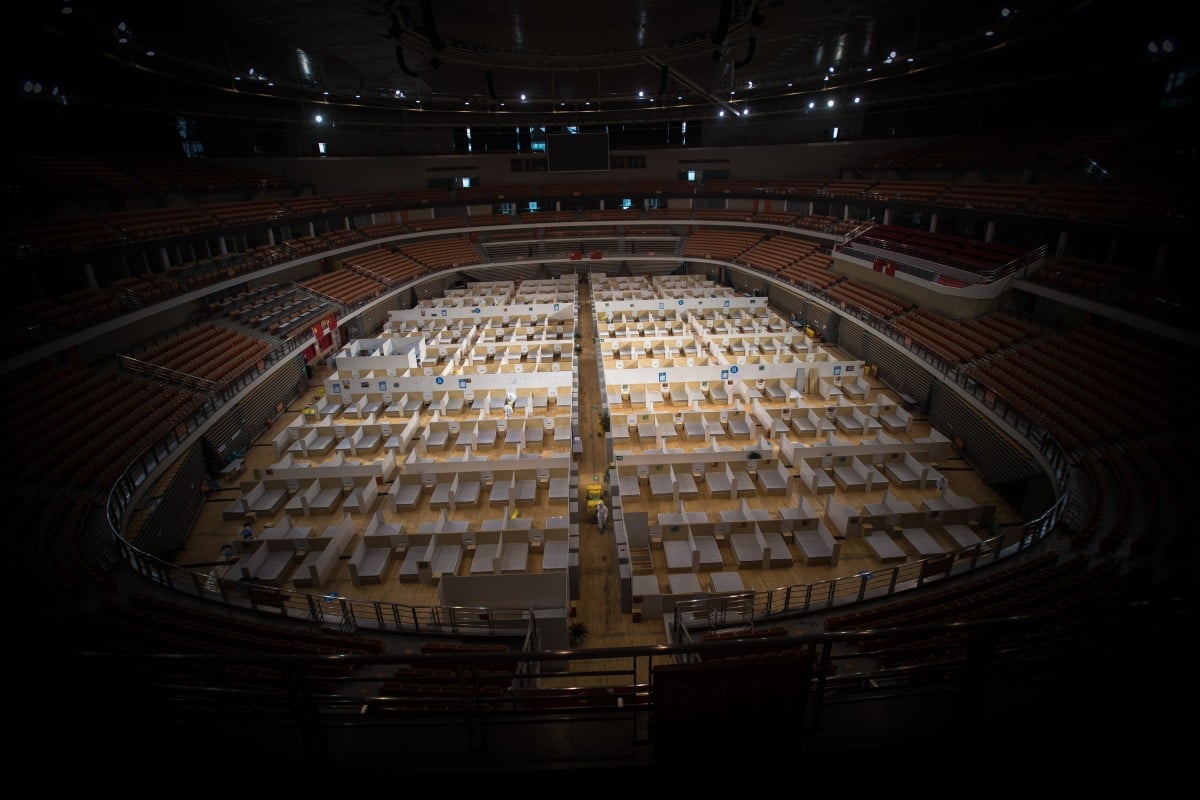
- Throughout the world, overworked health care professionals are being infected with Covid-19, yet the Lion City has kept numbers low
- Preparation, planning, patient ratios and protective equipment have all played a part. Still, even the best gear cannot guard against discrimination
Health care staff in the country say patients are packed into emergency wards and intensive care units (ICUs), further raising the risk of infections. They also report shortages of ventilators, face masks, gowns and shields.
The US Centres for Disease Control and Prevention on March 7 released interim guidelines saying health care workers exposed to the coronavirus could be asked to return to work as long as they wore face masks and were not showing symptoms, if their employers had no other manpower available.

Experts suggest this has been more than just luck, pointing to a case in which 41 health workers were exposed to the coronavirus in a Singapore hospital yet evaded infection.
The workers had all come within two metres of a middle-aged man with Covid-19 who was being intubated, a procedure which involves a tube being inserted into the patient’s trachea. The procedure is seen as being particularly hazardous for health workers as it is “aerosol generating” – patients are likely to cough.
The workers had not known at the time that the man had the virus and all were quarantined after he tested positive. However, on their release two weeks later, none of them had the virus.
Coronavirus: as Malaysia braces for third wave, doctors make their own face masks

The case has come to widespread attention partly because the workers were wearing a mix of standard surgical masks and the N95 mask, which doctors see as the gold standard as it filters out 95 per cent of airborne particles.
The conclusion, published in The Annals of Internal Medicine this month, was this: “That none of the health care workers in this situation acquired infection suggests that surgical masks, hand hygiene, and other standard procedures protected them from being infected.”
Surgeon and writer Atul Gawande mentioned the case in an article for The New Yorker on how health care workers could continue seeing patients without becoming patients. He said there were things to learn from Asia and that some of the lessons came out of the “standard public health playbook”. In other words, there is much to be said for social distancing, basic hand hygiene and cleaning regimens.

In a webinar organised by Caixin Global on Thursday night, Peng Zhiyong, an intensive care specialist at Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University, shared how they managed a shortage of personal protective equipment early on in the outbreak by rationing workers to two sets of gear per shift.
Meanwhile, in the Philippines, doctors from Manila’s Chinese General Hospital held a video conference call with doctors in Zhejiang to learn from China’s experience of treating Covid-19 patients.
Crowdsourcing platforms have also been created to share advice. The Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston has released guidelines for treating critically ill patients and its website includes information from Chinese doctors.
Why Singapore’s coronavirus response worked – and what we can all learn

The Jack Ma Foundation has also launched an online platform for doctors and nurses around the world to share knowledge on fighting the virus. “One world, one fight,” it said in a tweet.
Associate Professor Jeremy Lim from the global health programme at the Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health said it was crucial for countries to work together.
“Viruses don’t respect borders. Countries have to share information and help each other as we are only as strong as the weakest link. Any country can become a reservoir of disease and the world may then be forced to endure a ping-pong of outbreaks over and over again.”
And the advice of Lee, at Singapore’s Ministry of Health? “Practise good hygiene and wash hands regularly.”

Singapore has 13,766 doctors, or 2.4 doctors for every 1,000 people. That compares to 2.59 in the US, 1.78 in China and 4.2 in Germany. Places like Myanmar and Thailand have fewer than one doctor for every 1,000 people.
Coronavirus: Covid-19 could live on in Indonesia long after world recovers

“The objective is that you can run essential services with the greatest amount of security. Make sure functional units have redundancy built in, and are separate from each other. It depends on what you feel is sufficient to carry on services if one team is affected, factoring in rest periods and some system of rotation,” said Chia Shi-Lu, an orthopaedic surgeon.
The key is to ensure a good doctor-to-patient ratio and ensure there are enough specialists for the critical work, such as doctors and nurses who can provide intensive care, and know how to operate mechanical ventilators or machines to pump and oxygenate a patient’s blood outside the body.
At the emergency department where paediatrics emergency specialist Jade Kua treats Covid-19 cases in addition to regular emergencies, doctors are split into four teams of 21. Each team takes alternate 12-hour shifts and does not interact with other teams.
“We are in modular teams so the teams move together. So you and I would both do morning, off, night, off, morning off. Together. And then the other teams would do the same and we don’t intermingle,” said Kua.

In contrast, Singapore published its first Influenza Pandemic Preparedness and Response Plan in June 2005 and has since honed it to a tee. Hospitals regularly war-game scenarios such as pandemics or terrorist attacks and the simulations are sometimes observed by the Ministry of Health, which grades the performance and recommends areas for improvement.
The plan also covers the need to stockpile equipment to avoid the sort of shortages many countries are now facing, another lesson inspired by Sars when masks, gloves and gowns were in short supply.
In a pandemic preparation paper published in 2008, Singapore public health specialist Jeffery Cutter wrote that Singapore’s stockpile was sufficient to cover at least 5 to 6 months’ use by all front-line health care workers.
During the Covid-19 outbreak, it has also told citizens to not wear masks so it can conserve supply for medical staff.
Having enough protective gear has reassured Singapore’s health care workers such as Kua, a mother of six who blogged about her experience fighting Covid-19. Kua said: “I’m safe and my family is safe.”
There is a similar stigma in India, where the All India Institute of Medical Sciences has appealed to the government for help after health workers were forced out of their homes by panicked landlords and housing societies.
“Many doctors are stranded on the roads with all their luggage, nowhere to go, across the country,” the institute said in a letter.
Lim, from the Saw Swee Hock School of Public Health, said the worst human impulses and “every man for himself” attitudes could emerge in crises and “that is exactly why governments have to step in”.
Discrimination could affect both the performance and motivation of health care workers, Lim warned.
Meanwhile, when health care workers are infected, it creates a “triple whammy” threat.
“It means one fewer professional in an already-strained system, another patient to care for and, potentially, a team of colleagues who need to be quarantined,” said Lim.
“We must do everything possible to keep our health care workforce safe and free from Covid-19.” ■
Source: SCMP