18/03/2020
- Company making front-runner appeals for people to take part in trial stage, which nine potential Chinese vaccines are set to enter in April
- US trialling vaccine that copies virus’ genetic code, amid international search for a drug to help limit the outbreak’s human and economic impact
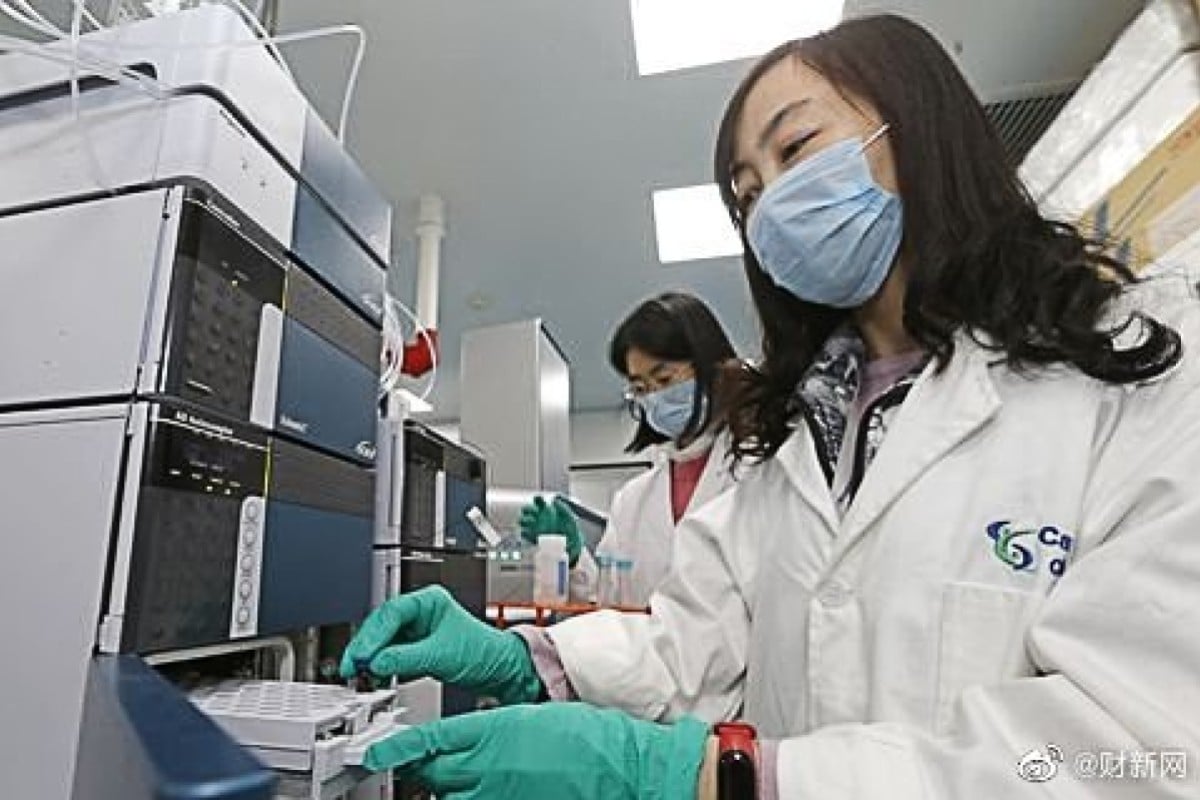
CanSino is recruiting healthy volunteers for a clinical trial of its vaccine candidate. Photo: Weibo
The race to develop a
Covid-19 vaccine is on, with the United States already starting a clinical trial and China close behind.
On Tuesday, vaccine producer CanSino Biologics, in Tianjin in China’s northeast, said it was looking for volunteers to take part in a six-month clinical trial of a treatment it had developed jointly with the Academy of Military Medical Sciences.
“The vaccine does not contain infectious substances, is highly safe and stable, and requires only one inoculation,” the Hubei Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) said in its request for volunteers.
Its announcement came a day after the first participant began a phase I trial for an experimental vaccine funded by the US National Institutes of Health and developed by biotech startup Moderna.
Chinese scientists identify two major types of the new coronavirus in preliminary study
It uses messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) technology that copies the genetic code of the virus instead of the actual virus. To date, no mRNA vaccine has been approved for humans.
China’s own mRNA vaccine candidate, jointly developed by the Chinese Centre for Disease Control and Prevention, Tongji University and Stermina in Shanghai, is undergoing animal trials and is expected to enter the clinical phrase in mid-April.
Developed by the CanSino and the Academy of Military Medical Sciences, the vaccine is the front-runner of nine that China is developing. All are in the process of completing preclinical trial studies and will enter clinical trials in April, with some expected to advance faster than others, according to Wang Junzhi, a biological products quality control expert and academician with the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
US Covid-19 testing accelerates as companies step in where government failed
“China’s research and development of a vaccine for the coronavirus is, generally speaking, among the most advanced in the world,” Wang said at a press briefing in Beijing on Tuesday. “[We] will not be slower than other countries.”
Coronavirus: Scientists dismiss claim that humans engineered the deadly contagion
Hopes have been pinned on developing a vaccine, especially for vulnerable groups such as the elderly, in the face of an epidemic with no known cure that has brought the world to a partial standstill.
Scientists around the world are conducting experiments, and the US is reported to have tried to buy a Germany vaccine developer so that it would supply to the US only – with the German government reportedly offering its own financial incentives for the biopharmaceutical company concerned, CureVac, to stay in the country.
“A vaccine is the most effective medical means for epidemic prevention and control as it can effectively stop the spread of the virus,” Lei Chaozi, director of science and technology at China’s Ministry of Education, said.
“Vaccines also play an important part in … stabilising the economy and enabling the country to return to normal as work and production resume.”
Why did a ‘cured’ coronavirus patient die in China? His widow wants answers
President Xi Jinping called for faster development of coronavirus vaccines and treatment drugs when he inspected the Academy of Military Medical Sciences two weeks ago.
About 1,000 Chinese scientists have been working on the push for vaccines, with nine vaccines developed through five different approaches, including an inactivated vaccine, a viral vector-based vaccine and a gene vaccine.
Wang said that the vaccines needed to satisfy strictly the relevant regulations and technical standards – as well as World Health Organisation requirements – before starting clinical trials.
The potential vaccine developed by CanSino and military researchers, led by virologist Chen Wei, is genetically engineered. “Spikes” on the surface of the coronavirus bind to human cells and enable the virus to invade the human cells, causing the sometimes fatal infection known as Covid-19. In theory, vaccines can rehearse such an attack and trigger the human body to be primed to respond to a real infection.
CanSino has submitted the pre-investigational new drug review application for the Ad5-nCoV vaccine to Chinese regulatory authorities, and is in the process of submitting the related technical documents.
According to the Hubei CDC, volunteers for the trial must be 18 to 60 years old with no history of coronavirus infection.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Academy of Military Medical Sciences, CanSino, China, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Clinical trial, coronavirus, COVID-19, cure, CureVac, developing, Germany, global, Hubei CDC, Hubei Centre for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), inoculation, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA), Moderna, potential, President Xi Jinping, race, Shanghai, Stermina, Tianjin, Uncategorized, United States, US National Institutes of Health, vaccines, volunteers, World Health Organisation |
Leave a Comment »
24/02/2020
- An insect-killing fungus has been turned into a mass-produced biopesticide that will face its biggest challenge in East Africa
- Current swarm has put 13m people at risk of famine and this will be the first large-scale test of its effectiveness
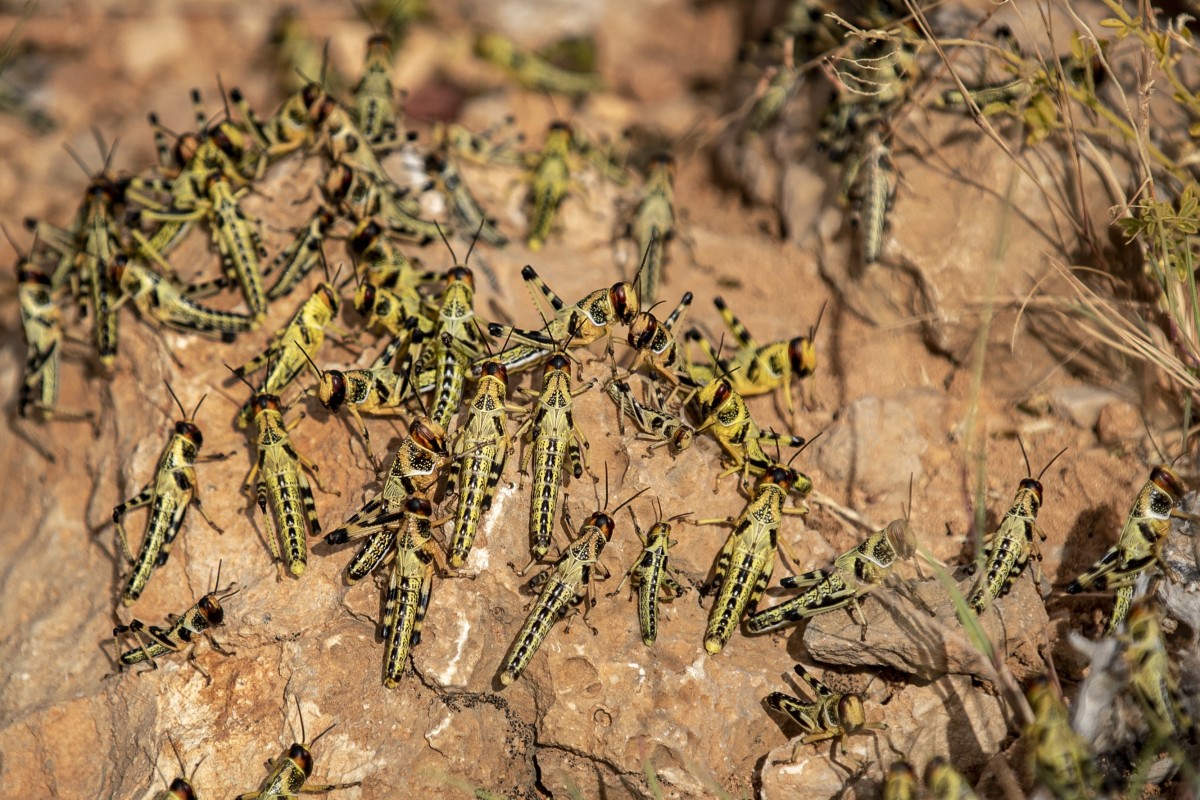
Young locusts in Somalia, where the fungus will be used to try to kill them. Photo: AP
Chinese factories are producing thousands of tonnes of a “green zombie fungus” to help fight the swarms of locusts in East Africa.
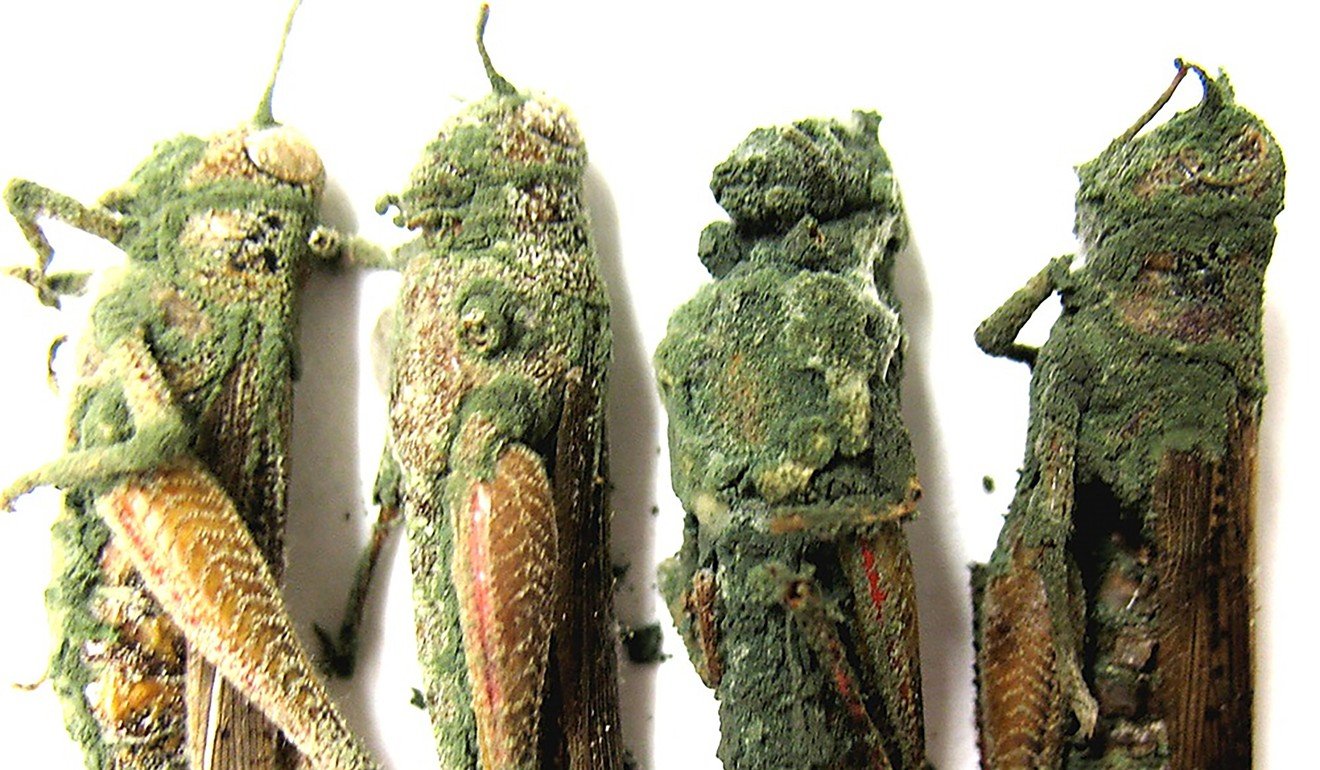
Metarhizium is a genus of fungi with nearly 50 species – some genetically modified – that is used as a biological insecticide because its roots drill through the insects’ hard exoskeleton and gradually poisons them.
In China it was named lu jiang jun, which means green zombie fungus, because it gradually turns its victims in a green mossy lump.
There are now dozens of factories across the country dedicated to producing its spores and despite the curbs introduced to stop the spread of Covid-19, many of them have resumed operations and are shipping thousands of tonnes to Africa.
Plague fears as massive East Africa locust outbreak spreads
These factories are set up in a similar way to breweries, growing the spores on rice which is kept in carefully controlled conditions to ensure the correct temperature and humidity.
Each plant can produce thousands of tonnes of fungi powder per year, each gram of which contains tens of billions of spores.
“I am sending off a truckload right now. Our stock is running out,” said the marketing manager of a production plant in Jiangxi province. “Some customers need it urgently. They need it to kill the locusts.”
The need is particularly pressing in East Africa at the moment, where abnormally high levels of rainfall during the dry season allowed hundreds of billions of locusts to hatch in recent months.
So far the swarms have devastated crops in countries such as Ethiopia, Kenya, Somalia and Uganda and are moving on to neighbouring countries.
Up to 13 million people face the risk of famine in East Africa. Photo: AFP
The UN’s Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO) has warned the situation could be the “worst in decades” and the resulting famine may affect 13 million people and cause international food prices to soar.
Last week, Science magazine reported that the Somalian government, working with the FAO, was preparing to a metarhizium species that only kills locusts and grasshoppers in what it described as the largest ever use of biopesticides against the insects.
Scientists do not believe that the fungus will be enough to solve the problem – monitoring the outbreak and targeting their breeding grounds will be more important in the long-run – but if it proves effective it could be an important weapon to target future outbreaks.
It will take time to gauge the effectiveness, partly because each fungus will take several days to take effect and partly because of the sheer scale of the challenge; a single swarm in Kenya was estimated to contain between 100 billion and 200 billion locusts.
By fair means or fowl: how Chinese herdsmen are planning to stop a locust invasion
The locusts have also swept eastward into the Middle East, travelling up to 150km (90 miles) a day, and are moving closer to China now that they have now reached some of its neighbours, including India and Pakistan.
At present China’s agriculture ministry believes some locusts may follow the monsoon into the country but “the chances of them causing damage is very small”.
Most scientists agree the swarms will not have lasting effect on food production but say developing countries can tap into China’s cutting-edge anti-locust technology.
Radar stations have been set up all the way along China’s western and southern borders to detect possible clouds of locusts, while unmanned devices lure the insects into traps to collect data about their species population and size.
A locust being eaten inside out by the metarhizium fungi. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences and the University of Maryland
The data is streamed to the ministry’s programme command, which is responsible for the planning and coordination of the national efforts to prevent an outbreak.
The scientists also said that planes loaded with biological and chemical sprays were standing by.
Today, most locust outbreaks happen in developing countries that do not have advanced monitoring networks and some of them are unable to produce pesticides on a mass scale, according to Li Hu, an associate professor with the China Agricultural University in Beijing.
The Chinese locust treatment technologies were highly advanced, and usually cheaper than competing solutions from the West, he said.
Chinese researchers are now working with colleagues in other countries to help them solve the problem.
One disadvantage of the Chinese research is that it is mostly focused on local species, or the East Asia migratory locust. The desert locusts currently swarming East Africa have different genes and behaviour, and Li warned that some methods that work in China might not work elsewhere.
A giant indoor farm in China is breeding 6 billion cockroaches a year. Here’s why
There were some sightings of the species reported in Yunnan and Tibet in the past, but they did not build up to large colonies, Professor Kang Le, lead scientist of the locust research programme with the Institute of Zoology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, told China Science Daily last week.
The vast west China region of Xinjiang, which shares a border with eight countries, is currently too cold for a locust migration, but once temperatures start to rise in the spring it could see locusts swarming across the border with Afghanistan.
Shi Wangpeng, a senior government locust expert, told China Business Network on Sunday that China should be on high alert because many Afghan farms had already been affected.
“These areas share a long border with us, there are almost no barriers,” he was quoted as saying by the Shanghai-based magazine.
China has a long and bitter history of locust swarms, with more than 840 being recorded in the official records over the past 2,700 years.
One famine, in the year 628 was so devastating that even the Tang dynasty emperor Taizong was reported to have run short of food and resorted to eating the insects to survive.
China has a long and bitter history of locust swarms. Photo: AFP
This, in turn, means that China’s rulers have long been looking for innovative ways to solve the problem
In the past farmers tried remedies such as building huge fires, burying the insects in ditches or trying to kill them with sticks.
In one campaign organised by prime minister Yao Chong in 715, the farms collected 9 million sacks of dead locusts and managed to save a significant proportion of their crops, according to historic text.
In more recent times more sophisticated technologies have been deployed to tackle the menace.
Some researchers have spent decades chasing locust colonies and studying their individual and collective behaviour everywhere from coastal areas to inland deserts, and in 2014 Chinese scientists released the world’s most comprehensive genetic map of locusts.
Researchers have also developed chemical agents that can disorient swarms of locusts and disperse them.
Chinese scientists first became interested in the green zombie’s potential in the 1980s after discovering that South Pacific islanders had been using them to kill insects on coconut trees.
Research by US scientists confirmed its effectiveness in the 1990s and the Chinese started importing the fungus from the United States and Britain.
Their experiments led to the development of newer and deadlier strains and mass production started in the past decade.
Other fungi or bacteria can be used to fight locusts, and some laboratories are working with agricultural technology companies to modify their genes to turn them into more deadly or precise killers.
One genetically engineered species of microsporidia, another type of insect-killing fungus, for instance, can generate three times as many as the spores to those produced by nature species, according to a document from the China Association of Agricultural Science Societies last year.
While it remains to be seen whether the current swarms will reach China, these treatments have been effective in the past and there has not been a locust outbreak in China for a decade.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Afghan farms, Afghanistan, Agriculture ministry, Beijing, Britain, China Agricultural University, China Association of Agricultural Science Societies, China Business Network, China Science Daily, China’s, Chinese Academy of Sciences, cockroaches, coconut trees, desert locusts, different genes and behaviour, East Africa’s, East Asia migratory locust, Ethiopia, famine, fighting, Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), green zombie fungus, hold ke, hold key, India, insect-killing fungus, Institute of Zoology, Jiangxi Province, Kenya, locust treatment technologies, locusts, mass-produced biopesticide, microsporidia, Middle East, monsoon, Pakistan, Plague fears, Radar stations, Science, Somalia, South Pacific islanders, swarms, Taizong, Tang dynasty emperor, Tibet, Uganda, Uncategorized, United States, Xinjiang, Yunnan |
Leave a Comment »
19/02/2020
Traditional Chinese medicine has never missed a single fight against epidemics throughout Chinese history. After over 2,000 years, the long-tested oriental wisdom is still making its due contributions to the well-being of Chinese people.
by Xinhua writers Cao Bin, Zhang Yujie, Wu Zhonghao and Wang Haiyue
WUHAN, Feb. 18 (Xinhua) — Another 1,701 patients infected with the novel coronavirus (COVID-19) were discharged from hospitals Monday, bringing the total number of discharged patients in China to over 12,000 since the epidemic.
When scrutinizing the commonalities of those people, the contributions of traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) can not go unnoticed.
“Western medicine offers important life-supporting measures such as respiratory and circulatory assistance, while TCM focuses on improving patients’ physical conditions and immune function. They complement each other,” said Zhang Boli, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering.

Zhang Boli, an academician of the Chinese Academy of Engineering, speaks during an interview with Xinhua about the effect of integrated treatment with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and Western medicine at Jiangxia temporary hospital in Wuhan, capital city of central China’s Hubei Province, Feb. 14, 2020. (Xinhua/Cheng Min)
Last Friday, the first phase of a sports center-turned hospital began operation in Wuhan, the epicenter of the COVID-19 outbreak. It is the city’s first TCM-oriented temporary hospital. A total of 800 patients will receive treatment there once the second phase is completed.
The medical team of 209 doctors and nurses from 20 TCM hospitals in five provinces led by Zhang have since been carrying out TCM clinical treatment and research at the hospital.
The recommended TCM treatment plan includes multiple herbal prescriptions targeting fever, heavy coughing, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, shortness of breath and tiredness.
A specific chapter detailing TCM treatment during a patient’s medical observation, clinical treatment and recovery was included in the latest version of the COVID-19 diagnosis and treatment scheme released by the National Health Commission.

A pharmacist weighs Chinese herbal medicines for patients infected with the novel coronavirus at Anhui Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Hefei, east China’s Anhui Province, Feb. 18, 2020. (Xinhua/Bai Bin)
Wuhan’s coronavirus control headquarters have since ordered integrated treatment of TCM and Western medicine, especially among non-critical patients, and observation of TCM’s curative effects at designated hospitals.
Statistics show that 2,220 medics from TCM hospitals and institutions across China have been sent to aid the epidemic fight in Hubei so far. Over 75 percent of COVID-19 patients are receiving TCM treatment in Hubei and over 90 percent in other parts of China.

A medical worker tests the pulse of a patient infected with the novel coronavirus at the Affiliated Hospital of Jiangxi Traditional Chinese Medicine University in Nanchang, east China’s Jiangxi Province, Feb. 18, 2020. (Xinhua/Hu Chenhuan)
On Feb. 6 alone, 23 patients in Hubei were discharged after receiving integrated treatment of TCM and Western medicine.
Zhang said patients with mild symptoms showed obvious improvement after TCM treatment, and for critical patients, TCM decreased their lung exudation, stabilized blood oxygen saturation and reduced respiratory support and antibiotic use.
TCM has never missed a single fight against epidemics throughout Chinese history. TCM classics have provided sufficient evidence of how TCM cured epidemic diseases such as smallpox over the past several thousand years.
The 2003 SARS fight was a recent example. TCM offered timely and effective solutions to the treatment and recuperation of SARS patients.
“Compared with Western medicine, TCM offers highly varied prescriptions to each and every patient based on their unique conditions during different stages of the disease, which is more flexible and targeted,” said Xiong Jibai, a TCM expert and consultant to the coronavirus treatment group of neighboring Hunan Province.
Hunan has sent hundreds of medical workers to help fight the epidemic in the city of Huanggang, one of the hardest-hit cities in Hubei.
Zeng Puhua, vice president of the affiliated hospital of Hunan Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine, has been working around the clock in the SARS treatment-model hospital of Huanggang since late January.
“Clinical experience has repeatedly proven that TCM plays an active and effective role in the treatment of pneumonia-related epidemics,” he said.
According to Hunan’s health commission, TCM was used in the treatment of nearly 95 percent of the admitted patients. Among the discharged, over 90 percent underwent integrated treatment of TCM and Western medicine.

Cured novel coronavirus pneumonia patients, who have received integrated treatment with traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) and Western medicine, are discharged from a hospital in Wuhan, central China’s Hubei Province, Feb. 6, 2020. (Xinhua/Wang Yuguo)
In the city of Bozhou, eastern China’s Anhui Province, TCM has shortened the course of treatment and reduced medical expenses for seven discharged COVID-19 patients taking herbal soups or capsules.
“Patients showed quickened fever reduction after using TCM, and obvious alleviation of certain symptoms such as coughing, tiredness and loss of appetite. Some critical patients became non-critical,” said Zhang Nianzhi, a chief doctor at the respiratory medicine department of Anhui Provincial Hospital of TCM.
Discharged patients are required to stay home for another 14 days. Zhang said a 14-day herbal compound treatment based on TCM theories is prescribed to help them restore their pre-illness state.
Zhang has planned to include 100 discharged patients into the herbal compound treatment group, to follow their symptoms, physical and chemical indicators, CT results and living quality for one year. Thirty patients have so far been taking the prescription.
Non-drug treatment such as cupping, acupuncture and scraping is another feature of TCM, which can help patients recover more effectively after being discharged from hospitals, said Tong Xiaolin, an academician of Chinese Academy of Sciences and head of the treatment group of the state administration of TCM.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Anhui Provincial Hospital of TCM, Anhui Provincial Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Chinese Academy of Engineering, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese history, COVID-19, Hefei, Huanggang, hubei province, Hunan Province, Hunan's health commission, Jiangxia temporary hospital, novel virus, oriental wisdom, outbreak, SARS treatment-model hospital, Traditional Chinese medicine, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM), Uncategorized, Western medicine, Wuhan, Xinhua |
Leave a Comment »
02/11/2019
- Chinese academics and young scientists join global scientific elite to explore frontiers of research
- International joint laboratory announced at Shanghai forum
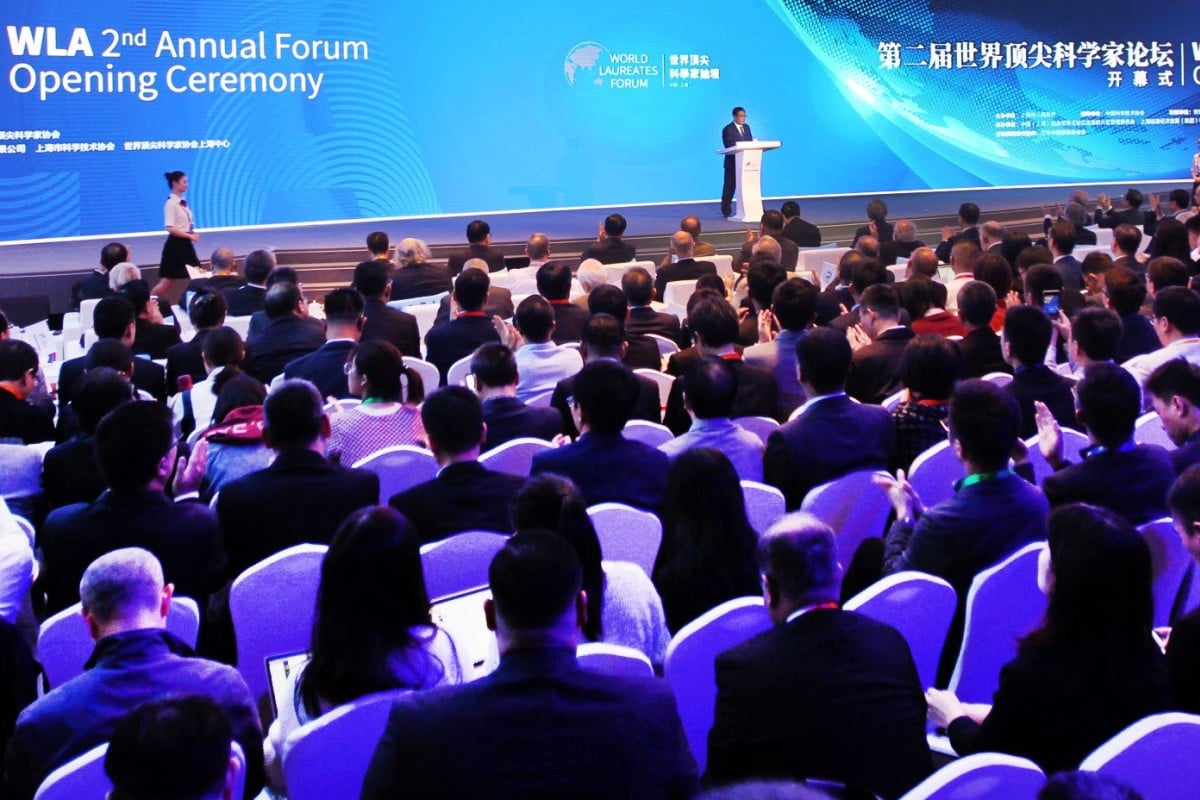
More than three dozen Nobel Prize winners for science were among the gathering in Shanghai for the second annual forum of the World Laureates Association. Photo: Xinhua
Shanghai hosted one of the largest gatherings of Nobel laureates in the world last week, with 44 Nobel Prize-winning scientists in the city for a government-sponsored forum with the lofty goal of discussing science and technology for the “common destiny of mankind”.
The four-day forum, which brought together young Chinese scientists and the cream of the international scientific crop, was a signal of China’s ambitions for its own researchers to take their place at the forefront of development and bring home their own prizes.
Experts agreed the event – the second in an annual “World Laureates Forum” – was hardly a public relations stunt, but a testament to China’s deep-seated, steadfast desire to learn from the world’s top scientists and join them, and their home countries, as leaders on the frontier of science and produce regular home-grown contenders for top prizes.
“The Nobel Prize is the holy grail for China, and it is still quite elusive for Chinese indigenous scientists to be awarded this prestigious recognition,” said Chengxin Pan, an associate professor of international relations at Australia’s Deakin University. “You could say China has a Nobel Prize complex.”
China says US tech ban is a barrier but will not halt scientific advance
Becoming a leader in the sciences was more than just an issue of driving economic expansion through technology and innovation, it was a matter of national preservation with deep roots in Chinese history, Pan said.
“China sees the lack of power, lack of scientific achievements and modern technology as largely responsible for the backwardness and humiliation it suffered during much of the 19th century and early 20th century,” he said.
“They need to make up for lagging behind by engaging with the top leading scientists in the world, wherever they are from.”
To that end, celebrated theoretical physicists, organic chemists, neuroscientists and biologists joined Chinese academics and youth scientists for the conference organised by the Shanghai city government and an association of top global scientists known as the World Laureates Association.
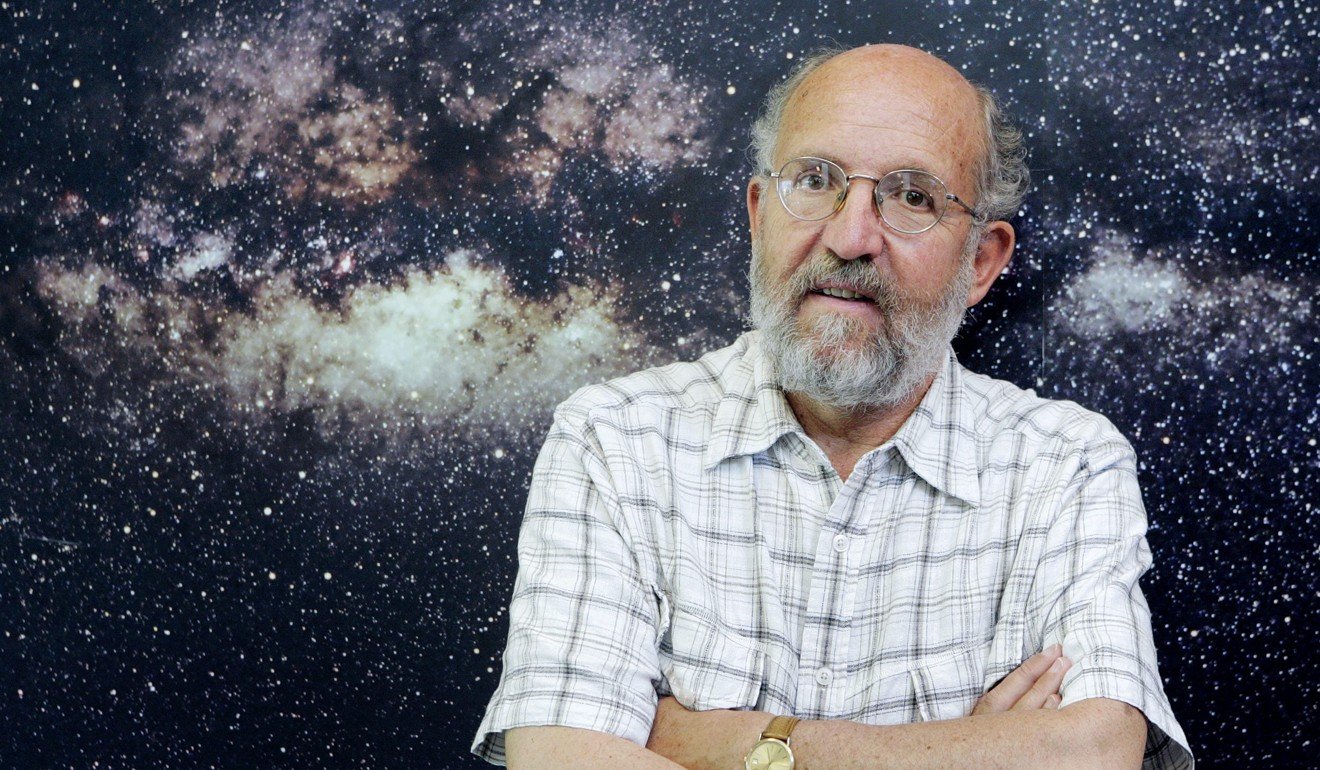
Among them were 2019 Nobel Prize for physics laureates Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz, as well as winners of other top prizes including the Wolf Prize, Lasker Award, and Fields Medal for mathematics. Discussions included the latest breakthroughs in disease prevention and drug development, sustainability and new energy, aerospace and black holes, as well as what drives their scientific curiosity.
Swiss professor Michel Mayor, astrophysicist and director of the Geneva Observatory, was one of the co-winners of the 2019 Nobel Prize in physics and among the attendees at the forum in Shanghai. Photo: EPA-EFE
The event, which culminated with the announcement of an international joint research laboratory for the world’s top scientists, to be established in Shanghai, was lauded by President Xi Jinping in an open letter to the attendees.
“China attaches great importance to the development of the frontier fields of science and technology,” Xi said, stressing China’s willingness to “work with all countries of the world” to “address the challenges of our age”.
The high calibre meeting was a rare opportunity for China to broadcast its message of commitment to scientific advancement, at a time when the reputation of its universities, academics and hi-tech companies have been taking a broad hit as part of a blowback from the US-China trade and tech wars, as well as suspicion among Western countries of China’s geopolitical aims.
In the past year, a number of major global Chinese tech companies, including Huawei and Hikvision, have been blacklisted in the US, while US tech giants like Google and Apple noticeably skipped out on China’s annual state-run World Internet Conference last month. Academic ties between Chinese and Western universities have also been called into question over suspicions of espionage, fraud, and intellectual property theft.
“China is saying we are still open for business and, at this juncture, we more warmly welcome foreign scientists and collaboration between countries in science and technology,” said Zhu Tian, an economics professor at the Chinese Europe International Business School in Shanghai.
60 science groups demand US end crackdown on foreign-born researchers
The past decade has seen China advance rapidly in the sciences. A surge in government funding, along with successive top level strategies to build up science and tech – including the Made in China 2025 innovation blueprint – and a significant uptick in international collaborations, have propelled the nation on to the global scientific stage.
Recent developments, like the first successful landing of a probe on the far side of the moon earlier this year, the dominance of the 5G network technology created by China’s Huawei, and the opening of the world’s largest radio telescope in Guizhou in 2017, have also raised the country’s profile in emerging tech and science.
But, so far, China’s rising visibility as a scientific powerhouse has been largely driven by scale. A June report by the journal Nature found researchers affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences contributed the greatest number of “high-quality natural sciences research” to international journals compared with their peers at other institutions, while last month the journal found the top four “fastest rising” new universities for research output were all from mainland China.
“To some in the outside world, China is already a powerhouse in innovation … but in terms of the quality of innovations or scientific research, China still lags behind developed countries like the US, UK or Switzerland,” Zhu said.
Despite “making the fastest progress among all countries”, and significant leaps as a developing nation, “China is not at the frontier of technology or science yet,” he said, which is why international engagement, like the recent summit, is key to China’s growth.
“In order to catch up you have to know what is the frontier, you have to learn from those who are at the frontier.”
It is a point further underlined by the numerous blog posts and widely circulated articles in Chinese media about China’s meagre Nobel track record. Apart from one celebrated exception – 2015 Nobel laureate for medicine Tu Youyou – Chinese-born scientists who have won the prize did so for their work in overseas laboratories, or after changing citizenship.
Nobel Prize winner may have found solution to malaria drug resistance
Tu was the People’s Republic of China’s first Nobel Prize winner in the sciences and the country’s first woman to win the prize in any category.
Among China’s other Nobel laureates in the sciences are 1957 physics prizewinners Li Zhengdao and Yang Chen-ning, who won their award while in the US, having left China before the Communist Party takeover in 1949. Both later became US citizens. In 2017,
relinquishing his US citizenship to become a Chinese citizen.
China has worked hard to reverse the damage of brain drain, for example with its flagship “Thousand Talents” programme, a high-profile, state-backed recruitment drive set up in 2008 to attract overseas Chinese students and academics back to China with generous funding.
But reaching the frontiers of science, and making Nobel-worthy advancements, will also require China to do some reshuffling of its domestic priorities, which have been heavy on producing innovations in applied sciences and tech, but lighter on the basics – like physics, chemistry, and biology – whose mysteries are probed by the leading labs around the developed world.
Chinese scientists turn black coal by-product into gleaming white paper
“China in the past has been known as a place for incremental innovation, and not the place where really radical innovation and big breakthroughs have come from, but they don’t want to be tinkering at the margins, they want to be a major innovation powerhouse,” said Andrew Kennedy, an associate professor in the policy and governance programme at the Australian National University.
To change this, China has begun to raise investment in basic sciences, Kennedy said, pointing to National Bureau of Statistics figures which indicate an average spending increase of more than 20 per cent each year between 1995 to 2016. Even so, spending at the end of that period – some US$11.9 billion at market rates – still lagged well below the figure cited for the US in 2015, which rang up US$83.5 billion, he said.
Chinese scientists develop laser that could track submarines
The gathering of science laureates itself was further indication of that shift to place more emphasis on basic sciences, the kinds of disciplines the laureates lead, and could be a major boost to that agenda, according to Naubahar Sharif, associate professor of social science and public policy at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
“This [event] is a rocket-propelled, massive injection of scientific power into one place, and China has ambitions to gear up their own scientists to this level,” Sharif said, “and I’m sure the local Chinese scientists have been prepped to take advantage of it.”
While China has work to do in pushing back on criticism of questionable practices in intellectual property transfer, or the extent to which they share their own advances with others, collaboration with leading scientists is a crucial part of China’s “long-haul” vision in the sciences, Sharif said.
“If you rub shoulders with the most prestigious scientists of your era, your local scientists will learn something, and there’s going to be knowledge exchange and making linkages and a start to partnerships,” he said.
“This is the way that getting to that frontier can be achieved.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in 2019 Nobel Prize, Aerospace, Apple, astrophysicist, Australian National University, “Thousand Talents”, “World Laureates Forum”, biologists, black holes, blacklisted, Brain drain, China’s, Chinese academics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Chinese Europe International Business School, Deakin University, disease prevention, Dozens, drug development, Fields Medal, Geneva Observatory, Google, Hikvision, holy grail, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), Huawei, Lasker Award, meet, National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), neuroscientists, new energy, Nobel ambitions, Nobel Prize winner, on show, organic chemists, People's Republic of China's, physics, President Xi Jinping, science laureates, Shanghai, Sustainability, Switzerland, theoretical physicists, UK, Uncategorized, US, US tech giants, Wolf Prize, World Internet Conference, World Laureates Association, youth scientists |
Leave a Comment »
26/09/2019
- An increasing proportion of young people no longer willing to wait tables in China as restaurant owners look to new technology for answers
Catering robots developed by Pudu Tech, the three-year-old Shenzhen start-up, have been adopted by thousands of restaurants in China, as well as some foreign countries including Singapore, Korea, and Germany. Photo: Handout
Two years ago, Bao Xiangyi quit school and worked as a waiter in a restaurant for half a year to support himself, and the 19 year-old remembers the time vividly.
“It was crazy working in some Chinese restaurants. My WeChat steps number sometimes hit 20,000 in a day [just by delivering meals in the restaurant],” said Bao.
The WeChat steps fitness tracking function gauges how many steps you literally take and 20,000 steps per day can be compared with a whole day of outdoor activity, ranking you very high in a typical friends circle.
Bao, now a university student in Hangzhou, Zhejiang province, quit the waiter job and went back to school.
“I couldn’t accept that for 365 days a year every day would be the same,” said Bao.
“Those days were filled with complete darkness and I felt like my whole life would be spent as an inferior and insignificant waiter.”
Olivia Niu, a 23-year-old Hong Kong resident, quit her waiter job on the first day. “It was too busy during peak meal times. I was so hungry myself but I needed to pack meals for customers,” said Niu.
Being a waiter has never been a top career choice but it remains a big source of employment in China. Yang Chunyan, a waitress at the Lanlifang Hotel in Wenzhou in southeastern China, has two children and says she chose the job because she needs to make a living.
Catering robots developed by Pudu Tech, the three-year-old Shenzhen start-up. Photo: Handout
Today’s young generation have their sights on other areas though. Of those born after 2000, 24.5 per cent want careers related to literature and art. This is followed by education and the IT industry in second and third place, according to a recent report by Tencent QQ and China Youth Daily.
Help may now be at hand though for restaurants struggling to find qualified table staff who are able to withstand the daily stress of juggling hundreds of orders of food. The answer comes in the form of robots.
Japan’s industrial robots industry becomes latest victim of the trade war
Shenzhen Pudu Technology, a three-year-old Shenzhen start-up, is among the tech companies offering catering robots to thousands of restaurant owners who are scrambling to try to plug a labour shortfall with new tech such as machines, artificial intelligence and online ordering systems. It has deployed robots in China, Singapore, Korea and Germany.
With Pudu’s robot, kitchen staff can put meals on the robot, enter the table number, and the robot will deliver it to the consumer. While an average human waiter can deliver 200 meals per day – the robots can manage 300 to 400 orders.
“Nearly every restaurant owner [in China] says it’s hard to recruit people to [work as a waiter],” Zhang Tao, the founder and CEO of Pudu tech said in an interview this week. “China’s food market is huge and delivering meals is a process with high demand and frequency.”
Pudu’s robots can be used for ten years and cost between 40,000 yuan (US$5,650) and 50,000 yuan. That’s less than the average yearly salary of restaurant and hotel workers in China’s southern Guangdong province, which is roughly 60,000 yuan, according to a report co-authored by the South China Market of Human Resources and other organisations.
As such, it is no surprise that more restaurants want to use catering robots.
According to research firm Verified Market Research, the global robotics services market was valued at US$11.62 billion in 2018 and is projected to reach US$35.67 billion by 2026.
Haidilao, China’s top hotpot restaurant, has not only adopted service robots but also introduced
a smart restaurant with a mechanised kitchen in Beijing last year. And in China’s tech hub of Shenzhen,
it is hard to pay without an app as most of the restaurants have deployed an online order service.
Can robots and virtual fruit help the elderly get well in China?
China’s labour force advantage has also shrank in recent years. The working-age population, people between 16 and 59 years’ old, has reduced by 40 million since 2012 to 897 million, accounting for 64 per cent of China’s roughly 1.4 billion people in 2018, according to the national bureau of statistics.
By comparison, those of working age accounted for 69 per cent of the total population in 2012.
Other Chinese robotic companies are also entering the market. SIASUN Robot & Automation Co, a hi-tech listed enterprise belonging to the Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced their catering robots to China’s restaurants in 2017. Delivery robots developed by Shanghai-based Keenon Robotics Co., founded in 2010, are serving people in China and overseas markets such as the US, Italy and Spain.
Pudu projects it will turn a profit this year and it is in talks with venture capital firms to raise a new round of funding, which will be announced as early as October, according to Zhang. Last year it raised 50 million yuan in a round led by Shenzhen-based QC capital.
To be sure, the service industry is still the biggest employer in China, with 359 million workers and accounting for 46.3 per cent of a working population of 776 million people in 2018, according to the national bureau of statistics.
And new technology sometimes offers up new problems – in this case, service with a smile.
“When we go out for dinner, what we want is service. It is not as simple as just delivering meals,” said Wong Kam-Fai, a professor in engineering at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and a national expert appointed by the Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence. “If they [robot makers] can add an emotional side in future, it might work better.”
Technology companies also face some practical issues like unusual restaurant layouts.
“Having a [catering robot] traffic jam on the way to the kitchen is normal. Some passageways are very narrow with many zigzags,” Zhang said. “But this can be improved in future with more standardised layouts.”
Multi-floor restaurants can also be a problem.
Dai Qi, a sales manager at the Lanlifang Hotel, said it is impossible for her restaurant to adopt the robot. “Our kitchen is on the third floor, and we have boxes on the second, third, and fourth floor. So the robots can’t work [to deliver meals tdownstairs/upstairs],” Dai said.
But Bao says he has no plans to return to being a waiter, so the robots may have the edge.
“Why are human beings doing something robots can do? Let’s do something they [robots] can’t,” Bao said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in ability, answers, Artificial intelligence, artificial intelligence (AI), Beijing, careers, catering robot, China alert, China Youth Daily, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese University of Hong Kong, complain, Consumer, education, foreign countries, founder and CEO, Germany, global robotics services market, guangdong province, Hangzhou, hard to recruit, Hong Kong resident, hundreds of orders, increasing proportion, industrial robots industry, IT industry, Japan, juggle, Korea, labour shortfall, Lanlifang Hotel, latest victim, literature and art, machines, Multi-floor restaurants, national bureau of statistics, National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), new technologies, new technology, online ordering systems, plug, problem, Pudu Tech, restaurant owners, Shanghai, Shenzhen, Shenzhen Pudu Technology, Singapore, smart restaurant, start up, table number, Tech Companies, tencent qq, top hotpot restaurant, trade war, traffic jams, Uncategorized, venture capital firms, Verified Market Research, wait tables, WeChat, Wenzhou, willing, young people, Zhang Tao, zhejiang province, zigzags |
Leave a Comment »
17/09/2019
- Powerful zoom functions can reveal fingerprint details which may be copied by criminals
A cybersecurity awareness campaign in China has prompted a warning about criminals harvesting fingerprint information from a popular pose in pictures uploaded to the internet. Photo: Shutterstock
A popular hand gesture adopted by China’s online community in uploaded pictures could be used by criminals to steal people’s fingerprints, Chinese cybersecurity experts have warned.
The “scissor hand” pose – similar to the peace sign or “V” for victory– could reveal a perfect fingerprint if held close enough to the camera, according to Zhang Wei, vice-director of the Shanghai Information Security Trade Association.
Speaking at an event promoting a national cybersecurity awareness campaign in Shanghai on Sunday, Zhang said photo magnifying and artificial intelligence-enhancing technologies meant it was possible to extract enough detail to make a perfect copy of the sensitive information.
According to a report by online news portal Thepaper.cn, Zhang’s advice was that scissor-hand pictures taken closer than three metres (10 feet) could be vulnerable and should not be published on the internet.
Chinese face-swapping app sparks privacy concerns soon after its release
“A scissor-hand picture taken within 1.5 metres (four feet 11 inches) can be used to restore 100 per cent of people’s fingerprints, while pictures taken about 1.5-3 metres away can turn out 50 per cent of the fingerprints,” he said.
Based on the information extracted from the pictures, criminals could make models of the prints which could then be used to register at fingerprint-based identity recognition checks, such as door access and payment systems, Zhang said.
Feng Jianjiang, a professor on fingerprint identification from the Department of Automation at Tsinghua University, told the South China Morning Post that, theoretically, pictures could show fingerprints clearly enough to be copied, but said he was unsure of what distance would be safe.
“Some people’s fingerprints could not be captured [at any distance] because of skin problems [for example],” Feng said. “But the fingerprint images would be fairly clear if the distance, angle, focus and lighting were all ideal.”
Feng suggested people check the clarity of detail by zooming in on their fingerprints in pictures before uploading them to social media.
Zang Yali, a researcher from the Institute of Automation at the Chinese Academy of Sciences, agreed that the conditions required to be able to harvest sufficiently detailed fingerprint information were “very demanding”, according to a report in China Science and Technology Daily.
The warning had been viewed on China’s Twitter-like platform Weibo 390 million times within 24 hours of Zhang’s address on Sunday, with 49,000 comments left on the website by Monday afternoon.
“It’s horrifying. I always present a scissor hand in photos,” one Weibo user wrote.
“Advanced technology has brought us convenience but meanwhile has also brought us risk and danger. What can we do now?” another commenter wrote.
One social media user had the perfect solution, writing: “No worries. just show the back of your hand to the camera if you are concerned.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in awareness, Camera, campaign, China alert, China Science and Technology Daily, Chinese Academy of Sciences, criminals, cybersecurity threat, Department of Automation, fingerprint information, harvesting, Institute of Automation, scissor-hand, selfie-takers, Shanghai Information Security Trade Association, south china morning post, Thepaper.cn, Tsinghua University, Twitter, Uncategorized, warned, Weibo |
Leave a Comment »
15/09/2019
- An increasing proportion of young people no longer willing to wait tables in China as restaurant owners look to new technology for answers
Catering robots developed by Pudu Tech, the three-year-old Shenzhen start-up, have been adopted by thousands of restaurants in China, as well as some foreign countries including Singapore, Korea, and Germany. Photo: Handout
Two years ago, Bao Xiangyi quit school and worked as a waiter in a restaurant for half a year to support himself, and the 19 year-old remembers the time vividly.
“It was crazy working in some Chinese restaurants. My WeChat steps number sometimes hit 20,000 in a day [just by delivering meals in the restaurant],” said Bao.
The WeChat steps fitness tracking function gauges how many steps you literally take and 20,000 steps per day can be compared with a whole day of outdoor activity, ranking you very high in a typical friends circle.
Bao, now a university student in Hangzhou, Zhejiang province, quit the waiter job and went back to school.
“I couldn’t accept that for 365 days a year every day would be the same,” said Bao. “Those days were filled with complete darkness and I felt like my whole life would be spent as an inferior and insignificant waiter.”
Olivia Niu, a 23-year-old Hong Kong resident, quit her waiter job on the first day. “It was too busy during peak meal times. I was so hungry myself but I needed to pack meals for customers,” said Niu.
Being a waiter has never been a top career choice but it remains a big source of employment in China. Yang Chunyan, a waitress at the Lanlifang Hotel in Wenzhou in southeastern China, has two children and says she chose the job because she needs to make a living.
Catering robots developed by Pudu Tech, the three-year-old Shenzhen start-up. Photo: Handout
Today’s young generation have their sights on other areas though. Of those born after 2000, 24.5 per cent want careers related to literature and art. This is followed by education and the IT industry in second and third place, according to a recent report by Tencent QQ and China Youth Daily.
Help may now be at hand though for restaurants struggling to find qualified table staff who are able to withstand the daily stress of juggling hundreds of orders of food. The answer comes in the form of robots.
Japan’s industrial robots industry becomes latest victim of the trade war
Shenzhen Pudu Technology, a three-year-old Shenzhen start-up, is among the tech companies offering catering robots to thousands of restaurant owners who are scrambling to try to plug a labour shortfall with new tech such as machines, artificial intelligence and online ordering systems. It has deployed robots in China, Singapore, Korea and Germany.
With Pudu’s robot, kitchen staff can put meals on the robot, enter the table number, and the robot will deliver it to the consumer. While an average human waiter can deliver 200 meals per day – the robots can manage 300 to 400 orders.
“Nearly every restaurant owner [in China] says it’s hard to recruit people to [work as a waiter],” Zhang Tao, the founder and CEO of Pudu tech said in an interview this week. “China’s food market is huge and delivering meals is a process with high demand and frequency.”
Pudu’s robots can be used for ten years and cost between 40,000 yuan (US$5,650) and 50,000 yuan. That’s less than the average yearly salary of restaurant and hotel workers in China’s southern Guangdong province, which is roughly 60,000 yuan, according to a report co-authored by the South China Market of Human Resources and other organisations.
As such, it is no surprise that more restaurants want to use catering robots.
According to research firm Verified Market Research, the global robotics services market was valued at US$11.62 billion in 2018 and is projected to reach US$35.67 billion by 2026. Haidilao, China’s top hotpot restaurant, has not only adopted service robots but also introduced a smart restaurant with a mechanised kitchen in Beijing last year. And in China’s tech hub of Shenzhen, it is hard to pay without an app as most of the restaurants have deployed an online order service.
Can robots and virtual fruit help the elderly get well in China?
China’s labour force advantage has also shrank in recent years. The working-age population, people between 16 and 59 years’ old, has reduced by 40 million since 2012 to 897 million, accounting for 64 per cent of China’s roughly 1.4 billion people in 2018, according to the national bureau of statistics.
By comparison, those of working age accounted for 69 per cent of the total population in 2012.
Other Chinese robotic companies are also entering the market. SIASUN Robot & Automation Co, a hi-tech listed enterprise belonging to the Chinese Academy of Sciences, introduced their catering robots to China’s restaurants in 2017. Delivery robots developed by Shanghai-based Keenon Robotics Co., founded in 2010, are serving people in China and overseas markets such as the US, Italy and Spain.
Pudu projects it will turn a profit this year and it is in talks with venture capital firms to raise a new round of funding, which will be announced as early as October, according to Zhang. Last year it raised 50 million yuan in a round led by Shenzhen-based QC capital.
To be sure, the service industry is still the biggest employer in China, with 359 million workers and accounting for 46.3 per cent of a working population of 776 million people in 2018, according to the national bureau of statistics.
And new technology sometimes offers up new problems – in this case, service with a smile.
“When we go out for dinner, what we want is service. It is not as simple as just delivering meals,” said Wong Kam-Fai, a professor in engineering at the Chinese University of Hong Kong and a national expert appointed by the Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence. “If they [robot makers] can add an emotional side in future, it might work better.”
Technology companies also face some practical issues like unusual restaurant layouts.
“Having a [catering robot] traffic jam on the way to the kitchen is normal. Some passageways are very narrow with many zigzags,” Zhang said. “But this can be improved in future with more standardised layouts.”
Multi-floor restaurants can also be a problem.
Dai Qi, a sales manager at the Lanlifang Hotel, said it is impossible for her restaurant to adopt the robot. “Our kitchen is on the third floor, and we have boxes on the second, third, and fourth floor. So the robots can’t work [to deliver meals to downstairs/upstairs],” Dai said.
But Bao says he has no plans to return to being a waiter, so the robots may have the edge.
“Why are human beings doing something robots can do? Let’s do something they [robots] can’t,” Bao said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in ability, adopted, Art, artificial intelligence (AI), Bao Xiangyi, Beijing, careers, catering robots, CEO of Pudu tech, China alert, China Youth Daily, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Association for Artificial Intelligence, Chinese University of Hong Kong, complain, darkness, delivering meals, education, foreign countries, Germany, guangdong province, Haidilao, Hangzhou, hotpot restaurant, hundreds of orders, industrial robots industry, IT industry, Italy, Japan, juggle, Keenon Robotics Co, Korea, labour shortfall, Lanlifang Hotel, literature, machines, mechanised kitchen, online ordering systems, plug, Pudu Tech, QC capital, qualified table staff, quit, Restaurant, restaurants, robots, school, Shenzhen, Shenzhen Pudu Technology, SIASUN Robot & Automation Co, Singapore, smart restaurant, South China Market of Human Resources, Spain, start up, tencent qq, trade war, Uncategorized, university student, US, Verified Market Research, victim, waiter, WeChat, Wenzhou, worked, zhejiang province |
Leave a Comment »
06/09/2019
- Material that generates heat from sunlight could provide self-maintaining water supply on remote islands
An international research team used solar power to generate a supply of drinking water. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences
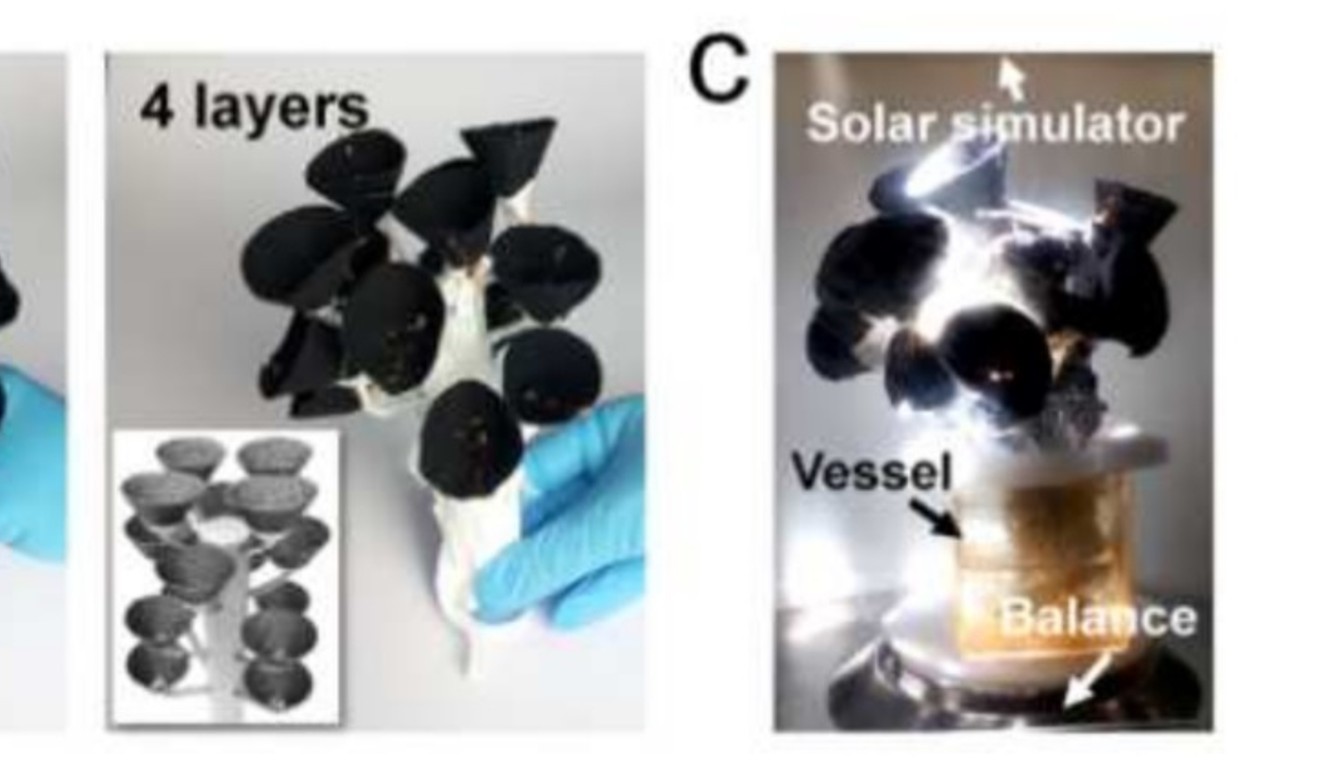
A Chinese-led international research team has created a “tree” that can generate clean drinking water.
Drawing its energy entirely from the sun just like a real tree, the “water tree” has a root made of cotton fabric that can absorb water from its surroundings, such as from sand on a beach.
After water moves up the stem, it is vaporised by “leaves” made of black-carbon paper cones that convert light energy to heat, reaching nearly 50 degrees Celsius (122 Fahrenheit). The tree sits in a glass chamber with a relatively cool surface that collects the vapour.
Using standard cotton fabric and a new nanomaterial that can be cheaply mass-produced from charcoal, a paper cone with a surface area as large as 1 square metre would cost only US$2, according to the researchers.
The cones, which function like leaves, could be mass-produced cheaply, researchers say. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences
A cone that size can generate up to 3.4kg (7.5lbs) of condensed water per hour, faster than any other solar-powered desalination methods previously reported.
Even on a cloudy day, the total output in seven hours of sunlight can reach 5.4kg, or three times the amount the typical adult needs to stay hydrated.
One tree can have multiple layers of branches, each with several cones to increase the vapour-producing surface area.
The study, published this month in the journal Nano Energy, was led by Professor Chen Tao at the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering in Zhejiang province, and also involved researchers from Singapore and Taiwan.
World’s thirst for fresh water is causing a big toxic problem
One of the paper’s co-authors, Dr Ouyang Jianyong, associate professor at the National University of Singapore’s department of materials science and engineering, told the South China Morning Post that the technology could be applied in remote places such as on islands in the South China Sea.
“It is particularly useful for isles far away without a stable drinking water supply,” Ouyang said. “These ‘trees’ may not be able to quench the thirst of a large city, but they can meet the critical demand of a small community, especially in emergencies.
“We are already in contact with some companies [to commercialise the technology],” he added.
The material used to make the cone has several advantages, according to Ouyang. The cones can absorb a wide spectrum of sunlight, maximising the amount of energy they can collect, and their porous structure allows them to release vapour quickly.
Lawmakers endorse plan for HK$7.7 billion desalination plant
When used to desalinate a supply of seawater, the trees would be self-cleaning at night, by water washing away salt residue without being vaporised as it would during sunlight hours.
The vapour-producing fabric is as thin and lightweight as a few sheets of paper. It can be folded and sewn into almost any shape, or cleaned in a washing machine, and can operate effectively for several years in a harsh environment, the researchers say.
The condensed water meets stringent safety standards for direct drinking set by the World Health Organisation, according to the researchers.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Chinese Academy of Sciences, cleaned, department of materials science and engineering, desalinate, desalination plant, Drinking water, lawmakers, Nano Energy, National University of Singapore, night, Ningbo Institute of Material Technology and Engineering, paper, remote islands, sea, Seawater, self-cleaning, self-maintaining water supply, sewn, shape, sheets, Singapore, solar-powered ‘tree’, solar-powered desalination methods, south china morning post, South China Sea, Taiwan, turns, Uncategorized, vapour-producing fabric, washing machine, World Health Organisation, zhejiang province |
Leave a Comment »
06/09/2019
- Researchers bend super-thin sheet using a single electrically charged atom in breakthrough that could eventually pave the way for powerful new computer processors
- Success follows decades of fruitless attempts by scientists around the world
The team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted the “world’s smallest work of origami” with a sheet of graphene. Photo: Handout
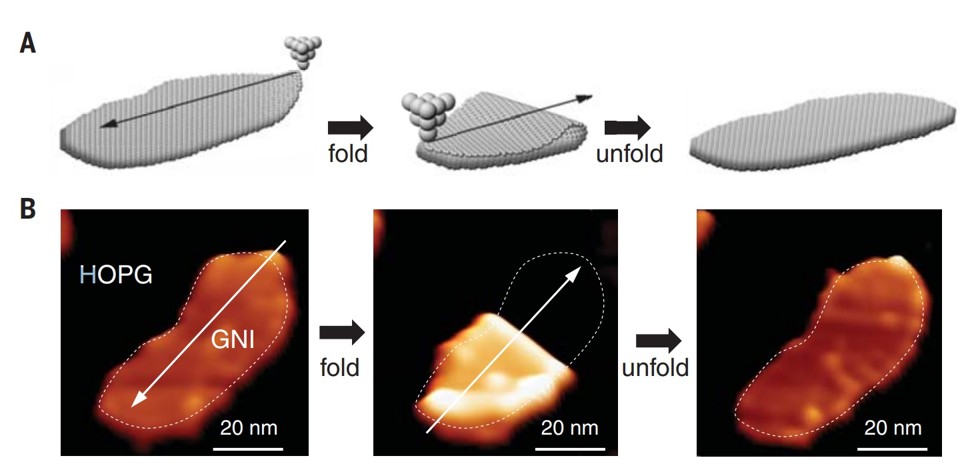
Chinese scientists have taken the ancient art of origami to the atomic level by finding a way to fold microscopically small graphene, according to a new study.
The team managed to fold a 20 nanometre wide sheet of graphene into various shapes and forms using an extremely sharp needle with a single electrically charged atom at the tip, according to a paper published in the latest edition of Science magazine.
The breakthrough could eventually enable a host of technological advances, including the development of faster and more powerful computer processors, the researchers said.
“This is the world’s smallest origami work,” said Dr Du Shixuan, the study’s lead scientist, adding that the team hoped to build on their success by making the graphene equivalent of a paper aeroplane.
Unlike previous experiments, in which the folding occurred randomly or by accident, the new technology allows scientists to control the transformation with atomic-scale accuracy, according to Du, from the Institute of Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing.
Microscopic images of the graphene folding process. Photo: Handout
Zhang Gengmin, a professor of physics at Peking University, said the team had managed something that other scientists had spent years trying to achieve.
Zhang, who was not involved in the study, said part of the difficulty was that atomic particles were influenced by quantum mechanics, a branch of physics whose laws are counter-intuitive to our daily experience.
In practice this means that folding a graphene sheet in one direction might cause it go in another direction or simply break apart.
Could these crystals be the next leap forward in China’s laser technology?
The new technology developed by Du’s team could have some critical applications, according to Zhang, who works at the university’s nano devices laboratory.
For instance, folding a sheet of graphene – formed from a single layer of latticed carbon atoms – into a “magic angle” will make it superconductive, a unique physical state that allows electrons to pass through without any resistance.
“It is a significant piece of work,” he said.
The 20 nanometre wide sheet was folded into various shapes. Photo: Handout
The paper by Du’s team withheld some of the technical details of their experiment, which means that other scientists may not be able to replicate the process simply by reading the paper.
Du defended the secrecy as a standard practice and necessary measure to maintain China’s lead in this field.
She said that the team’s success was down to many factors – including the hardware used, the strength of the electric current and the experience of the operator – and there were also lessons to be taken from their previous failed attempts.
The researchers said they hoped the technology would be used to improve the design and manufacturing of computer processors.
Chinese, US scientists develop AI technology to help detect submarines in uncharted waters
At present, commercial processors are made using a large piece of silicon board known as a wafer.
But as the size of components such as transistors shrink, it has become increasingly difficult to improve the speed and performance of the computer due to the challenges of controlling the structure and properties of each component on a near-atomic scale
The new technology could give designers more freedom to develop a “dream chip” by building a central processing unit on an atom-by-atom basis from the bottom up.
But Du said the commercial application of the new technology could be years away.
Her team folded the graphene sheets manually, one at a time, but mass production would need the development of new manufacturing methods to do it automatically. At present “we are working on it”, Du added.
Source: SCMP
Posted in AI technology, Art, Atomic origami, Beijing, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese scientists, folding graphene, graphene, Institute of Physics, master, new computer processors, Peking University, Science, submarines, superconductive, Uncategorized, uncharted waters, US scientists |
Leave a Comment »
06/09/2019
- Scientists find some chemicals can kill the cotton leaf curl Multan virus and others can boost cotton plants’ immunity to it
- It is feared the virus could wreak havoc in China’s Xinjiang region, which produces most of the country’s cotton
A cotton picker in Xinjiang, where cases of the virus have been reported. Photo: Xinhua
Chinese scientists have found chemicals in medicinal herbs that could tame a destructive plant virus threatening the cotton industry in its western Xinjiang region.
Some small-molecule chemicals in herbs commonly used in Chinese medicine can effectively suppress cotton leaf curl Multan virus, according to ongoing research led by Professor Ye Jian at the Institute of Microbiology in Beijing.
By targeting WRKY20, a gene in the virus’ DNA, the chemicals could disrupt the viral infection and transmission, Ye’s team found.
Some early findings from their research were published last month in the journal Science Advances.
The leaf curl virus – a species of Begomovirus, the largest genus of plant viruses – poses a significant threat to the world’s cotton plantations, causing leaf curling, stunted growth and lower yields of cotton fibre. It costs the cotton industry in the Indian subcontinent about US$1 billion a year, according to a press release about the study from the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Were there to be a pandemic in China, the drop in output and measures to contain it could cost the cotton farming industry 50 billion yuan (US$7 billion), according to some researchers’ estimates, the academy added.
The first known cases of the virus in China over the past decade were limited to coastal areas in the country’s east, but several cases have now been reported in Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region.
“We are running out of time,” Ye told the South China Morning Post.
Cotton is a pillar industry in Xinjiang, which provides more than 80 per cent of China’s total cotton production. The industry also contributes up to 50 per cent of the income of farmers involved in it, according to government statistics.
Exact figures for infections in the region are not available, but outbreaks so far remain isolated, according to Ye and other researchers with knowledge of the situation.
Double threat to China’s cotton industry: warmer weather and mirid bug
However, Professor Gao Feng, cotton researcher at the Agricultural College of Shihezi University in Xinjiang, warned that leaf curl virus could reduce cotton production in an infected field to almost zero.
“A large-scale outbreak has not occurred yet, but the threat is very serious and people are very nervous,” Gao told the Post. “We are in desperate need of a solution.”
The challenges facing China’s pork industry highlight the danger viruses can pose to the domestic market. A swine fever outbreak that has wiped out 100 million pigs caused pork prices to rise, forcing China to look to new countries to import from, such as Portugal and Argentina.
Its biggest overseas supplier of cotton is the United States, with which it is locked in a protracted trade war. In July, the government allowed some Chinese companies to buy a total of 50,000 tonnes of cotton from the US without tariffs being charged.
The central and regional governments fear that falling incomes caused by the impact of an outbreak on the cotton industry would increase the risk of ethnic conflict, social instability and anti-government thoughts.
Ye’s team adopted two approaches to fighting the virus.
How trade war with the US is changing China’s cotton industry
Some chemicals they discovered could improve cotton plants’ immunity against the infection by stimulating them to generate an antibody that killed the virus. The other chemicals they found could target the virus, directly reducing its intensity.
“They can be used as sprays,” Ye said, adding that he planned to reveal the chemical composites and related herbs in a paper to be published in a peer-reviewed journal in the coming months.
The discovery could offer an environmental benefit, too. Cotton farmers in Xinjiang use pesticides to deter the whiteflies that transmit the virus, but their overuse has affected Xinjiang’s delicate ecology, which in its desert areas is particularly vulnerable to disturbance.
In the agricultural research community, there is growing concern that some whitefly species will become resistant to pesticides. “If that happens, we will have a major problem,” Ye said.
He said the chemicals identified in the ongoing study would not harm the environment.
“These chemicals come from plants, so the negative impact to the environment would be minimal,” he said.
The study also found that it may be possible to use the cotton leaf curl Multan virus to benefit farmers. It stimulates cotton plants to generate a chemical that is harmful to other insects, such as the bollworm, that compete with whiteflies for food, meaning that it could be genetically modified into a pest control agent.
Most cotton species in commercial plantations are genetically modified to produce an insecticide to kill bollworm. Ye said a man-made virus could reduce the dependence on genetically modified plants.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Agricultural College of Shihezi University, agricultural research community, Argentina, Begomovirus, Beijing, bollworm, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese medicine herbs, cotton, cotton leaf curl Multan virus, cotton virus, defeat, devastating, ethnic conflict, indian subcontinent, Institute of Microbiology, pandemic, pork industry, Portugal, Science Advances, scientists, social instability, south china morning post, swine fever outbreak, Uncategorized, whiteflies, wreak havoc, xinjiang region, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region |
Leave a Comment »