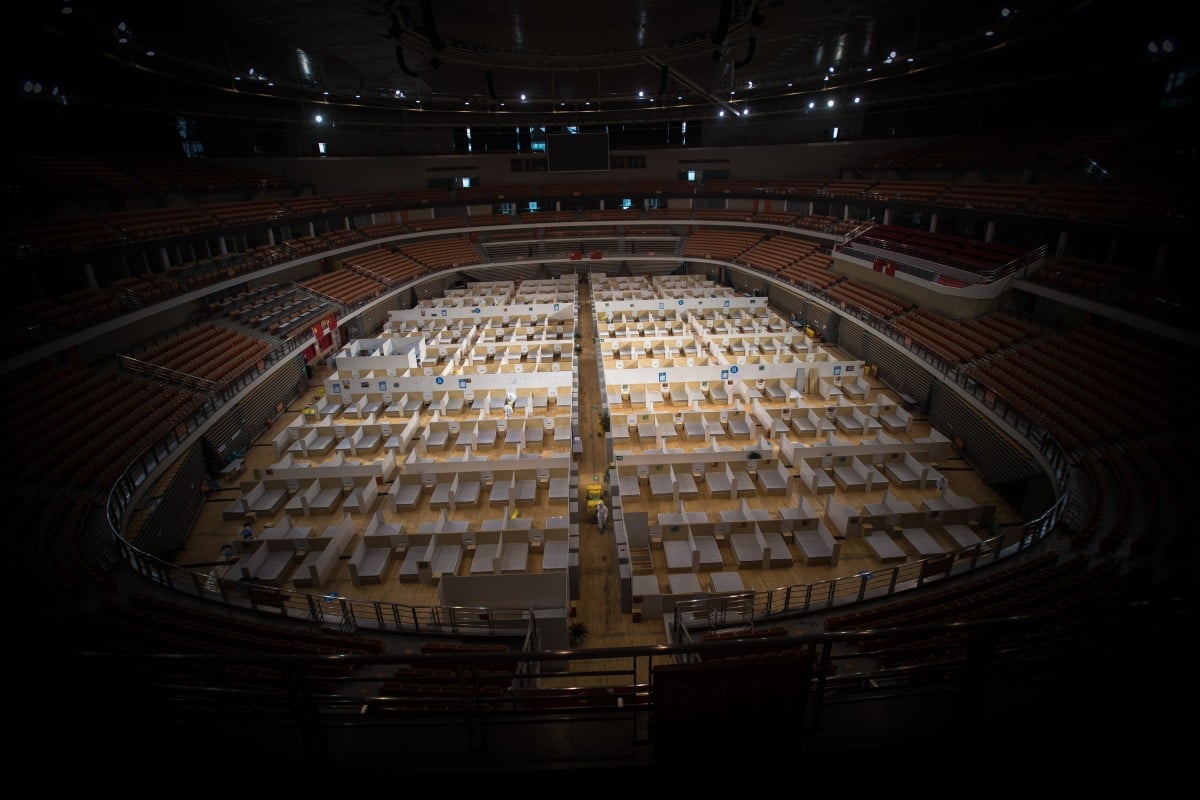
Image copyright EPA
Image copyright EPAThe lockdown in Wuhan, the Chinese city where the global coronavirus outbreak began, will be partially lifted on 8 April, officials say.
Travel restrictions in the rest of Hubei province, where Wuhan is located, will be lifted from midnight on Tuesday – for residents who are healthy.
A single new case of the virus was reported in Wuhan on Tuesday following almost a week of no reported new cases.
Countries around the world have gone into lockdown or imposed severe curbs.
The UK is getting to grips with sweeping new measures to tackle the spread of coronavirus, including a ban on public gatherings of more than two people and the immediate closure of shops selling non-essential goods.
 Image copyright AFP
Image copyright AFPMeanwhile, health experts say Americans must limit their social interactions or the number of infections will overwhelm the health care system in the US.
Spanish soldiers helping to fight the coronavirus pandemic have found elderly patients in retirement homes abandoned and, in some cases, dead in their beds, the defence ministry has said.
An ice rink in Madrid is to be used as a temporary mortuary for Covid-19 victims.
The World Health Organization (WHO) has warned that the pandemic is accelerating, with more than 300,000 cases now confirmed. It is urging countries to adopt rigorous testing and contact-tracing strategies.
- LIVE: Latest updates on the coronavirus outbreak
- Spain’s coronavirus death toll jumps 514 in 24 hours
- Father Berardelli among 50 priests killed
- How did Australia’s cruise ship debacle happen?
Wuhan has been shut off from the rest of the world since the middle of January. But officials now say anyone who has a “green” code on a widely used smartphone health app will be allowed to leave the city from 8 April.
Earlier, the authorities reported a new case of coronavirus in Wuhan, ending a five-day run of no reported new cases in the city.

It comes after health officials there confirmed that they were not counting cases of people who were positive but had not been admitted to hospital or did not show any symptoms of the disease.
Official government figures say there have been 78 new cases reported on the Chinese mainland in the last 24 hours. All but four of them were caused by infected travellers arriving from abroad.
This so-called “second wave” of imported infections is also affecting countries like South Korea and Singapore, which had been successful in stopping the spread of disease in recent weeks.
- South Korea’s ‘trace, test and treat’ may be saving lives
- The detectives racing to contain the virus in Singapore
South Korea has been seeing a drop in its daily tally of new cases. On Tuesday it reported its lowest number since 29 February.

China looks to repair its reputation
By Robin Brant, BBC News, Shanghai
China considers itself to be – very nearly – a “post corona” country.
In the last week we’ve heard Wuhan medics warning the UK and others that they need to do more to protect frontline health workers, citing the mistakes they made early on when some treated patients without wearing proper protective clothing.
But there’s also been reporting in state media of the reported death toll in Italy surpassing that in China. This has been combined with some commentary from prominent media figures that has appeared distasteful, almost triumphalist.
At the same time there is a panic about the threat of a second wave from imported cases – travellers arriving from abroad. This has fuelled the view – right or wrong – that some other countries aren’t taking the threat seriously because they aren’t doing what China did. (Almost all the cases in Beijing that have been made public are of Chinese nationals returning home).
Meanwhile, well away from senior leaders, there are some high-profile diplomatic figures using international-facing social media to spread theories that the US may have weaponised and dumped the virus in China. Or that Italy had cases that may have been Covid-19 earlier than China. China is sowing seeds of doubt and questioning assumed truths as it looks to repair its reputation.


- A SIMPLE GUIDE: What are the symptoms?
- AVOIDING CONTACT: Should I self-isolate?
- STRESS: How to protect your mental health
- MAPS AND CHARTS: Visual guide to the outbreak
- VIDEO: The 20-second hand wash

What’s the latest from around Asia?
- Almost all of India with its 1.3bn people is under lockdown. Buses, trains and other forms of public transport are suspended. On Monday, the authorities said domestic flights would also stopped. The country has reported 485 cases and nine people have died. Prime Minister Narendra Modi will address the nation again this evening.
 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGES- Neighbouring Pakistan has almost twice as many confirmed cases – 878 as of Monday evening. Sweeping restrictions are in place although the government has stopped short of imposing a nationwide lockdown. However, several provinces have announced them independently. The army is being brought in to help enforce the restrictions.
- Bangladesh, which has reported 33 cases and three deaths, is also deploying its armed forces to help maintain social distancing and boost Covid-19 preventive measures. The soldiers will also monitor thousands of quarantined expatriate returnees. Across South Asia, there are concerns that the actual number of cases could be much higher than is being reported.
- Indonesia, which has 49 confirmed Covid-19 deaths – the highest in South-East Asia – has converted an athlete’s village built for the 2018 Asian Games into a makeshift hospital for coronavirus patients. A state of emergency was declared in Jakarta on Monday.
- In Thailand, a month-long state of emergency which will include curfews and checkpoints will begin on Thursday. The government has been criticised for failing to take strong action so far. Four people have died and nearly 900 tested positive.
- Talks between the Japanese PM and the International Olympic Committee are expected this evening.
- The most populous country that was without a case until now – Myanmar – has announced two cases.
Europe’s battle against virus intensifies
UK Prime Minister Boris Johnson announced on Monday night that, with immediate effect, “people will only be allowed to leave their home…for very limited purposes”. They include shopping for basic necessities, taking one form of exercise per day, fulfilling any medical need, or travelling to work if working from home is impossible.

The number of people who have died in the UK rose to 335 on Monday.
In Italy, the worst-hit country in the world, the authorities said 602 people with Covid-19 had died in the past 24 hours, bringing the total death toll there to 6,077.
But the daily increase in cases was the smallest since Thursday, raising hope that the stringent restrictions imposed by the government were starting to have an effect.
Spain, however, said on Tuesday that its death toll had risen by 514 to 2,696. Nearly 40,000 are infected, about 5,400 of them healthcare workers.