22/04/2020
- Documentary puts China’s literary hero into context: there is Dante, there’s Shakespeare, and there’s Du Fu
- Theatrical legend Sir Ian McKellen brings glamour to beloved verses in British documentary
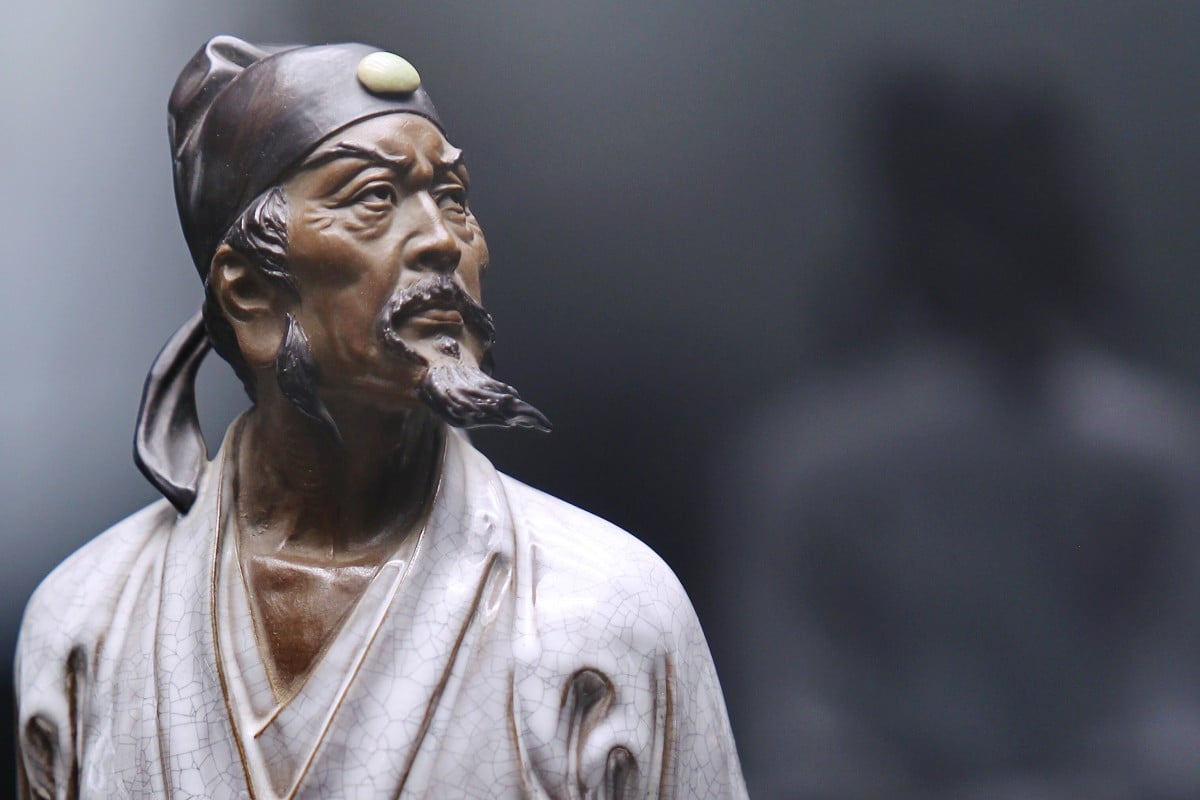
A ceramic figurine of Du Fu, a prominent Chinese poet of the Tang dynasty. Du is the subject of a new BBC documentary, thrilling devotees of his poetry. Photo: Simon Song
The resonant words of an ancient Chinese poet spoken by esteemed British actor Sir Ian McKellen have reignited in China discussion about its
literary history and inspired hope that Beijing can tap into cultural riches to help mend its image in the wake of
the coronavirus pandemic.
The BBC documentary Du Fu: China’s Greatest Poet has provoked passion among Chinese literature lovers about the poetic master who lived 1,300 years ago.
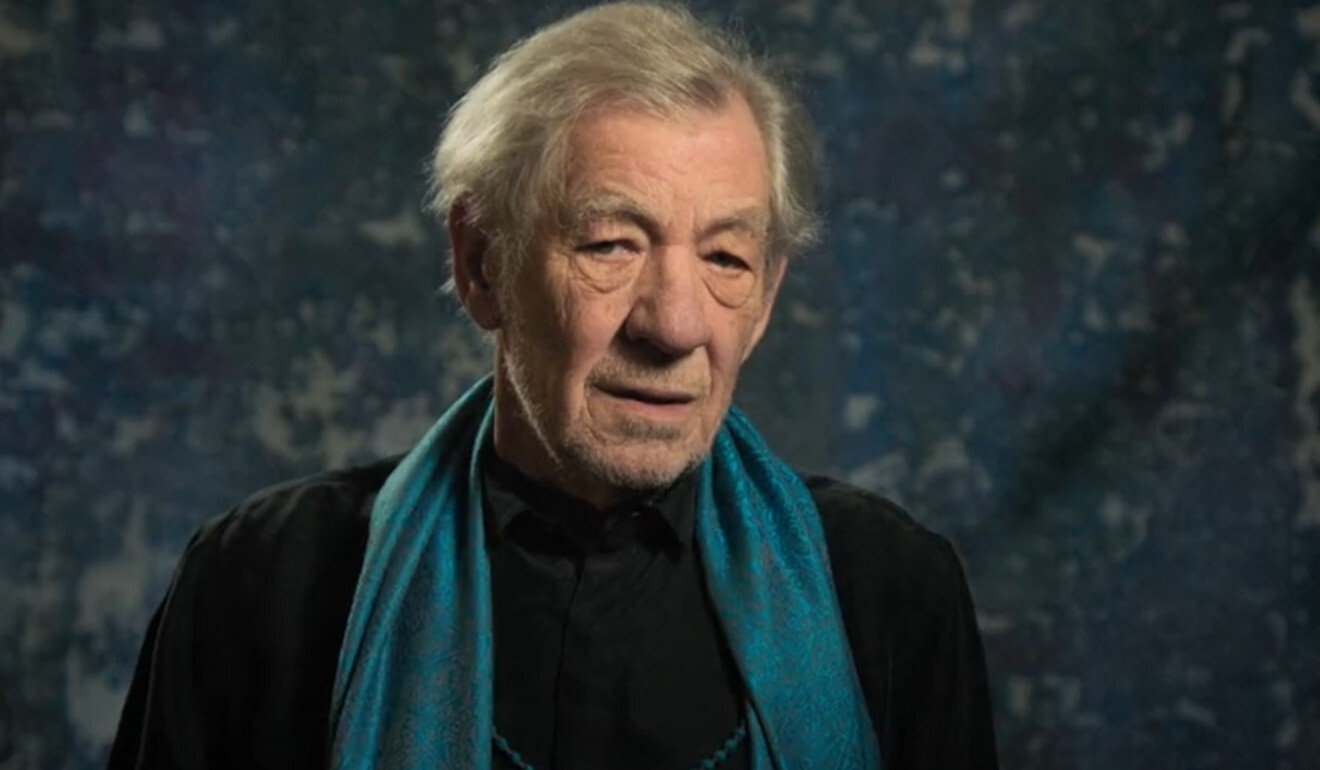
Sir Ian Mckellen read works of ancient Chinese poet Du Fu in Du Fu: China’s Greatest Poet. Photo: BBC Four / MayaVision International
The one-hour documentary by television historian Michael Wood was broadcast on television and aired online for British viewers this month but enthusiasm among Chinese audiences mean the trailer and programme have been widely circulated on video sharing websites inside mainland China, with some enthusiasts dubbing Chinese subtitles.
The documentary has drawn such attention in Du’s homeland that even the Communist Party’s top anti-graft agency has discussed it in its current affairs commentary column. Notably, Wood’s depiction of Du’s life from AD712 to 770 barely mentioned corruption in the Tang dynasty (618-907) government.
“I couldn’t believe it!!” Wood said in an email. “I’m very pleased of course … most of all as a foreigner making a film about such a loved figure in another culture, you hope that the Chinese viewers will think it was worth doing.”
Often referred to as ancient China’s “Sage of Poetry” and the “Poet Historian”, Du Fu witnessed the Tang dynasty’s unparalleled height of prosperity and its fall into rebellion, famine and poverty.
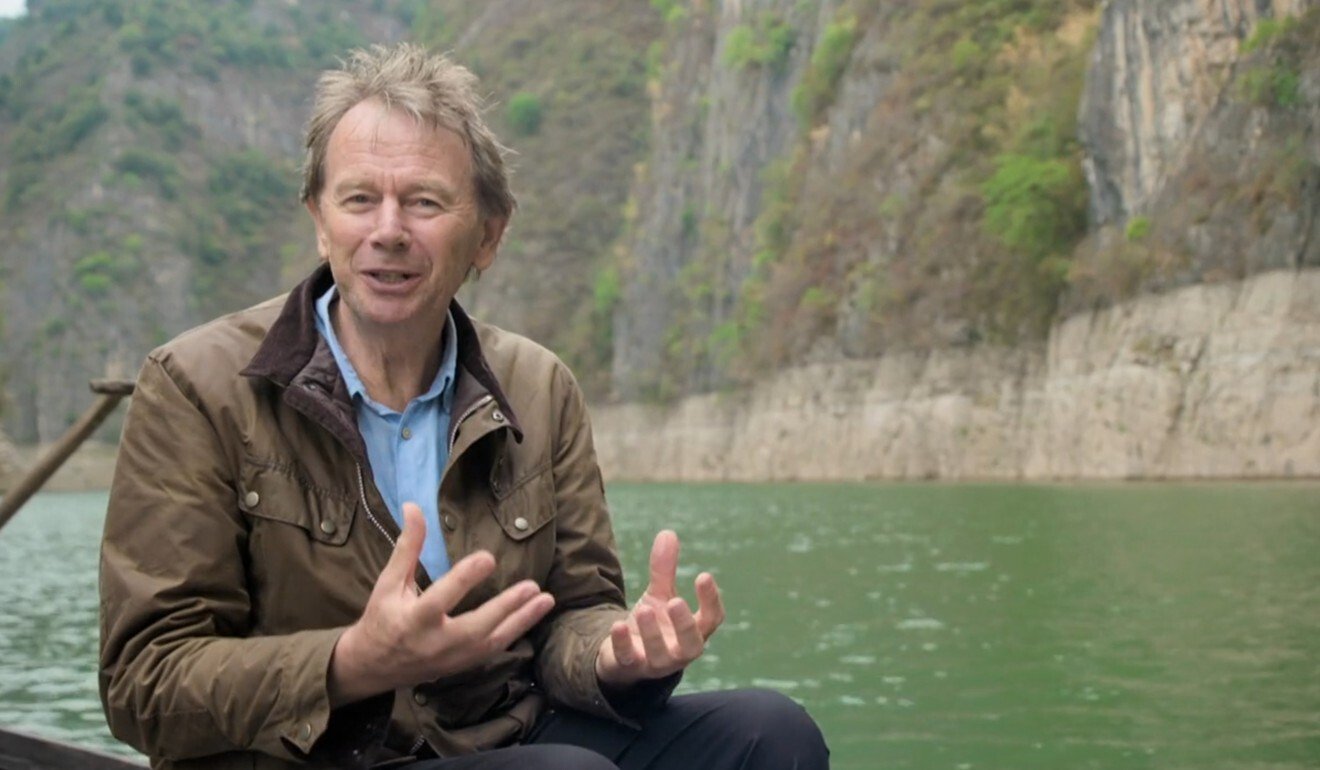
Writer, historian and presenter Michael Wood followed the footsteps of the ancient Chinese poet Du Fu in Yangtze River gorges. Photo: BBC Four / MayaVision International
Wood traced Du’s footsteps to various parts of the country. He interviewed Chinese experts and Western sinologists, offering historical and personal contexts to introduce some of Du’s more than 1,400 poems and verses chronicling the ups and downs of his life and China.
The programme used many Western reference points to put Du and his works into context. The time Du lived in was described as around the as the Old English poem
Beowulf was composed and the former Chinese capital, Changan, where
Xian is now, was described as being in the league of world cities of the time, along with Constantinople and Baghdad.
Harvard University sinologist Stephen Owen described the poet’s standing as such: “There is Dante, there’s Shakespeare, and there’s Du Fu.”
The performance of Du’s works by Sir Ian, who enjoyed prominence in China with his role as Gandalf in the Lord of the Rings movie series, attracted popular discussion from both media critics and general audiences in China, and sparked fresh discussion about the poet.
“To a Chinese audience, the biggest surprise could be ‘Gandalf’ reading out the poems! … He recited [Du’s poems] with his deep, stage performance tones in a British accent. No wonder internet users praised it as ‘reciting Du Fu in the form of performing a Shakespeare play,” wrote Su Zhicheng, an editor with National Business Daily.
A stone sculpture at Du Fu Thatched Cottage in Chengdu city, China. Photo: Handout
On China’s popular Weibo microblog, a viewer called Indifferent Onlooker commented on Sir Ian’s recital of Du’s poem My Brave Adventures: “Despite the language barrier, he conveyed the feeling [of the poet]. It’s charming.”
Some viewers, however, disagreed. At popular video-sharing website Bilibili.com, where uploads of the documentary could be found, a viewer commented: “I could not appreciate the English translation, just as I could not grasp Shakespeare through his Chinese translated works in school textbooks.”
Watching the documentary amid the coronavirus pandemic, some internet users drew comparisons of Du to Fang Fang, a modern-day award-winning poet and novelist who chronicled her life in Wuhan during the Covid-19 lockdown.

Shanghai pictured in April. Devastation wrought by the coronavirus pandemic has brought about a new suspicion of China. Photo: Bloomberg
The pandemic has infected more than 2.5 million people and killed more than 170,000. It has put the global economy in jeopardy, fuelling calls for accountability. British Foreign Secretary Dominic Raab last week called for a “deep dive” review and the asking of “hard questions” about how the coronavirus emerged and how it was not stopped earlier.
Steve Tsang, director of the SOAS China Institute at University of London, said the British establishment and wider public had changed its perception of Beijing as questions arose about outbreak misinformation and the political leverage of personal protective gear supply.
“The aggressive propaganda of the Chinese government is getting people in the UK to look more closely at China and see that it is a Leninist party-state, rather than the modernising and rapidly changing society that they want to see in China,” Tsang said.
On Sunday, a writer on the website of the National Supervisory Commission, China’s top anti-corruption agency, claimed – without citing sources – that the Du Fu documentary had moved “anxious” British audience who were still staying home under social distancing measures.
“If anyone wants to put the fear of the coronavirus behind them by understanding the rich Chinese civilisation, please watch this documentary on Du Fu,” it wrote, adding that promoting Du’s poems overseas could help “healing and uniting our shattered world”.
English-language state media such as CGTN and the Global Times reported on the documentary last week and some Beijing-based foreign relations publications have posted comments about the film on Twitter.
Wood said he had received feedback from both Chinese and British viewers that talked about “the need, especially now, of mutual understanding between cultures”.
“It is a global pandemic … we need to understand each other better, to talk to each other, show empathy: and that will help foster cooperation. So even in a small way, any effort to explain ourselves to each other must be a help,” Wood said.
He said the idea for producing a documentary about Du Fu started in 2017, after his team had finished the Story of China series for BBC and PBS.
Du Fu: China’s Greatest Poet first aired in Britain on April 7 on BBC Four, the cultural and documentary channel of the public broadcaster. It is a co-production between the BBC and China Central Television.
Wood said a slightly shorter 50-minute version would be aired later this month on CCTV9, Chinese state television’s documentary channel.
The film was shot in China in September, he said.
“I came back from China [at the] end of September, so we weren’t affected by the Covid-19 outbreak, though of course it has affected us in the editing period. We have had to recut the CCTV version in lockdown here in London and recorded two small word changes on my iPhone!” Wood said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 1,300, accountability, Actor, aired, amid, among, ancient poetry, anti-corruption agency, April, “deep dive”, “hard questions”, “healing and uniting our shattered world”, “Poet Historian”, “Sage of Poetry”, Baghdad, BBC, BBC Four, Beijing, beloved, Beowulf, brings, British, British Foreign Secretary, broadcast, brought, CCTV9, ceramic figurine, Changan, Chengdu, China, China Central Television, China’s, Chinese, Chinese audiences, Chinese capital, Chinese civilisation, Chinese experts, Chinese poet, Chinese subtitles, chronicling, co-production, composed, Constantinople, context, coronavirus, Coronavirus pandemic, COVID-19 outbreak, cultural riches, Dante, Devastation, devotees, different, director, discussion, documentary, downs, Du Fu, Du Fu Thatched Cottage, Du Fu: China’s Greatest Poet, dubbing, earlier, email, emerged, enthusiasm, enthusiasts, esteemed, fall, famine, Film, followed, footsteps, former, Gandalf, glamour, global economy, Global Times, gorges, Harvard University, height of prosperity, help mend, historian, hope, image, inside, inspired, into, iPhones, jeopardy, league of world cities, legend, literary hero, literary history, literature lovers, lived, lockdown, London, Lord of the Rings, Mainland China, mean, Michael Wood, National Business Daily, National Supervisory Commission, new, Old English poem, online, passion, PBS, poems, poetic master, poetry, poverty, presenter, programme, prominent, provoked, puts, rebellion, recorded, recut, reignited, resonant, review, September, Shakespeare, Shanghai, shot, show, side, sinologist, Sir Ian McKellen, SOAS China Institute, spoken, stopped, Story of China, subject, Sunday, suspicion, tap, Television, television historian, Theatrical, there, there’s, this month, thrilling, trailer, Twitter, Uncategorized, unease, University of London, unparalleled, UPS, verses, video sharing, viewers, wake, websites, Weibo, Western sinologists, widely circulated, witnessed, words, writer, wrought, Xi’an, Yangtze River, years ago |
Leave a Comment »
01/03/2020
- Materials can bought cheaply online and combined to filter out germs, while people exchange tips in online chat groups
- Urgent demand has forced individuals and hospitals alike to get to work to meet the shortfall
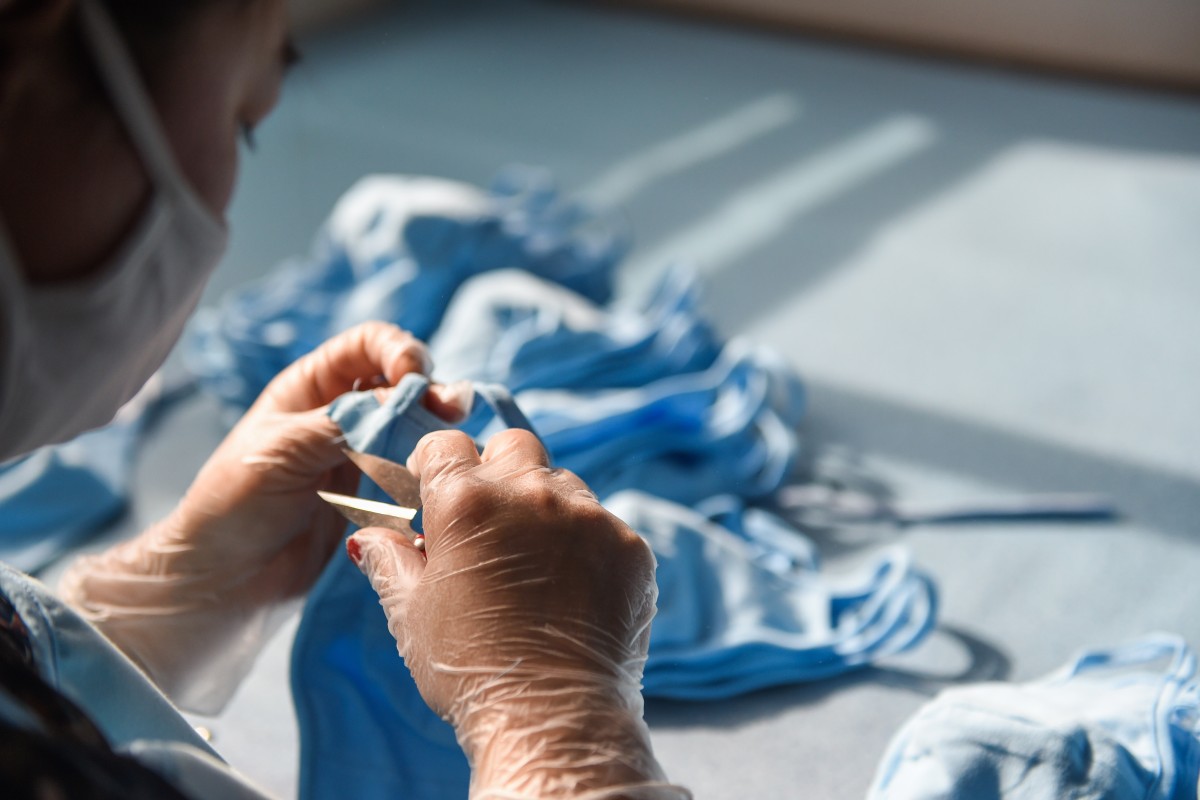
A worker in northern China makes a face mask as companies strive to match demand – but some people are buying similar materials to assemble at home. Photo: Xinhua
Living in the scenic Puer city in southwestern China’s Yunnan province, 30-year-old Zhang Jianing had thought the
coronavirus outbreak in Hubei was far away and irrelevant, until cases were confirmed in her province and then her city at the end of January.
Heeding the warnings to protect herself, Zhang rushed out to buy masks, only to find them all snapped up. When she plucked up the courage to go out to buy groceries, she realised she needed to have a mask on to be allowed to enter shops.
After doing some research online, Zhang made a mask herself: two layers of cotton on the outside, with a sheet of plastic food wrap inside.
“The mask fit my face well and protected me from droplets,” Zhang said. “There was just one thing: it was too difficult to breathe through.”
Experts devise do-it-yourself face masks to help people battle coronavirus
When a nation of 1.4 billion people was suddenly alerted and in many cases ordered to wear masks not only in public indoor places but also in the open air, the huge demand quickly exhausted supply.
Mask production capacity in China was 22 million a day – insufficient for the country’s population. There were hopes that the supply of masks would pick up after a Lunar New Year holiday that was extended to help prevent further spread of infection, but things did not look promising after factories reopened. By Monday, despite mask manufacturers making 10 per cent more than in early February, masks remained a rare commodity.
Making DIY masks became the top trending topic on Chinese online shopping site Taobao for several days. Materials became much sought-after, from nose bars to the non-woven fabric used in disposable surgical masks to filter out viral droplets. An online shop based in Fujian, southeast China, said it had sold more than 5,500 packages of DIY mask materials that can make 50 to 200 surgical masks apiece.
Surgical masks ‘protect more from germs on fingers than viruses in the air’
Zhang spent 200 yuan (US$29) on materials online, from which she made 60 surgical masks when they arrived last week. She is a qipao designer and has a sewing machine at home. The outer layer was a blue waterproof non-woven fabric, over a layer of melt-blown fabric that can filter out most germs and droplets. The inner layer was made with a face flannel.
Hongkongers make reusable fabric masks as Covid-19 epidemic leads to shortages and sky-high prices
“I sent some to my parents and relatives,” Zhang said. “I am not sure how protective they are, but the good thing is our city hasn’t had any new cases for a long time.”
DIY mask production is being taken very seriously, spawning online chat groups to discuss reliability of materials and disinfection methods as people try to make theirs as safe and professional as possible.
Alex Zhang, an office worker in Shanghai, donated her N95 masks to Wuhan, the epicentre of the coronavirus outbreak, when hospitals in the city appealed to the public for protective gear amid an acute shortage – but soon found herself short of masks herself.
Shanghai companies begin production of first reusable face masks
The Shanghai government allowed households to buy a certain number of surgical masks, but it was not enough for her family. Taking apart an N95 mask to see what it was made of, she felt assembling the layers of fabric required no special technique, and decided to do it herself.
Zhang spent 45 yuan on two square metres of melt-blown fabric to stop viruses, and sandwiched it with two layers of nonwoven fabric and an air pad. She sewed the layers together and put them in an electric oven at 70 degrees Celsius (158 Fahrenheit) for a minute, for disinfection. The finished mask is attached using a plastic band.
“Each mask cost about 3 yuan [43 US cents] and was almost like an N95 filter,” Zhang said. “I didn’t find it difficult. I am quite satisfied with my masks and feel very safe to wear them in crowded places.”
How to properly remove and discard face masks to reduce the risk of infection
She later bought nursing pads, which are already disinfected, to replace the layer closest to the face.
DIY masks have also been used where large amounts of protective gear are needed. Garment manufacturer Shenzhou International, in the coastal Zhejiang province, assigned 100 staff to make masks with melt-blown non-woven fabric to meet the needs of its factory workforce of nearly 15,000, who needed two masks each per day, according to a report by Ningbo Daily.
Hospitals short of masks have mobilised nurses to make their own using a non-woven fabric used to wrap disinfected medical products. At least three hospitals, in Xian in central China and in Jinhua, Zhejiang, have tried making masks for medical staff not serving on the front line, according to media reports.
DIY handmade face masks in Hong Kong
The World Health Organisation has said that wearing masks alone is not sufficient protection against the coronavirus, and should be combined with precautions including hand-washing with soap or an alcohol-based hand rub.
However, facing a shortage that will not end any time soon, health authorities have changed from saying people should discard masks every four hours to advising recycling them when possible.
A guideline issued by the National Health Commission said healthy people could wear masks repeatedly and for a longer time.
Chinese driver wears 12 face masks amid coronavirus outbreak
“Masks for repeat use can be hung in clean, dry and airy places or put in a clean paper bag,” its guidelines said. “The masks must be placed separately to avoid contact with other masks.”
Making masks with layers of cotton bandage is acceptable, because they can stay dry when breathed on, but plastic wrap is not recommended, because it blocks the ability to breathe entirely, according to Cai Haodong, an infectious diseases specialist at Beijing’s Ditan Hospital.
Coronavirus: Thais urged to make their own masks, sanitisers due to shortage
Cai said her hospital did not have surgical masks, nor N95s, during the severe acute respiratory syndrome (Sars) outbreak in 2003, and hospital staff made masks for use by front-line medics, disinfecting them with boiling water and drying them in the sun.
“The key is to keep the mask dry,” Cai said. “Self-made masks offer some degree of protection and it is better to wear them than nothing.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in alcohol-based hand rub, Beijing’s Ditan Hospital, China’s, coronavirus, coronavirus outbreak, COVID-19 epidemic, epicentre, face mask, Fujian, hand-washing, hubei province, inspired, Jinhua, Lunar New Year holiday, materials, National Health Commission, Ningbo Daily, People, qipao designer, sewing machine, Shanghai, shortage, soap, Thais, to learn, to make, Uncategorized, World Health Organisation, Wuhan, Xi'an, Yunnan Province, Zhejiang, zhejiang province |
Leave a Comment »