07/02/2020
- Cathay Pacific is latest to wield axe, while Taiwan’s new restrictions on visitors from Hong Kong is another blow
- More cancellations expected in the coming days as spread of deadly virus continues
The air industry in Hong Kong and beyond has been thrown into disarray by the coronavirus outbreak. Photo: Reuters
Hundreds more Hong Kong flights are set to be dropped as the floodgates open on airlines cancelling services during the city’s fight against the coronavirus.
Carriers based in Asia, Australia, South Africa and Middle East revealed on Friday morning and the previous night they would cut all or some of their flights to the city.
Cathay Pacific is the latest to wield the axe, announcing on Friday afternoon new suspensions of major Hong Kong routes to London, New York and across mainland China because of the virus.
Flights running on the busy route between Hong Kong and Taiwan’s capital Taipei are subject to major cuts. Photo: Shutterstock
The contagion, which started in the central Chinese city of Wuhan, has infected more than 31,400 people, mostly in mainland China, killing more than 635. In Hong Kong, 24 people have been infected, one of those fatally, as of Friday afternoon.
Passengers abandoning travel plans en masse have been compounded by the introduction of entry restrictions across the world against recent visitors to mainland China, some targeting those who had been to Hong Kong.
Destinations suspended by Cathay Pacific until March 28 include London Gatwick, Rome, Washington DC, Newark, Male, Davao, Clark, Jeju and Taichung.
All mainland cities with the exception of Beijing, Shanghai, Chengdu and Xiamen would also be dropped over that period. The company said the decision was made “in view of the novel coronavirus outbreak and the subsequent drop in market demand”.
Hong Kong airport to segregate all flights to and from mainland China
It followed Cathay Pacific Group revealing earlier this week there would be a 30 per cent reduction of flights across its worldwide schedule, as well as a 90% cut of mainland flights.
Budget carrier HK Express, controlled by Cathay, said on Thursday it would scrap 82 flights between February 12 and March 26, mostly to destinations such as Seoul and Osaka.
Hong Kong Airlines (HKA) at the same time revealed it would gradually impose even deeper cuts to flights it operated in mainland China and the rest of Asia until March 28.
The ailing carrier will suspend 10 routes and reduce flights on a further 15, amounting to an estimated 128 flights a week being axed. HKA has already cut 214 mainland Chinese flights between January 30 until February 11.
As Taiwan’s new restrictions took effect on Friday – ordering the home or hotel quarantine of anyone entering the self-ruled island who had visited Hong Kong or Macau within the previous 14 days – carriers based there slashed their schedules.
China Airlines would go from running 18 daily Hong Kong flights to just two from next week until March 28, according to Airline Route data published on Thursday.
Eva Air would switch from more than 11 daily flights to fewer than four a day for the rest of the month.
As health professionals treat coronavirus patients, global search for cures and vaccines accelerates
Eighty flights operate between Hong Kong and Taipei every week, a journey that regularly tops tables ranking the world’s busiest. But under the cuts to come more than half have already been scrapped.
Outside Asia, two airlines on Thursday cut ties with Hong Kong. The struggling Virgin Australia blamed the coronavirus and the anti-government protests that have gripped Hong Kong since June.
It concluded that “current circumstances demonstrate that Hong Kong is no longer a commercially viable route”.
The near-bankrupt South African Airways (SAA) has cancelled its route from Johannesburg amid a wholesale restructuring of the state-owned business. SAA had suspended flying to Hong Kong after November 21 last year amid the city’s civil unrest.
Hong Kong Airlines to axe 400 jobs as coronavirus adds to carrier’s cash woes
Meanwhile, American Airlines said on Thursday it would restart flights between Dallas Fort Worth and Hong Kong on February 21, while Hong Kong’s Airport Authority extended the cancellation of its Los Angeles flight to the city until March 27.
The US carrier warned its schedules were subject to an ongoing “review”. Currently there is no US carrier flying to Hong Kong International Airport after United Airlines also withdrew all services until February 20.
Among the Middle East carriers, Emirates was halving its four daily Airbus A380 flights to Hong Kong from next week until March 28. Etihad is also making minor adjustments, Airline Route data showed on Thursday.
Source: SCMP
Posted in across, air travel, Airbus A380, Airline Route, Asia, Australia, Beijing, cancelled, carriers, Cathay Pacific Group, Chengdu, China Airlines, Clark, contagion, coronavirus, Dallas Fort Worth, Davao, en masse, Etihad, Eva Air, hammers, Hong Kong, Hong Kong Airlines (HKA), Hong Kong flights, hundreds, Jeju, London, London Gatwick, Mainland China, Male, Middle East, New York, Newark, Osaka, routes, Seoul, Shanghai, South Africa, South African Airways (SAA), Taichung, Taipei, Uncategorized, Virgin Australia, Virus, Washington DC, Wuhan, Xiamen |
Leave a Comment »
23/01/2020
- H-6 bomber, early warning and control plane part of long-haul exercise that bypassed island’s southern tip en route to western Pacific, Taipei says
- Taiwan’s military will remain on high alert over Lunar New Year holiday, ministry says
A KJ-500 early warning and control aircraft was among the PLA military planes that staged an exercise close to Taiwan on Thursday. Photo: Weibo
A group of military aircraft from mainland China flew close to the southernmost tip of
on Thursday, just a week after President Tsai Ing-wen angered Beijing by saying the island was an independent country.
According to Taiwan’s defence ministry, the formation, which included a KJ-500 early warning and control aircraft and an H-6 bomber, passed through the Bashi Channel near Taiwan’s Orchid Island en route to the western Pacific Ocean.
It did not say how many aircraft were involved but said they had taken off from different airbases in southern China.
“They returned to their airbases from their morning flight path after a long-haul exercise,” the ministry said in a statement.
The ministry urged the public not to be alarmed by the aircraft’s presence, saying it constantly monitored the activities of the
People’s Liberation Army (PLA), both in the air and at sea.
Taiwan’s armed forces would also remain on high alert over the
Lunar New Year
holiday, which starts on Friday, it said.
“There is no holiday for national security,” it said.
The PLA exercise came just a week after Tsai said on January 15 that Beijing needed to face the reality of Taiwan’s independence.
“We don’t have a need to declare ourselves an independent state,” she said in an interview with the BBC. “We are an independent country already and we call ourselves the Republic of China, Taiwan.”
Tsai urges mainland China to review strained ties
Tsai’s comments came just days after she secured a second term as president with a record 8.2 million votes.
In her victory speech, she promised to continue to stand up to Beijing’s intimidation, while also strengthening Taiwan’s defences, partly by developing more home-grown military equipment, including submarines.
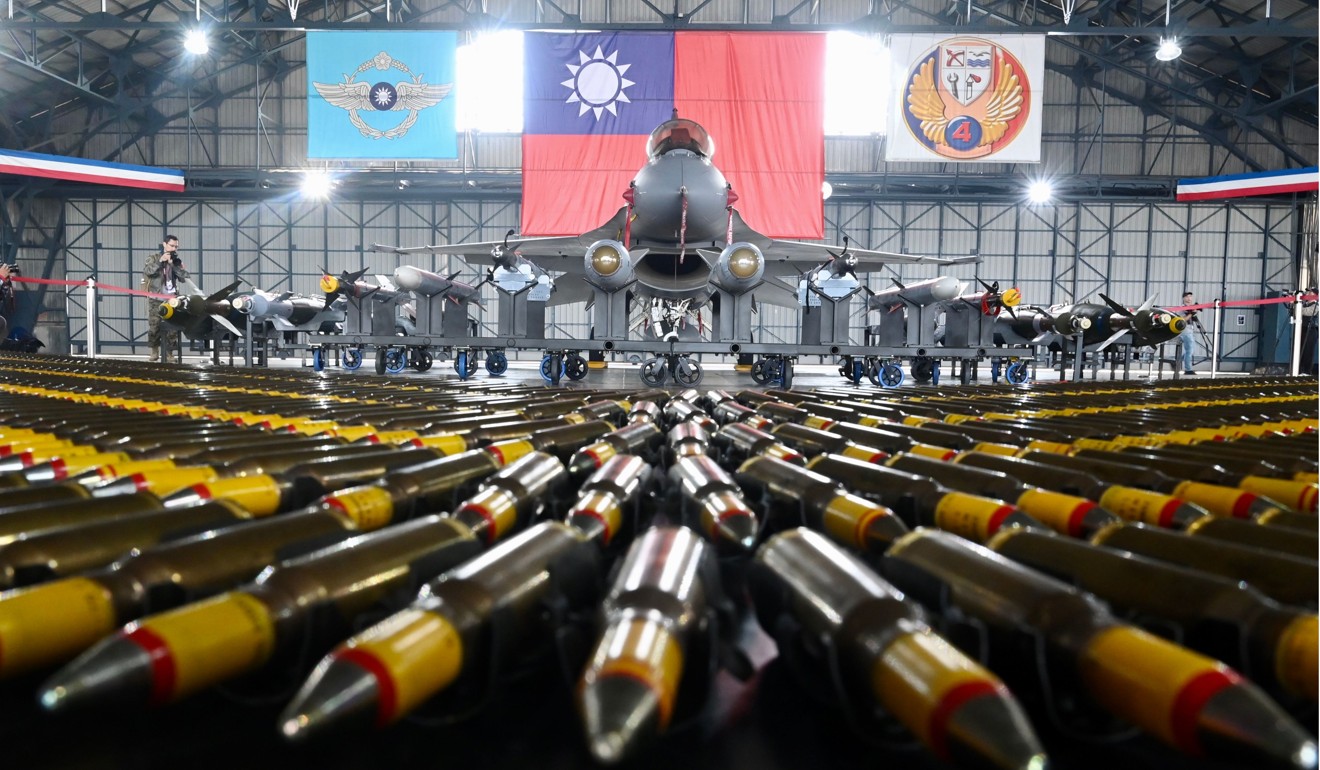
US-made F-16V fighters took part in a show of Taiwan’s military might last week. Photo: AFP
In response to Tsai’s “independent country” comments, Ma Xiaoguang, a spokesman for the mainland’s Taiwan Affairs Office, said: “We firmly attack and counter various forms of Taiwan independence and separatist activities to maintain overall peace and stability in the Taiwan Strait.”
Beijing regards Taiwan as part of its territory awaiting reunification, by force if necessary. Official ties between the two sides have been suspended since Tsai took office in 2016 and refused to accept the one-China principle – the political understanding that there is only one China with ambiguity over whether it is governed by Taipei or Beijing.
Over the past four years Beijing has ramped up the pressure on the island, by poaching its diplomatic allies and staging military drills.
Taiwanese Minister of National Defence Yen Te-fa said earlier that the mainland staged about 2,000 bomber patrols a year near the Taiwan Strait.
For their part, Taiwan’s army and air force last week gave two demonstrations of their readiness to defend the island against attack.
Posted in airbases, Bashi Channel, Beijing, Chinese military aircraft, defence ministry, early warning and control plane, F-16V fighters, fly, H-6 bomber, high alert, home-grown military equipment, independent country, island, KJ-500 early warning and control aircraft, Lunar New Year holiday, Minister of National Defence, one-China principle, Orchid Island, People's Liberation Army (PLA), PLA military planes, Republic of China, submarines, Taipei, Taiwan, Taiwan Affairs Office, Taiwan Strait, Taiwan’s army and air force, Taiwan’s military, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
27/12/2019
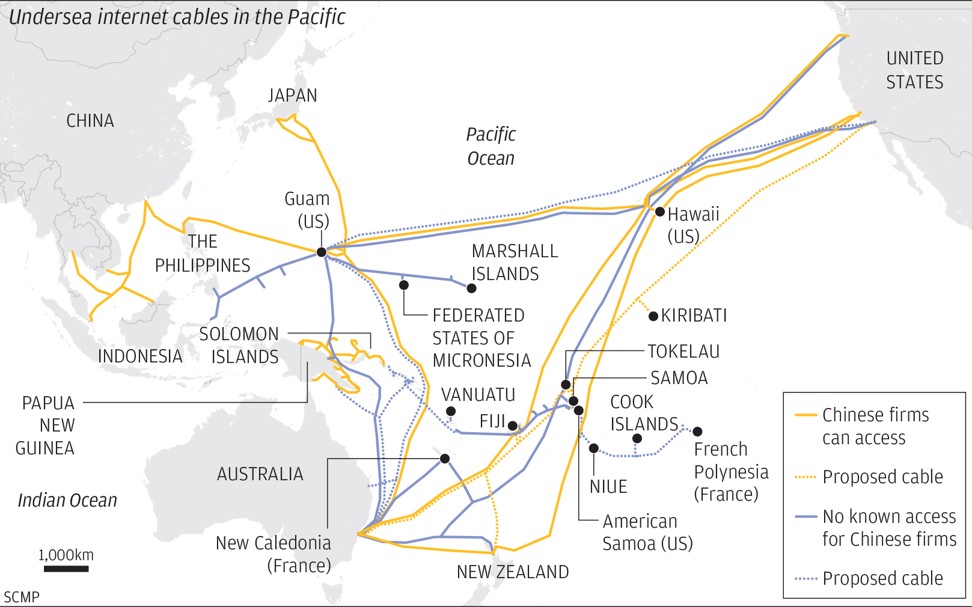
- A push to connect Pacific nations highlights a submarine struggle for dominance over the world’s technology infrastructure
- The ambitions of Chinese tech giants like Huawei, which have laid thousands of kilometres of cable, are of increasing concern to Washington
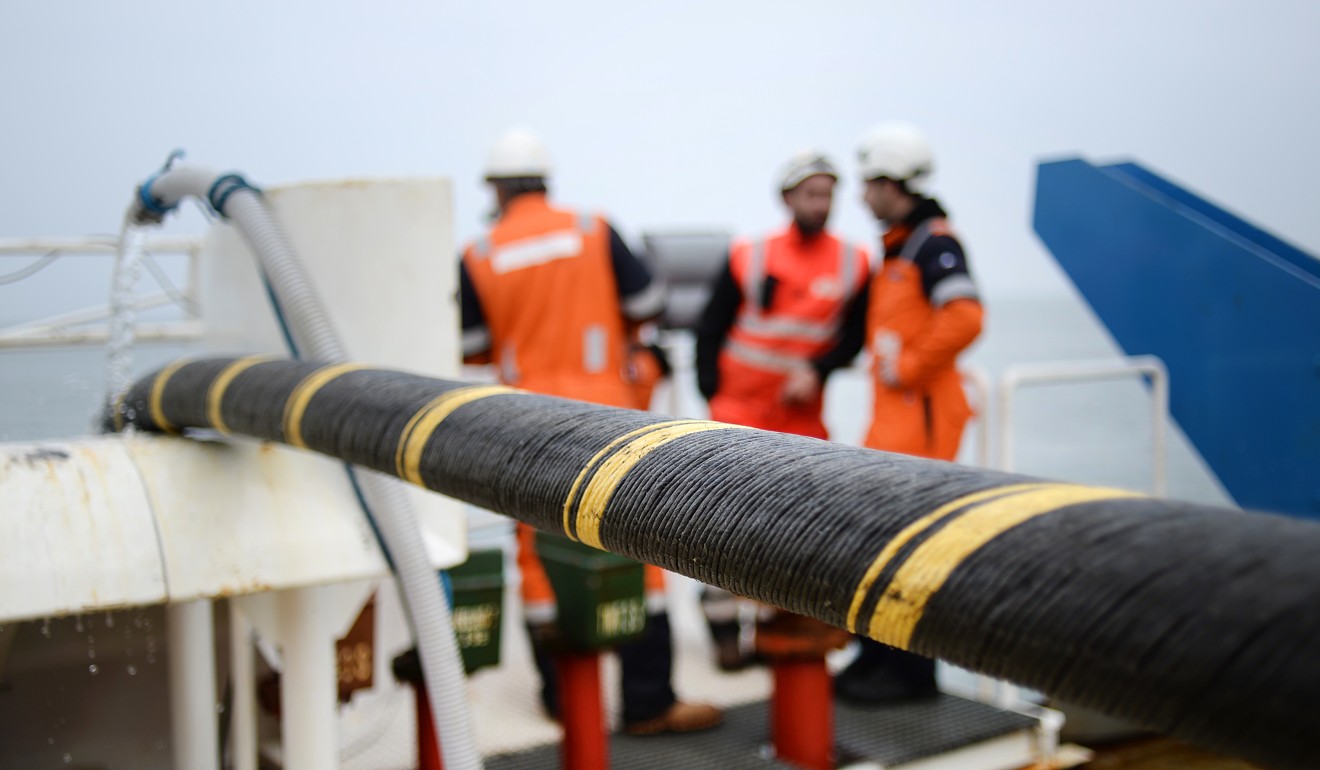
The ambitions of Chinese tech giants like Huawei, which have laid thousands of kilometres of cable, are of increasing concern to Washington. Photo: Reuters
I
n the contest between the
US and China for dominance over the world’s technology
infrastructure, the latest battle is taking place under the Pacific Ocean.
While the US has been upping the pressure on its allies not to include equipment made by Chinese telecom giants like Huawei and ZTE in their 5G systems, Chinese companies have gained a foothold in some of the world’s most essential communications infrastructure – undersea internet cables.
Smart telecom cables: climate change hope or submarine spying tech?
Almost all global data communications flow through cables under the ocean – just one per cent travels by satellite – and Chinese companies have quietly been eroding US, European and Japanese dominance over the backbone of the internet, the undersea cable market. Now, they have trained their sights on connecting one of the most virtually remote parts of the globe, the
Pacific Island countries.
Of the 378 cables currently operating worldwide, 23 are under the Pacific. But many of these cables run right by Pacific Island nations on their paths between hubs in Los Angeles, Tokyo and Singapore.
An electric submarine cable and optical fibre. File photo
Despite the volume of data flowing under the Pacific Ocean, just half a million of the 11 million people living in Pacific Island countries and Papua New Guinea – less than five per cent – have access to a wired internet connection and only 1.5 million to a mobile connection, according to the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for the Asia Pacific (UNESCAP), compared with 53 per cent of people in Thailand and 60 per cent in the Philippines.
More than US$4 billion worth of cables are to come into service by 2021, continuing a trend in which US$2 billion worth of cables have come online every year since 2016, and six of these cables will connect Pacific Island countries.
The push to connect Pacific Island nations to the latest generation of internet infrastructure has received extra scrutiny from the US and its allies like
Australia
over the involvement of Chinese tech companies.
Choose Beijing over Taipei, Solomon Islands task force recommends
While the US has moved to block Huawei from supplying equipment to its allies’ 5G networks, experts say Chinese tech companies could contest the US, EU and
long-standing dominance over global data traffic through investments in subsea cables.
Chinese tech giants like Huawei have entire divisions devoted to undersea connectivity that have laid thousands of kilometres of cable, and Chinese state telecommunication companies such as China Unicom have access to many of the existing trans-Pacific cables.
But a panel led by the US Department of Justice has held up a nearly complete trans-Pacific cable project over concerns about its Chinese investor, Beijing-based Dr Peng Telecom & Media Group.
The project, the Pacific Light Cable Network, could be the first cable rejected by the panel on the grounds of national security – despite being backed by American tech giants
Google and
Facebook – setting a precedent for a tougher US stance on Chinese involvement in subsea cables.
Chinese tech giants like Huawei have entire divisions devoted to undersea connectivity that have laid thousands of kilometres of cable. Photo: AP
Craige Sloots, director of sales at Southern Cross Cable Network, which operates the largest existing sets of trans-Pacific cables, said for any new cable, regulators were likely to scrutinise the ownership of the companies involved and the maker of the project’s equipment.
These two factors, said Sloots, “pragmatically limit some of the providers you can use if you want to connect through the US”.
Experts say that Hong Kong, where the stalled Pacific Light Cable would land, was previously considered a more secure shore landing point than mainland China. But people close to the project say the recent unrest in the city has made this distinction less relevant, according to The Wall Street Journal.
If these nations want to be part of the international economy, they need reliable communications: Bruce Howe, University of Hawaii
Similar concerns caused a proposed Huawei-backed cable linking Vanuatu with Papua New Guinea to be called off last year after Australia stepped in to fund its own cable instead.
Just months after the government-owned Solomon Islands Submarine Cable Company agreed to the project with Huawei in mid-2017, Canberra put up US$67 million to connect Sydney with the Solomon Islands and Papua New Guinea with cables laid under the Coral Sea by Nokia’s Alcatel Submarine Networks.
Simon Fletcher, CEO of Vanuatu company Interchange, which had been planning another cable in the neighbourhood connecting Vanuatu with the Solomon Islands, said the Coral Sea project undercut the viability for small private businesses to operate in the fledgling market, where services had historically been provided by international organisations like development banks. His company’s cable has been on pause since the announcement of the Coral Sea project, though Fletcher said it would go forward next year.
US-China battle for dominance extends across Pacific, above and below the sea
22 Jul 2019
VIRTUALLY REMOTE
For years, as Japan, Hong Kong and Singapore became global hubs of high-speed internet data traffic, the cables criss-crossing the ocean floor passed by just off the shores of Pacific Island countries en route between hubs on either side of the ocean.
Tiziana Bonapace, director of UNESCAP’s information technology and disaster risk-reduction division, said the Pacific Islands remain one of the most disconnected areas in the world, where “a vast proportion of the population has no access to the internet”.
Over the past five years, international organisations like UNESCAP, the Asia Development Bank and the World Bank have been pushing for better connectivity in the region. The World Bank’s Pacific Regional Connectivity Programme has invested more than US$90 million into broadband infrastructure for Fiji, the Federated States of Micronesia, Kiribati, the Marshall Islands, Palau, Samoa and Tuvalu.
Internet cables in the Pacific Ocean.
But the business case had never been good, said Bonapace.
“A cable has to travel thousands of kilometres just to connect a population smaller than one of Asia’s megacities,” she said. “As everything we do is somehow connected to the internet, the prospects for the Pacific to become virtually more remote are even higher.”
Even nations which are connected have tenuous infrastructure. In January, Tonga experienced a total internet blackout for two weeks after damage to its single cable. Most parts of the world were linked by multiple cables to prevent this type of outage, said Bruce Howe, professor of ocean and resources engineering at University of Hawaii.
“If these nations want to be part of the international economy, they need reliable communications,” Howe said.
Is Chinese support for Pacific nations shaping their stance on West Papua?
26 Aug 2019
DRAWING NEW LINES
In Papua New Guinea, where mobile internet currently reaches less than a third of the population, a partnership between local telecoms company GoPNG and the Export-Import Bank of China funded the new Huawei-built Kumul Domestic cable system, which came online this year.
The Southern Cross Next system, owned by Spark, Verizon, Singtel Optus and Telstra – the same group of shareholders which operates the massive 30,500km (19,000 mile) set of twin cables connecting the US with Australia and New Zealand known as Southern Cross – is planned to come online in 2022, and will connect directly to Fiji, Samoa, Kiribati and Tokelau.
Chinese telecoms company China Unicom counts the existing Southern Cross cables among its network capabilities – meaning it is likely to have access to the cable through a leasing agreement with one of the other companies that uses the cable, according to Canberra think tank the Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI).
An undersea fibre optic cable. Photo: AFP
China Unicom and China Telecom also list the Asia America Gateway Cable System as one of their network capabilities, according to ASPI. The 20,000km (12,400-mile) cable came online in 2009 and connects the US, Guam, Hong Kong, Brunei, the Philippines, Singapore, Malaysia, Vietnam and Thailand.
It is owned by a consortium of carriers including AT&T, Telekom Malaysia, Telstra and Spark.
A cable backed by Google and the Australian Academic and Research Network connecting Japan and Australia through Guam is to come online early next year.
China: the real reason Australia’s pumping cash into the Pacific?
28 Jul 2018
WHAT’S NEXT
Natasha Beschorner, senior digital development specialist at the World Bank, said that while there were challenges ahead in terms of broadband access and affordability, increased connectivity was starting to bring new opportunities to the Pacific.
“Digital technologies can contribute to economic diversification, income generation and service delivery in the Pacific,” Beschorner said. “E-commerce and financial technologies are emerging and governments are considering how to roll out selected services online.”
Experts say the industry has recently seen a switch from cables being mostly funded by telecommunication carriers to being funded by content providers, like Google and Facebook. Members of the private cable industry say content companies can afford to invest in cable infrastructure to ensure the supply chain for their customers, but that the competition puts the squeeze on the research-and-development budgets of other types of companies.
Sloots at Southern Cross predicted that the nations which connected directly to the massive next-generation cable – Samoa, Kiribati and Tokelau – would be able to function as connecting points for intra-Pacific cables.
“There’s a blossoming effect in capability once certain islands are connected,” Sloots said.
There is also the push to locate an exchange point within the Pacific so that internet data no longer has to travel to a hub in Tokyo or Los Angeles and back to Pacific nations when processing – a move that could ultimately lower the cost of broadband internet service for consumers in the Pacific.
Perhaps the most effective outcome could be for Pacific nations to cut the cord and receive their internet by satellite.
The Asian Development Bank has agreed to give a US$50 million loan to Singapore’s Kacific Broadband Satellites International to provide up to two billion people across the Asia-Pacific region with affordable satellite-based internet.
The project is to be launched into orbit by SpaceX next week and aims to begin providing service by early next year.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Alcatel Submarine Networks, Asia America Gateway Cable System, Asia Development Bank, Asian Development Bank, Australia, Australian Academic and Research Network, Australian Strategic Policy Institute (ASPI), Beijing, broadband internet service, Brunei, cables, Canberra, China Telecom, China Unicom, Dr Peng Telecom & Media Group, Export-Import Bank of China, Facebook, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, Google, GoPNG, Guam, Hong Kong, Huawei, Internet, Japan, Kiribati, Kumul Domestic cable system, Los Angeles, Malaysia, new battleground, New Zealand, Nokia, Pacific island countries, Pacific Light Cable Network, Pacific Regional Connectivity Programme, Papua New Guinea, Samoa, Singapore, Singtel Optus, Solomon Islands, Solomon Islands Submarine Cable Company, Southern Cross Cable Network, Southern Cross Next system, SpaceX, Spark, Taipei, Telekom Malaysia, Telstra, Thailand, the Coral Sea, the Philippines, The Wall Street Journal, think tank, Tokelau, Tokyo, Tonga, Uncategorized, undersea, United Nations Economic and Social Commission for the Asia Pacific (UNESCAP), University of Hawaii, US, US-China tech war, Vanuatu, Vanuatu company Interchange, Verizon, Vietnam, Washington, West Papua, World Bank, ZTE |
Leave a Comment »
17/12/2019
- Centre could make Taiwan more self-sufficient in its defence capability
- Latest arms deal is further evidence of closer relations under presidencies of US’ Donald Trump and Taiwan’s Tsai Ing-wen
A Taiwanese F-16V takes off during a drill in May. Photo: EPA-EFE
has further bolstered its defence links with the United States with plans to build an F-16 fighter jet maintenance centre, as the Taipei government continues to resist Beijing’s objective of unification.
The self-ruled island’s Aerospace Industrial Development Corporation (AIDC) and US defence contractor Lockheed Martin signed a strategic partnership agreement on Tuesday that aimed to promote the establishment of an F-16 fighter jet maintenance centre in Taiwan, to be completed by 2023.
It is the latest of several significant agreements with the US during Donald Trump’s presidency. Trump approved a US$2.2 billion arms sale on July 8 that included 108 American-made M1A2T Abrams tanks and 250 Stinger missiles.
He was quicker to approve F-16 sales than his predecessors, agreeing in August to sell the island 66 F-16V jets, which will mean Taiwan owns the most F-16s in the Asia-Pacific region.
Trump also approved, in September last year, a US$330 million deal to provide spare parts and other logistics for several types of the island’s military aircraft – less than a year after the US agreed to sell US$1.4 billion of missiles, torpedoes and an early warning system to Taiwan.
Beijing views Taiwan as a breakaway province to be reunited with the mainland by force if necessary.
‘Fighter jets trump battle tanks’ in Taiwan’s US arms priorities
Collin Koh, a research fellow at the S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies with Nanyang Technological University in Singapore, said the planned maintenance centre underlined how Taiwan-US military ties had become stronger under the more enthusiastic US administration of Trump and the Taiwanese presidency of
.
“The [F-16 fighter jet maintenance] centre, by improving the availability and readiness of the F-16 fleet, allows Taiwan to sustain its combat aviation, not only for daily operation but also for training,” Koh said.
“This does represent a step up. Taiwan is no longer just an end-user operating the American hardware, but will also be empowered to service it. It is designed to help Taiwan achieve better defence self-sufficiency, one of the key pledges by the Tsai administration.”
Tang Shaocheng, a senior researcher in international relations at Taiwan’s National Cheng-chi University, said the increasingly close relations between Taipei and Washington made dealing with the island more tricky for Beijing.
Beijing ‘interferes daily’ in Taiwan’s election, says Tsai Ing-wen
“The Tsai administration cares about what the US thinks but not what Beijing thinks, paving the way for ever-closer ties,” Tang said. “That definitely leaves less room for Beijing to get Taipei into its orbit, by using various economic measures.”
Beijing has suspended exchanges with Taipei and staged a series of war games around Taiwan to intimidate the island since Tsai, of the independence-leaning Democratic Progressive Party, became president in 2016 and refused to accept its one-China policy.
Beijing has also tried to isolate Taiwan internationally by poaching its
diplomatic allies
since Tsai took office, has repeatedly warned Washington against seeking closer military ties with Taipei, and has protested against every arms deal the two have made.
The US acknowledges the Chinese claim that it has sovereignty over Taiwan, which split from the mainland in 1949 and is self-governing. However, the US regards the status of Taiwan as unsettled and supports the island with arms sales and other measures, such as by sending warships through the Taiwan Strait that separates the island from China.
Posted in Aerospace Industrial Development Corporation (AIDC), Beijing, breakaway province, build, centre, defiant, Democratic Progressive Party, Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), F-16 fighter jet, fighter jet, mainland, message, National Cheng-chi University, one-China policy, partnership, President Donald Trump, President Tsai Ing-wen, reunited, S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies, sending, Singapore, Singapore’s Nanyang Technological University, sovereignty, Taipei, Taiwan, Taiwan Strait, Uncategorized, US, warships, Washington |
Leave a Comment »
27/11/2019
- But Washington still commands more diplomatic influence, analyst says
- Beijing extends its reach as its interests grow abroad and as Taipei loses allies
China has 276 embassies, consulates and other missions around the world, surpassing the US with 273 missions, according to a global index. Photo: AP
China has overtaken the United States to have the biggest number of diplomatic outposts around the world, as its international ambitions and economic interests expand.
According to the 2019 Global Diplomacy Index, released by the Lowy Institute in Australia on Wednesday, China has 276 embassies, consulates and other missions globally, surpassing the US with 273 missions. France was third on 267.
Bonnie Bley, the index report’s lead researcher, said that while a country’s total did not equate to diplomatic influence, “diplomatic infrastructure is still important”
“China’s newly held lead serves as a telling metric of national ambition and international priorities,” Bley said.
Beijing has 169 embassies or high commissions, while Washington has 168. However, China had 96 consulates while the US had 88, suggesting that Beijing’s diplomatic expansion was closely linked to its economic interests, she said.
Beijing bulks up diplomacy budget as China extends global reach
Renmin University international relations professor Shi Yinhong said China had close and growing trade and investment ties with many developing countries, especially those taking part in the Belt and Road Initiative, increasing the need for consulates.
“One of the consulates’ main goals is to serve the citizens and businesses located in those countries,” Shi said.
Beijing has also expanded its reach at Taipei’s expense. Since 2016, when the index was first published, Taiwan’s total number of embassies fell from 22 to 15, the biggest drop among the 61 places ranked.
China opened five new embassies – in El Salvador, Burkina Faso, Gambia, São Tomé and Príncipe and the Dominican Republic – countries that severed official diplomatic ties with Taiwan. This directly contributed to China’s lead over the US, the report said.
Beijing’s diplomatic expansion also comes as the US, under the administration of President Donald Trump, is taking an “America first” approach to foreign policy.
Sri Lanka rejects fears of China’s ‘debt-trap diplomacy’ in belt and road projects
Trump has sought to cut funding to the US State Department and the White House has not appointed US ambassadors for at least 17 countries, including Brazil and Egypt, according to the American Foreign Service Association.
“Even though the US has a strong diplomatic base but it is not so proactive any more. It has fewer consulates and fewer foreign service workers,” Shi said.
“For the long term, China is in a more advantageous position.”
But a country’s diplomatic ability and influence did not rest on the number of foreign service postings and the US still held more international diplomatic sway than China, he added.
Some of China’s biggest diplomatic missions include Islamabad in Pakistan, Washington and London.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 2019 Global Diplomacy Index, American Foreign Service Association, “America first”, Beijing, belt and road projects, biggest, boast, Brazil, Burkina Faso, China alert, commands, diplomatic, Dominican Republic, Egypt, Gambia, influence, Islamabad, London, network, Pakistan, President Donald Trump, Renmin University, São Tomé and Príncipe, São Tome, Sri Lanka, Taipei, Uncategorized, United States, US State Department, Washington, White House, world’s |
Leave a Comment »
04/11/2019
- Latest measures grant island’s people and enterprises more equal treatment with their mainland counterparts
- Package in March last year was dismissed by Taiwan’s Mainland Affairs Council as an attempt to buy political support
Taipei’s elections in January could influence the tone of cross-strait relations. Photo: EPA-EFE
Beijing announced a series of sweeteners for Taiwanese businesses and individuals on Monday – including participation in its 5G research and allowing Taiwanese to use mainland consular services – only two months before
Taiwan’s critical presidential election.
The latest 26 measures drawn up by 20 government departments, including the State Council’s Taiwan Affairs Office and the National Development and Reform Commission, are designed to attract more Taiwanese to live and work in mainland China, despite worsening cross-strait relations.
But Taiwan’s Mainland Affairs Council criticised the move as an attempt by the Chinese Communist Party to “divide Taiwan internally, and was a further reflection of attempts to try to interfere in and influence Taiwan’s election”.
It follows a similar package of 31 measures unveiled by Beijing in March last year, which included tax incentives, preferential land-use policies for Taiwanese businesses on the mainland and benefits for Taiwanese individuals in studying or living on the mainland.
Taiwan charges pro-Beijing politicians with accepting mainland cash
The latest measures to grant Taiwan-funded enterprises more equal treatment with their mainland counterparts include offering access to research and development in 5G technology, investment in passenger and cargo air services, the establishment of microlending and financing companies and the right to apply for financial guarantees from local government funds.
Taiwanese individuals will also be officially entitled to mainland Chinese consular protection abroad, will be treated the same as their mainland counterparts when buying residential property on the mainland, and will be able to train in Beijing for the 2020 Olympic Games.
Beijing claims sovereignty over self-ruled Taiwan, and has not renounced the use of force to take the democratic island into its fold. Beijing’s ruling Communist Party has stressed its intention to promote “peaceful reunification”, pledging in its communique from the
fourth plenary meeting of the party’s elite last week to “deepen cross-strait integration and development” while opposing Taiwanese independence.
The latest measures from Beijing came ahead of Taiwan’s presidential and legislative elections in January. Relations across the Taiwan Strait have been frozen under the administration of independence-leaning Taiwanese President, ostensibly over her refusal to accept the “1992 consensus”, or the understanding that there is only “one China” – something that Beijing considers a prerequisite for any talks with Taipei.
Taiwan’s Mainland Affairs Council said on Monday that the roll-out of the 26 measures one year later was intended to “cover up” the fact that the 31 measures had not been executed properly, and reflected administrative problems on the mainland amid slowing economic growth.
“Even more than that, it also reflects that during this period Taiwanese people have rejected ‘one country, two systems’ and do not agree with the results of the Communist Party’s united front divisions,” the council said.
“We urge the Communist Party officials to specifically implement protections for Taiwanese businesses and Taiwanese people in their investments and lives.”
Joseph Wu, Taipei’s foreign minister, also responded with a tweet written in simplified Chinese – which is used on the mainland – rather than the traditional Chinese used in Taiwan.
“China’s Taiwan Affairs Office came out with 26 measures and last year there were 31 – it looks like there are so many measures,” he wrote. “But we in Taiwan do not need one country, two systems, so there is really no need to be so polite. Giving your people more freedom is also good!”
Ongoing
anti-government protests in Hong Kong – which is semi-autonomous from Beijing under the one country, two systems model – have highlighted for many Taiwanese voters the threat from Beijing to the island’s sovereignty.
The latest polling by the MAC found that 89 per cent of respondents opposed the one country, two systems framework that Beijing proposed for Taiwan, up from 75 per cent in a similar survey in January.
Edward I-hsin Chen, a political-science professor at Chinese Culture University in Taipei, said the impact of the 26 measures on the election would depend on how they were implemented, but that one country, two systems was clearly not palatable for Taiwanese voters, whether they supported Tsai’s Democratic Progressive Party (DPP) or the mainland-friendly Kuomintang (KMT).
“Taiwan, of course, will not accept one country, two systems, so these policies will need to be more long-term. Mainland officials did not handle the Hong Kong issue very well, so it will be very hard for one country, two systems in Taiwan – blue and green will both reject it,” he said, referring to the party colours for the KMT and DPP. “But it is good for Taiwanese people and businesses to be able to take part in the 5G sector, and there will be more cooperation in the future.”
Lin Chingfa, former chairman of the Beijing-based Association of Taiwan Investment Enterprises, said he believed the new measures were intended to appeal to Taiwanese youth.
“A very important direction for cross-strait cooperation nowadays is to bridge the opportunities available in mainland China for young people who feel deprived from the slow Taiwanese economy. Some of these policies should be especially appealing to them because it shows that the country hopes to make it more convenient for young Taiwan people willing to come,” Lin said.
He said this approach was especially obvious in the measures that were introduced to provide equal treatment for Taiwan people on the mainland – for example the opportunities for Taiwan people to apply for scholarships and the expansion of places for Taiwanese students at universities.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 5G research, 5G technology, anti-government protests, Association of Taiwan Investment Enterprises, Beijing, cargo air services, China’s State Council, chinese communist party, Chinese Culture University, Democratic Progressive Party (DPP), Election, extends, Hong Kong, Mainland Affairs Council, microlending and financing companies, National Development and Reform Commission, National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), ne country, two systems model, one China, One country, two systems, passenger air services, presidential, sovereignty, State Council Taiwan Affairs Office, Sweeteners, Taipei, Taiwan Affairs Office, Taiwan’s, Taiwanese, Taiwanese President, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
19/10/2019
- Vice-Premier Hu Chunhua will lead delegation at two-day summit that is expected to be attended by 400 officials and 200 businesspeople
- Observers say it is Beijing’s latest effort to regain momentum in the region and will be closely watched in the US
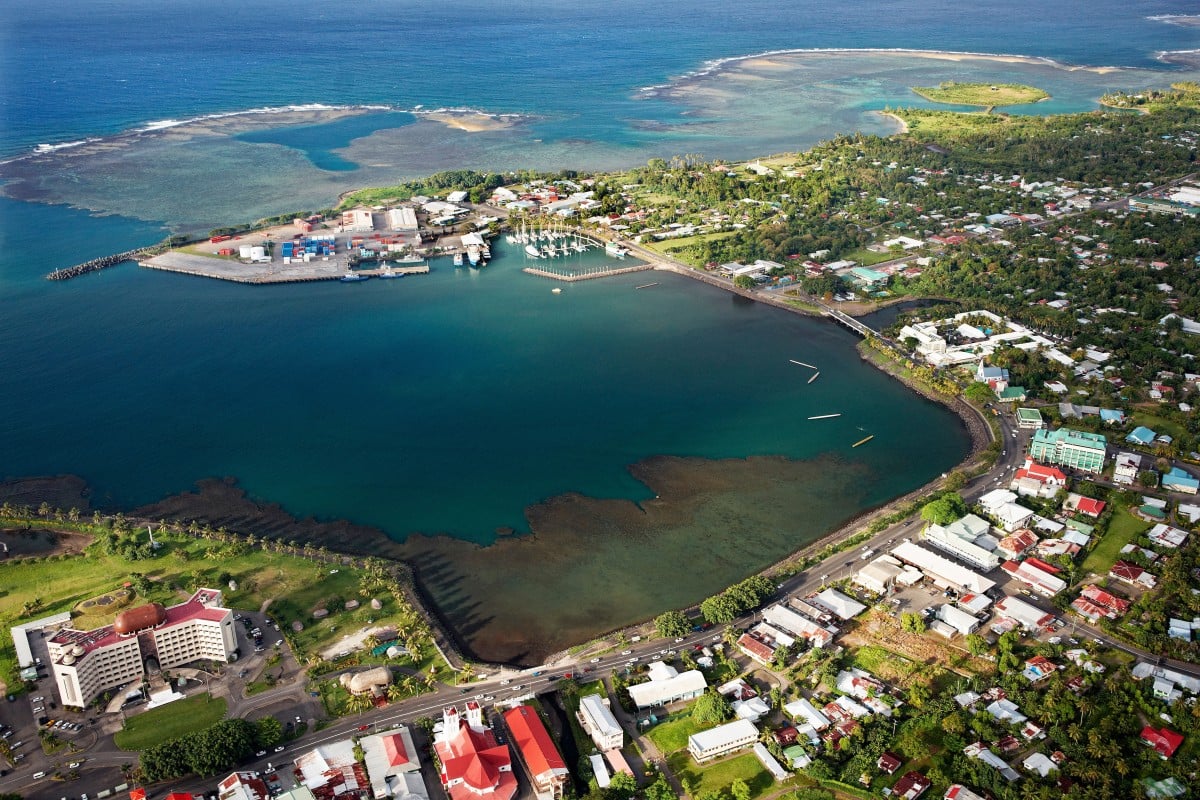
Samoan capital Apia will host the third China-Pacific Island Countries Economic Development Cooperation Forum, which begins on Sunday. Photo: Alamy
China will seek to expand its economic and diplomatic influence in the South Pacific at a forum this weekend, amid growing concern from the US and its allies over Beijing’s push in the strategically important region.
Vice-Premier Hu Chunhua will lead the Chinese delegation at the third China-Pacific Island Countries Economic Development Cooperation Forum in the Samoan capital Apia, which begins on Sunday. It is expected to be attended by 400 officials and more than 200 businesspeople.
Hu, the former Communist Party chief of China’s manufacturing powerhouse Guangdong who now overseas commercial and agricultural affairs, is expected to deliver a keynote speech at the opening ceremony.
Beijing sees the two-day forum as “timely” and “a good opportunity to deepen mutually beneficial cooperation between China and the Pacific”, a commerce ministry spokesperson told the official Economic Daily newspaper.
Trade, agriculture and fisheries, as well as tourism, infrastructure and climate change were at the top of the agenda for the forum, the spokesperson said.
Leaders of all the Pacific nations – except the four that do not have formal diplomatic ties with Beijing – are expected to attend the forum. Australia, which has “observer status” at the summit, will send Ewen McDonald, deputy secretary of the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade and the head of its Pacific office.
Vice-Premier Hu Chunhua will lead the Chinese delegation at the forum. Photo: EPA-EFE
The forum comes after China hailed a “new breakthrough” in the region following the decision last month by the Solomon Islands and then Kiribati – despite warnings from the US – to cut diplomatic ties with Taipei and switch to Beijing.
They are the latest of Taipei’s allies to be
poached by Beijing as it ramps up pressure on the self-ruled island that it sees as a renegade province to be reunited with the mainland, by force if necessary.
Observers said this weekend’s forum was Beijing’s latest effort to regain momentum in the Pacific.
“Having one of China’s top 25 officials visit the region so soon after [Chinese President] Xi Jinping spent close to three days in Papua New Guinea last November is certainly significant,” said Jonathan Pryke, director of the Pacific Islands programme at the Lowy Institute in Sydney, referring to Hu’s position in the 25-member Politburo.
“It shows clearly China’s attempt to recapture momentum after the West, and in particular Australia, have redoubled their efforts in maintaining and building relationships in the Pacific,” he said.
Papua New Guinea’s Prime Minister Peter O’Neill (second from left) and Chinese President Xi Jinping (second from right) pose for a photo during Xi’s visit in November. Photo: AFP
First held in Fiji in 2006, the forum is part of China’s efforts to expand its reach in the resource-rich region.
Back then, premier Wen Jiabao announced 3 billion yuan of concessional loans to Pacific nations and promised to facilitate more trade, medical aid and tourism with the countries. Chinese capital has been pouring into the region – particularly from the mining and fisheries sectors – ever since.
Of note was a 440 million yuan investment, supported by loans from the Export-Import Bank of China, to build a central business centre at Nuku’alofa, the capital of Tonga.
US and allies sideline China in PNG’s Bougainville by helping fund independence vote
As China’s influence grows, the South Pacific – a region traditionally under US hegemony, and on Australia’s doorstep – has “increasingly become a major power that cannot be neglected” and “an important part of China’s greater strategic landscape”, according to Shi Chunlin, an associate professor at Dalian Maritime University.
Trade has increased between China and the eight Pacific nations that have diplomatic ties with Beijing, rising to a combined US$4.32 billion last year – up 25 per cent from 2017.
China has also become the largest trading partner of new ally the Solomons, the second-largest to Papua New Guinea and Fiji, and the third-largest to Samoa.
China’s direct investment in the region has also jumped, reaching US$4.53 billion last year, a more than fourfold increase from the US$900 million of 2013.
Pryke said Beijing was expected to offer new support and loans to the Pacific nations.
“But the Pacific are much more picky about how they want to engage with all partners than they were a decade ago,” he added.
Returning from a trip to China earlier this month, Solomon Islands Prime Minister Manasseh Sogavare confirmed Beijing would provide a US$74 million grant to build a new stadium for the 2023 Pacific Games in the capital Honiara – something its former ally Taipei had committed to fund.
China Sam Group also reportedly signed an agreement on September 22 to lease the island of Tulagi in the Solomons, the site of a former Japanese naval base. The agreement mentioned the development of a refinery on the island, but critics said it could also potentially be used as a military base.
China is now the second-largest donor in the region, only after Australia, which has viewed Beijing’s financial largesse with suspicion.
Last year, in an apparent effort to counter China’s rising influence in the region, Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison announced that Pacific countries would be offered up to US$2.18 billion in grants and cheap loans to build infrastructure.
Australian Prime Minister Scott Morrison last year announced up to US$2.18 billion in grants and cheap loans for infrastructure in Pacific nations. Photo: EPA-EFE
The US, meanwhile, has also been wary of China’s push in the Pacific, amid an escalating geopolitical competition between the world’s two largest economies across many fronts – from trade to tech supremacy and security. The US has long maintained exclusive defence access in the region through its Guam military base and security pacts with the Federated States of Micronesia, the Marshall Islands and Palau.
Derek Grossman, a senior defence analyst with the US-based Rand Corporation, said this year’s forum in Samoa was likely to be higher profile than previous years after Beijing lured away two more diplomatic allies from Taipei.
He said it would be “closely watched in the US for how Beijing continues to leverage sweet economic deals via its Belt and Road Initiative to potentially entice others to switch”.
“The US, along with close friends Australia, Japan and New Zealand, are becoming increasingly concerned over the prospects for China to one day curry enough influence in these small island states to gain port access that could be used for new naval bases,” he said.
The most important issue at the forum, he said, would be “whether the West assesses that China is making further inroads with these states”.
“The likely answer will be that it is, suggesting that the US and its partners will have to compete with China in this region to ensure that it remains ‘free and open’, per the US Indo-Pacific strategy,” he said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in agriculture, Apia, Australia, Beijing, Beijing’s, Belt and Road Initiative, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), China alert, China-Pacific Island Countries Economic Development Cooperation Forum, Chinese Vice-Premier Hu Chunhua, climate change, commercial and agricultural affairs, Dalian Maritime University, delegation, Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade, Economic Daily, economic forum, expected, Export-Import Bank of China, Federated States of Micronesia, Fiji, fisheries, Guam, guangdong province, Infrastructure, Japan, Japanese naval base, Kiribati, mainland, Marshall Islands, New Zealand, Nuku’alofa, Pacific Games, Palau, Papua New Guinea, Papua New Guinea (PNG), Prime Minister Manasseh Sogavare, Prime Minister Peter O’Neill, ramp up, RAND Corporation, refinery, renegade province, reunited, Samoa, self-ruled island, Solomon Islands, South Pacific push, Sydney, Taipei, Tonga, Tourism, Trade, Tulagi, Uncategorized, US, US Indo-Pacific strategy |
Leave a Comment »
10/10/2019
President Tsai Ing-wen also vowed in a National Day speech to defend Taiwan’s sovereignty, saying her government would safeguard freedom and democracy as Beijing ramps up pressure on the self-ruled island it considers a wayward province.
Tsai, who is seeking re-election in January amid criticism of her policy towards China, referred to the arrangement for the return of the former British colony of Hong Kong to Chinese rule in 1997 as a failure.
Hong Kong has been hit by months of anti-government protests triggered by widespread resentment of what many city residents see as relentless efforts by Beijing to exert control of their city despite the promises of autonomy.
China has proposed that Taiwan be brought under Chinese rule under a similar arrangement, but Tsai said Beijing’s policies towards the island were a danger to regional stability.
“China is still threatening to impose its ‘one country, two systems’ model for Taiwan. Their diplomatic offensives and military coercion pose a serious challenge to regional stability and peace,” Tsai said.
“When freedom and democracy are challenged, and when the Republic of China’s existence and development are threatened, we must stand up and defend ourselves,” Tsai said, referring to Taiwan by its official name.
“The overwhelming consensus among Taiwan’s 23 million people is our rejection of ‘one country, two systems,’ regardless of party affiliation or political position.”
Taiwan’s National Day, marking the anniversary of the start of a 1911 uprising that led to the end of dynastic rule in China and the founding of a republic, was celebrated in Taipei with singing, dancing and parades.
Cold War hostility between the island and the mainland had eased over the past decade or so as both sides focused more on expanding business ties, but relations have cooled considerably since Tsai took office in 2016.
China suspects Tsai and her independence-leaning Democratic Progressive Party of pushing for the island’s formal independence, and this year threatened it with war if there was any such move.
Tsai denies seeking independence and reiterated that she would not unilaterally change the status quo with China.
FLASHPOINT
Despite her assurances, Beijing has stepped up pressure on the island to seek “reunification” and backed up its warnings by flying regular bomber patrols around it.
Beijing also says Taiwan does not have the right to state-to-state relations and is keen to isolate it diplomatically.
Seven countries have severed diplomatic ties with the Taiwan and switched allegiance to Beijing since Tsai coming to power. It now has formal diplomatic ties with just 15 nations.
But Tsai said Taiwan was undaunted.
“The determination of the Taiwanese people to embrace the world has never wavered,” she said, adding that Taiwan must work with “like-minded countries” to ensure peace and stability across the Taiwan Strait.
Tsai said under her watch Taiwan has boosted its combat capabilities with the purchase of advanced weapons and development of home-made aircraft.
Taiwan unveiled its largest defence spending increase in more than a decade in August, aiming to purchase more advanced weapons from overseas.
The island has long been a flashpoint in the U.S.-China relationship.
In July, the United States approved the sale of an $2.2 billion worth of weapons to Taiwan, angering Beijing.
The United States has no formal ties with Taiwan but is bound by law to help provide it with the means to defend itself.
Source: Reuters
Posted in Beijing, British colony, China alert, Chinese rule, Cold War hostility, Democratic Progressive Party, failure, Hong Kong, independence, island, leader, mainland, National Day, offer, One country, two systems, rejects, Republic of China, self-ruled island, Taipei, Taiwan, U.S.-China relationship, Uncategorized, United States, wayward province |
Leave a Comment »
28/09/2019
NEW YORK (Reuters) – China and the Pacific island state of Kiribati restored diplomatic ties on Friday after the former diplomatic ally of Taiwan abandoned Taipei.
A poor but strategic country which is home to a mothballed Chinese space tracking station, Kiribati announced last week that it was cutting relations with self-ruled Taiwan in favour of China, which claims Taiwan as a wayward province with no right to state-to-state ties.
China and Kiribati had ties until 2003, when Tarawa established relations with Taipei, causing China to break off diplomatic relations.
Up until that time, China had operated a space tracking station in Kiribati, which played a role in tracking China’s first manned space flight.
The Chinese government’s top diplomat State Councillor Wang Yi and Kiribati’s President Taneti Maamau signed a communique on restoring diplomatic relations at the Chinese mission to the United Nations in New York.
“We highly prize this important and the correct decision,” Wang told a news conference. “Let’s hope for our friendship to last forever. We will work together to grow together towards a bright and prosperous future.”
Speaking alongside Wang, Maamau said there was much to learn from China.
“I do believe that there is much to learn and gain from the People’s Republic of China and the re-establishment of our diplomatic relations is just the beginning,” he said.
There was no mention of the space tracking station at the news conference, nor in the joint communique between the two countries released by China’s Foreign Ministry.
China’s space programme is overseen by the military.
China’s Defence Ministry this week declined comment on the Kiribati facility.
Last week was difficult for Taiwan, as the Solomon Islands also ditched it for Beijing. The Solomon Islands foreign minister signed a deal on diplomatic ties in China last Saturday.
Both the Solomon Islands and Kiribati are small developing nations but lie in strategic waters that have been dominated by the United States and its allies since World War Two. China’s moves to expand its influence in the Pacific have angered Washington.
A former Taiwanese ambassador to Kiribati, Abraham Chu, told Taiwan’s Central News Agency last weekend that China had never fully removed the tracking station in Kiribati and that it “could come back at any time”.
Taiwan now has formal relations with just 15 countries, mostly small and poor nations in Latin America and the Pacific, including Nauru, Tuvalu and Palau. China has signalled it is coming for the rest of Taiwan’s allies.
Source: Reuters
Posted in abandoned, allies, angered, Beijing, China alert, China’s Foreign Ministry, defence ministry, diplomatic ally, diplomatic ties, foreign minister, influence, Kiribati, Latin America, Military, Nauru, New York, Pacific, Pacific island state, Palau, People’s Republic of China, President Taneti Maamau, restores, site, Solomon Islands, space programme, space tracking station, State Councillor Wang Yi, state-to-state ties, Taipei, Taiwan, Tarawa, ties, Tuvalu, Uncategorized, United Nations, United States, Washington, World War Two |
Leave a Comment »
23/09/2019
BEIJING (Reuters) – China will formally resume ties soon with Kiribati, the foreign ministry said on Monday, following the Pacific island state’s decision to ditch relations with Taiwan.
But it did not say what will happen to a space tracking station that China used to operate in Kiribati and is now closed.
Kiribati announced last week that it was cutting relations with self-ruled Taiwan in favour of China, which claims Taiwan as a wayward province with no right to state-to-state ties.
China and Kiribati had ties until 2003, when Tarawa established relations with Taipei, causing China to break off diplomatic relations.
Until then, China had operated the space tracking station in Kiribati, which played a role in tracking China’s first manned space flight in 2003, just before the suspension of ties.
Speaking in Beijing, Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesman Geng Shuang did not answer a question about what would happen with the former space tracking station.
On the timing of when China and Kiribati will formally resume diplomatic relations, Geng said: “What should happen will come sooner or later. Everybody should remain patient.”
“We look forward to resuming diplomatic relations with Kiribati and opening a new page in the two countries’ relations,” Geng said.
He said China also believed this would serve both countries’ people and would be beneficial for peace, stability and prosperity for Pacific island countries.
China has welcome Kiribati’s decision though the two have not yet officially signed an agreement to resume ties.
Last week was a difficult one for Taiwan, as the Solomon Islands also ditched Taipei for Beijing. The Solomon Islands foreign minister signed a deal on diplomatic ties with Beijing in China on Saturday.
Both the Solomon Islands and Kiribati are small developing nations but lie in strategic waters that have been dominated by the United States and its allies since World War Two, and China’s moves to expand its influence in the Pacific have angered Washington.
A former Taiwanese ambassador to Kiribati, Abraham Chu, told Taiwan’s Central News Agency over the weekend that China had never fully removed the tracking station in Kiribati and said China’s then-ambassador in Kiribati was a space expert.
The equipment was locked away and guarded by four fishermen, Chu said.
“It seems it can come back at any time,” he added, referring to the tracking station.
The Kiribati government did not respond to a request for comment.
China’s space programme is overseen by the military. China’s Defence Ministry did not respond to a request for comment.
Taiwan now has formal relations with just 15 countries, mostly small and poor nations in Latin America and the Pacific, including Nauru, Tuvalu and Palau. China has signalled it is coming for the rest of its allies.
Source: Reuters
Posted in Beijing, China alert, Kiribati, Latin America, Nauru, Pacific, Pacific island state, Palau, space tracking station, state-to-state ties, Taipei, Taiwan, Tuvalu, Uncategorized, wayward province |
Leave a Comment »