18/04/2020
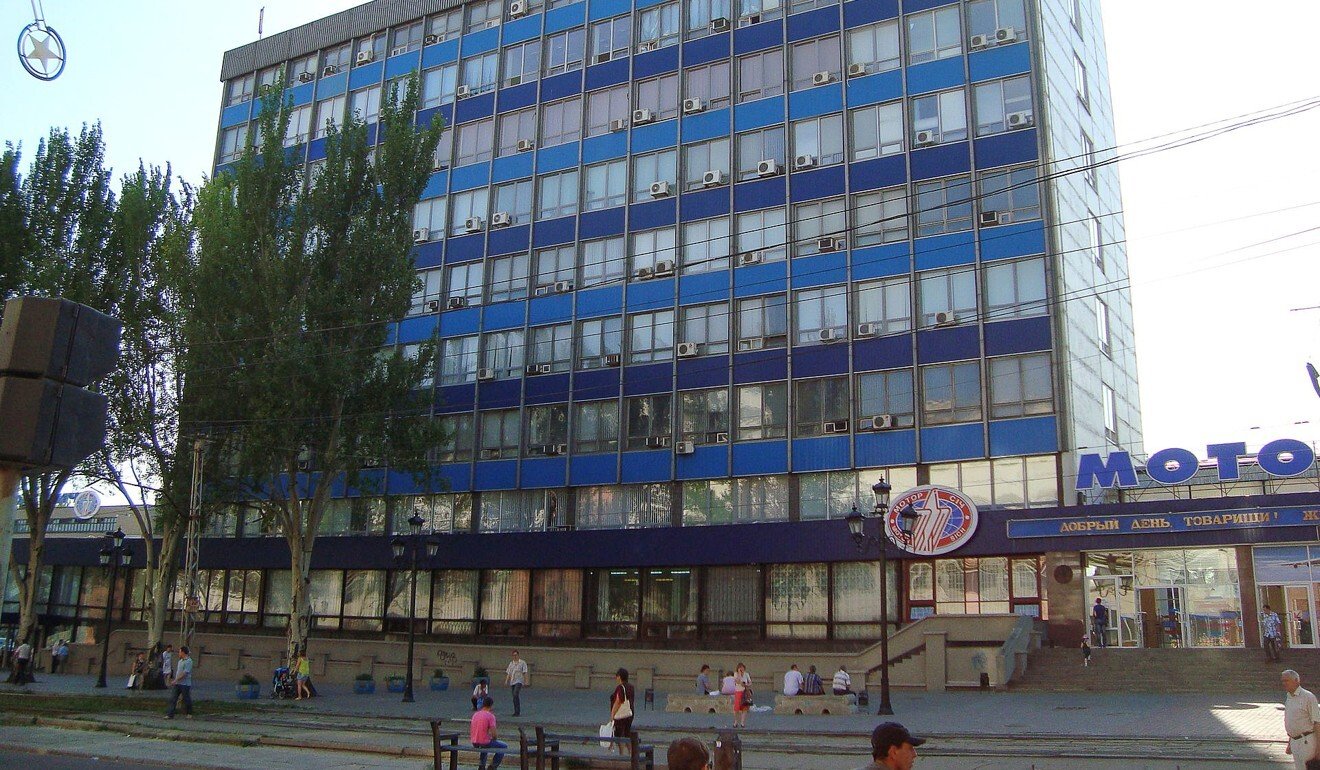
- China’s Skyrizon Aircraft Holdings bought a majority stake in Motor Sich, but the shares were frozen in 2017 pending an investigation by Ukraine’s security service
- Washington and Beijing have competed for influence in Ukraine since its relations with Moscow soured when Russia annexed the Crimea peninsula in 2014
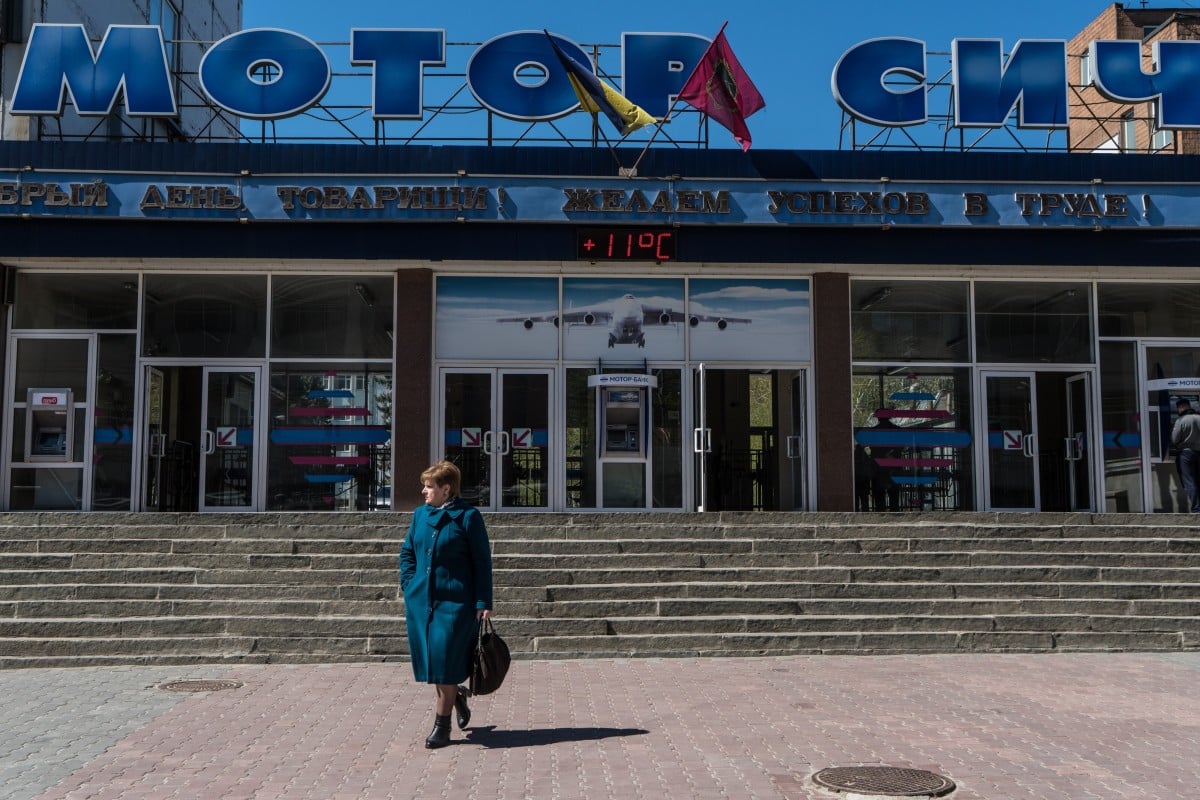
Chnia’s Skyrizon says it will appeal a Kiev court’s decision to block its purchase of Ukrainian aircraft engine maker Motor Sich. Photo: Getty Images
A court in Kiev has rejected an appeal by Chinese investors to unfreeze the shares of a Ukrainian aircraft engine maker, a setback for the Chinese company that sought to buy the Ukrainian firm in a deal opposed by the United States.
China’s Skyrizon Aircraft Holdings bought a majority stake in Motor Sich, but the shares were frozen in 2017 pending an investigation by Ukraine’s security service (SBU). Washington wants the deal scrapped.
The US and China have competed for influence in Ukraine since its relations with Moscow soured when Russia annexed the Crimea peninsula in 2014.
In its ruling, the court kept the shares frozen, citing the SBU investigation into whether selling Motor Sich sabotages national security by allowing sensitive technology into foreign hands. The ruling was dated March 13, shared with the parties this week.
Skyrizon plans further appeals, said a lawyer involved in the case, speaking anonymously due to the political sensitivity of the case. Zelensky’s office, the US embassy and the Chinese embassy did not respond to requests for comment. Motor Sich and the SBU declined to comment.
Motor Sich severed ties with Russia after the annexation of Crimea. Photo: Wikipedia
Motor Sich severed ties with Russia, its biggest client, after the annexation of Crimea. The wrangle over its future has held up efforts to find new markets, and supporters of a quick resolution say it is now operating at less than half capacity.
“Motor Sich has become a hostage to the geopolitical situation,” former prime minister Anatoliy Kinakh, chairman of an industrial union which has called for the government to resolve the dispute quickly, said.
The state’s anti-monopoly committee has launched its own investigation and says it is waiting to receive more documents before deciding whether to sanction the sale.
President Volodymyr Zelensky’s administration has had to balance strengthening ties to Beijing with keeping the United States, its biggest military aid donor, onside. In recent weeks, Beijing and Washington have both offered aid to Ukraine to fight the
coronavirus.
At the moment it is a very difficult task when we have the biggest powers in the world and their interests are in conflict in Ukraine,” Oleksandr Danylyuk, a former top security official under Zelensky, said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 2014, 2017, administration, Aerospace, Aid, aircraft engine maker, allowing, annexed, anonymously, anti-monopoly committee, appeal, balance, Beijing, biggest, both, bought, China’s, Chinese appeal, Chinese embassy, competed, coronavirus, court, court’s decision, Crimea peninsula, deal, dispute, documents, fight, firm, foreign hands, frozen, geopolitical situation, Government, influence, investigation, investors, keeping, Kiev, launched, Lawyer, majority, military aid donor, Moscow, Motor Sich, National security, offered, onside, opposed, political sensitivity, President Volodymyr Zelensky’s, purchase, quickly, recent, rejects, relations, resolve, Russia, sabotages, sale, sanction, security service, security service (SBU), sensitive, shares, Skyrizon, Skyrizon Aircraft Holdings, soured, stake, strengthening, Technology, ties, to block, Ukraine, Ukraine’s, Ukrainian, Uncategorized, unfreeze, United States, US embassy, Washington, weeks, Zelensky |
Leave a Comment »
27/11/2019
- But Washington still commands more diplomatic influence, analyst says
- Beijing extends its reach as its interests grow abroad and as Taipei loses allies
China has 276 embassies, consulates and other missions around the world, surpassing the US with 273 missions, according to a global index. Photo: AP
China has overtaken the United States to have the biggest number of diplomatic outposts around the world, as its international ambitions and economic interests expand.
According to the 2019 Global Diplomacy Index, released by the Lowy Institute in Australia on Wednesday, China has 276 embassies, consulates and other missions globally, surpassing the US with 273 missions. France was third on 267.
Bonnie Bley, the index report’s lead researcher, said that while a country’s total did not equate to diplomatic influence, “diplomatic infrastructure is still important”
“China’s newly held lead serves as a telling metric of national ambition and international priorities,” Bley said.
Beijing has 169 embassies or high commissions, while Washington has 168. However, China had 96 consulates while the US had 88, suggesting that Beijing’s diplomatic expansion was closely linked to its economic interests, she said.
Beijing bulks up diplomacy budget as China extends global reach
Renmin University international relations professor Shi Yinhong said China had close and growing trade and investment ties with many developing countries, especially those taking part in the Belt and Road Initiative, increasing the need for consulates.
“One of the consulates’ main goals is to serve the citizens and businesses located in those countries,” Shi said.
Beijing has also expanded its reach at Taipei’s expense. Since 2016, when the index was first published, Taiwan’s total number of embassies fell from 22 to 15, the biggest drop among the 61 places ranked.
China opened five new embassies – in El Salvador, Burkina Faso, Gambia, São Tomé and Príncipe and the Dominican Republic – countries that severed official diplomatic ties with Taiwan. This directly contributed to China’s lead over the US, the report said.
Beijing’s diplomatic expansion also comes as the US, under the administration of President Donald Trump, is taking an “America first” approach to foreign policy.
Sri Lanka rejects fears of China’s ‘debt-trap diplomacy’ in belt and road projects
Trump has sought to cut funding to the US State Department and the White House has not appointed US ambassadors for at least 17 countries, including Brazil and Egypt, according to the American Foreign Service Association.
“Even though the US has a strong diplomatic base but it is not so proactive any more. It has fewer consulates and fewer foreign service workers,” Shi said.
“For the long term, China is in a more advantageous position.”
But a country’s diplomatic ability and influence did not rest on the number of foreign service postings and the US still held more international diplomatic sway than China, he added.
Some of China’s biggest diplomatic missions include Islamabad in Pakistan, Washington and London.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 2019 Global Diplomacy Index, American Foreign Service Association, “America first”, Beijing, belt and road projects, biggest, boast, Brazil, Burkina Faso, China alert, commands, diplomatic, Dominican Republic, Egypt, Gambia, influence, Islamabad, London, network, Pakistan, President Donald Trump, Renmin University, São Tomé and Príncipe, São Tome, Sri Lanka, Taipei, Uncategorized, United States, US State Department, Washington, White House, world’s |
Leave a Comment »
28/09/2019
NEW YORK (Reuters) – China and the Pacific island state of Kiribati restored diplomatic ties on Friday after the former diplomatic ally of Taiwan abandoned Taipei.
A poor but strategic country which is home to a mothballed Chinese space tracking station, Kiribati announced last week that it was cutting relations with self-ruled Taiwan in favour of China, which claims Taiwan as a wayward province with no right to state-to-state ties.
China and Kiribati had ties until 2003, when Tarawa established relations with Taipei, causing China to break off diplomatic relations.
Up until that time, China had operated a space tracking station in Kiribati, which played a role in tracking China’s first manned space flight.
The Chinese government’s top diplomat State Councillor Wang Yi and Kiribati’s President Taneti Maamau signed a communique on restoring diplomatic relations at the Chinese mission to the United Nations in New York.
“We highly prize this important and the correct decision,” Wang told a news conference. “Let’s hope for our friendship to last forever. We will work together to grow together towards a bright and prosperous future.”
Speaking alongside Wang, Maamau said there was much to learn from China.
“I do believe that there is much to learn and gain from the People’s Republic of China and the re-establishment of our diplomatic relations is just the beginning,” he said.
There was no mention of the space tracking station at the news conference, nor in the joint communique between the two countries released by China’s Foreign Ministry.
China’s space programme is overseen by the military.
China’s Defence Ministry this week declined comment on the Kiribati facility.
Last week was difficult for Taiwan, as the Solomon Islands also ditched it for Beijing. The Solomon Islands foreign minister signed a deal on diplomatic ties in China last Saturday.
Both the Solomon Islands and Kiribati are small developing nations but lie in strategic waters that have been dominated by the United States and its allies since World War Two. China’s moves to expand its influence in the Pacific have angered Washington.
A former Taiwanese ambassador to Kiribati, Abraham Chu, told Taiwan’s Central News Agency last weekend that China had never fully removed the tracking station in Kiribati and that it “could come back at any time”.
Taiwan now has formal relations with just 15 countries, mostly small and poor nations in Latin America and the Pacific, including Nauru, Tuvalu and Palau. China has signalled it is coming for the rest of Taiwan’s allies.
Source: Reuters
Posted in abandoned, allies, angered, Beijing, China alert, China’s Foreign Ministry, defence ministry, diplomatic ally, diplomatic ties, foreign minister, influence, Kiribati, Latin America, Military, Nauru, New York, Pacific, Pacific island state, Palau, People’s Republic of China, President Taneti Maamau, restores, site, Solomon Islands, space programme, space tracking station, State Councillor Wang Yi, state-to-state ties, Taipei, Taiwan, Tarawa, ties, Tuvalu, Uncategorized, United Nations, United States, Washington, World War Two |
Leave a Comment »
10/08/2019
- Three-year-old security treaty between US and two key allies under threat as tensions between Seoul and Tokyo continue to escalate
- End of General Security of Military Information Agreement risks undermining Washington’s influence in the region
South Korean protesters hold signs saying “No Abe” during a rally demanding the abolition of the General Security of Military Information Agreement. Photo: AP
The possible termination of a military information-sharing pact between South Korea and Japan would be a symbolic victory for China, a security analyst has warned.
Recent tension between the two countries recently threatened to spill over into the sphere of intelligence after Seoul signalled that it may pull out of the General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA) pact.
The agreement signed in 2016 enables three-way intelligence gathering between the US and its two allies and provides a crucial framework for coping with North Korea’s nuclear and missile threats.
But the escalating trade dispute between Seoul and Tokyo, prompted by a dispute about Japan’s colonial legacy, has left the future of the deal in jeopardy as the annual deadline for its renewal looms.
Japan approves first hi-tech exports to South Korea since start of ‘trade war’ – but with a warning
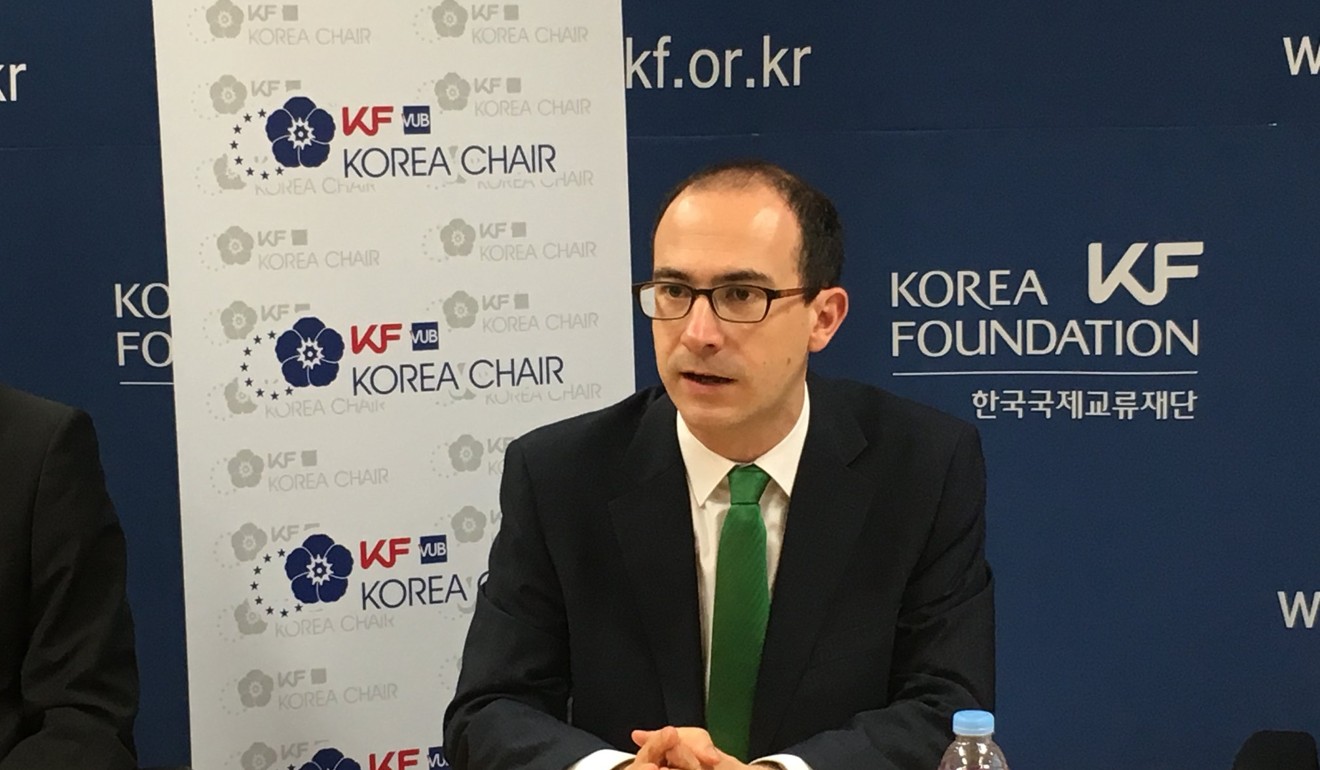
Ramon Pacheco Pardo, the first Korea chair at the Institute for European Studies at Vrije Universiteit Brussel in Belgium, said scrapping the pact would help strengthen China’s influence in the Asia-Pacific region at the expense of the US.
“It is undeniable that termination of GSOMIA would dent the US-South Korea-Japan alliance. The alliance system in northeast Asia will be weaker, strengthening China in relative terms in the process. “This could embolden China and Russia to strengthen their military cooperation in northeast Asia, said Pardo, a member of the non-governmental EU Council for Security Cooperation in the Asia-Pacific.
“Ending GSOMIA would signal that South Korea and Japan are not ready to follow Washington’s lead in the way the latter would like, given the political capital that successive US administrations spent in convincing both countries to share intelligence.”
Ramon Pacheco Pardo said the collapse of the pact would have a largely symbolic impact on China. Photo: Facebook
But Pardo also stressed that the intelligence alliance was not directly targeting China.
“While it is true that GSOMIA serves to connect the weakest link of the US-South Korea-Japan security triangle, ultimately South Korea’s security posture and the capabilities of each country independently mean that it is difficult to argue that the agreement is a concerted effort to contain China.”
“After all, Beijing does not share any significant information on North Korea’s nuclear and missile programmes with South Korea, Japan or the US.
“This is not going to change any time soon. So the good news for China would be symbolic rather than substantial.”
US missiles, jittery neighbours and South Korea’s big security dilemma
Beijing warned on Tuesday that it would take “countermeasures” if the US deployed ground-based missiles in either Japan or South Korea, and Pardo argued that scrapping the intelligence-sharing pact would expose the weaknesses in their co-ordinated approach towards China.
The security deal is automatically renewed every year unless one party decides to pull out. To do so, it must notify the others 90 days before its expiry – a deadline that falls on August 23.
The trade row was sparked by a recent South Korean court ruling that Japanese should compensate individual victims of wartime forced labour. Tokyo believes it settled all necessary compensation under a treaty signed in 1965, but Seoul believes that individual victims’ right to file a claim has not expired.
Relations between South Korea and Japan have deteriorated following a court ruling over forced labour in the wartime era. Photo: Shutterstock
Last week Japan said it would remove South Korea from its “white list” of countries with preferential trade status. Seoul has threatened to respond in kind, but also warned that it may reconsider whether to renew the intelligence-sharing pact.
Both the US and Japan have said they want the arrangement to continue, but Pardo said the effect of the termination would remain largely symbolic.
South Korea has already been investing in its own satellite and anti-submarine programmes to monitor the North’s activities, while Japan has also been developing its own intelligence programmes.
“This shows that neither South Korea nor Japan wants to rely on each other or third parties, namely the US, when it comes to monitoring North Korea’s military activities,” Pardo said.
But he argued that this behaviour already indicated that the alliance was weakening and suggested that terminating the treaty would increase China’s room for manoeuvre.
South Korea buys helicopters worth US$800 million after Trump seeks contribution for US presence
Since the 1990s successive US administrations have pushed for intelligence-sharing arrangements with Japan and South Korea to help build a framework to check Chinese and Russian military expansion in the Pacific.
“Beijing and Moscow are clearly moving in the direction of closer cooperation anyway. GSOMIA or not, military cooperation will continue … as long as Xi Jinping and Vladimir Putin lead each country and most probably even beyond then,” Pardo said.
China and Russia flexed their muscles in the region last month as the trade dispute between the two key allies intensified.
Russian and Chinese long-range military aircraft conducted their first-ever joint air patrol over the Sea of Japan – also known as the East Sea – and the East China Sea.
“The East Asian security landscape would be reshaped insofar that China, North Korea and Russia would see that their main opponent in the region – the US – is unable to convince its two key allies, South Korea and Japan, to cooperate on a key issue,” Pardo said.
“The current dispute between South Korea and Japan will need a negotiated solution … In any case, Japan will have to learn to live with the fact that former colonisers will, from time to time, receive criticism by many of their former colonies, criticism that sometimes will escalate.
“It happens to former European colonial powers, for example, and it is only logical because the interpretation of the past is always in flux.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in anti-submarine programmes, Asia, Belgium, China alert, collapse, colonial legacy, countermeasures, escalate, EU Council for Security Cooperation in the Asia-Pacific, General Security of Military Information Agreement, General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA), GSOMIA, helicopters, hi-tech export, influence, Institute for European Studies, intelligence pact, Japan, jittery neighbours, military cooperation, missile threats, North Korea, nuclear threats, own intelligence programmes, President Trump, region, Russia, satellite programmes, security treaty, Seoul, South Korea, symbolic victory, Tokyo, trade war, Uncategorized, undermining, US, US missiles, Vrije Universiteit Brussel, Washington |
Leave a Comment »
28/07/2019
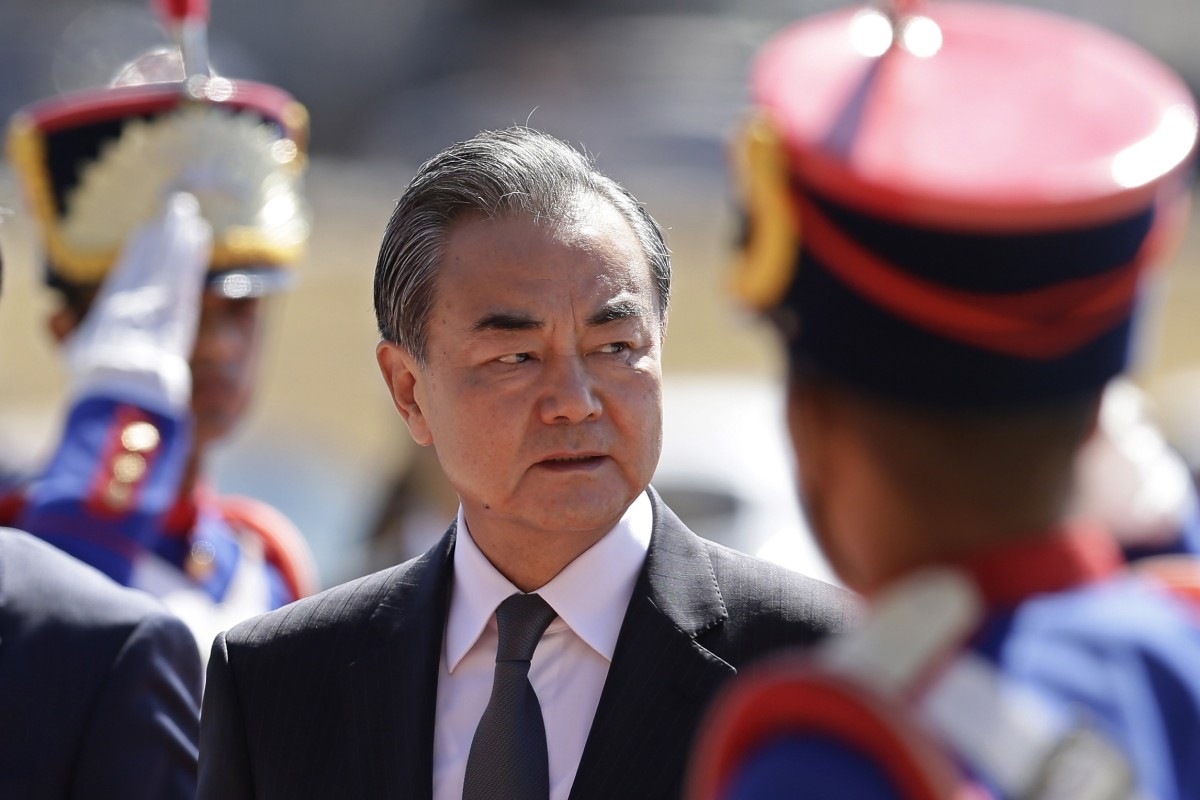
- Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi wraps up tour of Brazil and Chile, as Colombian president heads for Beijing
- Ecuador president tells US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo ‘smaller countries pay when the big ones fight’
Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi is greeted by an honour guard as he arrives at the Itamaraty Palace for a meeting with his Brazilian counterpart Ernesto Araujo on Thursday. Photo: AP
Latin American countries are caught in the middle of a geopolitical tug of war between Beijing and Washington as China boosts its ties in the region in a bid to counterbalance the effects of its trade war with the US.
China’s Foreign Minister Wang Yi wraps up a tour of Latin America on Sunday which began last week in Brazil and ended with an official visit to Chile. He returns to Beijing on the same day Colombia’s President Ivan Duque Marquez arrives for a three-day state visit to China which will include a meeting with Chinese President Xi Jinping.
Wang was in Brazil for the latest summit of foreign ministers from the BRICS countries – an association of emerging countries made up of Brazil, Russia, India, China and South Africa – as well as the third China-Brazil foreign ministers’ comprehensive strategic dialogue with Brazilian Foreign Minister Ernesto Araujo.
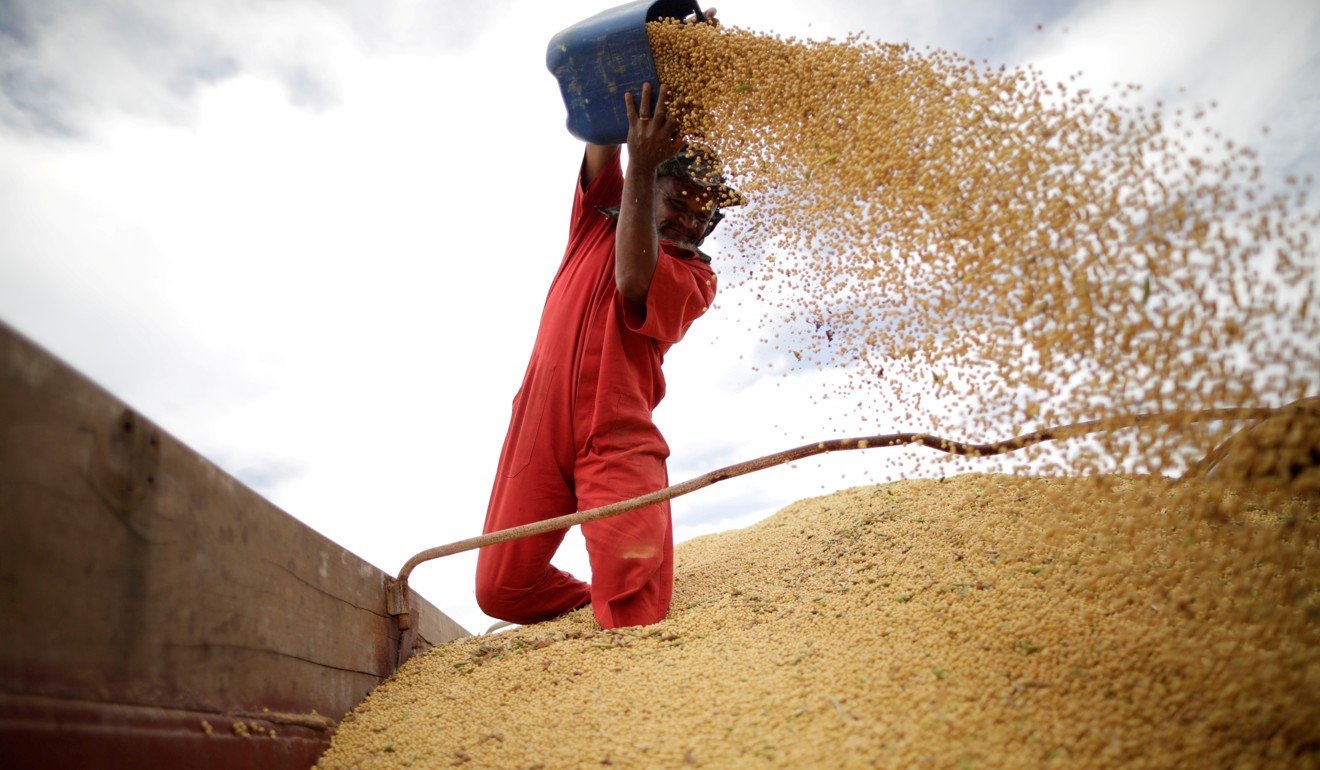
China has overtaken the US as Brazil’s largest trading partner, with Brazilian soybeans – one of the country’s biggest exports – and other agricultural products replacing American imports since the start of the US-China trade war a year ago.
Brazilian soybeans – one of the country’s biggest exports – and other farm products are being sold to China as a result of the trade war. Photo: Reuters
The growing importance of China to Brazil’s economy has created a difficult position for President Jair Bolsonaro, who accused Beijing of trying to buy Brazil during his election campaign, but changed tack on assuming office in January.
In March, Bolsonaro called China his country’s “main partner, politically as well as economically and commercially” and announced plans to travel to Beijing this year, a visit which was confirmed on Tuesday for late October.
China is now Latin America’s second largest trading partner with bilateral trade at US$307.4 billion, growing 18.9 per cent over the previous year, according to China’s ministry of commerce, in a relationship focused on commodity imports, including mining products like copper and energy, as well as soybeans and other agricultural goods.
While the US and China have tentatively agreed to resume talks in Shanghai next week, China and Latin American countries are likely to continue deepening their trade relations as production chains realign as a result of the trade war, according to Gustavo Oliveira, assistant professor of global and international studies at the University of California, Irvine.
“This means Chinese imports of Latin American agricultural and mineral commodities, and Latin American imports of Chinese manufactured products and hi-tech, might contribute to China’s ability to stand its ground against US pressure,” he said.
China in Latin America: partner or predator?
Oliveira said domestic contradictions in most Latin American countries complicated relations with China, as few leaders had the capacity to press or leverage China for much. “Unfortunately, therefore, most in this crop of Latin American leaders are basically placing themselves as junior partners or pawns in the geopolitical tug of war between the US and China.”
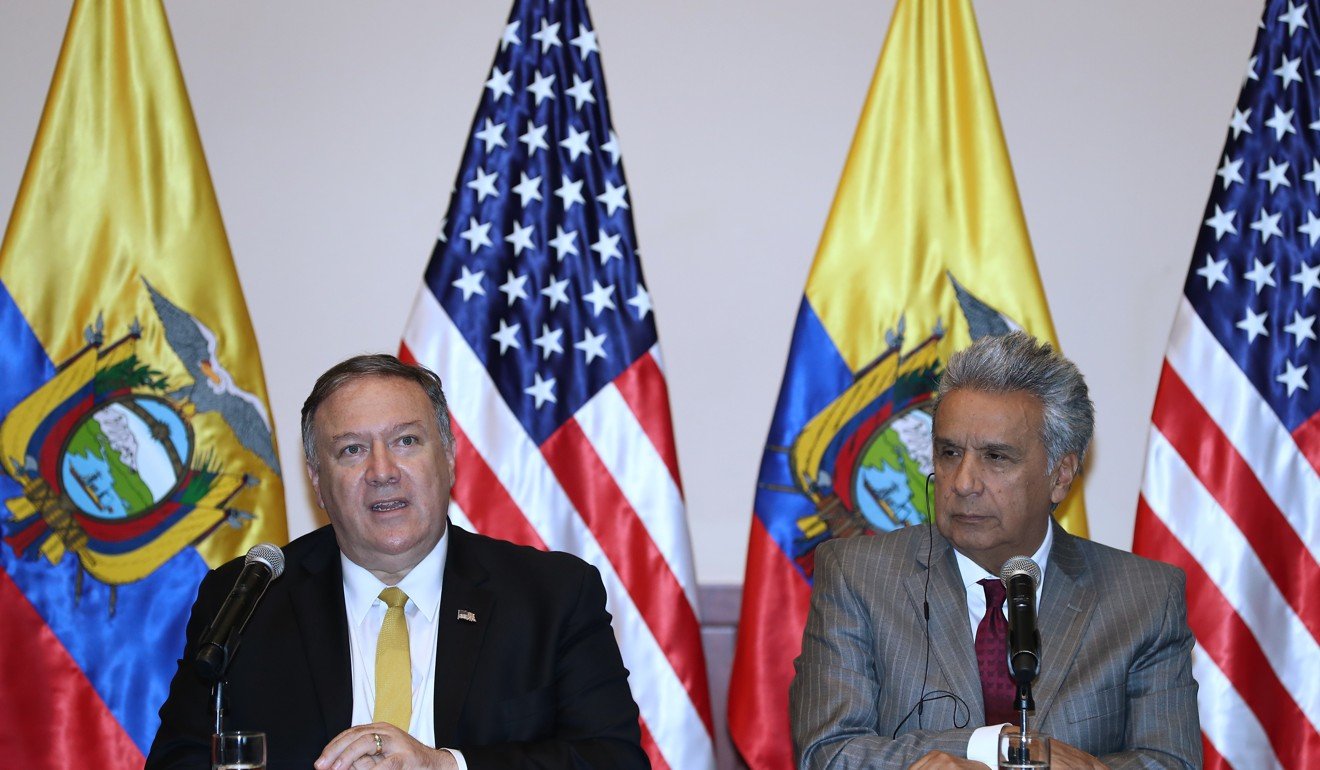
US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo put the pressure on Latin American countries over their relationship with China during his four-day tour of the region last weekend, when he visited Argentina, Ecuador, Mexico, and El Salvador.
In a joint interview with Pompeo during the visit, Ecuador’s new President Lenin Moreno defended the country’s China ties, and urged Washington and Beijing to resolve their conflicts for the benefit of other nations in the region.
“We hope that the US and China, the greatest powers in the world now, will find agreement easily because, unfortunately, when the big ones are discussing or fighting and have conflicts, the ones that are paying for all of that are the smaller countries,” he said.
“Now, when two elephants fight, the ones who lose are the insects who are of course being crushed by the elephants in the attempt to evade them.”
US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo (left) and Ecuadorian President Lenin Moreno hold a joint press conference during Pompeo’s tour of Latin America on July 20. Photo: EPA-EFE
Pompeo blasted China’s role in the region during a previous tour of South America in April, when he singled out Beijing’s support for President Nicolas Maduro of Venezuela. Maduro is backed by Beijing, Russia and other allies, while the US and many European countries have supported opposition leader Juan Guaido as legitimate president since elections in January.
Speaking from Chile on that tour, Pompeo said Beijing’s calls for non-intervention in Venezuela were “hypocritical” and aimed at protecting Beijing’s investments in the country, as well as debts owed to China by Venezuela.
Pompeo also accused Beijing of “sowing discord” in the region through debt traps. “When China does business in places like Latin America, it often injects corrosive capital into the economic bloodstream, giving life to corruption and eroding good governance,” he said.
Professor Cui Shoujun of Renmin University in Beijing said Washington’s concerns about “debt trap diplomacy” in Latin America reflected concerns that China’s growing involvement in financing infrastructure and development projects would make the region more pro-China.
“China’s interests in Latin America go beyond raw materials extraction,” he said. “The biggest point of tension between the US and China in the region is perhaps that China presents an alternative model for development that is very different from the Western model.”
‘Mr Pompeo, you can stop’: China hits back over Latin America criticism
While the US was drumming up tensions about China across the world, Beijing was not openly retaliating but responding with investment and trade for global partners, said Kevin Gallagher, researcher on China-Latin America ties, and professor at Boston University.
“The US points fingers and makes angry speeches in the region as China cuts investment deals and helps address infrastructure needs,” he said.
“Latin American countries’ governments are rightly keeping their heads down on the broader geopolitical winds, and are getting down to business with their largest trading partner.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Argentina, Beijing, Boston University, Brazil, Brics countries, Chile, China alert, Chinese foreign minister Wang Yi, Chinese President Xi Jinping, Colombian president, copper, Ecuador, Ecuador president, El Salvador, elephants, energy, Ernesto Araujo, European countries, grows, India alert, influence, insects, Itamaraty Palace, Ivan Duque Marquez, Latin America, Mexico, Mike Pompeo, mining products, President Lenin Moreno, President Nicolas Maduro, Renmin University, Russia, Shanghai, South Africa, soybeans, Trade, tussle, Uncategorized, University of California, Irvine, US, US Secretary of State, Venezuela, Washington |
Leave a Comment »
04/12/2018
Portugal welcomes China’s money as its influence worries EU partners
- Xi Jinping’s visit to Lisbon follows EU countries’ agreement on regulation of foreign investment, particularly from China
- EU-IMF bailout of Portugal in 2011 prompted privatisations that brought flood of Chinese investment
PUBLISHED : Tuesday, 04 December, 2018, 5:56pm
UPDATED : Tuesday, 04 December, 2018, 6:09pm
Fresh from a visit to Spain last week, Xi’s two-day stay in Portugal will include a meeting with President Marcelo Rebelo de Sousa and the signing of cooperation agreements.
One of them will bring the Portuguese port of Sines, in the southwest, into China’s “Belt and Road Initiative”, a strategy that offers loans to build railways, roads and ports across Asia, Europe and Africa.
In an opinion editorial published on Sunday in Portuguese newspapers, Xi stressed the importance of China’s relationship with Portugal as part of a broader network of trade links.
It’s not just the US: around the world, doors are shutting on Chinese investment
But China’s growing influence in Europe, welcomed by Greece and several eastern European countries, is viewed warily by others on the continent
At the initiative of France and Germany, EU countries last week agreed a framework regulating foreign investment, particularly from China.
Portuguese Prime Minister Antonio Costa said on Friday that Lisbon did not back the idea and was relieved that the final accord provided for only an advisory role on the part of the European Commission.
Foreign investment does not worry Portugal, and the EU should not “take the path of protectionism” in the face of globalisation, he said.
German president heads to China as Beijing courts European economic ties
Portugal, one of western Europe’s poorest countries, was open to Chinese investment after being hit hard by the 2008 global financial crisis.
Its 78 billion euro (US$89 billion) EU-IMF rescue package in 2011 came with required austerity policies – and a wide-ranging privatisation programme that opened the doors to Chinese investment.
Chinese investment accounted for 3.6 per cent of Portugal’s GDP between 2010 and 2016, according to figures from Spain’s ESADE business school.
China now owns a 28 per cent stake in Portuguese energy utility EDP, the country’s largest firm, via China Three Gorges and China’s state-owned international investment company CNIC.
Why China buying up ports is worrying Europe
It also has a stake in Portugal’s biggest private bank, BCP, and its leading insurance company, Fidelidade.
Perhaps the most contentious issue is China Three Gorges’ bid to take a controlling stake in EDP, of which it is already the main stakeholder. The 9 billion euro operation was launched in May.
But although it has been welcomed by the Portuguese government, it still risks falling foul of barriers imposed by regulators in around 15 countries where EDP operates, including the United States.
Luis Castro Henriques, head of Portugal’s trade and investment agency Aicep, says Chinese investment in Portugal has been good for the country.
China has risen to Portugal’s 11th-largest trade partner in the decade since 2008, when it was 28th on the list.
“We want now to attract large-scale industrial investment, notably in the automobile and agro-food sectors,” Castro Henriques said.
Posted in China alert, EU, influence, money, partners, Portugal, Uncategorized, worries |
Leave a Comment »












COMMENTS: