02/11/2019
- Team from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics says its goal is to ‘develop an all-season battery that is low cost but high safety for consumer products’
- Researchers make breakthrough by using hard carbon and lithium vanadium phosphate
Chinese researchers say they have made a breakthrough in the development of small lithium batteries that can withstand low temperatures. Photo: Xinhua
Chinese researchers say they have found a way to produce a tiny, lightweight lithium battery for use in mobile phones and electric cars that can hold up to 80 per cent of its charge in temperatures as low as minus 40 degrees Celsius.
The breakthrough came by using a combination of a new material called hard carbon along with lithium vanadium phosphate, the team from the Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics said in a paper published in this month’s edition of the scientific journal Nano Energy.
“Our goal is to develop an all-season battery that is low-cost but high-safety for consumer products,” said Song Zihan, its lead author.
It was an unprecedented approach, but “we proved it works”, he said.
The idea of a battery that can withstand extreme cold is not new. Photo: Shutterstock
The idea of a battery that can withstand extreme cold is not new, and they are already in use in space and in the Arctic and Antarctic.
But they tend to be very bulky because of the heating system and large amount of insulation they need to function properly at sub-zero temperatures.
Such measures are neither physically nor economically viable for applications like smartphones, cameras, laptops or electric cars. The trick, Song said, was replacing the soft graphite in normal lithium batteries with hard carbon.
Graphite is a good conductor and often used for the anode at the bottom of a battery, where electrons are generated. But the performance of graphite drops as the mercury slides.
How military tech sparked a robot revolution in firework factories
Song said that hard carbon was a new material that had attracted a lot of research interest in recent years, and compared with graphite, it had a much higher tolerance for the cold.
That was because of its highly irregular and “almost messy” structure, comprising layers of carbon atoms that are interconnected with each other, he said.
However, hard carbon also caused a rapid depletion of the lithium ions that served as an agent carrying the electric flow in battery, he said.
The researchers want to make battery suitable for use in consumer products. Photo: EPA-EFE
In the past, researchers have tried adding lithium powders or flakes to improve battery life, but the approach has proven costly and dangerous, mostly because pure lithium is highly reactive.
So Song and his colleagues used a composite material called lithium vanadium phosphate as the positive cathode on top of the battery.
The composite was capable of providing enough extra lithium ions for the hard carbon’s need without increasing the risk of fire or explosion, and it was cheap, he said.
“The pairing of hard carbon and lithium vanadium phosphate worked a charm,” Song said.
But the technology is still a long way from being commercially viable.
The battery Song’s team made is far too small for any real-life applications, and enlarging it would require some “innovative engineering solutions”, he said.
Another scientist involved in the project said the team was working with battery manufacturers to see if the technology could be commercialised.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Antarctica, Arctic, cameras, capable, Chinese scientists, create, Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics, electric cars, laptops, lithium batteries, low temperatures, Nano Energy, smartphones, Space, tiny battery, ultra-low temperatures, Uncategorized, withstand, working |
Leave a Comment »
06/09/2019
- Researchers bend super-thin sheet using a single electrically charged atom in breakthrough that could eventually pave the way for powerful new computer processors
- Success follows decades of fruitless attempts by scientists around the world
The team from the Chinese Academy of Sciences conducted the “world’s smallest work of origami” with a sheet of graphene. Photo: Handout
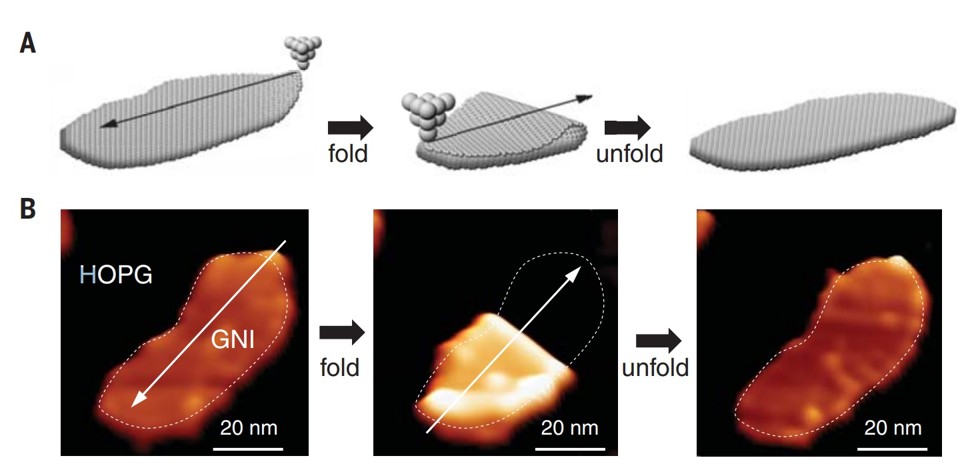
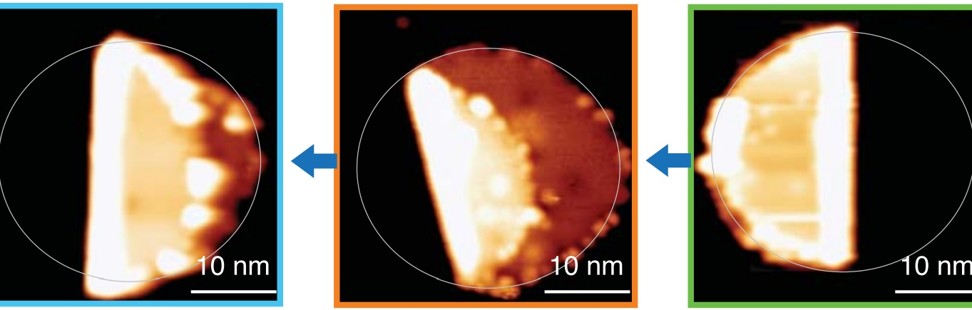
Chinese scientists have taken the ancient art of origami to the atomic level by finding a way to fold microscopically small graphene, according to a new study.
The team managed to fold a 20 nanometre wide sheet of graphene into various shapes and forms using an extremely sharp needle with a single electrically charged atom at the tip, according to a paper published in the latest edition of Science magazine.
The breakthrough could eventually enable a host of technological advances, including the development of faster and more powerful computer processors, the researchers said.
“This is the world’s smallest origami work,” said Dr Du Shixuan, the study’s lead scientist, adding that the team hoped to build on their success by making the graphene equivalent of a paper aeroplane.
Unlike previous experiments, in which the folding occurred randomly or by accident, the new technology allows scientists to control the transformation with atomic-scale accuracy, according to Du, from the Institute of Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing.
Microscopic images of the graphene folding process. Photo: Handout
Zhang Gengmin, a professor of physics at Peking University, said the team had managed something that other scientists had spent years trying to achieve.
Zhang, who was not involved in the study, said part of the difficulty was that atomic particles were influenced by quantum mechanics, a branch of physics whose laws are counter-intuitive to our daily experience.
In practice this means that folding a graphene sheet in one direction might cause it go in another direction or simply break apart.
Could these crystals be the next leap forward in China’s laser technology?
The new technology developed by Du’s team could have some critical applications, according to Zhang, who works at the university’s nano devices laboratory.
For instance, folding a sheet of graphene – formed from a single layer of latticed carbon atoms – into a “magic angle” will make it superconductive, a unique physical state that allows electrons to pass through without any resistance.
“It is a significant piece of work,” he said.
The 20 nanometre wide sheet was folded into various shapes. Photo: Handout
The paper by Du’s team withheld some of the technical details of their experiment, which means that other scientists may not be able to replicate the process simply by reading the paper.
Du defended the secrecy as a standard practice and necessary measure to maintain China’s lead in this field.
She said that the team’s success was down to many factors – including the hardware used, the strength of the electric current and the experience of the operator – and there were also lessons to be taken from their previous failed attempts.
The researchers said they hoped the technology would be used to improve the design and manufacturing of computer processors.
Chinese, US scientists develop AI technology to help detect submarines in uncharted waters
At present, commercial processors are made using a large piece of silicon board known as a wafer.
But as the size of components such as transistors shrink, it has become increasingly difficult to improve the speed and performance of the computer due to the challenges of controlling the structure and properties of each component on a near-atomic scale
The new technology could give designers more freedom to develop a “dream chip” by building a central processing unit on an atom-by-atom basis from the bottom up.
But Du said the commercial application of the new technology could be years away.
Her team folded the graphene sheets manually, one at a time, but mass production would need the development of new manufacturing methods to do it automatically. At present “we are working on it”, Du added.
Source: SCMP
Posted in AI technology, Art, Atomic origami, Beijing, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese scientists, folding graphene, graphene, Institute of Physics, master, new computer processors, Peking University, Science, submarines, superconductive, Uncategorized, uncharted waters, US scientists |
Leave a Comment »
05/09/2019
- New material is almost identical in structure to human enamel, which does not regenerate itself
- Crystal-like mineral can grow on teeth and last permanently, researchers say
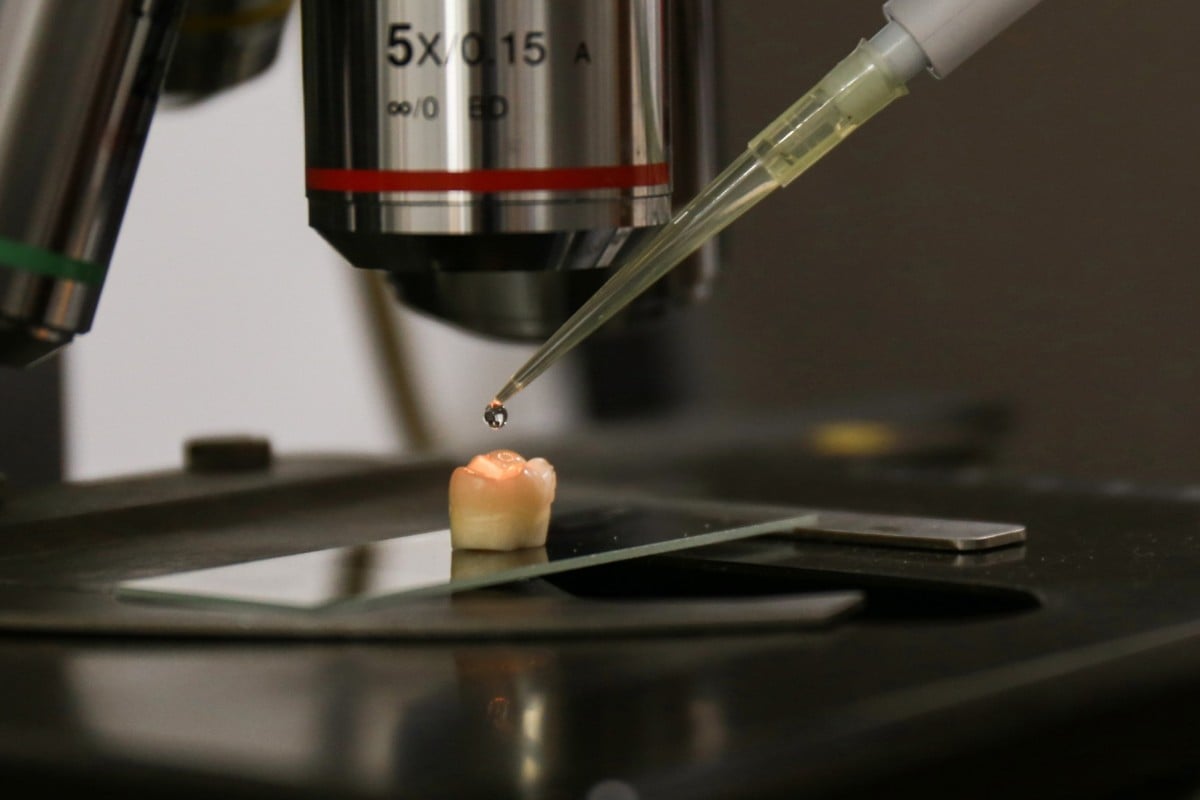
Drops of the liquid solution are applied to a human tooth. Photo: Zhejiang University
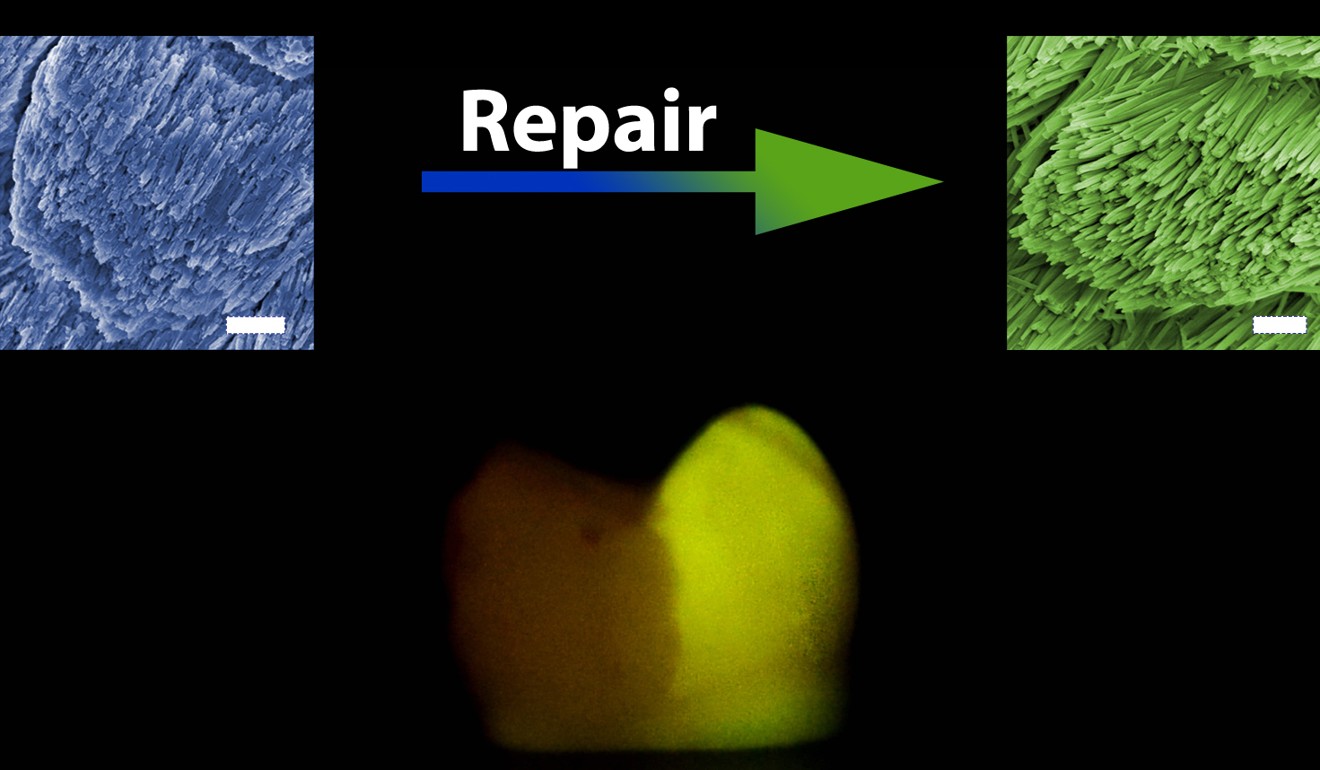
Scientists at a Chinese university say they have discovered the world’s first material that can repair damaged tooth enamel once and last for life.
A few drops of the liquid solution can fix all invisible cracks and wear on an ageing molar, according to researchers at Zhejiang University in Hangzhou, eastern China, whose work was published on Friday in the journal Science Advances.
The material, calcium phosphate ion clusters, can grow a thin layer of protective shield on teeth, the research showed. The transparent, crystal-like mineral has a structure resembling fish scales and a high mechanical strength – almost identical to the enamel on a human tooth.
Its repair of the tooth “would be permanent”, wrote the researchers, led by Professor Tang Ruikang at the university’s chemistry department.
A tooth’s non-repaired left side (darker) and repaired right side (lighter) are compared using a fluorescent chemical. Photo: Zhejiang University
The technology could be developed as an effective remedy in clinical practice for enamel erosion, the main cause of tooth decay, Tang’s team said. Tooth decay affects almost half of the world’s population, costing dental patients in the United States and European Union a combined US$200 billion annually, according to the World Dental Federation.
Enamel, the outer covering of teeth, is the hardest tissue in the human body, protecting teeth during biting and chewing food.
Unlike other tissues such as muscle, bone and skin, enamel is generated by cells that die immediately after completing their job. The human body cannot produce more of them, so when enamel breaks or chips, it will not regenerate itself.
For decades, researchers around the world have conducted studies to seek a solution, but the artificial materials tested previously could not recreate precisely the fine structure of natural enamel, leaving gaps or holes that could cause it to break off real enamel.
Wouldn’t it be nice if our teeth fixed themselves, just like pandas’ do?
Tang’s team claim their new material can grow seamlessly on human teeth. They mixed two different types of repairing material together to form tiny clusters of mineral particles only 1.5 nanometres in diameter – smaller than a strand of human DNA.
Unlike in previous experiments, these clusters could remain stable for a long time without clumping together, making precise reconstruction of an enamel-like structure possible.
Chen Haifeng, associate professor at Peking University’s biomedical engineering department, said that the research was a positive step but that the new material might need improvements before clinical use.
For instance, the artificial layer requires two days to grow, which could be difficult for dentists to schedule with patients.
Many children use so much toothpaste it’s unhealthy, experts warn
The liquid solution contains triethylamine, a toxic substance with a very strong smell, which may pose a health risk, according to Chen. “But it doesn’t mean we can’t do anything,” he said.
The researchers said the chemical would quickly vaporise and none would be left in the teeth after the protective shield had formed.
Some products preventing enamel erosion and decay, such as toothpaste with enamel-strengthening ingredients, are already available in shops.
“Prevention is the best approach,” Chen said. “We should never wait until the damage is done. Our teeth are a miracle of nature. Artificial replacement will never do the job as well.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in ageing molar, almost, biomedical engineering department, bone, calcium phosphate ion clusters, chemistry department, Chinese scientists, Crystal-like mineral, dental patients, Enamel, European Union, first, fish scales, fix, grow, Hangzhou, human enamel, identical, invisible cracks, itself, last permanently, make, muscle, New material, pandas, Peking University, perfect replica, regenerate, researchers, Science Advances, skin, structure, teeth, tooth enamel, triethylamine, Uncategorized, United States, wear, World Dental Federation, Zhejiang University |
Leave a Comment »
31/08/2019
- Researchers say system should allow them to track any sound-emitting source – from nuclear subs to whales – using a simple listening device mounted on a buoy, underwater drone or ship
- Breakthrough builds on previous work by team from Beijing and San Diego
A new AI system developed by Chinese and US scientists could make detecting nuclear submarines possible even in unknown waters. Photo: Xinhua
Scientists from China and the United States have developed a new
artificial intelligence
-based system that they say will make it easier to detect submarines in uncharted waters.
The technology builds on earlier work by the team, led by Dr Niu Haiqiang from the Institute of Acoustics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, which saw them develop a deep-learning algorithm that could improve the speed and precision of detection.
The algorithm, however, needs a large amount of data to work, so its use is limited to waters that have already been fully charted. In contrast, the upgrade works in all waters, charted or otherwise.
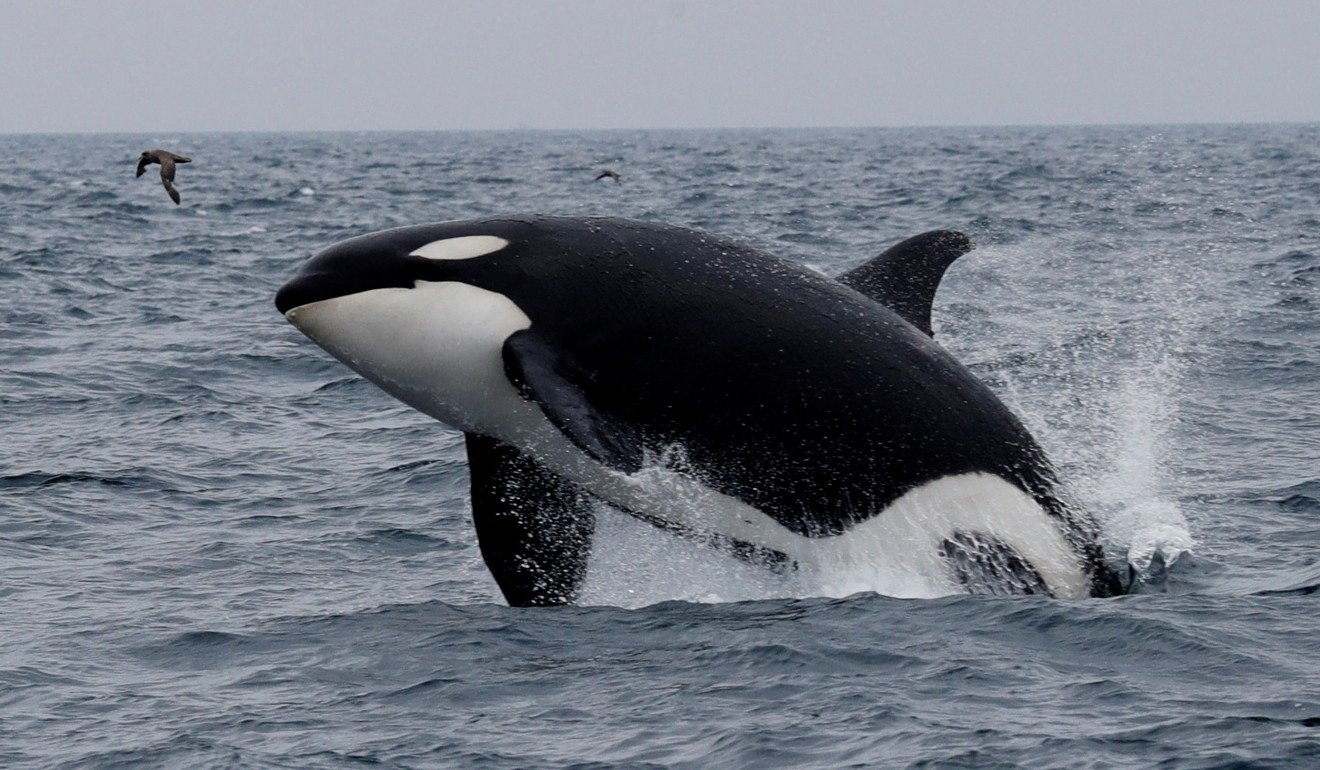
Even killer whales will be unable to hide from the new technology. Photo: Reuters
Niu and his colleagues, who included scientists from the Scripps Institution of Oceanography at the University of California San Diego, started by developing a simulator to generate a wide range of virtual environments from which the algorithm was able to learn.
Once it had assimilated that information, the simulator was able to analyse real-life data taken from the world’s oceans and seas, the team said in a paper published in the July issue of The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America.
It is now able to help a single hydrophone locate more than 80 per cent of underwater targets within an uncharted area with a margin of error of less than 10 metres (33 feet), the paper said.
Chinese monitoring devices installed near US submarine base
The researchers said the new technology should allow them to track any sound-emitting source – be it a nuclear submarine, a whale or even an emergency beeper from a crashed aircraft – using a simple listening device mounted on a buoy, underwater drone or ship.
The scientists worked together to improve the sensitivity and accuracy of passive underwater surveillance technology, according to the academy’s website.
The new technology might also be able to detect emergency beepers from crashed aircraft. Photo: AFP
Locating targets in unfamiliar waters is challenging because the AI relies on environmental data parameters such as underwater currents and seabed landscapes.
But obtaining such information is not easy, and often impossible.
For instance, the United States does not allow China to collect information in waters close to its west coast, while Beijing forbids the US from getting too close to its military facilities in the South China Sea.
Murder suspect ‘caught by AI software that spotted dead person’s face’
Professor Zhang Renhe, a researcher at the Institute of Acoustics who was not involved in the study, said the latest development was encouraging.
“AI can be a useful assistant to underwater target recognition,” he said. “In a way it is similar to the speech recognition technology on our mobile phones.”
But he said scientists were still wrestling with exactly how the technology worked.
“It is like a black box with some inner workings that are still unexplained,” he said.
Researchers were now working on ways to combine the new AI technology with the physical models for underwater target detection that have been developed in recent decades, Zhang said.
“This is a new frontier for fundamental science,” he said. “It requires international cooperation.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in AI technology, Beijing, breakthrough, buoy, China alert, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese monitoring devices, Chinese scientists, crashed aircraft, deep-learning algorithm, detect, develop, emergency beeper, hydrophone, Institute of Acoustics, international cooperation, listening device, military facilities, mobile phones, Murder suspect, nuclear submarines, researchers, San Diego, Scripps Institution of Oceanography, ship, sound-emitting source, South China Sea, speech recognition technology, submarines, subs, The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, Uncategorized, uncharted waters, underwater drone, underwater surveillance technology, underwater targets, United States, University of California San Diego, US scientists, US submarine base, west coast, whales |
Leave a Comment »
14/08/2019
- Researchers at academy of science believe electromagnetic wave model is key that will herald new era in radar detection and avoidance for military ships and aircraft
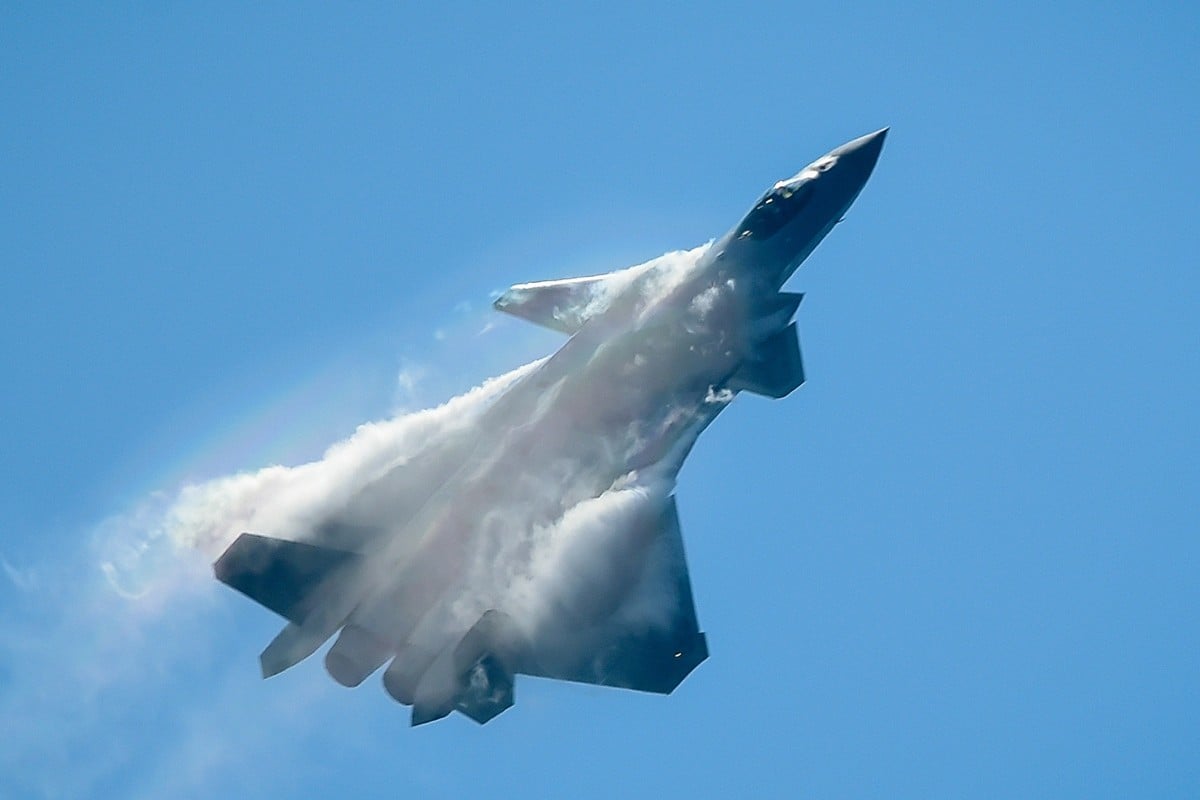
China’s J-20 stealth fighter. Photo: AFP
Chinese scientists have achieved a series of breakthroughs in stealth materials technology that they claim can make fighter jets and other weaponry lighter, cheaper to build and less vulnerable to radar detection.
Professor Luo Xiangang and colleagues at the Institute of Optics and Electronics, Chinese Academy of Sciences in Chengdu, Sichuan province, said they had created the world’s first mathematical model to precisely describe the behaviour of electromagnetic waves when they strike a piece of metal engraved with microscopic patterns, according to a statement posted on the academy’s website on Monday.
With their new model and breakthroughs in materials fabrication, they developed a membrane, known as a meta surface, which can absorb radar waves in the widest spectrum yet reported.
At present, stealth aircraft mainly rely on special geometry – their body shape – to deflect radar signals, but those designs can affect aerodynamic performance. They also use radar absorbing paint, which has a high density but only works against a limited frequency spectrum.
In one test, the new technology cut the strength of a reflected radar signal – measured in decibels – by between 10 and nearly 30dB in a frequency range from 0.3 to 40 gigahertz.
A stealth technologist from Fudan University in Shanghai, who was not involved in the work, said a fighter jet or warship using the new technology could feasibly fool all military radar systems in operation today.
“This detection range is incredible,” the researcher said. “I have never heard of anyone even coming close to this performance. At present, absorbing technology with an effective range of between 4 and 18 GHz is considered very, very good.”
China’s new radar system could spot stealth aircraft from at long range
The lower the signal frequency, the longer a radar’s detection range. But detailed information about a moving target can only be obtained with higher frequency radio waves. Militaries typically use a combination of radars working at different frequencies to establish lines of defence.
The Medium Extended Air Defence System, Nato’s early warning radar, operates at a frequency range of 0.3 to 1 GHz. The American Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system, the missile defence radar that caught Beijing’s attention when it was deployed in South Korea in 2017, operates at frequencies around 10 GHz.
Some airports use extremely short-range, high-frequency radars running at 20 GHz or above to monitor vehicle and plane movements on the ground, but even they might not be able to see a jet with the new stealth technology until it is overhead.
“Materials with meta surface technology are already found on military hardware in China, although what they are and where they are used remains largely classified,” the Fudan researcher said.
Professor Luo Xiangang. Photo: Baidu
Luo and his colleagues could not be reached for comment. But according to the academy’s statement and a paper the team published in the journal Advanced Science earlier this year, the stealth breakthroughs were based upon a discovery they made several years ago.
They found that the propagation pattern of radio waves – how they travelled – in extremely narrow metallic spaces was similar to a catenary curve, a shape similar to that assumed by chains suspended by two fixed points under their own weight.
China tests stealth ‘invisibility cloaks’ on regular fighter jets
Inspired by catenary electromagnetics, the team developed a mathematical model and designed meta surfaces suitable for nearly all kinds of wave manipulation.
These included energy-absorbing materials for stealth vehicles and antennas that can be used on satellites or military aircraft.
Zhu Shining, a professor of physics specialising in meta materials at Nanjing University, said the catenary model was a “novel idea”.
“The Institute of Optics and Electronics in Chengdu has conducted long-term research in this area which paved a solid foundation for their discoveries. They have done a good job,” Zhu said.
“Scientists are exploring new features of metal materials, some of them are already in real-life applications.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Advanced Science, aerodynamic, airports, American, blind, body shape, breakthroughs, catenary electromagnetics, Chengdu, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese scientists, discovery, early warning radar, fabrication, fighter jets, Fudan University, ground, hail, incredible, Institute of Optics and Electronics, invisibility cloaks, J-20 stealth fighter, materials, Medium Extended Air Defence System, membrane, meta surface, Military, Nanjing University, NATO, paint, performance, plane movements, radar absorbing, radar systems, Shanghai, sichuan province, South Korea, stealth breakthrough, Terminal High Altitude Area Defence system, Uncategorized, vehicle movements, warship |
Leave a Comment »
09/08/2019
WASHINGTON, Aug. 8 (Xinhua) — Chinese scientists discovered the oldest fossil forest in Asia, lending more clues to how those ancient plants evolved to become coal finally.
The study published on Thursday in the journal Current Biology reported the largest example of a patch of forest that grew in the Devonian period, which was 419 million to 359 million years ago.
It was made up of 250,000 square meters of fossilized lycopsid trees near Xinhang Town in east China’s Anhui Province.
The lycopsids in the fossilized forest resembled palm trees, and grew in a coastal environment prone to flooding. They were normally less than 3.2 meters tall, but the tallest one was estimated at 7.7 meters, according to the study.
Giant lycopsids would later thrive in a period that followed the Devonian, and became much of the coal that is mined today. The Xinhang forest in Anhui showed the early root systems, which made their height possible in the Carboniferous period (359 million to 299 million years ago), according to the study.
The forest also contributes to our understanding of atmospheric carbon dioxide decline and coastal consolidation at that time.
“The large density as well as the small size of the trees could make Xinhang forest very similar to a sugarcane field, although the plants in Xinhang forest are distributed in patches,” said the paper’s lead author Wang Deming, a professor in the School of Earth and Space Sciences at Peking University.
“It might also be that the Xinhang lycopsid forest was much like the mangroves along the coast, since they occur in a similar environment and play comparable ecologic roles,” said Wang.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in ancient plants, Anhui province, Asia, Chinese scientists, Current Biology, Devonian period, discover, ecologic roles, fossil forest, lycopsids, mangroves, oldest, palm trees, Peking University, School of Earth and Space Sciences, Uncategorized, Xinhang Town |
Leave a Comment »
13/06/2019
- Findings support earliest record of cannabis use, written in 440BC
- Researchers speculate psychoactive THC had role in grim funeral rites
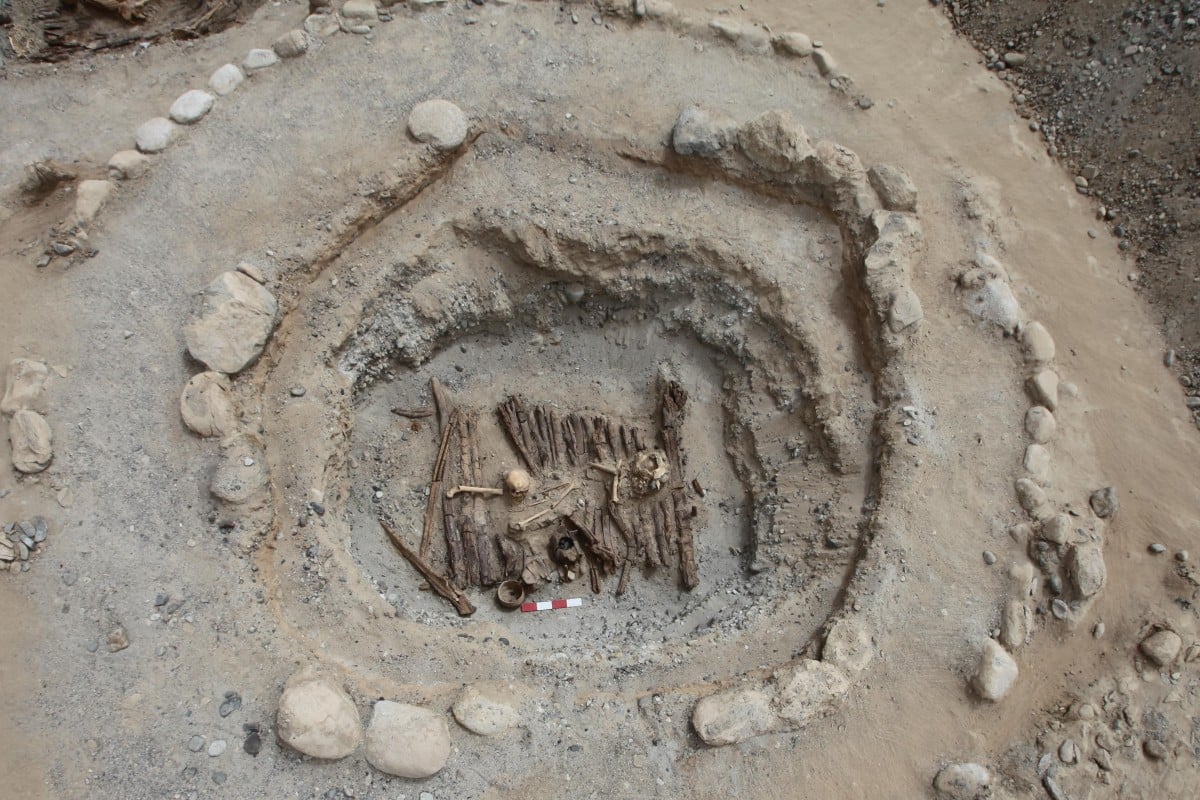
Researchers say their findings at a burial site in Xinjiang about cannabis use 2,500 years ago back up a Greek record written around 440BC. Photo: Handout
Scientists say a burial site in mountainous northwestern China contains evidence that cannabis smoke was used there as far back as 2,500 years ago, corroborating the earliest record of the practice, written by the ancient Greek historian Herodotus.
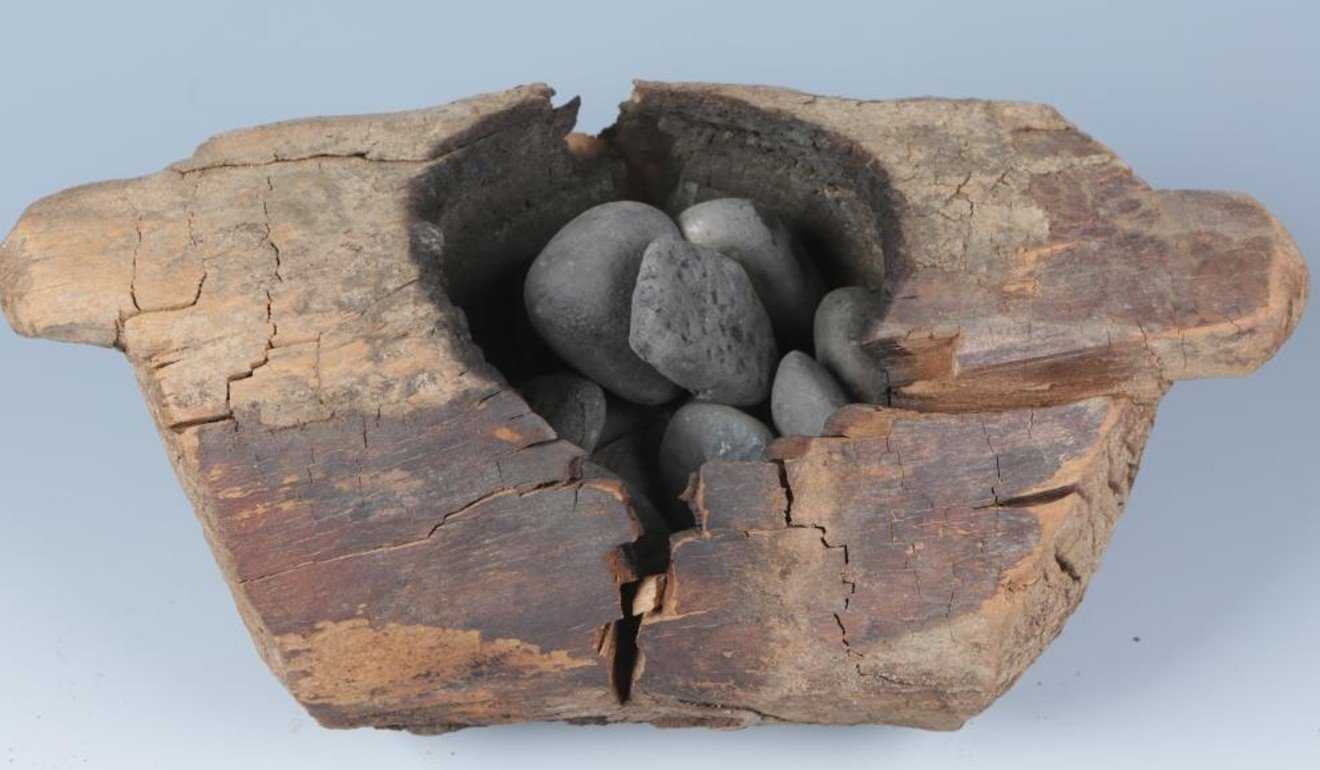
They said the evidence was found in a wooden bowl containing blackened stones unearthed at a Scythian cemetery in the Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region. Chemical analysis showed traces of THC – tetrahydrocannabinol – the potent psychoactive component in cannabis.
Yang Yimin, lead author of a paper published in the journal Science Advances on Thursday, said the discovery at Jirzankal Cemetery, close to the border of Tajikistan, Pakistan and India, was “jaw-dropping”.
Scythians were horseback warriors who roamed from the Black Sea across central Asia and into western China more than 2,000 years ago. Herodotus wrote in The Histories around 440BC that they used marijuana, the earliest written record of the practice.
Scientists in Xinjiang found hemp had been burned on stones inside these wooden bowls 2,500 years ago. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences and Max Planck Institute
“The Scythians take the seed of this hemp and … they throw it on the red-hot stones. It smoulders and sends forth so much steam that no Greek vapour-bath could surpass it.
The Scythians howl in their joy at the vapour-bath,” Herodotus wrote.
Yang, who led an international team of researchers from the Chinese Academy of Sciences, the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History in Germany and the University of Queensland, said that until now there was no evidence to back up the Greek historian’s account.
“There was never any archaeological proof to the claim. We thought – is this it?” Yang said.
The discovery posed a question for the research team: where would the plants have come from? While hemp was commonly found in many parts of the world and was used for fabric, cooking and medicine, most wild species contained only small amounts of THC.
Ruins of 2,000-year-old coin workshop found in central China’s Henan province
Yang and his colleagues speculated that the altitude, 3,000 metres (9,843 feet) above sea level, and strong ultraviolet radiation might have resulted in a potent plant strain with THC levels similar to those in marijuana today.
“From here it was selected, probably domesticated and then went to other parts of the world along ancient trade routes with the Scythian nomads, forming an enormous ring of culture that shared the ritual of smoking cannabis,” Yang said.
Archaeologists said the site, with its 40 circular mounds and marked by long strips of black and white stones, could have been a burial ground for tribal members, with human sacrifice and cannabis part of the last rites.
Researchers suspect a potent strain of cannabis grew close to the Xinjiang burial site. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences and Max Planck Institute
So the early pot party might not have been the kind of celebration Herodotus described, the study’s authors suggested.
While the Scythians might have been inhaling the smoke to try to communicate with the dead in the next world, evidence suggested that a sacrifice – perhaps a war captive or a slave – was struck repeatedly on the head with a sword and the body hacked to pieces nearby, the researchers said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in cannabis, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese scientists, evidence, first stoners, found, Germany, graveyard, Greek record, grim funeral rites, hemp, Henan province, Herodotus, human sacrifice, India alert, Jirzankal Cemetery, marijuana, Max Planck Institute, Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, Pakistan, psychoactive THC, Science Advances, Scythians, Tajikistan, tetrahydrocannabinol, ultraviolet radiation, Uncategorized, University of Queensland, vapour-bath, Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region |
Leave a Comment »
04/06/2019
- Study of children prone to recurring colds identifies abnormally high presence of skin affecting bacteria
- More research needed but study holds out prospect of future treatments
Scientists in China believe they have identified the reason why some children repeatedly catch the common cold. Photo: Shutterstock
A team of Chinese researchers has found that an acne-causing parasitical microorganism could be the reason some children catch colds more frequently than others.
Professor Zhang Chiyu and his colleagues at the Institute Pasteur of Shanghai, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, have found that a bacterium known as Propionibacterium is closely related to recurring infections, raising the possibility of future drugs or treatments, according to their paper in the May issue of Nature Communications.
The scientists analysed clinical samples from 4,407 children diagnosed with the common cold during a period of six years, from 2009 to 2015, at Nanxiang Hospital in Shanghai, and found an abnormally high presence of the bacterium.
Propionibacterium is a parasite microorganism usually found on human skin. It can cause acne and other skin problems. Some forms of the bacteria are also used to create the holes in some popular varieties of cheese.
A computer illustration of Propionibacterium, a microorganism known to cause acne and other skin problems, and now implicated in frequent colds in some children. Photo: Alamy
Zhang said the research team had found an abnormally high presence of Propionibacterium phages – a signature virus which uses the bacterium as a host – in the clinical samples, and it was likely the large colonies of the microorganism had thrived in the sick children’s respiratory ducts.
The imbalance between different microorganism groups could lead to more frequent, prolonged inflammation and cause further damage on respiratory tissues, he said.
“Living environment can be something worth checking,” Zhang said, suggesting that parents could reduce unnecessary exposure of their children to Propionibacterium infections by keeping them from kissing faces with pimples.
The common cold kills four million children under the age of five worldwide every year.
Frequent recurrence of the common cold is not uncommon. Causes for the phenomenon remain very much unknown, in part due to the difficulty of obtaining a large number of blood samples from under-aged patients.
China is making better, cheaper drugs – and its reasons may surprise you
Zhang said some uncertainties remained following the study and cautioned that the results were imperfect. For example, the quality of some samples was not ideal, due to a long period of refrigeration, and the interactive mechanism between the bacterium and infection was not entirely clear.
The findings “should not be immediately applied in clinical practice,” Zhang said.
A confirmation study is underway to monitor the conditions of selected child patients over the next two years and, if the results are positive, a testing kit may soon be available to identify children more vulnerable to recurrent colds, he said.
Medical intervention such as therapy or drugs may also be developed to address the issue of bacterium imbalance.
Antibiotic overdose is a severe problem in China and rest of the world, Zhang said. “Hopefully our study will help find a precise target,” he added.
Source: SCMP
Posted in acne, bacteria, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese scientists, common cold, find link, Institute Pasteur of Shanghai, Nanxiang Hospital, Propionibacterium, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
09/03/2019
- Researchers say they spend so much time on grant applications that they get no time to do science
- Funding applications are said to be too onerous and inflexible
Chinese scientists say funding applications are too onerous and restrictive. Photo: Xinhua
Chinese scientists are appealing for a bigger say over research funding as they buckle under a rigid and bureaucratic application system.
The appeal from delegates to the country’s peak advisory body, the Chinese People’s Political Consultative Conference, comes as the central government prepares to launch a pilot project that will give research teams greater flexibility in the way funds are used.
Despite slowing economic growth, the central government also plans to increase the budget for science and technology by 13.4 per cent this year to 354.31 billion yuan (US$52.7 billion) as Beijing tries to challenge the United States in the race for high technology.
But researchers have been hampered by a funding structure that demands they clearly state the use of their research and submit a detailed plan with a deadline for delivery of results.
Application rules have become stricter in the last few years, partly a result of a crackdown on corruption, which has led to a dozen university presidents and top scientists being arrested for embezzling research and infrastructure funding.
Chinese science minister warns scientists not to overstep ethical bounds after He Jiankui’s gene-edited babies scandal
CPPCC delegate Yuan Zhiming, an agricultural scientist from the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Wuhan, said he spent so much time filling out funding applications that he did not have time to do any research.
“It’s not easy to complete the budget with detailed outcomes, because I don’t already know my research results,” Yuan said in an open panel discussion on the sidelines of the CPPCC.
Wang Liming, a CPPCC delegate from China National Nuclear Corporation, agreed, saying funding applications were too onerous and inflexible. “Money earmarked for buying soy sauce cannot be used to buy vinegar,” he joked.
People’s Daily, the Communist Party’s mouthpiece, reported in December 2016 that it took a scientist a month to finish an annual report for a regular research project and much longer for a major one.
The fears about more bureaucracy in research intensified last year when the National Natural Science Foundation – which manages science funding and promotes research – was downgraded and put under the Ministry of Science and Technology.
The authorities said the change was aimed at strengthening the government’s “research-driven development strategy” and “optimising the distribution of funding on science and technology”, while scientists said it meant funding approval would be more stringent.
China’s science and tech minister calls on private enterprises to develop ‘core technologies’
But senior Chinese officials said they understood the need to speed up research for China to transform itself into an innovation powerhouse.
Science and Technology Minister Wang Zhigang said on Friday that China would overhaul the way funding was managed to give researchers more incentives.
“The ministry [of science and technology] has done a series of things to ease the burden on researchers, so that they will not be bothered by forms, reimbursements, titles and prizes and have more time to do real research,” Wang said.
“The upcoming reforms will be centred on how to ignite researchers’ enthusiasm, initiative and creativity.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in agricultural scientist, Beijing, buying soy sauce cannot be used to buy vinegar, China alert, China National Nuclear Corporation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese People's Political Consultative Conference, Chinese scientists, Communist Party’s mouthpiece, CPPCC delegate, He Jiankui, Ministry of Science and Technology, National Natural Science Foundatio, People’s Daily, Red tape, research funding, rigid and bureaucratic application system, science and tech minister, Science and Technology Minister, Uncategorized, United States, Wang Liming, Wang Zhigang, Wuhan, Yuan Zhiming |
Leave a Comment »
26/02/2019
QINGDAO, Feb. 26 (Xinhua) — China has launched a project for the large-scale cultivation of salmon in the cold water mass of the Yellow Sea to cater to growing seafood demand in Chinese markets.
The project will build a salmon farm about 130 nautical miles off the shore of Rizhao in east China’s Shandong Province, with the aim of producing 45,000 tonnes of salmon annually, said Dong Shuanglin, a professor at the Ocean University of China and the project’s chief scientist.
Initiated by the university and two Chinese firms, the project involves a total investment of over 4.3 billion yuan (642 million U.S. dollars) and has demarcated a cultivation area of 3,000 hectares.
It plans to erect the “Shenlan 2” salmon cage in the second half of this year, following a successful trial of salmon farming at “Shenlan 1,” the world’s largest fully-submersible fish cage.
The “Shenlan 2” cage is 80 meters tall, compared with the 35 meters of “Shenlan 1,” and can accommodate 1 million fish, a large increase from its predecessor’s 300,000, according to Dong.
The project also includes the construction of an onshore industrial park, R&D facilities and a fry cultivation base. The first batch of salmon from the farm is scheduled to hit the market by the end of 2020.
Chinese scientists have in recent years started to test rearing salmon in the Yellow Sea’s cold water mass, a seasonal low-temperature water body, as the country’s offshore fish farming faces a lack of space, disease outbreaks and other environmental problems.
The 13-million-hectare cold water mass in the Yellow Sea is large enough to raise 500 million salmon, and its strong self-purification means lower risks of diseases and parasite outbreaks, according to the university.
Salmon farming in that sea area is also expected to herald a new trend in China’s marine aquaculture following seaweed, shrimp, shellfish, fish and sea cucumber, while offering a platform for cooperation with countries like Norway and Japan in farm management, diseases and parasites control, according to sources familiar with the industry.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in aquaculture, China alert, Chinese scientists, diseases, farm management, fish cage, fully-submersible, Japan, Norway, parasites control, Rizhao, salmon farming, sea cucumber, seaweed, self-purification, shandong province, shellfish, Shenlan 1, Shenlan 2, shrimp, Uncategorized, Yellow Sea |
Leave a Comment »