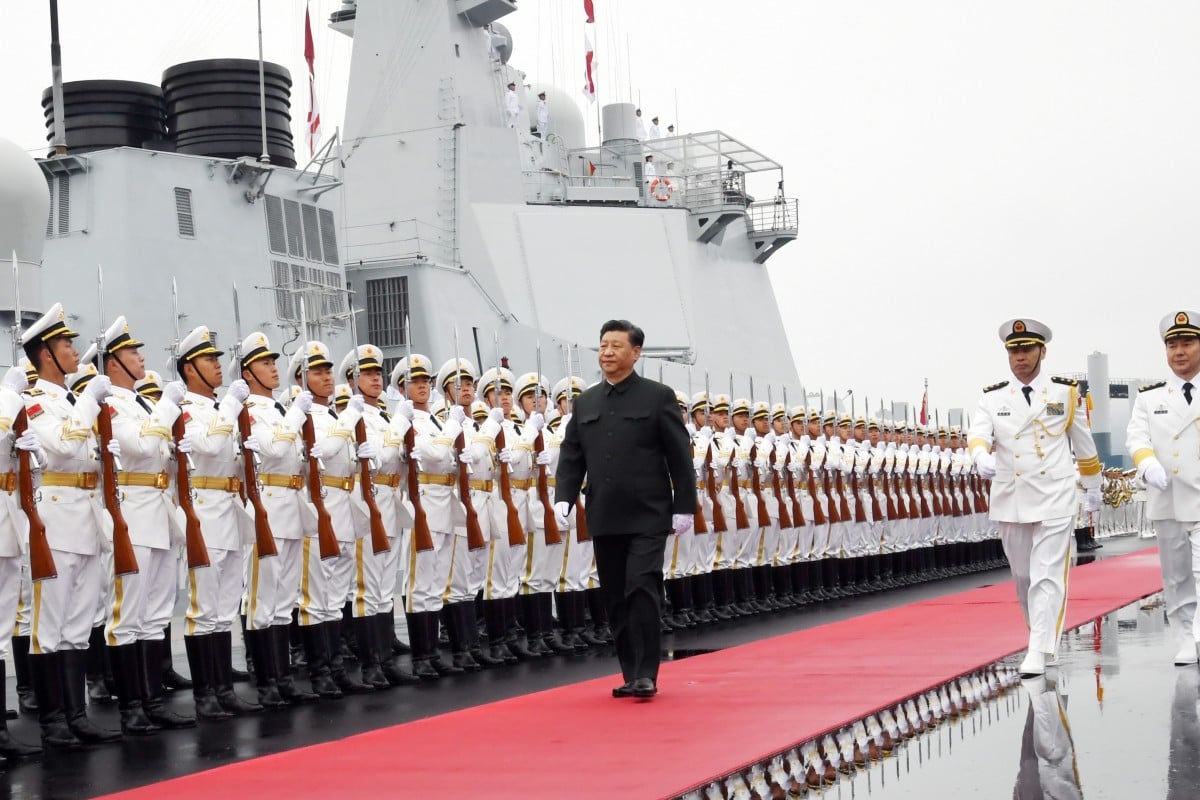
- With a defence budget second only to the US, China is amassing a navy that can circle the globe and developing state-of-the-art autonomous drones
- The build-up is motivating surrounding countries to bolster their own armed forces, even if some big-ticket military equipment is of dubious necessity

– responsible for 64 per cent of military
spending in the region. With a defence budget that is second only to the
, China is amassing a navy that can circle the globe and developing state-of-the-art autonomous drones. The build-up is motivating surrounding countries to bolster their armed forces too – good news for purveyors of submarines, unmanned vehicles and warplanes.
in
, a security conference attended by
chiefs, was sponsored by military contractors including Raytheon,
and
.
Kelvin Wong, a Singapore-based analyst for Jane’s, a trade publication that has been covering the defence industry for 121 years, has developed a niche in infiltrating China’s opaque defence industry by attending obscure trade shows that are rarely advertised outside the country.
and Taiwan Strait. It has lifted a ban on working with
’s special forces over atrocities committed in
. And it is considering restarting arms sales to the
.

has an Achilles’ heel: its own personnel.
That is what Bernard Loo Fook Weng, a military expert at Singapore’s S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies, told the author Robert Kaplan for his 2014 book, Asia’s Cauldron, about simmering tensions in the South China Sea.
He was describing the competition for big-ticket military equipment of dubious necessity.
is littered with examples of such purchases.
owns an aircraft carrier without any aircraft. Indonesia dedicated about one-sixth of its military budget to the purchase of 11
Su-35 fighter jets. And
splurged on two
submarines it could not figure out how to submerge.
“It’s keeping up with the Joneses,” Wong said. “There’s an element of prestige to having these systems.”
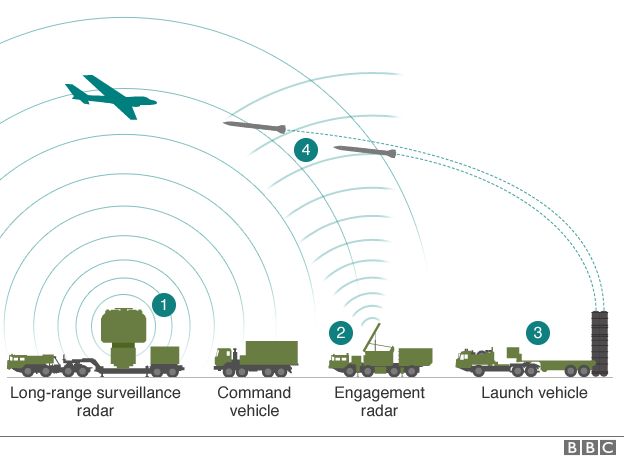
Submarines remain one of the more debatable purchases, Wong said. The vessels aren’t ideal for the South China Sea, with its narrow shipping lanes hemmed in by shallow waters and coral reefs. Yet they provide smaller countries with a powerful deterrence by enabling sneak attacks on large ships.
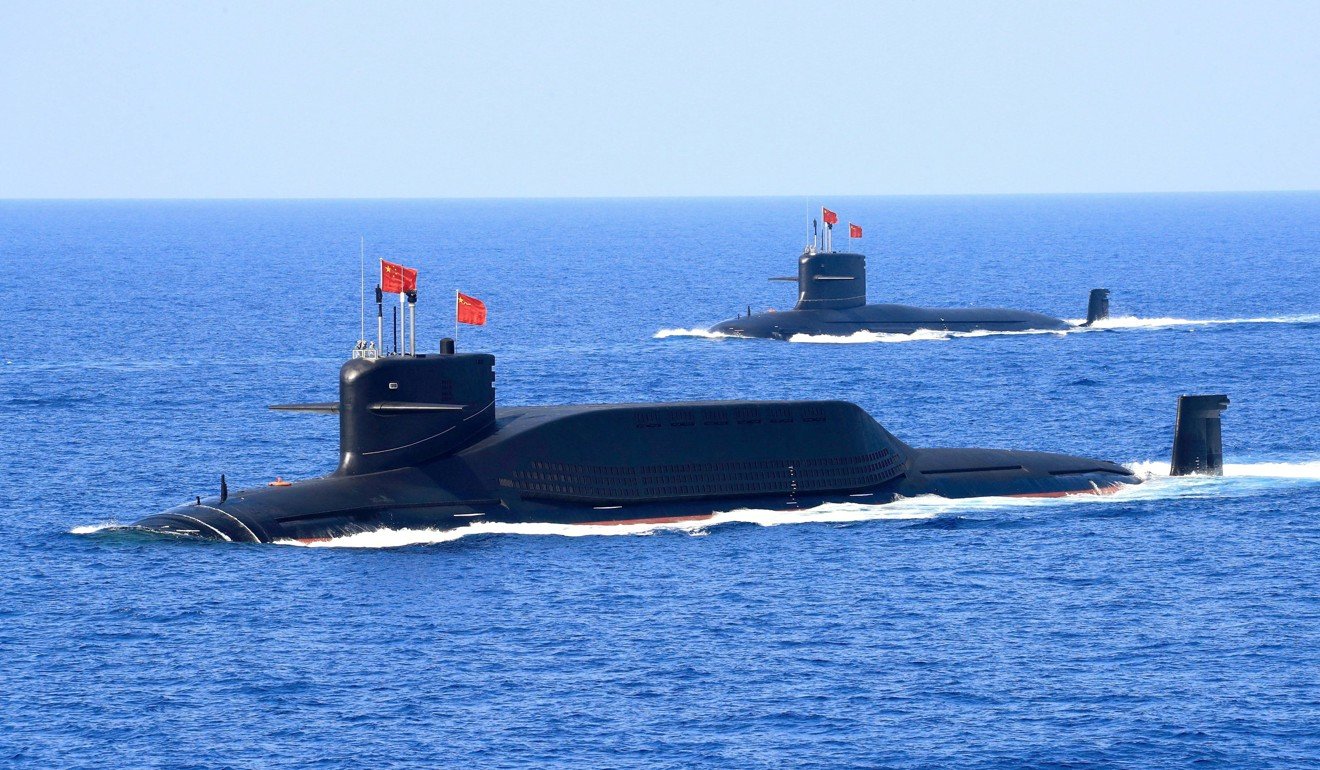

are home to 245 submarines, or 45 per cent of the global fleet, according to the US-based naval market intelligence firm AMI International.
Type 218 submarines with propulsion systems that negate the need to surface more frequently. If the crew did not need to eat, the submarine could stay under water for prolonged periods. Wong said the craft were specially built for Asian crews.
the country dedicates 3.3 per cent of its gross domestic product to defence, a rate higher than that of the United States.
“We always have to punch above our weight,” he said.
Source: SCMP