04/09/2019
- Prototype tested last month transports high-voltage power and liquefied natural gas side by side
- It could cut the high cost and waste involved in sending energy from the far west to the east coast
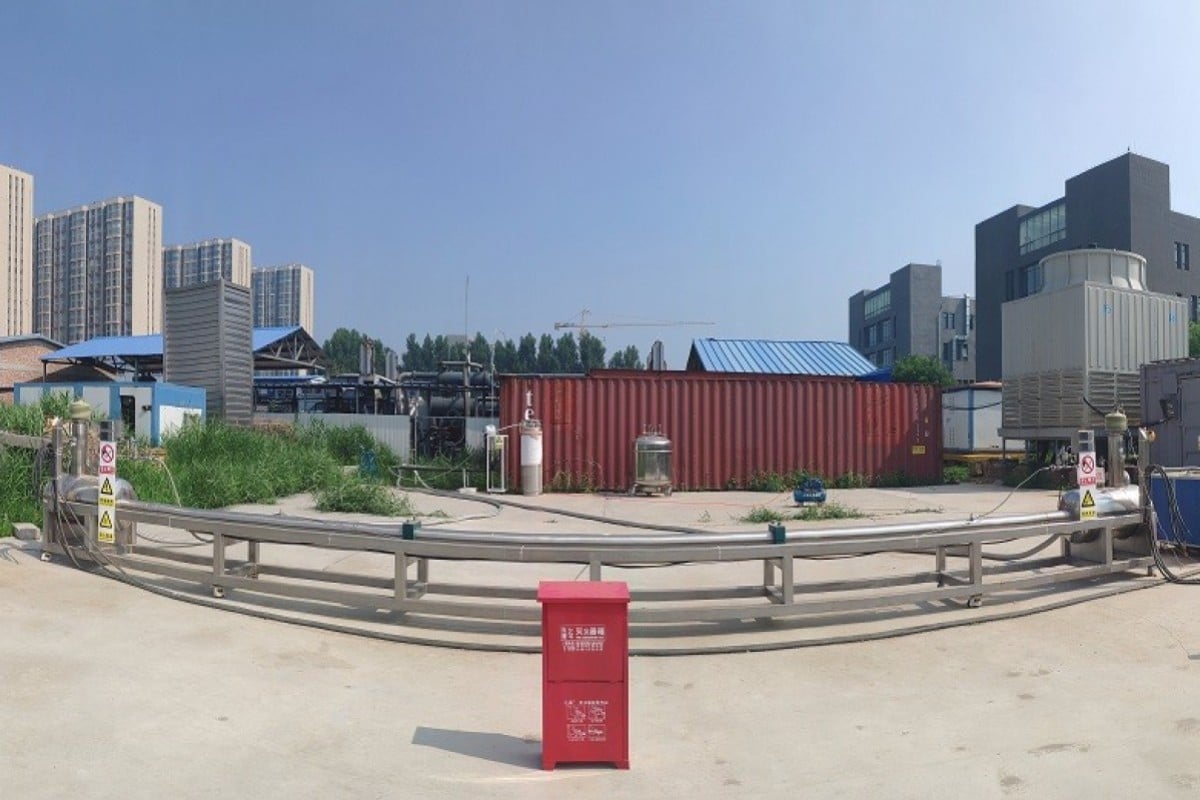
The 10-metre prototype line, combining high-voltage electricity and liquefied natural gas. Photo: Chinese Academy of Sciences
Chinese scientists have developed the world’s first prototype of a superconducting hybrid power line, paving the way for construction of a 2,000km (1,243-mile) line from energy-rich Xinjiang in the country’s far west to its eastern provinces.
The 10-metre, proof-of-concept wire and liquid natural gas hybrid transmission line was up and running at the Chinese Academy of Sciences’ Institute of Electrical Engineering in Beijing last month to show the feasibility of the technology.
The line contains a superconducting wire which can transmit nearly 1,000 amps of electric current at more than 18,000 volts with zero resistance.
In a further difference from a traditional power line, the gap between the superconducting wire and the power line’s outer shell is filled by a flow of slowly moving natural gas liquefied at low temperatures – between minus 183 and minus 173 degrees Celsius (minus 279 to minus 297 Fahrenheit). This allows the line to transfer electricity and fossil fuel at the same time.
Professor Zhang Guomin, the government research project’s lead scientist, told the South China Morning Post that the voltage and current could be much higher in its real-world applications.
“This technology can take the overall efficiency of long-distance energy transport to new heights,” he said.
Existing infrastructure to transfer energy from Xinjiang Uygur autonomous region to the developed eastern areas such as Shanghai has high operational costs because almost 10 per cent of the energy is lost in transmission, according to some studies.
That infrastructure includes the world’s most advanced high-voltage power line and four natural gas pipes, each thousands of kilometres long. One of the natural gas pipelines, from Xinjiang to Shanghai, cost 300 billion yuan (US$42 billion).
The superconductor and natural gas hybrid line offered a possible solution, Zhang said.
Loss of electricity over the superconducting wire would be almost zero because of the elimination of resistance to the movement of electrons, he said.
The transport of liquefied natural gas would also be efficient, because one cubic metre (1,000 litres) of it would be equivalent to 600 cubic metres of the same fuel in gas form.
The temperature needed for liquefaction of natural gas is almost identical to that required for occurrence of superconductivity, at about minus 163 degrees.
Wang Gengchao, professor of physics at East China University of Science and Technology in Shanghai, said the combination was a “smart idea”.
Superconducting materials are not new but their applications have been limited by the difficulty and cost of creating and maintaining the low-temperature environment.
“They are trying to kill two birds with one stone,” Wang, who was not involved in the study, said.
China is preparing to buy US liquefied gas and soybeans again
“But whether the technology can find a use in large-scale infrastructure depends on other things, such as safety. Not everyone will feel comfortable with the idea of putting a high-voltage electric line and flammable natural gas side by side.”
Zhang said another new prototype line, about 30 metres long, was being developed and the 2,000km project was awaiting government approval.
He said the team had solved some major technical obstacles, including reducing the risk of accidents from electrical sparks and gas leakage.
“Many problems remain to be solved, but we are confident this technology will work,” he said. “It will protect the environment. It will save a lot of land from being used for power and gas lines.”
Xinjiang has more energy resources than any other Chinese province or region. It has nearly half of the nation’s coal reserves, a third of its oil and gas, and some of the largest wind and solar farms, according to government statistics.
Source: SCMP
Posted in China alert, Chinese Academy of Sciences, coal reserves, Country, develops, East China University of Science and Technology, east coast, far west, high-voltage power, hybrid power line, Institute of Electrical Engineering, Natural gas, oil and gas, prototype, Shanghai, south china morning post, soybeans, span, superconducting, superconducting wire, transports, two birds with one stone, Uncategorized, US liquefied gas, wind and solar farms, Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uygur Autonomous Region, zero resistance |
Leave a Comment »
30/08/2019
- ‘Forbes’ magazine reported that China’s central bank will launch its own sovereign digital currency to coincide with the Singles’ Day online shopping festival
- The People’s Bank of China is seeking to address financial risks and counter the current dominance of the US dollar
The Singles’ Day is a holiday celebrated in China on November 11 and has become the largest online shopping day in the world. Photo: Simon Song
China’s desire to launch the world’s first government-backed digital currency could see the possible rival to Facebook’s Libra be launched in time for November’s Singles’ Day online shopping festival despite a Chinese media report playing down the timing as “inaccurate speculation”.
Several central bank officials have publicly spoken out over the past several weeks about the need for China to launch its own digital currency since Facebook unveiled its plans for Libra, and the People’s Bank of China (PBOC) appear to be making rapid progress ahead of an expected launch.
Forbes magazine reported this week, citing a source who previously worked for the Chinese government, that China’s central bank could launch the digital currency as soon as November 11 as its bids to address financial risks and to counter the current dominance of the US dollar.
The PBOC did not respond to a faxed request for comment on the Forbes story, although Sina.com said that the report was “inaccurate speculation” citing an unnamed source close to the central bank.
China’s central bank is expected to distribute its digital currency through the big four state-owned banks – the Industrial and Commercial Bank of China, China Construction Bank, the Agricultural Bank of China, and the Bank of China – and mobile payments systems Alipay and WeChat Pay, as well as UnionPay, the state-supported credit card provider, according to the Forbes report. Alibaba is the owner of the South China Morning Post.
Ma Changchun, deputy chief of the Payment and Settlement Division of the PBOC, said at the start of August that a digital currency prototype existed and that the central banks’ Digital Money Research Group had already fully adopted
blockchain architecture to ensure its use in retail transactions.
“The People’s Bank digital currency can now be said to be ready,” said Ma on August 11.
The People’s Bank digital currency can now be said to be ready Ma Changchun
Former central bank governor Zhou Xiaochuan said last month that, in addition to central banks, “commercial entities” should be allowed to issue banknotes backed by their own private currency assets, although he did not elaborate on what kind of “commercial entities” might be appropriate to issue a digital currency in China.
China is also ready to make Shenzhen a pilot zone for digital currency as part of plans for the city to become a socialist model city, according to a statement summarising a meeting between the Shenzhen party secretary Wang Weizhong and central bank governor Yi Gang released on Thursday.
The PBOC implemented a blanket crackdown in China on trading of cryptocurrency, including bitcoin, which are not backed by any government, viewing them as risks to China’s financial stability and security. At the same time, in 2014 the central bank created its own academy to study digital currencies and the related blockchain technology.
Neil Woodfine, director of marketing at blockchain start-up Blockstream, said a digital currency created by the PBOC would be “just like cash” and “would be fully controlled by the central bank.”
“If it’s digital instead of physical, they can close accounts and monitor all activities [in the entire financial system]. Commercial bank deposits are difficult for them to monitor, control or pull information out of for verification because the numbers are in each bank’s data centre,” Woodfine said.
Wang Xin, director of the central bank’s research bureau, said last month that
to create its own digital currency have pushed Beijing to speed up its own digital currency plan as Libra could potentially pose a challenge to Chinese cross-border payments, monetary policy and even financial sovereignty.
Leonhard Weese, the president of the Bitcoin Association of Hong Kong, said that a government-backed digital currency may enhance the PBOC’s control of China’s monetary system, cutting reliance on commercial banks to transmit changes in monetary policy.
“It would be similar to just killing the commercial banks,” Weese said.
which would be a non-sovereign digital currency controlled by a Swiss-based company, has come under intense scrutiny by regulators and central banks worldwide. Last month, the Group of Seven industrialised nations, known as the G7, called for urgent regulatory measures and other types of action to address serious concerns over Libra.
Central banks, however, have expressed interest in launching their own digital currencies to counter the US dollar and to gain more control of their own monetary systems.
Mark Carney, governor of the Bank of England, argued last week that the US dollar, the current dominant reserve currency, could be replaced by a global digital alternative to tackle ultra-low interest rates.
Facebook’s Libra, which is expected to be launched next year, will be pegged to a basket of convertible currencies – so it could serve as a stable online currency – while its payments will be endorsed by Visa and Mastercard. Photo: Reuters
A digital currency “could dampen the domineering influence of the US dollar on global trade”, Carney said last week at the US Federal Reserve’s annual conference, adding that a digital currency has the edge to counter shocks emanating from the US through trade and exchange rates.
Daniel Wang, chief executive and co-founder of blockchain start-up Loopring, said that a Chinese government-backed digital currency may provide a new way for the yuan to compete globally.
“If the central bank wants to increase the global competitiveness of the yuan through its digital currency, only an open and standard-based competitor carries any hope,” said Wang.
A digital yuan would “remain a sovereign currency under a centralised sovereign,” continuing to require the trust from users in the Chinese central bank and government institutions behind it, Wang added.
Alfred Schipke, senior resident representative for China at the International Monetary Fund (IMF), said that the bank is “open” to digital currencies, including the one being developed by China’s central bank.
The IMF in principle is looking at these things favourably. It’s a two-way process where we learn from China, which is often at the forefront of development. Alfred Schipke
“We don’t have a specific view on a particular currency, we haven’t looked at the details of the latest proposals from China,” Schipke said on Thursday. “The IMF in principle is looking at these things favourably. It’s a two-way process where we learn from China, which is often at the forefront of development.”
Blockstream’s Woodfine said that Beijing’s move also reflects a growing concerns among central banks that a financial disaster is on the horizon.
The 30-year US Treasury bond yield fell to an all-time low 1.976 per cent on Thursday, while yields around the world also plunged to multi-year or record low, triggering rising fears over a global recession.
Central banks around have also been driving down interest rates, with the PBOC recently unveiling a key interest rate reform that effectively cuts borrowing costs for companies to boost its slowing economy.
“We’ll see a move by governments and central banks to take back control over the financial system and use that power to direct their economies, continuing to pump money into the system to keep it afloat,” Woodfine added.
“A digital currency would be the perfect channel for helicopter money,” he said in reference to the idea that a central bank could stimulate the economy by giving out large quantities of money to the public, as if dumped from the sky. “They can send out free money to consumers.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Agricultural Bank of China, Alibaba, Alipay, autumn, Bank of China, Bank of England, Bitcoin, Bitcoin Association of Hong Kong, blockchain architecture, blockchain technology, Blockstream, Central bank, China alert, China Construction Bank, Commercial bank deposits, cross-border payments, cryptocurrency, digital currency, Digital Money Research Group, Facebook, Facebook’s Libra, financial sovereignty, Forbes, Forbes magazine, G7, governor, Group of Seven industrialised nations, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), International Monetary Fund (IMF), launching, Libra, Loopring, Mark Carney, MasterCard, Monetary policy, Payment and Settlement Division, PBOC, People’s Bank of China (PBOC), pilot zone, Reserve currency, Shenzhen, Sina.com, Singles Day, south china morning post, sovereign digital currency, Swiss-based company, to beat, Uncategorized, UnionPay, US dpllar, US Federal Reserve, US Treasury bond, verification, Visa, WeChat Pay |
Leave a Comment »
28/08/2019
- Military insiders say the aircraft appears to have beaten the FC-31 in the race to become the PLA Navy’s fighter of the future
- A military source close said it would be almost impossible to develop both aircraft over the next few years given the risk of an economic downturn
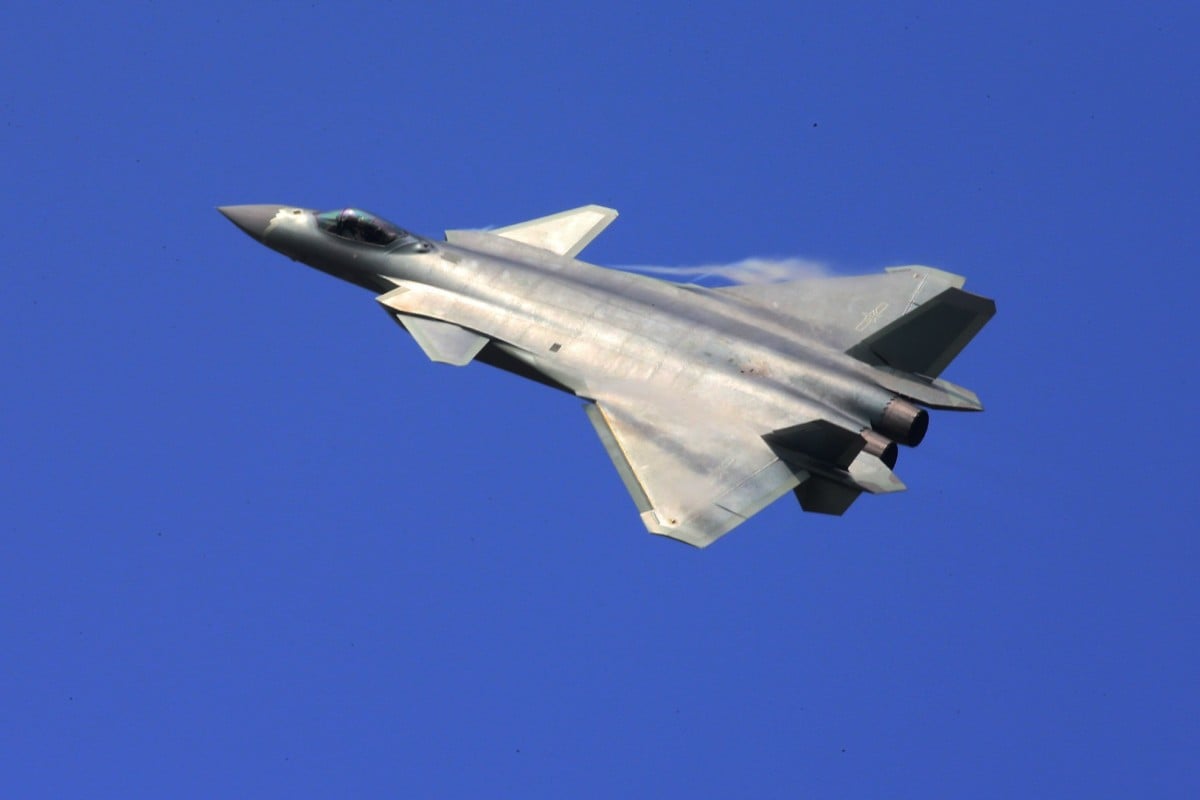
The J-20 stealth fighter is likely to be modified to serve on China’s next generation aircraft carriers. Photo: Xinhua
China’s military is likely to pick the country’s first active stealth fighter, the J-20, for its next generation aircraft carriers, according to military sources and a recent report on state media.
The J-20, made by the Chengdu Aerospace Corporation (CAC), appears to have a won a head-to-head contest with the FC-31, a fighter made by another company which is still undergoing testing.
A military insider told the South China Morning Post that the Central Military Commission, the People’s Liberation Army’s top decision-making body, now favoured adapting the J-20 for its new carriers.
“The Chengdu Aerospace Corporation will announce some new products, which will include a new version of their J-20. You can guess what type it will be,” the military insider, who requested anonymity because of the sensitivity of the subject, said.
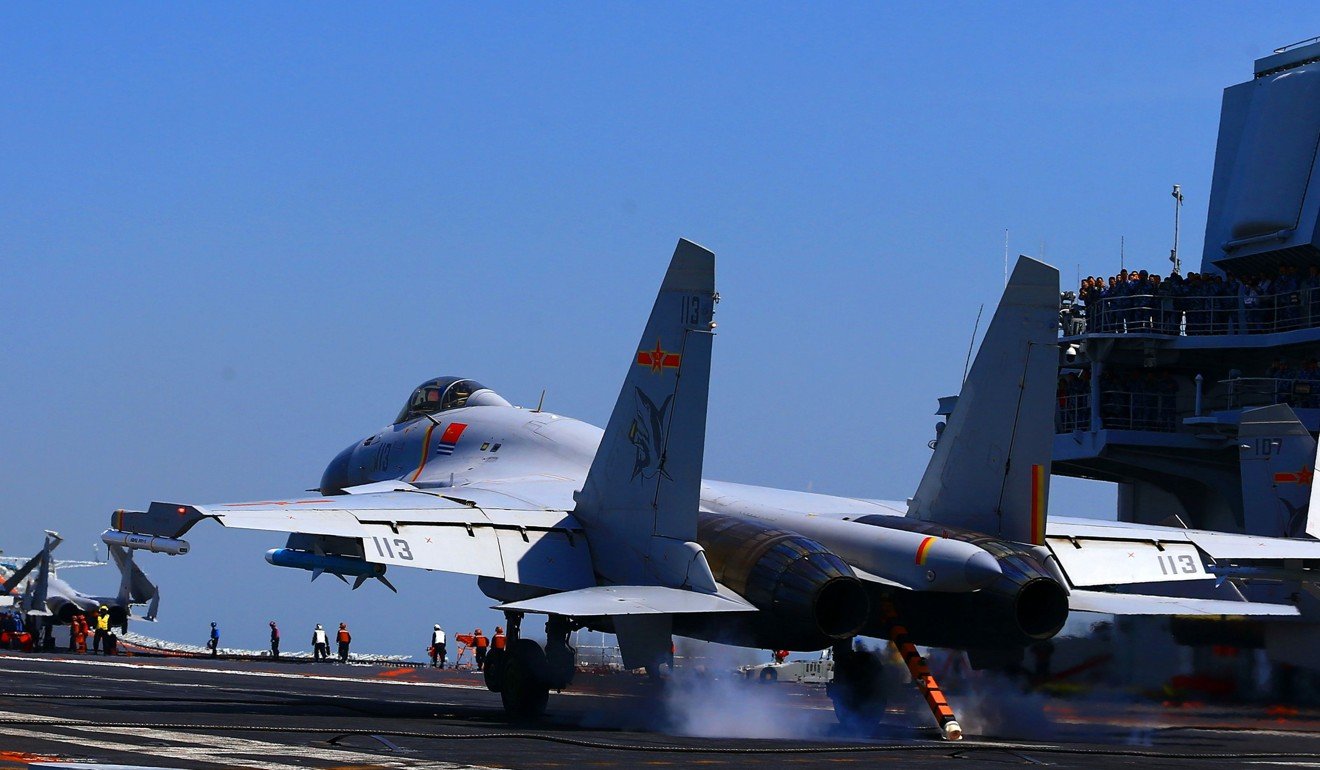
The FC-31 was independently developed by CAC’s sister company Shenyang Aircraft Corporation (SAC), which also produced the J-15 – the jets currently in use on the country’s only active aircraft carrier, the Liaoning.
Both aerospace firms are subsidiaries of the state-owned giant Aviation Industry Corporation of China, which specialises in designing and developing military aircraft, and were set up to ensure benign competition between manufacturers.
However, the SAC has faced criticism from some military leaders and experts for being too conservative and failing to innovate because of its bureaucratic structure.
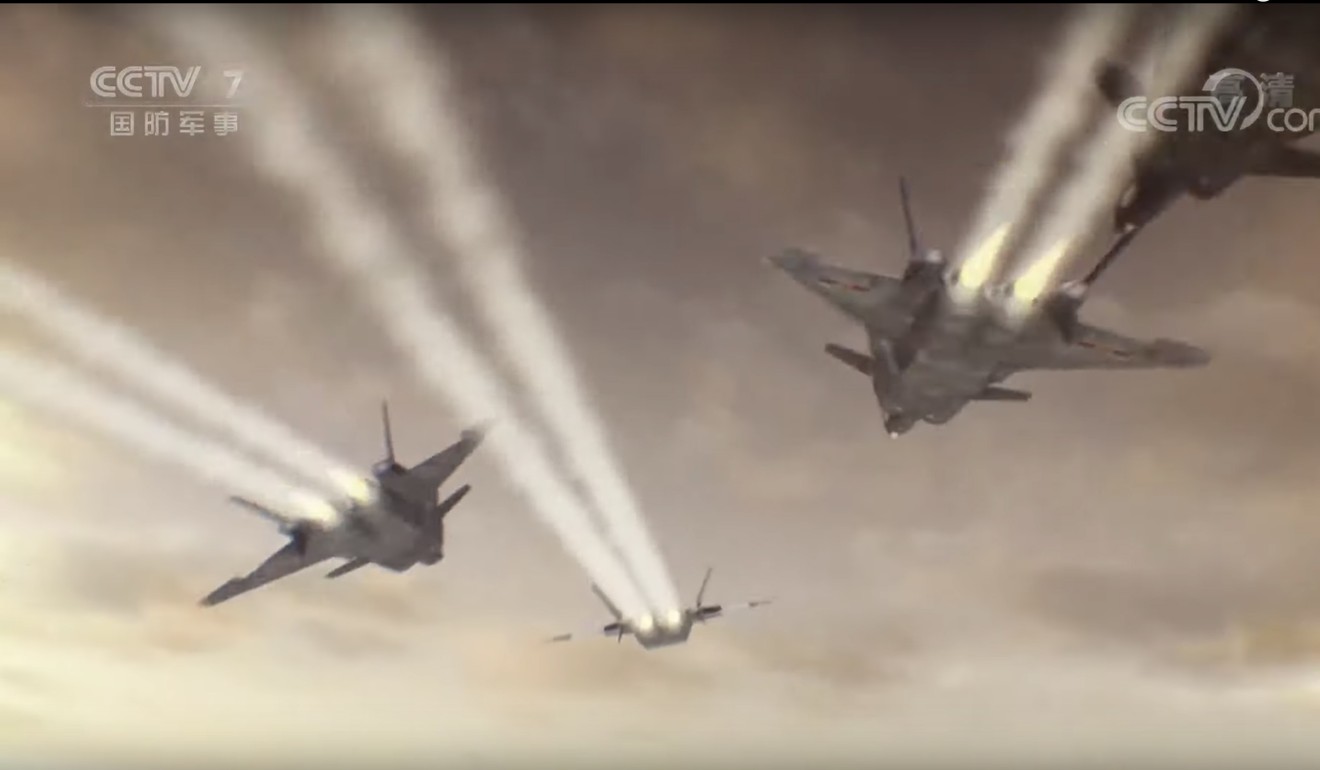
A recent programme aired by the state broadcaster China Central Television also suggests the J-20 will be chosen.
An episode of Military Documentary shown on August 16 reported how the PLA Navy was selecting candidates for pilot training and illustrated the feature with a mock-up of jets that looked like J-20s taking off from a carrier.
Ground-based J-20s – also known as Powerful Dragons – entered service with the PLA Air Force in 2017.
as China stepped up its efforts to counter the deployment of American F-22s and F-35s in the Asia-Pacific region.
A J-15 fighter lands on the Liaoning. Photo: AFP
If the selection of the J-20 is confirmed it will mark the end of a lengthy debate between its supporters and advocates of the FC-31 as to which would make a better carrier-based fighter.
Those who favoured the J-20 said it was more advanced and reliable than the FC-31, but its supporters said it was more light and nimble.
“Both the J-20 and FC-31 have their advantages. The size of the J-20 is similar to the J-15 since both are powerful heavy fighters,” Song Zhongping, a military commentator for Hong Kong-based Phoenix Television, said.
Song said the lighter FC-31 could be developed into a medium-sized carrier fighter that would complement the J-20 in future.
But another military source close to the PLA Navy said it would be almost impossible to develop both aircraft over the next few years given the risk of an economic downturn as the trade war with the US continues to escalate.
A video simulation broadcast on state television earlier this month showed fighters that resembled the J-20 taking off from a carrier. Photo: CCTV
The source said China’s next generation aircraft carriers would be with equipped electromagnetic catapults similar to those used on the US Navy’s Ford-class supercarriers.
These enable the use of heavier fighters because they are more powerful than the older diesel systems used on older carriers.
“The key problem of the J-20 is not weight, but length. If it wants to be a carrier-based fighter jet, it needs to be made shorter.”
Military insiders have previously said that CAC engineers are working to produce a shorter version of the J-20 that will work with the new launch system.
At present both the J-20 and F-31 still rely on Russian engines. The WS-15 engine that has been purpose built for the J-20 has undergone hundreds of hours of testing b
ut has yet to meet reliability targets while the F-31 prototype does not have a purpose-built engine.
China’s navy plans to build at least four carrier battle groups by 2030, three of which will be active at any given time.
Military analysts say China will need at least a decade to develop its new generation carrier-based fighters, so the J-15 will remain in service for at least a decade, if not two.
The J-15 made its maiden flight in 2009 and has been in service since 2012. They are the only fighters based on the Liaoning and will be used by its sister ship the Type 001A when it enters service, probably later this year.
Source: SCMP
Posted in aircraft carriers, Aviation Industry Corporation of China, benign competition, CAC engineers, carrier battle groups, carrier-based fighter, carriers, Central Military Commission, Central Military Commission (CMC), Chengdu Aerospace Corporation, Chengdu Aerospace Corporation (CAC), China Central Television, China Central Television (CCTV), China’s navy, electromagnetic catapults, Ford-class supercarriers, J-20 stealth jets, Liaoning, manufacturers, Military aircraft, Military Documentary, mock-up, new launch system, next generation, People’s Liberation Army, People’s Liberation Army (PLA), Phoenix Television, pick, pilot training, PLA Air Force, pla navy, Powerful Dragons, Russian engines, selecting candidates, Shenyang Aircraft Corporation (SAC), south china morning post, State broadcaster, state broadcaster CCTV, Uncategorized, US Navy |
Leave a Comment »
14/08/2019
- New facility is designed to help scientists study particles that help deflect cosmic rays in the high atmosphere
- Despite scepticism among some scientists, those familiar with the project insist radar will have a range about 10 times greater than existing ones
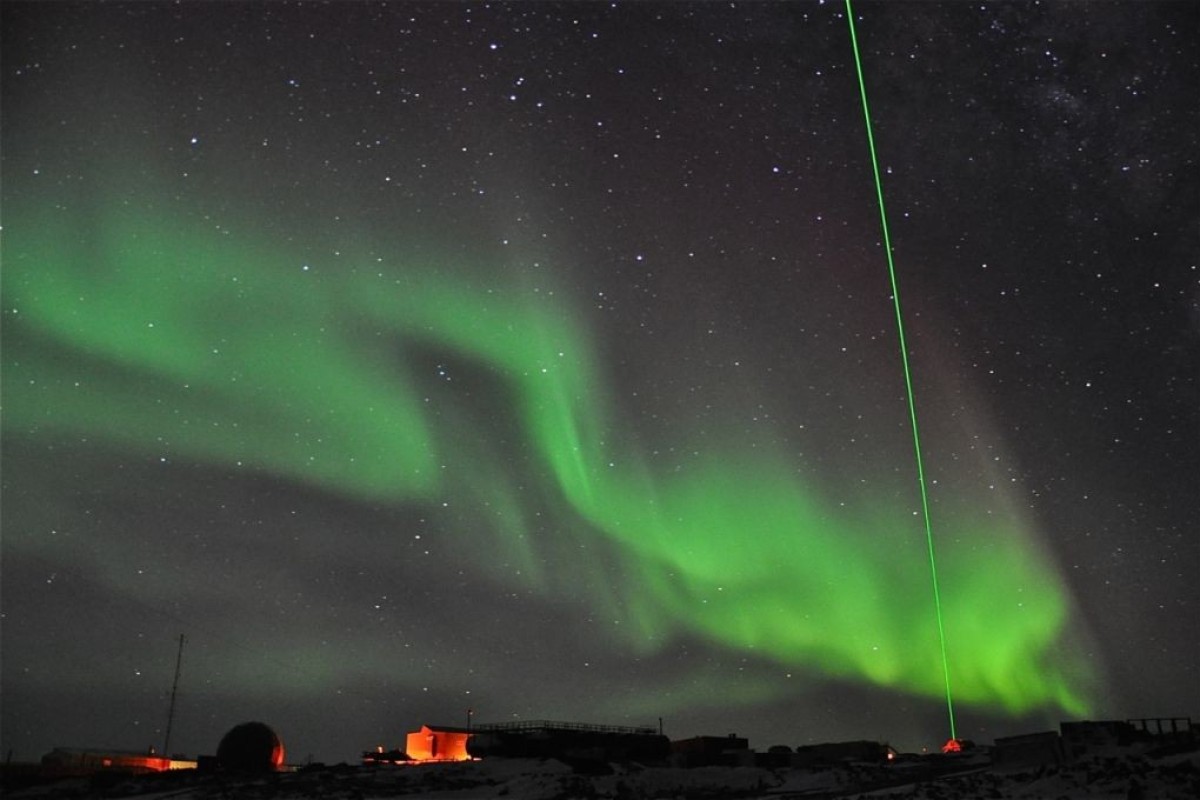
When completed the new laser radar will be used to study the high atmosphere. Photo: Handout
China has started building the world’s most powerful laser radar designed to study the physics of the Earth’s high atmosphere, according to state media reports and scientists informed of the project.
It is described as having a detection range of 1,000km (600 miles) – 10 times that of existing lasers – and will be used to study atmospheric particles that form the planet’s first line of defence against hostile elements from outer space such as cosmic rays and solar winds.
The facility, to be built on a site that remains classified, is expected to be up and running within four years and will form part of an ambitious project to reduce the risk from abnormal solar activities.
The radar will use a high-energy laser beam that can pierce through clouds, bypass the International Space Station and reach the outskirts of the atmosphere, beyond the orbiting height of most Earth observation satellites.
Lasers help tell ghostly story of doomed Nazi submarine U-576 and its entombed crew
There, the air becomes so thin that scientists will be able to count the number of gas atoms found within a radius of several metres.
These high-altitude observations could greatly expand our knowledge of a part of the atmosphere that has been little studied because the distances involved mean no one has been able to make direct observations from the ground.
“The large-calibre laser radar array will achieve the first detection of atmospheric density of up to 1,000km in human history,” said a statement posted on the website of the Chinese Academy of Sciences on Tuesday, a day after the launch of the project.
But the claim has been greeted with some scepticism in the scientific world.
“I think the 1,000km is a misprint!” professor Geraint Vaughan, director of observations at the National Centre for Atmospheric Science in the UK, replied when asked about the project.
Vaughan, who is also a Fellow of the Royal Meteorological Society, said that while he thought the Chinese announcement was “very interesting”, it did not seem possible with existing technology.
At present, the effective range of atmospheric lasers is about 100 kilometres.
Some other senior scientists in China and overseas also expressed doubt about the project, although they requested anonymity due to the sensitivity of the issue.
US warns airmen to beware of laser attacks near China’s military base in Djibouti
“There are other approaches, such as launching a satellite. Building such a huge, expensive machine on the ground does not make sense,” said a Beijing-based laser scientist.
But several researchers told the South China Morning Post that the project did exist, and insisted that 1,000km range was not a mistake.
Hua Dengxin, a professor at Xian University of Technology and a lead scientist in China’s laser radar development programmes, said: “I have heard of the project, yes. But I cannot speak about it.”
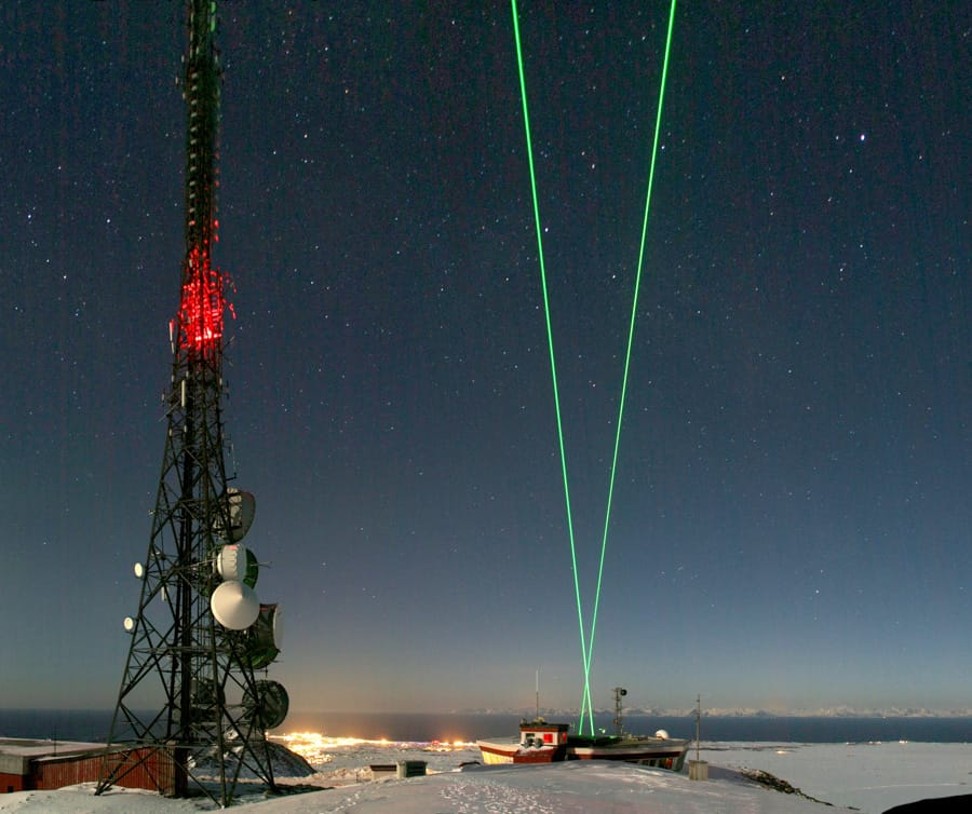
Powerful telescopes will pick up the signals reflected back to earth. Photo: Handout
According to publicly available information, the facility will use several large optical telescopes to pick up the faint signals reflected by the high-altitude atoms when the laser is fired at them.
The project is part of the Meridian Space Weather Monitoring Project, an ambitious programme that started in 2008 to build one of the largest, most advanced observation networks on Earth to monitor and forecast solar activities.
By 2025 Meridian stations containing some of the world’s most powerful radar systems will be established across the world – with facilities in Arctic and Antarctic, South China Sea, the Gobi desert, the Middle East, Central Asia and South America.
China in race for counter-drone tech and laser weapons as it tries to catch up with US
The purpose of the Meridian project, according to the Chinese government, is to reduce the risk abnormal solar activities pose to a wide range of Chinese assets including super-high voltage power grids, wireless communication, satellite constellations, space stations or even a future base on the Moon.
Chinese laser scientists have developed some of the world’s most sophisticated systems in recent years, including ranging stations that can track the movement of satellites and space debris, which the Pentagon has claimed have temporarily blinded some American scientists.
Last year researchers based in Xian, the capital of Shaanxi province, announced that they had developed a “ laser AK-47” that could set fire to target from a distance of 800 metres.
The Chinese government is also funding the development of a laser satellite that can penetrate seawater to a depth of 500 metres from space to detect the waves generated by submarines.
The use of such a powerful laser raises concerns that passing objects such as planes, satellites or spacecraft – to say nothing of birds – may be at risk from its beams.
But Professor Qiao Yanli, engineer in chief at the Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, part of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, said there was an “extremely low” risk of this happening.
“The sky is enormous. Getting hit by a tiny beam is almost impossible,” he said.
Some much smaller laser radars, such as those installed in auto-driving test vehicles, have reportedly damaged digital cameras by burning a few pixels on sensor.
But spacecraft such as earth observation satellites, according to Qiao, usually have some protection mechanisms, such as a warning system, to avoid permanent damage caused by an accidental laser hit.
‘Laser AK-47’? Chinese developer answers sceptics with videos of gun being tested
Professor Li Yuqiang, a researcher at the Yunnan Observatories in Kunming, whose team has measured the distance between the Earth and the Moon by shooting lasers at a reflector placed on the lunar surface during the US Apollo 15 mission, said detecting atom-sized targets on the fringes of the atmosphere posed many technical challenges.
“The number of photons [particles of light] reflected by the sparse gas particles will be very small. Even if they can be picked up by large telescopes on the ground, the analysis will require some very good algorithms to separate the useful signals from the noise,” Li said.
“How that can be achieved is beyond the scope of my knowledge.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in algorithms, Anhui Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Antarctica, Arctic, Building, Central Asia, China alert, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Djibouti, Earth's solar shield, Gobi Desert, high atmosphere, International Space Station, Kunming, Meridian Space Weather Monitoring Project, Middle East, Moon, National Centre for Atmospheric Science, Nazi submarine, Pentagon, physics, powerful laser radar, Royal Meteorological Society, shaanxi province, south china morning post, South China Sea, study, Uncategorized, Xi'an, Xian University of Technology, Yunnan Observatories |
Leave a Comment »
01/08/2019
- Fears are growing in the city that the military could be called in to quell unrest
- But the costs and complexities of doing so mean Beijing is highly unlikely to give the orders, observers say
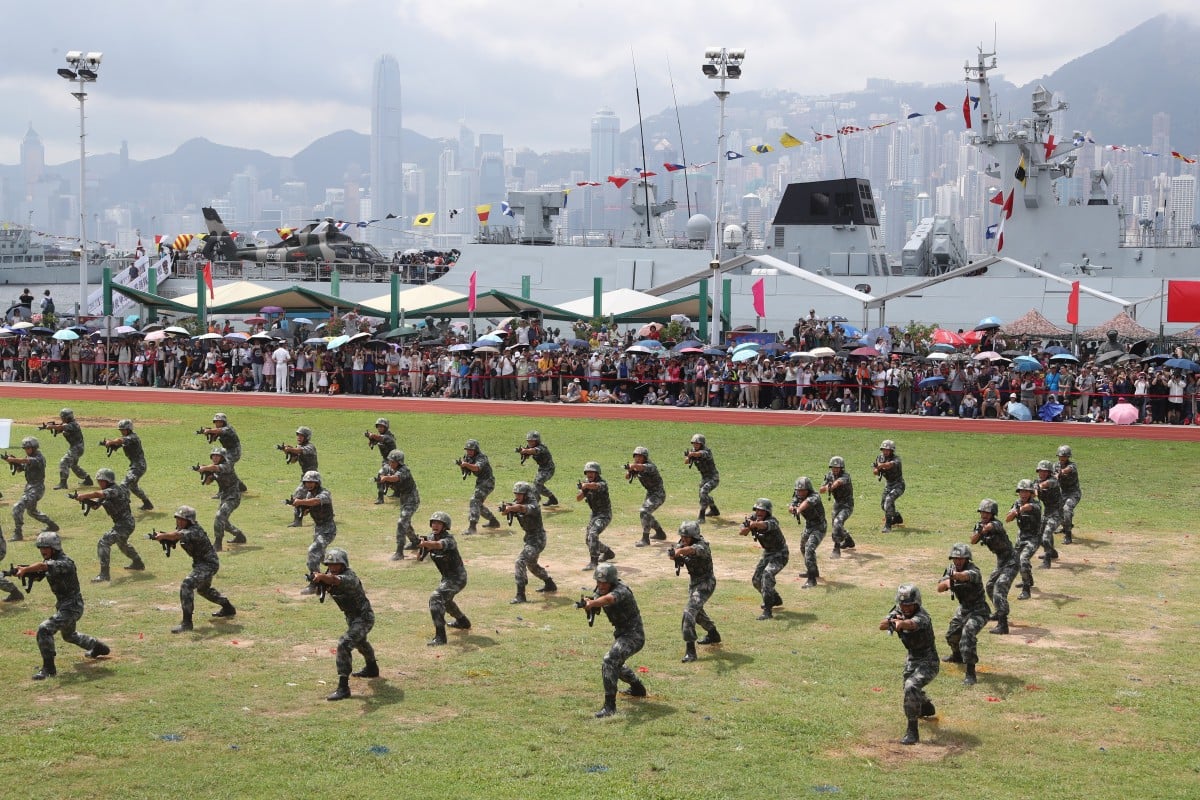
PLA soldiers show their skills during a naval base open day in Hong Kong. The PLA has had a presence in Hong Kong since the city’s return to Chinese sovereignty. Photo: K.Y. Cheng
It is a prospect dreaded by many in Hong Kong, but debate is growing in mainland China about whether the central government should end weeks of upheaval in the city by sending in the People’s Liberation Army (PLA).
The PLA has had a presence in Hong Kong since the city’s return to Chinese sovereignty but – unlike in mainland China – memories of the military’s bloody suppression of pro-democracy students and activists in Beijing in 1989 are still strong in the city three decades on.
Still, images of protesters vandalising Beijing’s liaison office in downtown Hong Kong on Sunday have fanned nationalist anger across the mainland, prompting calls for PLA intervention.
Concerns only deepened on Wednesday when defence ministry spokesman Wu Qian commented on the recent clashes and protests in Hong Kong. Without suggesting any action or plans by the PLA, Wu made clear that the Garrison Law, which governs the operations of PLA troops in Hong Kong, already stipulates that the PLA is legally allowed to help the city maintain law and order at the request of Hong Kong’s government.
“We are closely following the developments in Hong Kong, especially the violent attack against the central government’s liaison office by radicals on July 21,” Wu said.
“Some behaviour of the radical protesters is challenging the authority of the central government and the bottom line of ‘one country, two systems’,” he warned, referring to the formula that grants Hong Kong a high degree of autonomy for 50 years. “This is intolerable.”
Both Article 14 and Article 18 of the Basic Law – the city’s mini-constitution – spell out how and under what circumstances the PLA troops in Hong Kong can be used.
While the legality is clear, analysts still believe that given the exorbitant political cost and complexities involved, using the military would remain an unlikely last resort.
Even Hu Xijin, editor-in-chief of China’s nationalist tabloid Global Times, has spoken out against the idea, citing its “huge political cost” and the “severe uncertainty” it might bring to the situation.
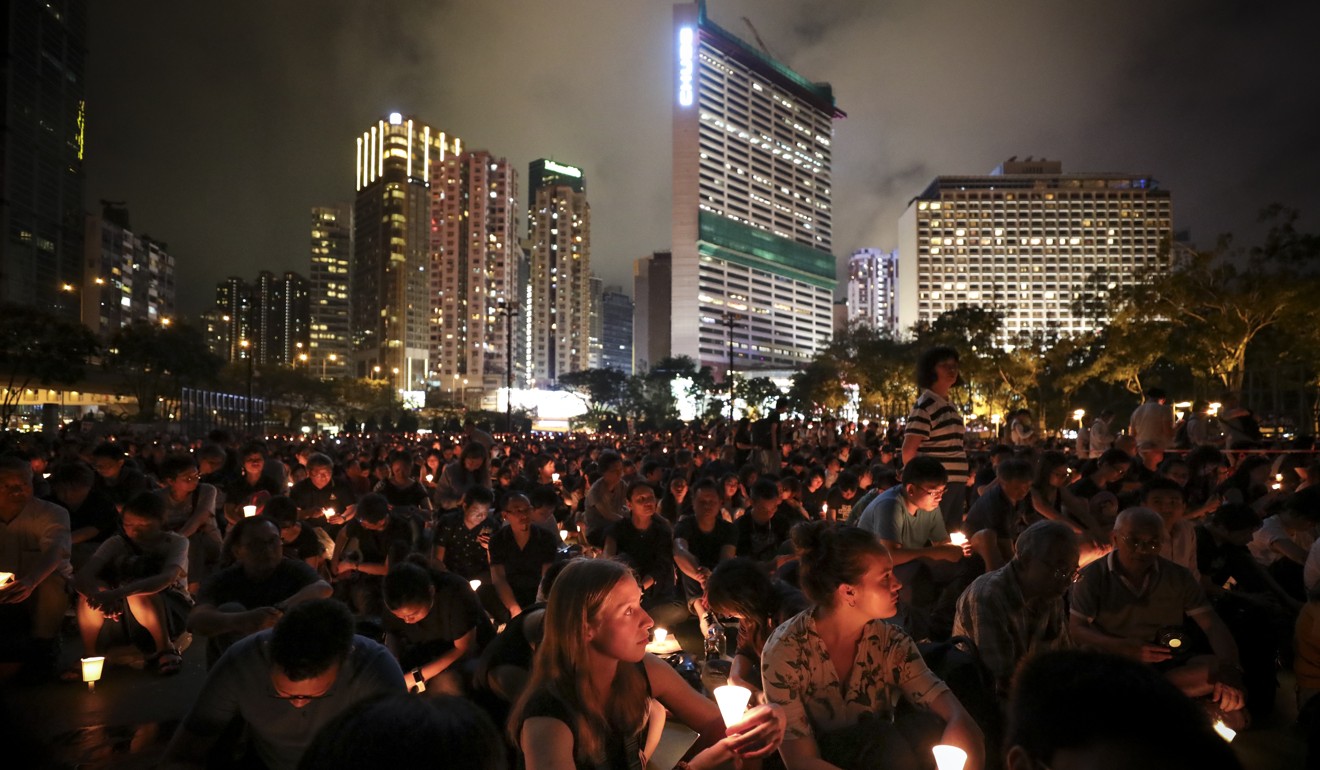
Crowds hold candles at a vigil in Victoria Park in Hong Kong in June to mark the 30th anniversary of the Tiananmen Square crackdown. Photo: James Wendlinger
“Once the PLA has taken charge of the situation in Hong Kong and quelled the riots, what’s next?” Hu said in a social media post on Monday.
Hu said there were no governance procedures in place that would allow the PLA to operate in Hong Kong and return things to normal. He also warned that any such action would be followed by international condemnation and a severe backlash among the Hong Kong public.
“The [PLA’s] Hong Kong garrison is the symbol of national sovereignty. It is not a fire brigade for law and order in Hong Kong,” he said.
Any move to use the Chinese troops will create a furore in the US Congress … They will re-examine the Hong Kong Policy Act very carefully Larry Wortzel, senior fellow at American Foreign Policy Council
The South China Morning Post reported last week that military force was not an option for mainland leaders working on a strategy to resolve the city’s biggest political crisis in decades.
And in June Major General Chen Daoxiang, commander of the Hong Kong garrison, assured David Helvey, US principal deputy assistant secretary of defence for Indo-Pacific security affairs, that Chinese troops would not interfere in the city’s affairs, according to Reuters.
The comments support analysts’ assessments that deploying the PLA is not a viable solution to Hong Kong’s crisis.
“Will the mobilisation of PLA troops further inflame the situation? There might be people who will resist or even revolt against the PLA, and that may lead to bloodshed,” said Lau Siu-kai, vice-chairman of the Chinese Association of Hong Kong and Macau Studies, a semi-official think tank.
The last time Beijing sent in troops to quell pro-democracy protests was during the Tiananmen Square crackdown on June 4, 1989 – bloodshed that has stained the PLA and the Communist Party to this day, despite decades of efforts to wipe it from public memory.
The last time Beijing sent in troops to quell pro-democracy protests was during the Tiananmen Square crackdown in 1989. Photo: Reuters
“Although they don’t like to admit it, they know they made a mistake in the way they used the PLA [in 1989],” said Larry Wortzel, a long-time PLA watcher, who witnessed the crackdown as an assistant military attache at the US embassy in Beijing 30 years ago.
“In subsequent years, when there were major demonstrations, they managed to handle them with either the People’s Armed Police [PAP] or the Public Security Bureau [PSB], or in some cases a combination of both,” said Wortzel, now a senior fellow in Asian security at the American Foreign Policy Council in Washington.
If the military was deployed [in Hong Kong], it would mean China was ready to shut its doors completely Chen Daoyin, a Shanghai-based political analyst
The PAP is a 1.5 million-strong paramilitary police force tasked with maintaining domestic security and order, while the PSB is the country’s police force.
The June 4 crackdown is still widely remembered in Hong Kong, where tens of thousands gather every year on its anniversary for a candlelight vigil in the heart of the city.
“The activities in Hong Kong and the Chinese Communist Party’s conduct there have really had a profound impact on thinking in Taiwan. It has killed any chance with any political party of [supporting] the one country, two systems,” Wortzel said.
Chinese military can be deployed at Hong Kong’s request to contain protests, Beijing says
“The last thing President Xi Jinping and the Politburo Standing Committee would want to do, if they can avoid it, is to use the PLA [in Hong Kong].”
The situation in Hong Kong is also being closely watched in the West, with many international firms basing regional headquarters in the Asian financial hub, thanks to its capitalist system and rule of law.
Deploying the PLA to Hong Kong would certainly spark an international outcry and draw huge pressure from Western countries, said Liang Yunxiang, an international affairs expert at Peking University.
“Britain, of course, would have the harshest criticism since it governed Hong Kong for a long time and signed treaties with China to ensure Beijing would keep its commitment to one country, two systems,” Liang said.
In the United States, the repercussions could go beyond verbal condemnation to a shift in policy that might fundamentally change Hong Kong’s status as an international financial centre and prompt an exodus of businesses, according to Wortzel.
“Any move to use the Chinese troops will create a furore in the US Congress … They will re-examine the Hong Kong Policy Act very carefully,” he said, referring to the bill passed in 1992 that allows Hong Kong to be treated as a non-sovereign entity distinct from mainland China on trade and economic matters.
Hong Kong head blasts violence, amid further extradition bill unrest
“They will simply treat Hong Kong like another Chinese city, which affects export controls and how the financial industry operates.”
Just last month, members of Congress reintroduced the bipartisan Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act. If the legislation is passed, the US could revoke Hong Kong’s special status under American law if Beijing fails to ensure the city has “sufficient autonomy”.
The crisis comes as Beijing’s ties with Washington are already strained by a year-long trade war that has spilled into other areas of bilateral relations.
PLA troops go through their paces for the public at their Hong Kong barracks during an open day. Photo: Edward Wong
There is also mounting international pressure on China over issues such as its mass internment and political indoctrination of an estimated million or more members of Muslim minorities in Xinjiang, despite the Chinese government’s repeated denials of ill-treatment of the inmates and attempts to defend its policies.
Chen Daoyin, a Shanghai-based political analyst, said the increasing scrutiny China faced from Western countries – whether in the form of punitive tariffs or restrictions on technology – made it all the more important for China to keep Hong Kong as an open channel to connect with the world.
“If the military was deployed [in Hong Kong], it would mean China was ready to shut its doors completely,” Chen said.
Lau, from the Chinese Association of Hong Kong and Macau Studies, said the PLA should only be deployed as a last resort.
Two calls per second ‘jammed emergency lines’ during Hong Kong violence
“It would be a huge blow to the principle of ‘letting Hong Kong people govern Hong Kong with a high degree of autonomy’, since it will prove that Hong Kong people are not up to the task of governing themselves,” he said.
Hu, from Global Times, said the PLA troops could be used only if the authorities lost control of the city or an armed rebellion broke out.
Short of that, he said, the central government should let the chaos in Hong Kong run its course and wait for the public mood to flip.
This strategy of sitting it out hinges on the city’s police force holding the line and stopping Hong Kong’s slide into total anarchy.
Wortzel also warned that there were lines protesters should not cross – or risk provoking the use of military force.
“For instance, to this point, demonstrators have not gone up against the PLA garrison or any of its outposts. If they did that, I think it’s possible – actually it is very likely – that there will be a limited mobilised response [to defend the facilities],” he said.
While most analysts said the chance of Beijing resorting to military force was slim, the very idea – ludicrous to even discuss three months ago – has become a popular topic on social media on the mainland, where the discussion is not censored and many commenters support it.
The official media have been careful not to touch the subject but they too have stepped up rhetoric against the protests in Hong Kong.
In a rare move, state-run China Central Television has run commentaries and reports about protests in Hong Kong during its main evening news for five days in a row.
Only the most politically important issues receive such unusual treatment.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Asian financial hub, Beijing, Britain, capitalist system, China Central Television, Chinese Association of Hong Kong and Macau Studies, Chinese sovereignty, Chinese troops, crackdown, garrison, Global Times, Hong Kong, Hong Kong barracks, Hong Kong Human Rights and Democracy Act, Hong Kong Policy Act, Indo-Pacific security affairs, Major General Chen Daoxiang, Muslim minorities, One country, two systems, Peking University, PLA, politburo standing committee, President Xi Jinping, protests, Rule of law, send in the troops, south china morning post, stamp out, Tiananmen Square, Uncategorized, United States, Washington, Western countries, Xinjiang |
Leave a Comment »
29/07/2019
- China last year poured US$2.5 billion into firms in India, which is a healthy breeding ground for up-and-coming tech outfits
- Active cooperation between these investors and entrepreneurs holds a multitude of benefits for both sides, according to industry pundits
Chinese venture capitalists are injecting funds into a variety of cash-hungry Indian businesses. Photo: Shutterstock
C
hinese President Xi Jinping and
look set for another informal summit in October, and a key item on the agenda will be
.
Indian start-ups have become a major target for
, who have been looking to emulate their United States counterparts such as Tiger Global and Sequoia Capital that dominate the sector.
On top of this, a slowdown in start-up deals in China has nudged the country’s investors to look beyond their borders, and
’s affordable labour market and strong economic growth provide a healthy breeding ground for young tech outfits.
Can Bollywood be the bridge that binds India and China?
Led by heavyweights such as Shunwei Capital, Fosun International, Tencent Holdings, Xiaomi and Alibaba Group Holding – which owns the
South China Morning Post –
have been injecting funds into a variety of cash-hungry Indian businesses.
For many of these start-ups, the knowledge and technology of Chinese investors act as the backbone of their business Ntasha B, Venture Gurukool
Beneficiaries have included advertising firm Media.net, e-commerce operator Snapdeal, digital payment provider Paytm, online travel firm MakeMyTrip, messaging platform Hike, health tech start-up Practo and news aggregator Dailyhunt.
“For many of these
, the knowledge and technology of Chinese investors act as the backbone of their business, along with the operational expertise of Indians in the domestic market,” said Ntasha B, co-founder of Venture Gurukool, a mentoring platform for start-ups which works closely with Indian diplomatic missions in China.
Chinese President Xi Jinping and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi are set to meet again in October. Photo: Xinhua
She added that Chinese investors usually had a hands-on approach and were a bit inflexible, unlike their American counterparts, who gave some elbow room in hiring local teams.
A senior executive with an Indian start-up, who did not wish to be identified, said it was sometimes straightforward to convince Chinese investors as they could relate to Indian business models and requirements that were dissimilar to those from the Western world.
The world’s second-largest economy invested nearly US$2.5 billion in Indian start-ups last year, a figure that has touched almost US$1 billion so far this year, according to finance research firm Venture Intelligence. The number of such deals jumped from just one in 2013 to 27 last year.
What does Amazon’s China departure mean for its Indian e-commerce battle?
Indian start-ups are estimated to have raised US$3.9 billion from around the globe in the first six months of this year, and the inflow from Chinese behemoths played a key role in pushing them to turn east to source funding.
“What’s more interesting about [Chinese investors’] strategy is that they’re paying more attention to rural India. If you look at the companies they’ve invested in, a fair amount of their businesses target the rural segment,” said Sandeep Murthy, managing partner at venture capital firm Lightbox Ventures, which keeps a close watch on Chinese investments. He said the brisk economic activities in India’s tier two and tier three towns are more attractive to Chinese investors than India’s urban centres.
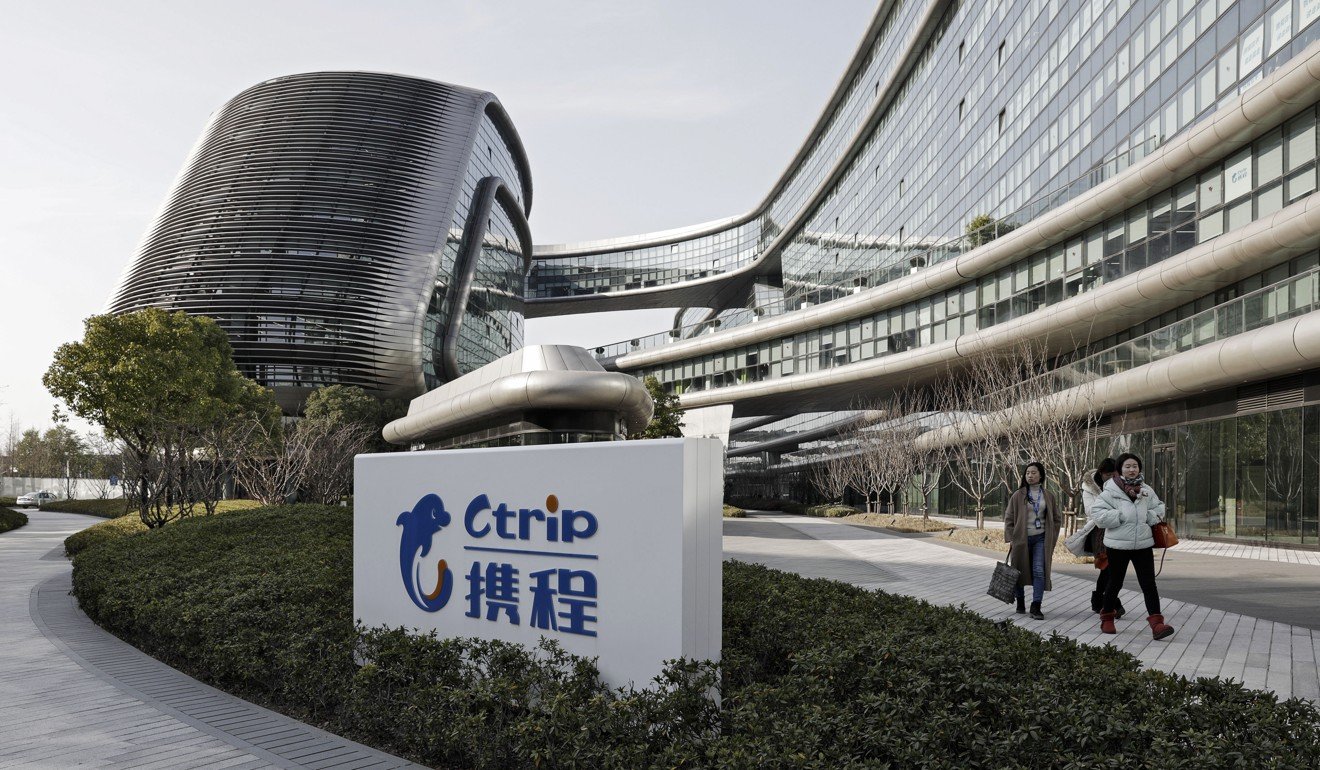
Ctrip, China’s largest online travel agency, is drawn to the size and rapid advancement of the Indian market. Photo: Bloomberg
For Ctrip – China’s largest online travel agency, which in April took a 49 per cent stake in MakeMyTrip – the appeal of India was its whirlwind technological advancement and the disposable income of its massive young population.
“[MakeMyTrip has] achieved fast growth in the online travel market and is becoming well recognised in the Indian market. Their comprehensive products and services, management team and the opportunities in India result in our confidence that they will continue to succeed,” said Wei Yuan Min, a member of Ctrip’s global team. Behind the US and China, India houses the world’s third-largest start-up ecosystem in terms of the number of companies. As for the number of unicorns – start-ups valued at over US$1 billion – India ranks third, offering a vibrant habitat for entrepreneurial ventures. The country is home to 32 such firms, with the addition of nearly half a dozen so far this year and 15 last year.
In India, one man took on Chinese firm ByteDance to shut down TikTok – and he wants to do it again
New Delhi expects there to be 12,000 tech start-ups in the country by next year, up from 7,200 last year. There were 1,200 new tech firms in the sector last year, according to industry body Nasscom.
One of those capitalising on this opportunity is the Beijing-headquartered technology company Xiaomi, which last year promised to pump US$1 billion into 100 Indian start-ups over the next five years. Most of these Indian firms are involved in businesses that are ancillary to Xiaomi’s key operations.
Chinese firm Xiaomi is banking on Indian start-ups to strengthen its own products. Photo: Reuters
“These start-ups help us in building a stronger product offering,” a Xiaomi spokesperson said. “The idea is to invest in start-ups which can further boost the mobile ecosystem in India. They could be into mobile gaming, service providers, value-added services or servicing the mobile industry.”
Xiaomi has been rapidly expanding its businesses in India, selling smartphones, television sets, security cameras, speakers, power banks, and more. India was the first market outside China where Xiaomi introduced its television sets.
Asked which sector would be Xiaomi’s focus for investment in the coming years, the spokesperson said the company was looking to focus on hardware-related start-ups in the ecosystem which could offer “robust solutions” to its Indian requirements.
Amazon, Uber and Google struggled in China, but Indian hotel chain Oyo is succeeding.
Here’s why
While hopes for India’s start-up sector are high, there have been some disappointments. There were reports this month that Alibaba, a major shareholder in Paytm, was unhappy with the Indian firm’s performance, pressuring it to realign its strategies and looking unlikely to provide fresh capital.
Paytm, a digital-payment-system unicorn, launched its own e-commerce Paytm Mall in 2016 when Walmart-backed Flipkart and Amazon were dominating the market.
However, the venture has yet to take off and is burning through cash.
Paytm refused to comment on the matter.
Paytm has attracted investment from Alibaba, but its Paytm Mall venture is struggling. Photo: Bloomberg
Chinese firms’ coordinated effort to enter the Indian start-up scene has made it easy for Indian ventures to access new sources of revenue. For instance, the state-run Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), the country’s largest lender, launched an India-specific investment fund for Chinese investors in May last year.
Several Chinese venture capitalists are also providing platforms for entrepreneurs through fellowship schemes. Four Indian ventures – Zefo, Healthy Buddha, NowFloats and Grozip – took part in one such fellowship initiative run by Alibaba last year.
Gold, jewels, ‘Islamic’ finance: how India’s I Monetary Advisory built a US$365 million Ponzi scheme
India has warmly welcomed these initiatives. Amitabh Kant, chief executive of state-backed policy think tank Niti Aayog and a close aide of Modi, has publicly said China should become the topmost investor in its neighbour.
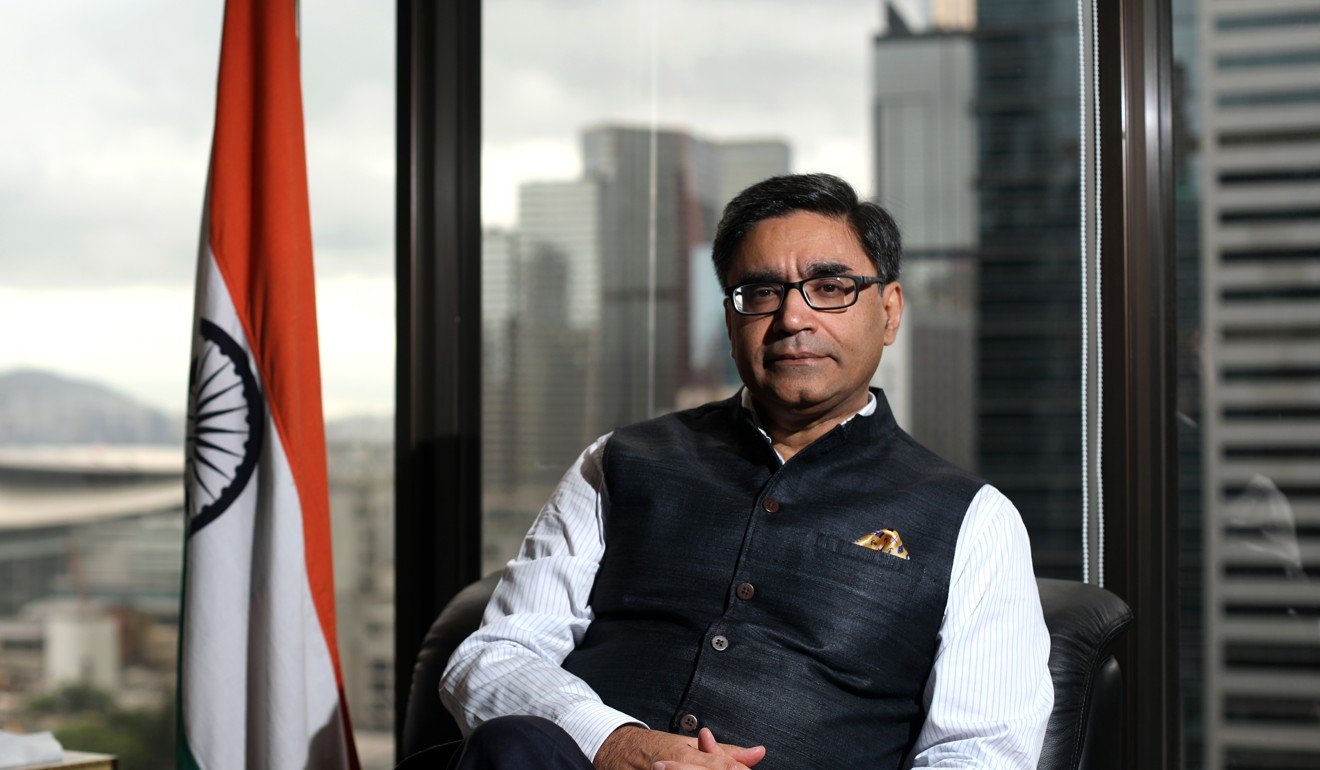
Vikram Misri, India’s ambassador to China, has also been pushing for increased economic cooperation and Chinese investment since he took charge in January, despite expressing concerns over New Delhi’s widening trade deficit with Beijing.
Vikram Misri, India’s ambassador to China, is looking for more economic cooperation between the two countries. Photo: Xiaomei Chen
The increased Chinese investment in Indian ventures has coincided with the Modi administration’s 2015 launch of the Startup India initiative, an umbrella scheme aimed at easing related activities through measures such as tax exemptions and simplified paperwork.
Industry pundits say active cooperation between Chinese investors and Indian entrepreneurs holds a multitude of benefits for both sides.
“The cooperation gives Chinese investors global scale and opportunity to diversify their investments,” said Neil Shah, partner and research director at the technology market research firm Counterpoint.
The cooperation gives Chinese investors global scale and opportunity to diversify their investmentsNeil Shah, Counterpoint
“For Indian start-ups, this gives cross-border learning, guidance from their global investors on dos and don’ts, tactical and long-term strategy, how to create value, run operations efficiently as well as expand beyond India.”
Nilaya Varma, partner and leader of markets enablement at KPMG India, said there was a cultural shift happening in the country where young Indians brimming with ideas wanted to pursue their dreams rather than work for someone else. This brought out the entrepreneurial spirit of this generation, he said.
“The knowledge, concepts, ideas and innovations of the small start-ups in India will have a global appeal. So it makes a lot of sense for Chinese big players to invest here,” he said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Alibaba Group Holding, Amazon, Beijing, Bollywood, Bytedance, Chinese money, Chinese President Xi Jinping, Counterpoint Research, E-commerce, Flipkart, Fosun International, Google, Grozip, Healthy Buddha, I Monetary Advisory, India’s ambassador to China, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Indian start-ups, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), KPMG India, MakeMyTrip, Nasscom, New Delhi, NowFloats, online travel agency Ctrip, OYO, Paytm, Paytm Mall, Ponzi, powering, Sequoia Capital, Shunwei Capital, south china morning post, Tencent Holdings Ltd, Tiger Global, TikTok, Travel agency Ctrip, Uber, Uncategorized, unicorn, United States, Vikram Misri, Walmart, Xiaomi, Zefo |
Leave a Comment »
08/07/2019
- Compact plants proposed to ease pollution but backers must win over wary public
China is exploring the idea of using small nuclear power plants to phase out coal- and gas-fired heating generators in smog-afflicted northern China. Photo: Reuters
China plans to build a pilot small-scale nuclear reactor that could replace coal or gas to heat towns and cities in its colder northern regions, an official with the state-owned developer in charge of the project said on Monday.
The small heating reactor was planned for the city of Jiamusi in northeastern Heilongjiang province, one of two proposed units with a combined capacity of 400 megawatts, Wang Xujia, a senior engineer with the State Power Investment Corp, said on the sidelines of an industry conference.
“The project is still under central government review for approval,” Wang said, adding that the developer aimed to put the project into operation by 2024.
China has been exploring the use of small nuclear reactors – less than a fifth of the size of a standard reactor – as alternative heating systems in smog-prone northern regions.
The state provides heating throughout northern China from November to March, using predominantly coal- or gas-fired boilers.
State-owned China National Nuclear Corp (CNNC) has already conducted trial runs for a “district heating reactor” (DHR) design, which it says can supply heat to 200,000 urban households.
China-built nuclear reactors may enjoy home advantage as delays and costs stymie foreign competitors
The DHR model consists of a reactor core immersed in a water-filled tank. It is estimated to require investment of 1.5 billion yuan (US$217 million) and take three years to build, making it cheaper and quicker to construct than conventional reactors.
However, while the various designs will use only a fraction of the radioactive material of a conventional nuclear plant, officials acknowledge the biggest challenge is convincing the public the reactors are safe and reliable.
“The planned project in Jiamusi will be located in a remote area of the city which undermines its economic efficiency, but since it is just a demonstration project we just want to complete one first and show it to the public,” Wang said.
China aims to raise total nuclear capacity to 58 gigawatts by the end of next year, but it has not launched any new conventional reactors in more than three years.
China expected to miss target for 2020 nuclear capacity
After Japan’s Fukushima accident in 2011, China conducted a root-and-branch safety review and decided it would only use the most advanced “third generation” technology for any new projects.
However, those technologies – including Westinghouse’s AP1000 and the Areva-developed EPR – have proved to be expensive, complex and prone to long construction delays.
In a bid to broaden its options, the country is developing smaller units and plans to launch its first “small modular reactor” on the island province of Hainan at the end of this year.
China also planned to launch floating nuclear reactors with the aim of developing a fleet of ship-mounted nuclear generators that could be deployed on islands in Southeast Asia, Song Danrong, a reactor designer at CNNC, told Monday’s conference.
This article appeared in the South China Morning Post print edition as: Pilot nuclear reactor may replace coal in north

After brief pause, China rushes to build more nuclear power plants

China General Nuclear Power and rival China National Nuclear plan to build four more reactors on mainland

Under draft rules, nuclear power projects in China will need local support
Posted in Areva-developed EPR, “district heating reactor” (DHR), China General Nuclear Power, China National Nuclear Corp (CNNC), China National Nuclear Corporation, coal, coal or gas, coal- and gas-fired heating generators, floating nuclear reactors, Fukushima accident, heat, Heilongjiang province, Jiamusi, Pilot nuclear reactor, ship-mounted nuclear generators, small test nuclear reactor, smog-prone north, south china morning post, State Power Investment Corp, Uncategorized, Westinghouse’s AP1000 |
Leave a Comment »
05/07/2019
- Riot police deployed after week of unrest over proposed plant next to residential areas – echoing recent years’ protests against incinerators elsewhere in the country
- District government urges people to ignore rumours and says plant’s location has yet to be finalised
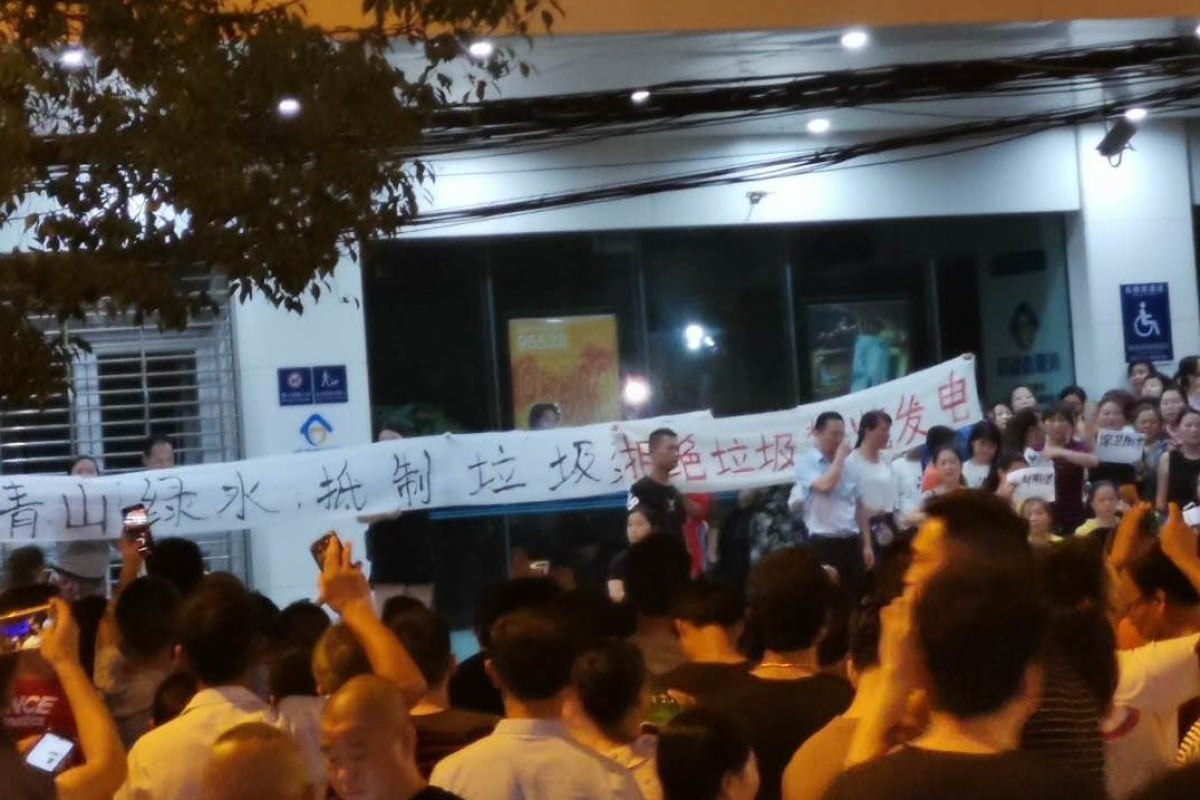
People in Yangluo protest against the proposed incineration plant on Thursday night. Photo: Handout
Thousands of people took to the streets in central China on Thursday night in a seventh day of protests against the construction of a waste incineration plant.
Protesters carried banners and chanted as they marched against a waste-to-energy plant that could be built next to residential areas in Yangluo, near Wuhan, the capital of Hubei province.
Residents were angered by plans to build the plant on a garbage landfill site that had been expected to be turned into a public park.
They shouted slogans such as “Return us the green mountain and clear waters” and “Garbage burning plant get lost from Yangluo”.
Riot police move in as protests continue in Yangluo on Thursday. Photo: Handout
A letter to the public by the Xinzhou district government on Wednesday had urged people “not to listen to or spread rumours”, and said that a location had yet to be finalised for the plant.
“What is rumoured online to be the garbage burning project that has already started is in fact demolition work for a railway construction project,” the letter said.
Converting waste to energy by burning it has been adopted in China as an alternative to burying rubbish in landfill sites – which causes pollution and requires a lot of land – but it has been widely resisted because of fears that it is a health hazard. Large protests against incinerators have been held in recent years in Zhejiang, Jiangsu, Hubei, Beijing and Guangdong.
“We understand the need to dispose of garbage in an environmentally friendly way, but does it have to be that close to our homes? Two universities and more than 10 residential areas are within a 3km (1.86 miles) radius,” said the man, referring to the Wuhan University of Bioengineering and Wuhan Engineering Institute.
Yangluo, designated as an economic and technology development area, is 30km northeast of downtown Wuhan and has a population of 300,000. The incineration plant would handle 2,000 tonnes of waste per day, the Wuhan urban management committee said last month.
Residents asked about the progress of the project in early June and were told that the authorities were still choosing a site.
Protests broke out last Friday after rumours spread that the project had already started – forcing the district government to say on Saturday that it would “not start without approval from the public”.
Nonetheless, thousands of protesters – about 10,000, according to one source – marched on Saturday and Sunday, leading to some arrests, although those detained at the weekend had since been released, protesters said.
After minor protests on Monday and Tuesday, residents gathered in greater numbers in Yangluo on Wednesday and Thursday nights, met by a heavy police presence.
Videos seen by the South China Morning Post show hundreds of riot police marching through the streets, equipped with helmets, shields and batons
The crowd dispersed at about 10pm as police began to round up some protesters. They were taken aboard a coach and two men were handled roughly, the videos showed.
Chinese town residents clash with riot police over incinerator
An official from the Xinzhou district government’s publicity department stressed to the Post that the project would not begin without public approval and its location had not yet been chosen.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Beijing, economic and technology development area, garbage landfill site, Guangdong, Hubei, hubei province, Jiangsu, public park, south china morning post, Thousands protest, Uncategorized, waste incineration plant, Wuhan, Wuhan Engineering Institute, Wuhan University of Bioengineering, Xinzhou, Yangluo, Zhejiang |
Leave a Comment »
04/07/2019
- China’s talent is turning away from multinationals and towards domestic tech champions in the search for a more fulfilling career
- Change in sentiment comes amid raging US-China tech war and perceptions of ‘bamboo ceiling’ in the West
An increasing number of Chinese jobseekers are looking towards domestic tech firms. Image: SCMP
Molly Liu left her hometown Beijing to pursue a master’s degree in the United States in the 1990s.
After graduation, she fought hard to win an entry-level position at a US-based consultancy and after a period was later sent back to China to help the company’s expansion.
In the land of opportunity, the ambitious US firm showered her with avenues to pursue her career and she ended up working in Hong Kong as well as being one of the first people on the ground for the consultancy in Shanghai, Beijing, Taipei and Singapore.
Times have changed, though. Recently, her only son, Ben Zhang, turned down a hard-to-get job offer from a Boeing subsidiary in the US after gaining a master’s degree in computer science from Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
Chinese students educated in the US are now looking more at jobs in China. Photo: SCMP
He decided to return to Beijing in 2018 and now works as a product manager at Chinese smartphone maker Xiaomi. He is convinced that the start-up turned tech major can offer him the same sort of opportunities today that the US tech consultancy offered his mother in the 1990s.
This family story about the career choices of two different generations of US-educated Chinese students reflects a wider trend. Once upon a time, US corporations could cherry-pick top Chinese talent from American universities with the promise of large salaries, generous benefits and the chance to work at market-leading organisations.
Today, China’s cutting-edge technology companies – often referred to as China Tech Corporation (CTC) – are the most sought-after employers among many Chinese students, who want more than just a cushy life.
This marks another blow for multinational corporations (MNCs) already struggling to do business in China amid a myriad of restrictions and growing hostility towards them as the US-China trade and tech war gathers pace.
“What I look for in a job is not money. My parents are not counting on me to support them,” says 28-year-old Zhang, whose team in Xiaomi is working on a wide array of connected devices, from televisions to lamps to smart locks. “What I care about most is personal improvement and access to the best resources a company can offer.”
“In Boeing, I could probably work on a new product once every two to three years. But at Xiaomi, every three months, we can roll out a new product,” he added. “You can bring so many things into people’s everyday lives in China, like using your voice to control a TV or an air conditioner – things you can only imagine in the US.”
Zhang is not alone and many Chinese today perceive a “bamboo ceiling” in the US, where they are more often seen as engineers rather than executives.
One Chinese executive who now oversees the technology unit of a listed finance and insurance firm in China said that he used to lead a team of 20 engineers at one of the world’s most valuable tech companies in Silicon Valley.
“My job was to keep optimising the performance of a product [in Silicon Valley],” he said.
“But within three years in China, I was promoted to the chief scientist of our entire company, leading a team of 1,000,” said the man, who asked to remain anonymous as some of his family still reside in the US.
How Trump’s assault on Huawei is forcing the world to contemplate a digital iron curtain
According to an April survey by professional networking site LinkedIn, an increasing number of Chinese jobseekers share Zhang’s outlook. LinkedIn compiled a list of the top 25 most desired employers in China, and about 60 per cent were local Chinese companies, with 13 of them internet firms.
CTC bagged four of the top five spots, with e-commerce giant Alibaba, search giant operator Baidu and Bytedance – which operates short video hit TikTok – taking the lead.
Tesla ranked sixth behind its Chinese challenger Nio. Amazon, the only other foreign company in the top ten, ranked eighth.
Alibaba is the owner of the South China Morning Post.
Li Qiang, executive vice-president of Zhaopin, one of China’s largest online recruiters, described the rising status of CTC among jobseekers as “the dawning of a new era”.
“Nowadays, there is nothing a multinational can offer that a domestic firm cannot, be it a compensation package or the chance to be part of international expansion,” said Beijing-based Li.
“Jobseekers are not particularly looking for domestic firms or multinational firms. They are after good firms and most of the good firms in China these days happen to be domestic tech firms,” said Li.
Li’s comments reflect the wider opportunities within the domestic economy for Chinese jobseekers today, after the rise of many successful private-sector companies and a thriving start-up scene over the past 10 years, meaning it’s not just a one-way street to a state-owned enterprise (SOE) any longer.
A survey by Zhaopin in late 2018 found that 28 per cent of Chinese university students said MNCs were their employer of choice, down from 33.6 per cent in 2017.
Even on pay and benefits, CTC is catching up with multinationals. Zhang said Xiaomi matched the offer from the Boeing unit in the US and many leading tech firms offer benefits such as gym memberships and childcare facilities.
And the rags-to-riches stories of many leading China tech entrepreneurs, some of whom have become billionaires, continue to grab media attention and inspire the younger generation.
To be sure, Chinese students would still rather work for an MNC than an SOE – but the rise of CTC can be seen in company rankings and in the total number of CTC companies in the top employer list, according to Zhaopin.
For a growing number of Chinese students, the doors to America are closing
William Wu, China country manager of global employer brand consultancy Universum, said that the one element Chinese jobseekers pay most attention to these days is whether or not a job can be “a good reference point for a future career”. And a growing number of private Chinese companies now have global brand recognition.
A recent survey by Universum shows that Apple and Siemens were the only two Western names in the top 10 ideal employers for Chinese students in the engineering sector this year, while there were four foreign firms in the top 10 list in 2017.
Huawei Technologies, the Chinese telecoms giant that has been put on a US trade blacklist after the Trump administration said it was a national security risk, ranked top in the Universum list. Xiaomi, the smartphone maker Ben Zhang works for, ranked second while Apple, one of the most valuable tech firms in the US, ranked seventh.
It seems that China’s rising clout in the world is now an attractive factor for jobseekers.
“Every engineer would like to see the technology they’ve worked on have the potential to change the world one day,” said Li Yan, head of multimedia understanding at Chinese short video major Kuaishou. “In the old times Chinese companies were at the bottom of the global value chain, now they are climbing up, providing more opportunities for talent to create world-changing products.”
At Beijing-based Kuaishou, Li’s 100-strong artificial intelligence algorithm team – many of whom joined from Microsoft Asia Research – is working to make machines understand content better than humans by studying the millions of user-generated videos on the company’s platform every day.
CTC companies do have a strong home advantage, with big Western firms having to navigate a myriad of restrictions.
For example, the “Great Firewall” lets Chinese authorities control the content and information reaching the country’s 800 million-plus internet population. Western firms also face other forms of red tape, such as having to form joint ventures with local partners.
Amazon earlier this year announced the close of its China marketplace, giving up the brutal fight with Chinese online shopping giants such as Alibaba to capture domestic e-commerce market share. Oracle China reportedly laid off 900 people in March as it winds down its research and development center in the country.
Job applicants visit a provincial job fair at Qujiang International Conference and Exhibition Center in Xian, northwest China’s Shaanxi Province in February. Photo: Xinhua
Oracle has never confirmed the number of lay-offs but said the job cuts formed part of an overall global strategy transformation.
However, there has been little sympathy for those losing their jobs in China, judging by social media posts.
Some people posted that those working for big US tech firms are not “wolf” enough compared with counterparts who work for local tech firms, referring to the long work-hours culture of the domestic tech scene.
A viral story titled “Why there should be no pity for the sacked Oracle China employees” said the company was Beijing’s biggest nursery because of the flexible “work from home” culture and generous compensation package offered to employees.
Oracle said to begin mass lay-offs in China as part of global move to cloud services
“They had every chance to join rising domestic internet firms. But they settled for high salary and low work pressure, which eventually made them frogs in boiling water. Why pity them?” said the article, adding that the earlier people give up on the “glory” of working for MNCs, the quicker they will benefit.
Not all Chinese workers would agree, and there has been a recent backlash against the “996” culture within China’s tech sector, where people routinely work from 9am to 9pm, six days a week.
With geopolitical uncertainty growing day by day, though, many Chinese are asking why leave the family behind for an uncertain fate overseas?
A survey done by consultancy BCG and The Network in 2018 showed that only one in three China residents was willing to move abroad for work, down from 61 per cent in 2014. The country is also the 20th most popular destination worldwide to relocate for a job, compared with 29th in the 2014.
“One of my graduate classmates in the US just gave up a six-digit package at Oracle and joined drone maker DJI in Shenzhen,” said Ben Zhang. “I asked what prompted his return to China. He sent me the viral article and asked, ‘who wants a life that one can see the end of from the very beginning?’”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Alibaba, Apple, ‘bamboo ceiling’, “Great Firewall”, Baidu, Beijing, big brand multinationals, Boeing, Bytedance, Carnegie Mellon University, China Tech Corporation (CTC), China’s top talent, Hong Kong, huawei technologies, Kuaishou, LinkedIn, multinational corporations (MNCs), Nio. Amazon, Oracle China\, Pennsylvania, Pittsburgh, Qujiang International Conference and Exhibition Center, rising domestic tech stars, shaanxi province, Shanghai, Siemens, Silicon Valley, Singapore, south china morning post, state-owned enterprise (SOE), Taipei, Tesla, TikTok, Uncategorized, Universum, wants to work, Xi'an, Xiaomi |
Leave a Comment »
19/06/2019
- Osaka summit intended to pull bilateral ties away from brinkmanship that has dragged relations to lowest point in decades
- Trade war just one of the items on the agenda, analysts say, along with principles of relationship, North Korea, and Huawei
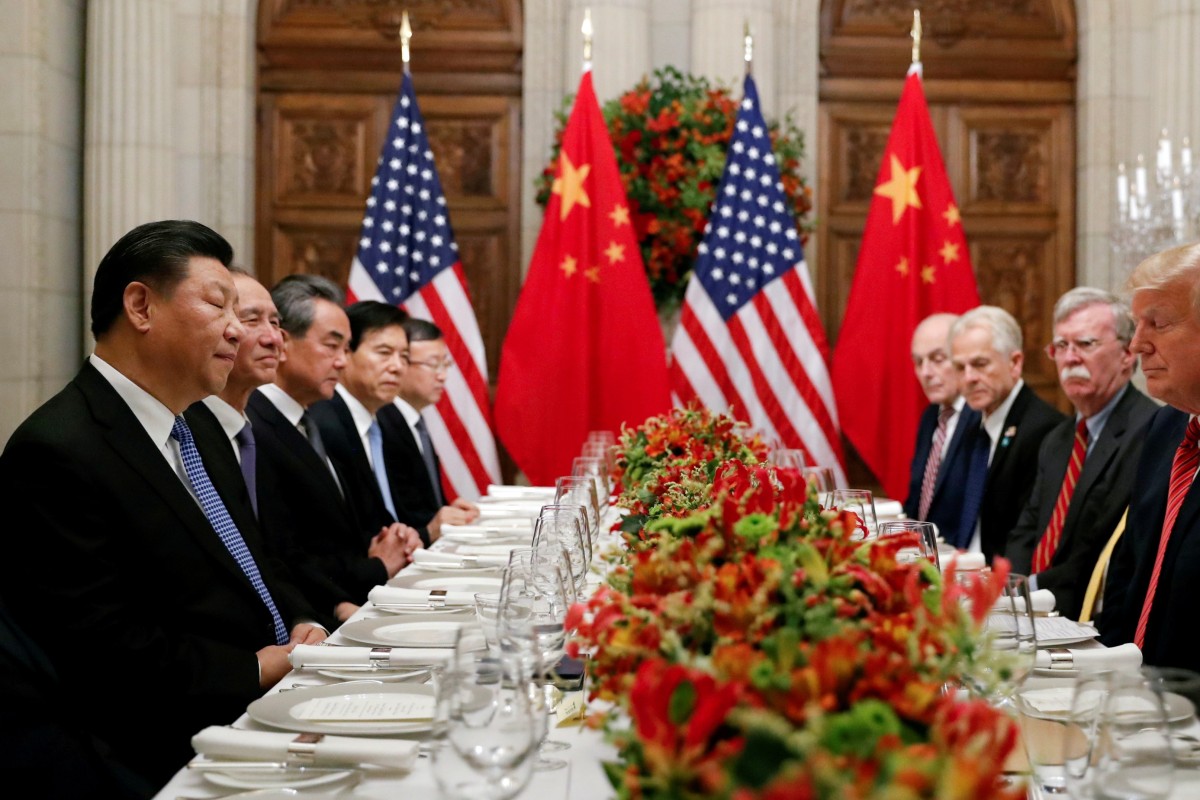
The last time the US President Donald Trump and China’s President Xi Jinping met was in Buenos Aires in December. Analysts are confident that their meeting at the G20 Summit in Osaka this month can yield a freeze in the escalation of the trade war. Photo: Reuters
When Chinese President Xi Jinping meets his US counterpart Donald Trump in Japan at the end of the month they are expected to discuss a broad range of issues, including the trade war, in an effort to stop the relationship from tilting towards sustained confrontation, analysts said.
Neither side has provided an agenda for the meeting on the sidelines of the G20 leaders summit in Osaka, despite confirmation coming from both sides that it was to take place, after weeks of speculation.
A summary of Tuesday’s phone conversation between Xi and Trump published by Xinhua, however, implied that the leaders would cover more strategic issues, leaving the nuts and bolts of a trade deal to their negotiating teams. Meanwhile, China’s foreign ministry spokesperson Lu Kang said at a regular press conference on Wednesday that the two leaders would discuss the overall direction of bilateral relations, but he did not elaborate further.
Both China and the United States have confirmed that their leaders will meet in Osaka at the end of June, at a time when US-China relations have nosedived. Photo: AP
, a former vice-minister at China’s Ministry of Commerce, predicted that Beijing would use the meeting to make clear a few principles regarding the bilateral relationship.
“It’s inevitable [for China and the US] to have problems in certain fields, but both sides should resolve the problems through dialogue on an equal footing rather than opting for a trade war, a tech war, or a financial war,” said Wei, now a vice-chair at the state-backed China Centre for International Economic Exchanges, a think tank.
He added that China would try to convince the US that it had no intention of challenging its global hegemony, but that China’s own “core interests”, including its sovereignty, territorial rights and room to develop, “must be respected”.
A government official in Beijing, who declined to be identified, said China was pinning its hopes on the leaders’ summit to ease general tensions between Beijing and Washington, even though the chances of the leaders reaching any concrete agreements in Osaka was small.
“Without a leaders’ summit, it would be difficult to push ahead the work [to reach agreements] at the ministerial or lower levels,” the source said.
Wei Jianguo, a former vice-minister at China’s Ministry of Commerce, predicted that Beijing would use the meeting to make clear a few principles regarding the bilateral relationship. Photo: Handout
The last summit between Trump and Xi in Buenos Aires in December resulted in a tariff truce and negotiations that continued until early-May. But the talks failed to achieve a deal to end the conflict, resulting in the US more than doubling tariffs on US$200 billion of Chinese imports and threatening tariffs on almost all remaining Chinese imports, valued at US$300 billion by the US government.
Tuesday’s telephone call, in which
he was willing to exchange views with Trump on “the fundamental issues” affecting China-US relations, came at a low point in recent China-US relations.
The tariff increase followed the collapse of trade talks in early-May, while hostile rhetoric has spread into the political and military spheres. The US labelled China a “strategic competitor” and accused Beijing of conducting sustained espionage to impede US’s national security, while China blamed the US for trying to thwart China’s development by targeting Huawei and infringing on China’s sovereignty over Taiwan and Hong Kong.
Zhou Rong, a senior fellow from the Chongyang Institute for Financial Studies at the Renmin University of China, said the two leaders have a long list of issues to talk about this time in addition to trade, including Taiwan, the South China Sea, as well as the treatment of Chinese companies in the US. China can offer to help on some issues but “the US should not force China to swallow bitter fruit it cannot digest”, Zhou said.
Ni Feng, a specialist in Sino-US relations at the Chinese Academy of Social Sciences, said they would discuss the “overall direction” of their bilateral relationship, including where the two nations could engage in “competition and cooperation”.
He added that North Korea may be on the agenda because “China and the US share the same goal of the denuclearisation of the Korean peninsula.”
a two-day state visit to Pyongyang on Thursday.
Another source in the Chinese government, who wished to remain anonymous, said Xi was very likely to bring up the US’ blacklisting of Huawei, China’s leading technology firm. Washington has effectively banned American companies from providing key components to the Shenzhen-based company.
Meng Wanzhou, Huawei’s chief financial officer and the daughter of founder Ren Zhengfei, is currently on bail in Canada awaiting extradition to the US to face charges that both she and Huawei violated US sanctions on Iran.
During Tuesday’s call, Xi told Trump that China “hopes the US side can treat Chinese businesses fairly”, Xinhua reported.
China’s President Xi Jinping waits for the start of the G20 summit in Buenos Aires, Argentina, Friday, Nov. 30, 2018. Photo: AP
At the same time, Trump and Xi agreed that the two countries’ trade negotiators would start to talk again before the meeting in Japan, raising prospects for a second truce in the trade war, or even a deal to end the conflict.
Matthew Goodman, a researcher at the Centre for Strategic and International Studies in Washington, wrote in a note that a Trump-Xi deal on trade-in Osaka “is certainly possible”.
The most likely outcome is similar to the one reached in Buenos Aires in December last year, when Trump and Xi “agreed to a temporary truce while trade negotiators work to hammer out a deal”, Goodman wrote. “This would postpone the worst effects of the current escalation but is unlikely to solve the deepening and dangerous rift in US-China relations”.
The South China Morning Post previously reported that the Osaka summit meeting, which is likely to take place on Saturday June 29, could also be a sit-down dinner between Trump, Xi and their top economic and security aides, as occurred in Buenos Aires. Trump tweeted Tuesday night that he would have an “extended” meeting with Xi in Japan.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Beijing, broaden agenda, Buenos Aires, Centre for Strategic and International Studies, China Centre for International Economic Exchanges, China’s Ministry of Commerce, Chinese Academy of Social Sciences (CASS), Chongyang Institute for Financial Studies, G20 summit, Japan, North Korea, Osaka, President Donald Trump, President Xi Jinping, south china morning post, Uncategorized, US-China trade war, Washington |
Leave a Comment »