The Republic of Congo has since restructured its borrowings from China, which holds about a third, or US$2.5 billion, of the Congolese debt, by extending the repayment period by an additional 15 years.
A number of other African countries struggling to service their loans from Beijing have also pursued concessions. Ethiopia has had part of its Chinese debt written off and terms relaxed for the US$3.3 billion loan it took to build its railway, while Zambia is seeking similar adjustments for its borrowings used to build airports and highways.
Critics say countries on the continent are being burdened with unrealistic levels of debt for inviable infrastructure backed and built by China without adequate transparency and scrutiny.
The biggest concern is that several African countries will be left with huge debts and grandiose infrastructure that they cannot maintain and run profitably. I liken it to borrowing money to buy a Tesla when you don’t have adequate access to electricity: Obert Hodzi of the University of Helsinki in Finland
But Chinese observers say the West must take some of the blame for the countries’ debt problems and that the support China offers will benefit the host countries in the long run.
In the early 1990s, when China began to embrace Africa again after years of isolation from the outside world, the aspiring manufacturer was at a serious disadvantage in the race for raw materials and markets for its industrial goods.
The former colonial powers of the West had already sewn up deals for many of the continent’s most lucrative and readily exploitable reserves, from fossil fuels to minerals.
China needed new strategies to convince African governments to allow it access raw materials for its industries and markets for its products to a largely unfamiliar partner.
China also wanted to challenge the dominance of the US in global trade and politics so it courted allies in Africa to help it push for political legitimacy in international institutions.
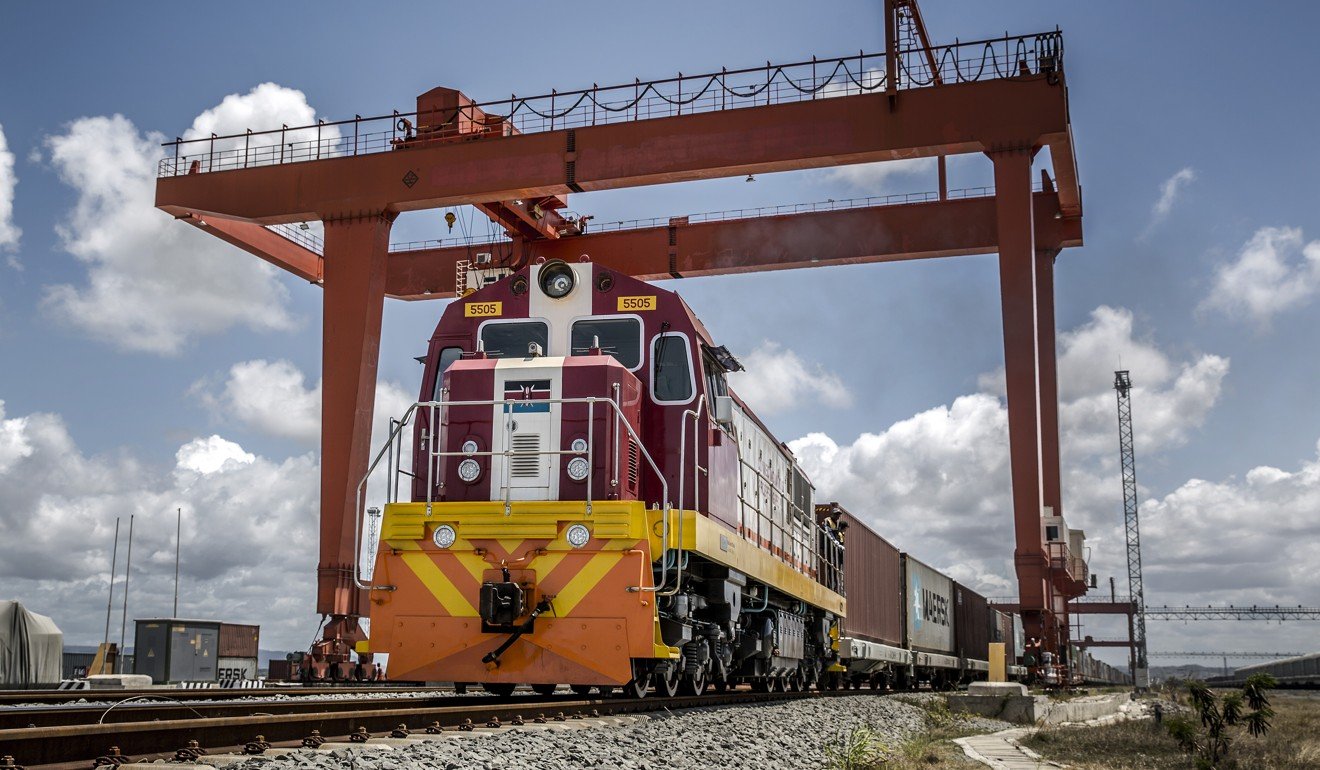
A Kenya Railways freight train leaves the port station on the Mombasa-Nairobi railway in Mombasa, Kenya, a huge project backed by China. Photo: Bloomberg
At the time, many African leaders were under fire to liberalise their economies. China’s approach was to promise not to meddle in individual country’s internal affairs and assure African countries that they could get billions in exchange for future delivery of minerals through resource-backed deals.
Beijing sold its policies that it had no conditions attached to its development finance. In the drive to drum up business, China promised affordable loans for African countries to build roads, bridges, highways, airports and power dams.
Is Kenya’s Chinese-built railway a massive white elephant?
But Beijing also pursued tied finance, ensuring that countries borrowing from China used Chinese contractors to implement the projects rather than open them up to outside bids.
In addition, many of the deals were built on weak financial, technical and environmental conditions, with Chinese state firms conducting the technical feasibility, environmental impact assessment and financial viability studies for free for projects that they also build.
For example, in Kenya, the China Road and Bridge Corporation conducted a free feasibility study that was used in the construction of the railway.
The same company was handed the contract to implement the project and is operating both the passenger and cargo train service for a fee.
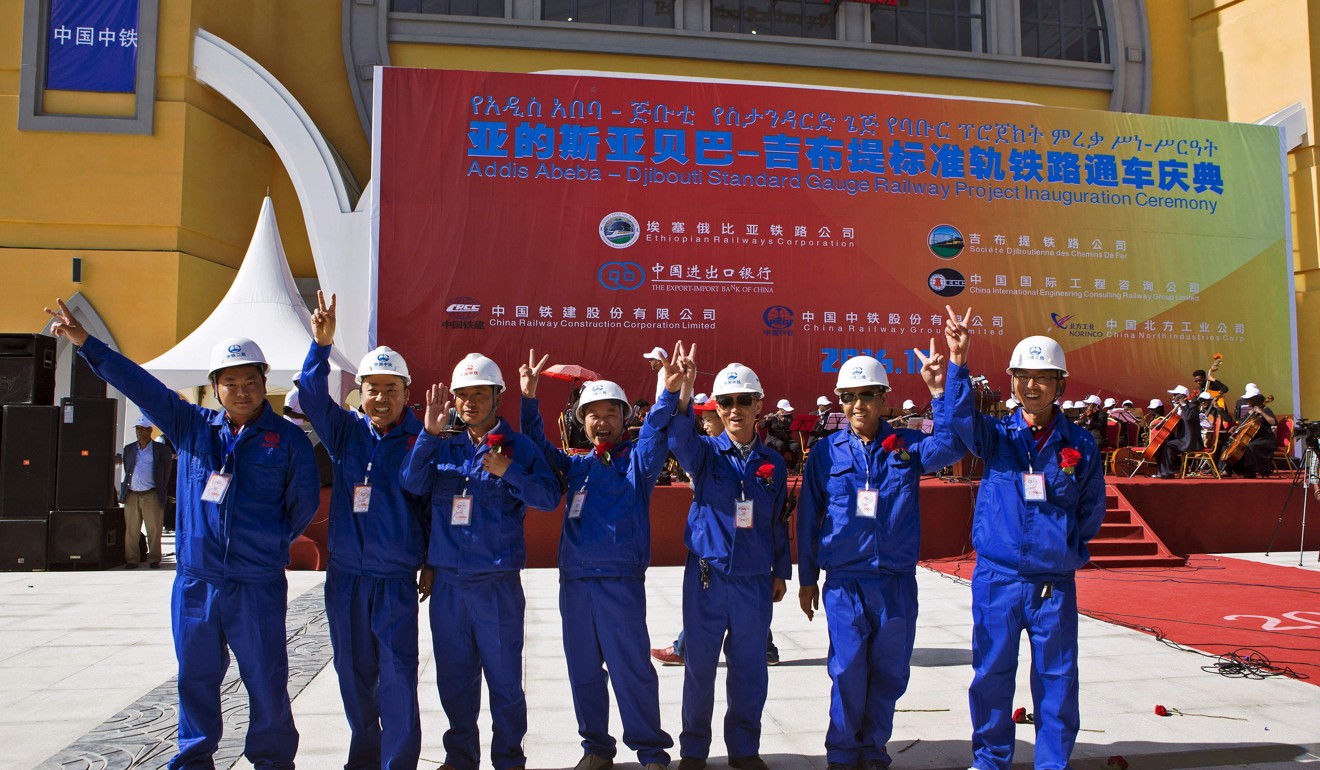
Chinese companies were responsible for the construction of a rail line between Addis Ababa and Djibouti. Photo: AFP
In contrast, the World Bank and its partner institution, the IMF, demand that such studies be done by an independent consultant and not by the company that implements the project.
According to data compiled by the China-Africa Research Initiative, at the Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies, Beijing has advanced loans worth US$143 billion to African countries since 2000, levels that some critics say are unsustainable for the borrowers.
China meets resistance over Kenya coal plant, in test of its African ambitions
For many of China’s new African partners, these arrangements – from easy lending terms, to non-competitive bidding and opaque contract details – have led to new problems – problems that corrupt or poorly managed governments now share substantial responsibility.
Some critics, both in the West and in host countries, suggest there is a “debt-trap strategy” at the heart of Beijing’s push for international business and influence, but there is no evidence that China deliberately pushes other countries into debt to seize their assets or gain sway.
However, the drive for overseas contracts and big business has led some countries into difficulties with new debts, and there are question marks over the viability of many of the projects the money is funding.
Obert Hodzi, an international relations expert at the University of Helsinki in Finland, said the Addis Ababa-Djibouti railway and the Mombasa-Nairobi railway were good examples of huge projects that were financed by easy borrowing terms from China but were not sustainable and that had in turn forced the African partners to seek further Chinese help.
“The biggest concern is that several African countries will be left with huge debts and grandiose infrastructure that they cannot maintain and run profitably,” Hodzi said. “I liken it to borrowing money to buy a Tesla when you don’t have adequate access to electricity.”
Ken Opalo, a Kenyan scholar at Georgetown University in Washington, said the key issue was the inability of African countries to design projects that were actually needed for the local economies.
A road is not just a means of transport but an economic belt or corridor that will catalyse the development of the whole region: Huang Xueqing, spokeswoman for the Chinese embassy in Nairobi
“Most African countries have been willing to accept projects designed, financed, and implemented by Chinese firms,” Opalo said.
“It would be better to decouple the feasibility studies and design phases of projects from the financing. That way African governments can ensure that they are truly getting value for money.”
But Chinese officials said Beijing had invested in infrastructure largely at the request of the host countries, adding that it could take time to yield returns on the projects.
Huang Xueqing, spokeswoman for the Chinese embassy in Nairobi, said the projects were valid assets with value that would grow in time.
“So, in the long run, it is beneficial to the host countries. Just like when young people buy a house with a mortgage, they may take some debts, but they have a place to live in and have their own assets,” Huang said.
“Underdeveloped infrastructure is the bottleneck that has been holding back Africa’s development. Up to today, many African countries, although in the same continent, are not connected with direct flights, railways or even roads. You have to fly to Paris or Zurich in order to get to some African countries.
“A road is not just a means of transport but an economic belt or corridor that will catalyse the development of the whole region.”
Huang said Beijing had advised the countries to act within their means and not to overstretch themselves when they considered projects that might not be in line with local conditions.
“When making investment decisions, the Chinese side, along with the recipient countries, carry out rigorous feasibility studies and evaluations. We do things according to our ability,” she said.
China’s leadership has also said it is paying close attention to the fiscal and financial difficulties faced by some African countries.
“As a good friend and good brother … the Chinese side is willing to lend a helping hand when needed by the African people to help them overcome temporary difficulties,” State Councillor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi said in January while on a trip to Ethiopia, adding that the debt situation in Africa is also a legacy issue.
China must allay any debt-trap fears in its dealings with Africa
“The African debt issue does not come up today, still less is it caused by the Chinese side. The African people know who are the initiators of African debt.”
The West should take a lot of the blame for worsening debt problems in some African countries, according to Li Anshan, from Peking University’s Centre for African Studies.
He cited the cases of Liberia and the Democratic Republic of Congo, two countries that have had close relations with the West for many years but remain ravaged by war and poverty despite immense natural resources.
“China-Africa relations have been going on for quite some time. Is there any African country which has got poorer because of its deal with China?” Li said.
Gyude Moore, a former Liberian minister of public works whose department oversaw construction and maintenance of various public infrastructure funded and built by China, said it would be difficult to imagine that China would knowingly ensnare its partners in debt.
“China attempts to differentiate itself from Western donors by limiting non loan-related conditionality. China also practices non-interference, so how a country manages its resources, treats its people or deploy its finances were considered ‘internal’,” he said.
“So, Chinese loans are negotiated faster and place less emphasis on public financial management.”
Moore, now a visiting fellow at the Centre for Global Development, said there were trade-offs in such situations.
China focuses on sustainable projects to dismiss fears of African debt trap
“If the loans are going to be fast – the due diligence will not be as rigorous. Chinese project selection mixes political with economic considerations. So, while a project may not make as much economic sense, it may pay political dividends,” he said.
He said non-transparent processes would invite abuse, be they Chinese, Western or African.
Other observers say the question of opacity is more directly related to China’s own economic system.
Howard French, author of China’s Second Continent: How a Million Migrants are Building a New Empire in Africa, said China has very limited transparency and public accountability in its own domestic processes.
The Mombasa railway station is seen in Mombasa, Kenya, in 2018. Photo: Xinhua
“So it would be unusual to expect that China would introduce greater transparency and accountability in its dealings with African countries than it is used to at home – that is, unless African governments insist on it,” French said.
“And this is where African governance comes in. African states should insist on contract transparency but often don’t do so because that offers leaders plentiful opportunities for graft.”
David Shinn, professor of international relations at George Washington University in Washington, agreed that China’s lack of loan transparency was a huge problem and increased the risk of corruption on both the African and Chinese sides. But he also said that in some cases, African governments might have negotiated poorly.
“This is, however, the responsibility of the African government. I don’t think China is purposely trying to encourage African debts in order to gain leverage,” Shinn said.
“In fact, China is becoming more careful about its lending because it is concerned it has made too much credit available to some African countries.”
China ‘ready to talk’ about trade deal with East Africa bloc
Huang Hongxiang, director of China House, a Nairobi-based consultancy that helps Chinese in Africa integrate better, agreed, saying the Chinese government needs to communicate more about projects in Africa but African countries also have a bigger part to play in ensuring better deals.
“On commercial viability, accountability, transparency and governance, I believe the responsibility does not lie with China, the US or the West but in the hands of African countries,” he said.
Wherever the fault lies, one thing is clear when money is wasted on ill-designed projects that have little to no economic return, according to Opalo.
“The lack of planning and transparency creates default risks … [and] African taxpayers will be left holding the bag.”
This article is the third in a series examining the local impact of Chinese investment and infrastructure projects in Africa. Read part one here and part two
The next report will examine whether African countries can speak with one voice in relations with China.
Source: SCMP
 Image copyright EPA
Image copyright EPA