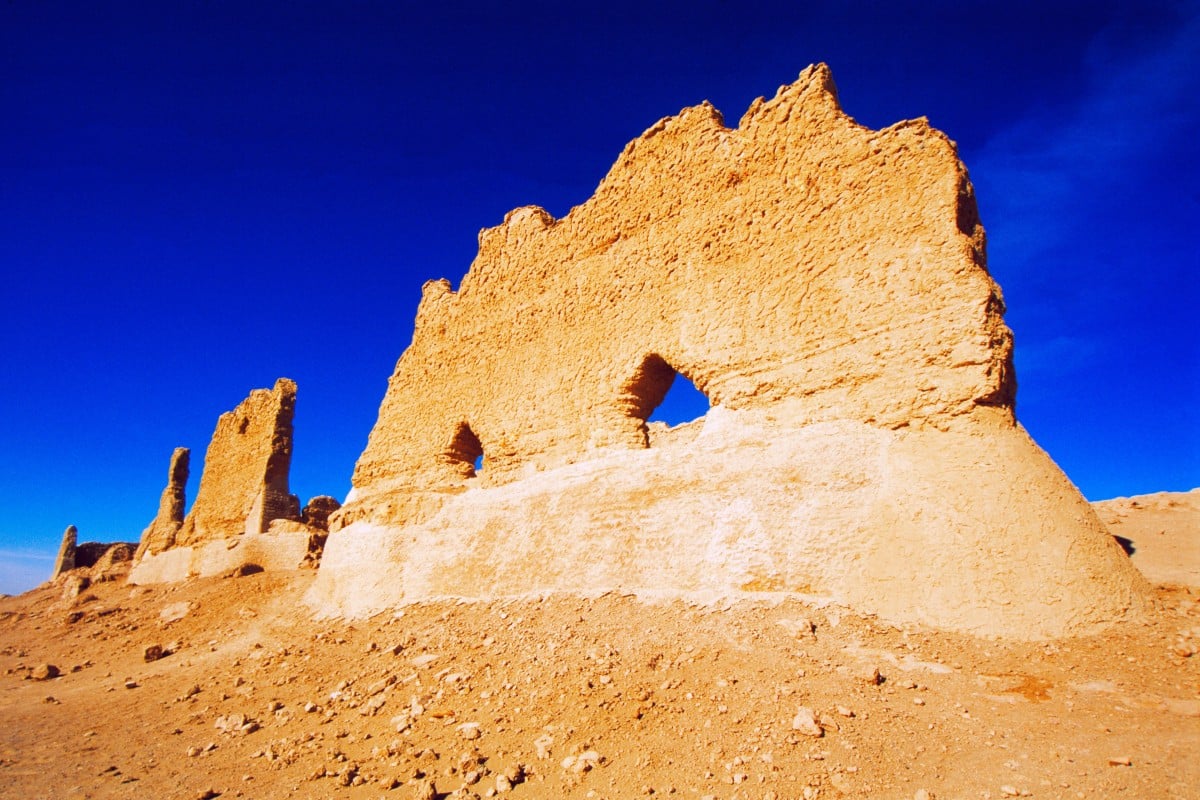
The ruins of a fortified gatehouse and customs post at Yunmenguan Pass, in China’s Gansu province. Photo: Alamy
We have a German geographer, cartographer and explorer to thank for the name of the world’s most famous network of transcontinental trade routes.
Formally established during the Han dynasty, in the first and second centuries BC, it wasn’t until 1877 that Ferdinand von Richthofen coined the term Silk Road (historians increasingly favour the collective term Silk Routes).
The movement of merchandise between China and Europe had been taking place long before the Han arrived on the scene but it was they who employed troops to keep the roads safe from marauding nomads.
Commerce flourished and goods as varied as carpets and camels, glassware and gold, spices and slaves were traded; as were horses, weapons and armour.
Merchants also moved medicines but they were no match for the bubonic plague, which worked its way west along the Silk Road before devastating huge swathes of 14th century Europe.
What follows are some of the countless kingdoms, territories, (modern-day) nations and cities that grew rich on the proceeds of trade, taxes and tolls.
China
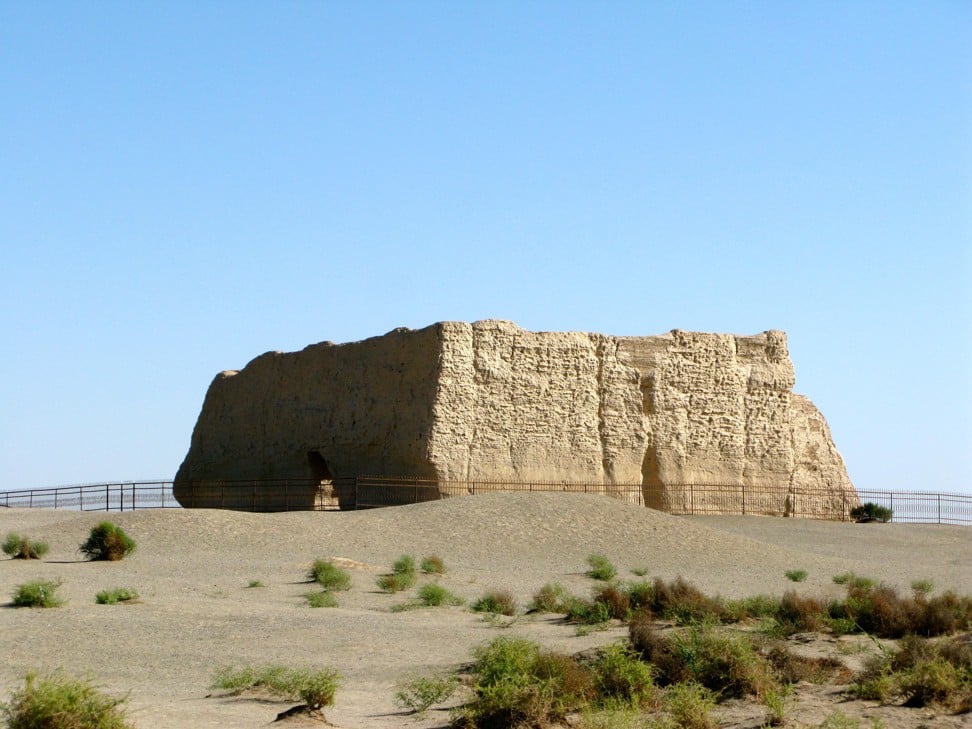
A watchtower made of rammed earth at Dunhuang, a desert outpost at the crossroads of two major Silk Road routes in China’s northwestern Gansu province. Photo: Alamy
Marco Polo worked in the Mongol capital, Khanbaliq (today’s Beijing), and was struck by the level of mercantile activity.
The Venetian gap-year pioneer wrote, “Every day more than a thousand carts loaded with silk enter the city, for a great deal of cloth of gold and silk is woven here.”
Light, easy to transport items such as paper and tea provided Silk Road traders with rich pickings, but it was China’s monopoly on the luxurious shimmering fabric that guaranteed huge profits.
So much so that sneaking silk worms out of the empire was punishable by death.
The desert outpost of Dunhuang found itself at the crossroads of two major Silk Road trade arteries, one leading west through the Pamir Mountains to Central Asia and another south to India.
Built into the Great Wall at nearby Yunmenguan are the ruins of a fortified gatehouse and customs post, which controlled the movement of Silk Road caravans.
Also near Dunhuang, the Mogao Caves contain one of the richest collections of Buddhist art treasures anywhere in the world, a legacy of the route to and from the subcontinent.
Afghanistan
Afghanistan’s mountainous terrain was an inescapable part of the Silk Road, until maritime technologies would become the area’s undoing. Photo: Shutterstock
For merchants and middlemen hauling goods through Central Asia, there was no way of bypassing the mountainous lands we know today as Afghanistan.
Evidence of trade can be traced back to long before the Silk Road – locally mined lapis lazuli stones somehow found their way to ancient Egypt, and into Tutankhamun’s funeral mask, created in 1323BC.
Jagged peaks, rough roads in Tajikistan, roof of the world
Besides mercantile exchange, the caravan routes were responsible for the sharing of ideas and Afghanistan was a major beneficiary. Art, philosophy, language, science, food, architecture and technology were all exchanged, along with commercial goods.
In fact, maritime technology would eventually be the area’s undoing. By the 15th century, it had become cheaper and more convenient to transport cargo by sea – a far from ideal development for a landlocked region.
Iran
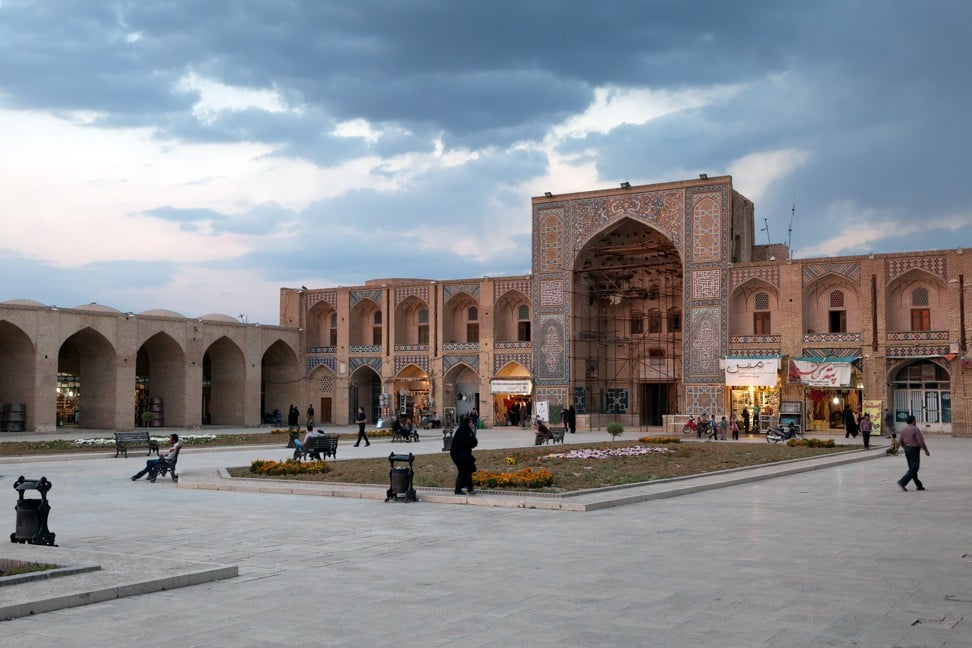
The Ganjali Khan Complex, in Iran. Photo: Shutterstock
Thanks to the Silk Road and the routes that preceded it, the northern Mesopotamian region (present-day Iran) became China’s closest trading partner. Traders rarely journeyed the entire length of the trail, however.
Merchandise was passed along by middlemen who each travelled part of the way and overnighted in caravanserai, fortified inns that provided accommodation, storerooms for goods and space for pack animals.
The good, bad and ugly sides to visiting Chernobyl and Kiev
With so many wheeler-dealers gathering in one place, the hostelries developed into ad hoc marketplaces.
Marco Polo writes of the Persian kingdom of Kerman, where craftsmen made saddles, bridles, spurs and “arms of every kind”.
Today, in the centre of Kerman, the former caravanserai building forms part of the Ganjali Khan Complex, which incorporates a bazaar, bathhouse and mosque.
Uzbekistan
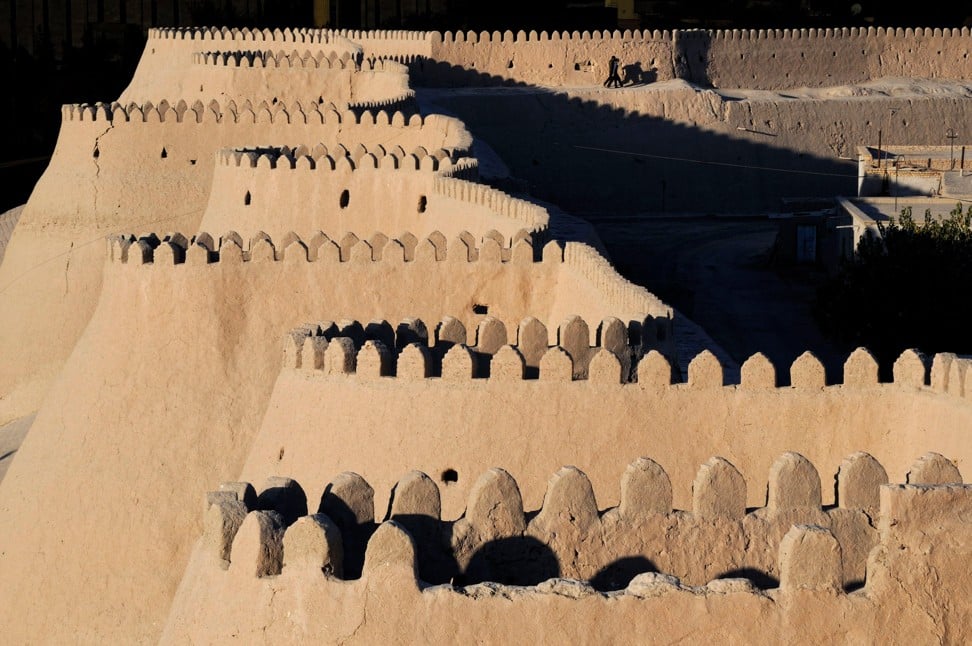
A fort in Khiva, Uzbekistan. Photo: Alamy
The double-landlocked country boasts some of the Silk Road’s most fabled destinations. Forts, such as the one still standing at Khiva, were built to protect traders from bandits; in fact, the city is so well-preserved, it is known as the Museum under the Sky.
The name Samarkand is also deeply entangled with the history of the Silk Road.
The earliest evidence of silk being used outside China can be traced to Bactria, now part of modern Uzbekistan, where four graves from around 1500BC-1200BC contained skeletons wrapped in garments made from the fabric.
Three thousand years later, silk weaving and the production and trade of textiles remain one of Samarkand’s major industries.
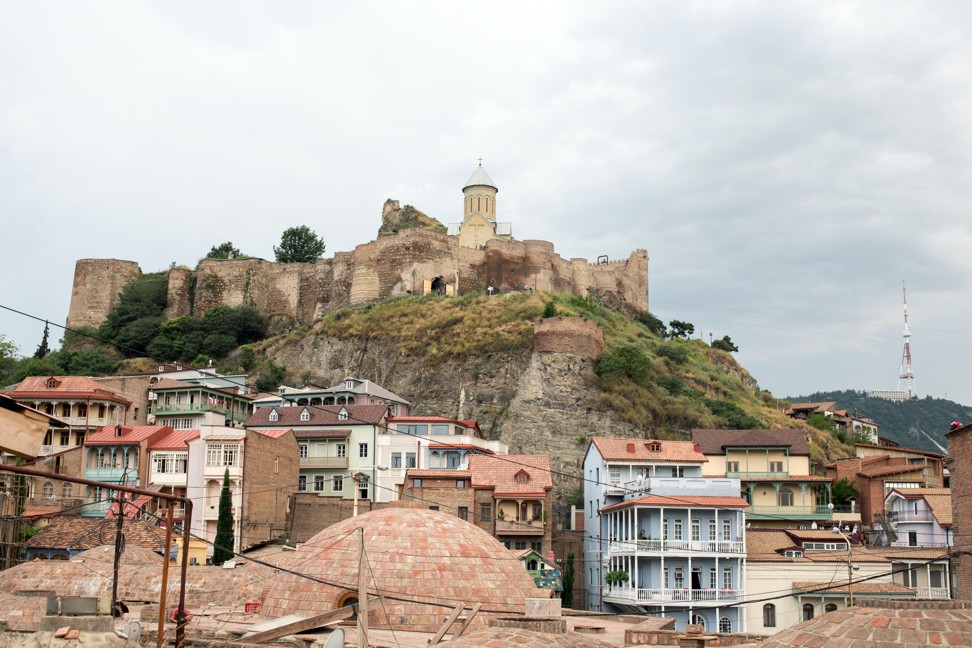
Georgia
A street in old town of Tbilisi, Georgia. Photo: Alamy
Security issues in Persia led to the opening up of another branch of the legendary trade route and the first caravan loaded with silk made its way across Georgia in AD568.
Marco Polo referred to the weaving of raw silk in “a very large and fine city called Tbilisi”.
Today, the capital has shaken off the Soviet shackles and is on the cusp of going viral.
Travellers lap up the city’s monasteries, walled fortresses and 1,000-year-old churches before heading up the Georgian Military Highway to stay in villages nestling in the soaring Caucasus Mountains.
Public minibuses known as marshrutka labour into the foothills and although the vehicles can get cramped and uncomfortable, they beat travelling by camel.
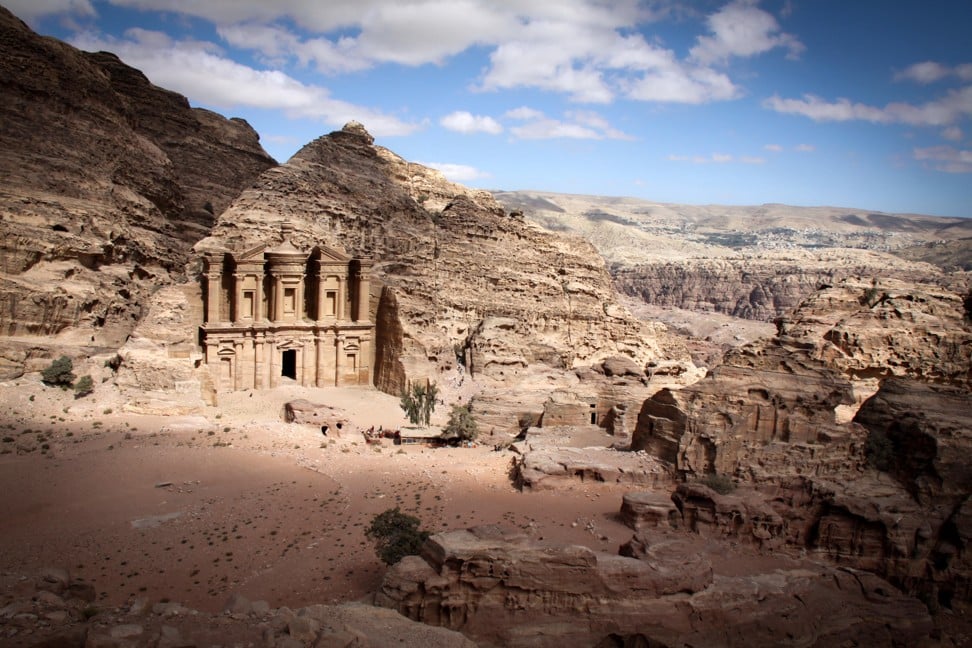
Jordan
Petra, in Jordan. Photo: Alamy
The location of the Nabataean capital, Petra, wasn’t chosen by chance.
Savvy nomadic herders realised the site would make the perfect pit-stop at the confluence of several caravan trails, including a route to the north through Palmyra (in modern-day Syria), the Arabian peninsula to the south and Mediterranean ports to the west.
Huge payments in the form of taxes and protection money were collected – no wonder the most magnificent of the sandstone city’s hand-carved buildings is called the Treasury.
The Red Rose City is still a gold mine – today’s tourists pay a hefty
. The Nabataeans would no doubt approve.
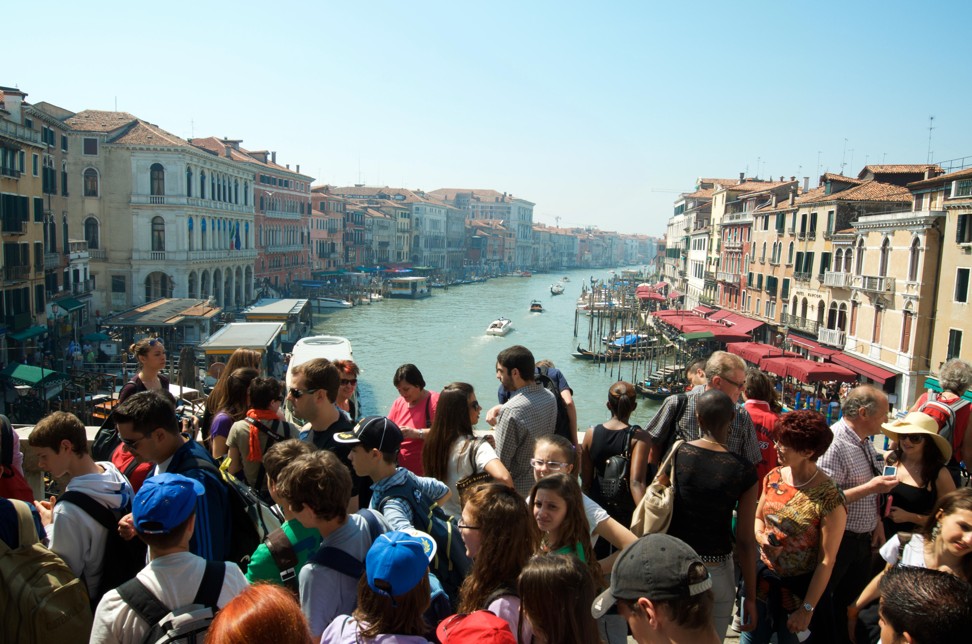
Venice
Tourists crowd onto Venice’s Rialto Bridge. Photo: Alamy
Trade enriched Venice beyond measure, helping shape the Adriatic entrepot into the floating marvel we see today.
Besides the well-documented flow of goods heading west, consignments of cotton, ivory, animal furs, grapevines and other goods passed through the strategically sited port on their way east.
Ironically, for a city built on trade and taxes, the biggest problem Venice faces today is visitors who don’t contribute enough to the local economy.
A lack of spending by millions of day-tripping tourists and cruise passengers who aren’t liable for nightly hotel taxes has prompted authorities to introduce a citywide access fee from January 2020.
Two thousand years ago, tariffs and tolls helped Venice develop and prosper. Now they’re needed to prevent its demise.
Source: SCMP
Posted in accommodation, Adriatic, Afghanistan, architecture, armour, arms, Art, Asia, Bactria, bandits, bathhouse, bazaar, Beijing, bridles, bubonic plague, Buddhist art treasures, camels, caravanserai, caravans, carpets, Caucasus Mountains, Chernobyl, cloth of gold, commercial goods, craftsmen, Death, Dunhuang, Egypt, Europe, exchanged, Ferdinand von Richthofen, floating marvel, Food, fort, from China to Italy, funeral mask, Ganjali Khan Complex, Gansu Province, garments, Georgia, Georgian Military Highway, German geographer, glassware, Gold, goods, Great Wall, grew rich, Han Dynasty, horses, hostelries, iran, Jordan, Kerman, Khanbaliq, Khiva, Kiev, languages, lapis lazuli, Marco Polo, maritime technology, marketplaces, marshrutka, medicines, Merchandise, Mesopotamian region, Mogao Caves, Mongol capital, Mosque, Museum under the Sky, Nabataean capital, pack animals, Palmyra, Pamir Mountains, paper, Persian kingdom, Petra, philosophy, punishable, Red Rose City, Rialto Bridge, saddles, Samarkand, Science, Silk Road, Silk Road destinations, silk worms, skeletons, slaves, sneaking, Space, spices, spurs, storerooms, Syria, Tajikistan, Tbilisi, Tea, Technology, towns, Trade, traders, Tutankhamun, Uncategorized, Uzbekistan, Venetian gap-year pioneer, Venice, weapons, Yunmenguan Pass |
Leave a Comment »