24/02/2020
- State-owned carrier’s chief says it wouldn’t be ‘morally acceptable’ to stop flying to the country, and it will stand with its ‘Chinese brothers and sisters’
- Dozens of airlines have cancelled or reduced services to the nation amid the virus outbreak, including two East African rivals
Ethiopian Airlines says it will continue flying to China. The routes are among its most profitable. Photo: Shutterstock
Ethiopian Airlines, Africa’s largest and most profitable carrier, will continue flying to China despite growing pressure for it to suspend services to the country as
.
Dozens of airlines around the globe have cancelled or reduced their services to cities in the world’s second-largest economy amid fears over the outbreak. Its East African rivals Kenya Airways and RwandAir have both suspended flights to China until the outbreak is contained.
But Ethiopian Airlines chief executive Tewolde GebreMariam said the carrier would not abandon the routes, which are among its most profitable.
Tewolde told media over the weekend that the airline had been flying to China since 1973 and it would not be ethical to suspend flights to the country.
“It will not be morally acceptable to stop flying to China today because they have a temporary problem,” he said, adding that the airline would stand with its “Chinese brothers and sisters”.
His remarks came days after Kenyan President Uhuru Kenyatta put pressure on the Ethiopian government – which wholly owns Ethiopian Airlines – to halt flights to China, citing the need to curb the spread of the virus into the East African region.
Global coronavirus deaths equal Sars, while new infections drop
The airline has bucked a trend that has seen major airlines – from the United States to Europe and Asia – staying away from Chinese airspace as governments around the world move to keep the deadly virus from their borders. The pneumonia-like illness has so far
in mainland China since the outbreak began in Wuhan in December, with cases reported in more than 20 other countries worldwide.
Speaking during a visit to Washington last week, Kenyatta – who is keen to court both China and the US – insisted that Kenya’s decision to suspend flights from Guangzhou to Nairobi was not political.
He said most African countries had weak health systems that would make it harder to handle the outbreak, so preventing its spread – even if through extreme measures such as grounding flights – was the only option.
“Our worry as a country is not that China cannot manage the disease. Our biggest worry is diseases coming into areas with weaker health systems like ours,” Kenyatta said while addressing members of US think tank the Atlantic Council.
Vaccine for new coronavirus unlikely to be ready before outbreak is over, says Sars expert
But Ethiopian Airlines said it would continue flying to Beijing, Shanghai, Guangzhou, Chengdu and Hong Kong and was taking measures to protect staff and passengers. Ethiopia receives about 1,500 visitors from mainland China every day.
According to Tewolde, if the airline halted its Chinese services, China and Africa would be completely disconnected.
“No one in Ethiopian Airlines would like to see this,” he said. “We have to take maximum precautions, but stopping flights is not one of them.”
He added: “Even if we stop flying, people will continue to come to Ethiopia through Singapore, Malaysia, Europe. The transmission of the disease will be dangerously hidden … British Airways stopped flying to China for its economic reasons. But Chinese carriers are flying to the UK.”
Chinese cities keen to get back to work but coronavirus concerns grow as workers return
In a separate statement, the carrier said China was “one of the strongest and one of the oldest markets for Ethiopian Airlines”.
“We have been connecting the great Chinese nation with the entire continent of African for almost half a century and it is our growth strategy,” the airline said, adding that it would continue operating in the five cities in compliance with international aviation and health guidelines.
Aside from seeking to shore up revenues, analysts noted that the airline was under tight state control, and Ethiopia would be reluctant to do anything that might harm its strong bilateral ties with China.
Ethiopia is among the nations on the continent with the highest number of Chinese immigrants. Most of them are workers involved in the construction of infrastructure projects including ports, railways, dams, bridges and malls. Those projects have been financed with billions of dollars in loans from China – Ethiopia is reportedly among the biggest recipients of Chinese lending in Africa.
Last year, China was forced to restructure Ethiopia’s debt after the latter edged closer to defaulting on a loan from Beijing for its standard gauge railway.
Chinese hotel workers arrested in Kenya after caning video prompts demands for action
Ethiopia, Algeria, Angola, Nigeria and Zambia together accounted for nearly 60 per cent of all Chinese workers on the continent at the end of 2017, according to a study by Johns Hopkins University.
Ethiopia is also a major recipient of direct foreign investment from China.
Source: SCMP
Posted in africa, Algeria, Angola, Asia, Atlantic Council, Beijing, bow, British Airways, Chengdu, China, coronavirus, direct foreign investment, East African, Ethiopian Airlines, Europe, Guangzhou, halt flights, Hong Kong, Kenya Airways, Kenyan president, Mainland China, Malaysia, Nigeria, pressure, refuses, rivals, SARs, Shanghai, Singapore, Uhuru Kenyatta, Uncategorized, United States, Zambia |
Leave a Comment »
24/02/2020
- Power-sharing agreement between rebel leader Riek Machar and President Salva Kiir gives hope to ending the conflict
- Beijing has invested tens of millions of dollars in the country’s oilfields and sent more than 1,000 peacekeeping troops there
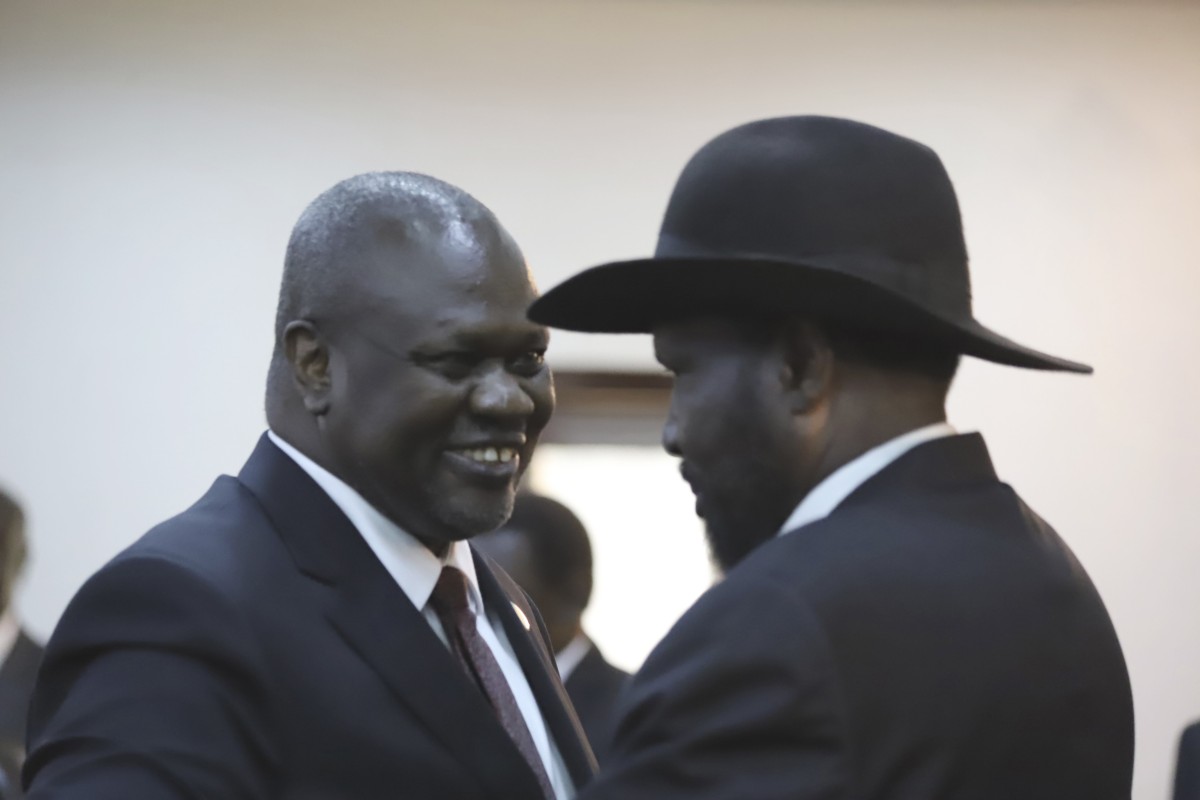
Rebel leader Riek Machar (left) and President Salva Kiir greet each other after the swearing-in ceremony at the State House in Juba on Saturday. Photo: AP
Beijing has welcomed “encouraging developments” in the South Sudan peace process after rebel leader Riek Machar and President Salva Kiir agreed to form a transitional coalition government.
Machar, the Sudan People’s Liberation Movement-In Opposition (SPLM-IO) leader, was among four vice-presidents sworn in on Saturday in the capital, Juba, in a power-sharing deal that gives hope to ending the more than six years of conflict which has killed some 400,000 people and displaced millions more.
“The Chinese side commends and welcomes these encouraging developments, especially the crucial consensus reached between President Kiir and Machar,” the Chinese embassy in Juba said in a statement.
Stability in South Sudan is important for China, which has invested tens of millions of dollars in the country’s oilfields as it seeks to meet energy needs at home. China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC) owns a 41 per cent stake in South Sudan’s largest oil consortium, Dar Petroleum Operating Company, while Sinopec, another Chinese state-owned firm, holds a 6 per cent stake.
Stability in South Sudan is important for China, which has major investments in the country’s oilfields. Photo: Reuters
China has also sent more than 1,000 troops to the United Nations’ peacekeeping mission in South Sudan, and has not followed the United States and other Western nations in imposing sanctions on leading political and military figures.
“We trust that the relevant parties of South Sudan will resolve the remaining issues in the spirit of mutual trust and understanding, and start a new chapter in the history of South Sudan,” the embassy statement added.
China has offered to help rebuild the country, promising to supply a unified security force that is supposed to be formed from the rival factions as part of the peace process. It has also helped to set up military camps to accommodate both government troops and members of the armed opposition.
Since the peace deal was signed between Kiir and rebel factions in September 2018, China said it had provided diplomatic and other support to military camps and training centres including 1,500 tonnes of rice, 2,500 tents, 50,000 blankets and 1,440 boxes of medicine.
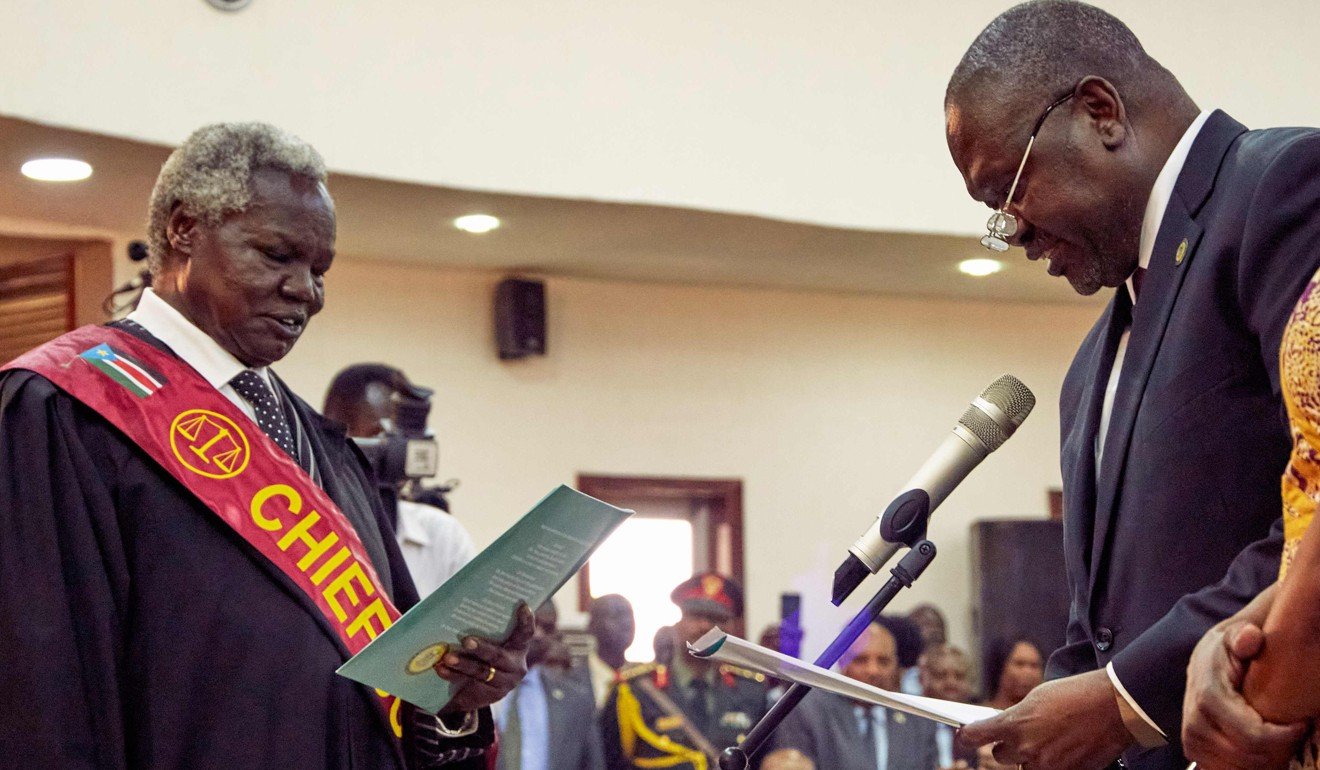
Riek Machar (right) is sworn in as the first vice-president of South Sudan. Photo: AFP
Machar was sworn in as the first vice-president alongside three others – James Wani Igga, Taban Deng Gai and Rebecca Nyandeng. Gai, a former ally of Machar who switched to the government side, was recently sanctioned by the US over serious human rights abuses. Nyandeng is the widow of John Garang, who led a long struggle for independence from Sudan before he died in a helicopter crash in 2005.
“I have forgiven my brother Riek Machar. I also ask for his forgiveness and I also forgive all those who still are holding out on this peace agreement,” Kiir said at a ceremony at the State House attended by regional leaders and diplomats.
After the swearing-in, Machar vowed to work together to end the suffering of South Sudanese.
“I reiterate my commitment to work closely with President Kiir to implement the agreement in letter and spirit,” Machar said.
From Angola to Zambia, China’s African partners brace for coronavirus blow to trade
The South Sudanese have seen more war than peace since the East African nation – whose oilfields contribute about 98 per cent of the government’s revenue – seceded from the Republic of Sudan in 2011. Kiir and Machar formed the independent government but disagreements followed, leading to Machar’s sacking, sparking a bloody war along ethnic lines.
They again agreed to work together in 2015, but the deal fell apart a year later following renewed fighting. After international pressure and peace talks, a new deal was signed in September 2018, but Kiir and Machar have had to push back two deadlines to form the coalition government as they could not agree on issues such as having a unified army and the number of states – highly contentious since it affects the control of oil-rich regions. Machar also wanted his security assured.
On Thursday, Kiir said he had agreed to abolish the 32 states he created in 2015 and revert to the original 10 states.
According to a report released last week on China’s approach to UN peacekeeping in the region, Beijing had used its “economic leverage” in South Sudan.
“China has used its leverage to encourage the government and the opposition parties to negotiate, to come to an agreement, and to implement the ceasefire agreements,” said the report by the Norwegian Institute of International Affairs. “It has reportedly used its economic leverage by signalling that it would be unable to renew and expand its support to the South Sudanese government and the economy as long as the fighting was ongoing.”
Africa is a test lab for how China approaches international security and peacekeeping
South Sudan had also provided an opportunity for Chinese soldiers to put their skills to the test on overseas missions and during armed conflict.
“South Sudan became a real-world laboratory [for China] to test the boundaries of its non-interference principle,” the report said.
Obert Hodzi, an international relations lecturer at the University of Liverpool in England, also said earlier that it was a way for China’s military to get the combat experience it needed.
“South Sudan provides ample opportunities for different segments of the Chinese army to practise, test their equipment and ability to conduct successful missions abroad,” Hodzi said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in africa, Angola, ‘encouraging developments’, Beijing, China, China National Petroleum Corporation (CNPC), Dar Petroleum Operating Company, England, form, oilfields, peacekeeping troops, Republic of Sudan, rivals, Sinopec, Uncategorized, United Nations’ peacekeeping mission, unity governmen, University of Liverpool, welcomes, Zambia |
Leave a Comment »
19/02/2020
- Forty countries will be able to diagnose the disease, and the Africa CDC is training health workers
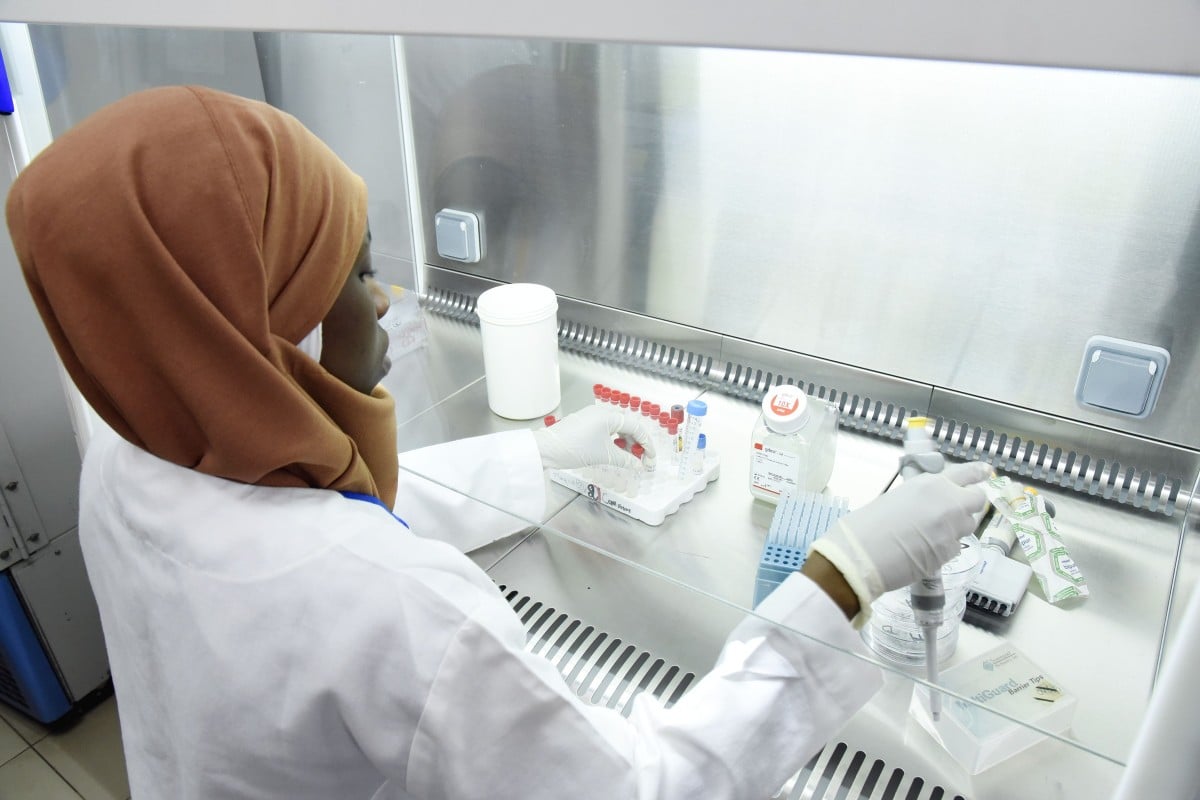
- Until two weeks ago, there were only two laboratories on the continent that could test for the virus, in Senegal and South Africa
A scientist researches the coronavirus at the Pasteur Institute in Dakar, Senegal, which until two weeks ago was one of just two labs in Africa that could test for the disease. Photo: AFP
Forty countries in Africa will be able to test for the
deadly new coronavirus
by the end of the week, the WHO said, after Egypt confirmed the first case on the continent last week.
The World Health Organisation said many of those nations had been sending samples elsewhere for testing and waiting several days for results.
“Now they can do it themselves, within 24 to 48 hours,” WHO director general Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus said in a media briefing on Tuesday.
Until about two weeks ago, there were only two laboratories in the continent of 54 countries – in Senegal and South Africa – with the reagents needed to test for the virus. That meant dozens of nations that had quarantined suspected patients were sending samples to South Africa or Senegal to be tested.
The WHO earlier this week sent reagent kits for coronavirus diagnosis to more than 20 countries in Africa to step up diagnosis of the virus, which causes a disease now known as Covid-19. The global health body said more countries in Africa were expected to receive testing kits this week.
In addition, the WHO last week sent testing kits to Cameroon, Ivory Coast, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Egypt, Ethiopia, Gabon, Ghana, Kenya, Morocco, Nigeria, Tunisia, Uganda and Zambia.
Coronavirus: WHO urges caution over study showing ‘decline’ in new Covid-19 cases in China
Tedros said some countries in Africa, including the Democratic Republic of Congo, were using systems developed to test for the deadly Ebola virus to now test for the coronavirus.
“This is a great example of how investing in health systems can pay dividends for health security,” Tedros said.
Several countries, including Ethiopia and South Sudan, were prioritising surveillance and monitoring at ports of entry, he said. “We’re also working with partners in some of the most fragile contexts, from Syria to the Central African Republic, to prepare countries for the arrival of the virus,” he said.
The WHO and Egyptian health officials on Friday confirmed that a 33-year-old foreigner had tested positive for the coronavirus. Egypt’s health ministry said the patient had tested positive for the virus without any symptoms, raising concern that there could be undetected cases on the continent, as countries scramble to equip labs to test for the disease.
The asymptomatic patient in Egypt was identified through contact screening of an index case who travelled to Cairo on a business trip from January 21 to February 4 and tested positive for the virus on February 11 in China, the WHO regional office said.
The new virus strain has killed more than 2,000 people and infected over 74,000 since the outbreak began in central China in December. It has spread to more than 20 countries.
Screening measures have been stepped up across Africa, including quarantining all passengers arriving from Chinese cities, amid fears that poorer countries with weaker health systems may struggle to cope if the virus spreads on the continent. More than a dozen countries still do not have the capacity to test for the pneumonia-like illness.
There are concerns that Africa’s close links with China put it at high risk for the spread of the new virus. Africa has become home to millions of Chinese since Beijing started looking to the continent for raw materials for its industries and markets for its products. China has been Africa’s largest trading partner since 2009, after it overtook the United States, with two-way trade standing at US$108 billion last year, according to China’s commerce ministry.
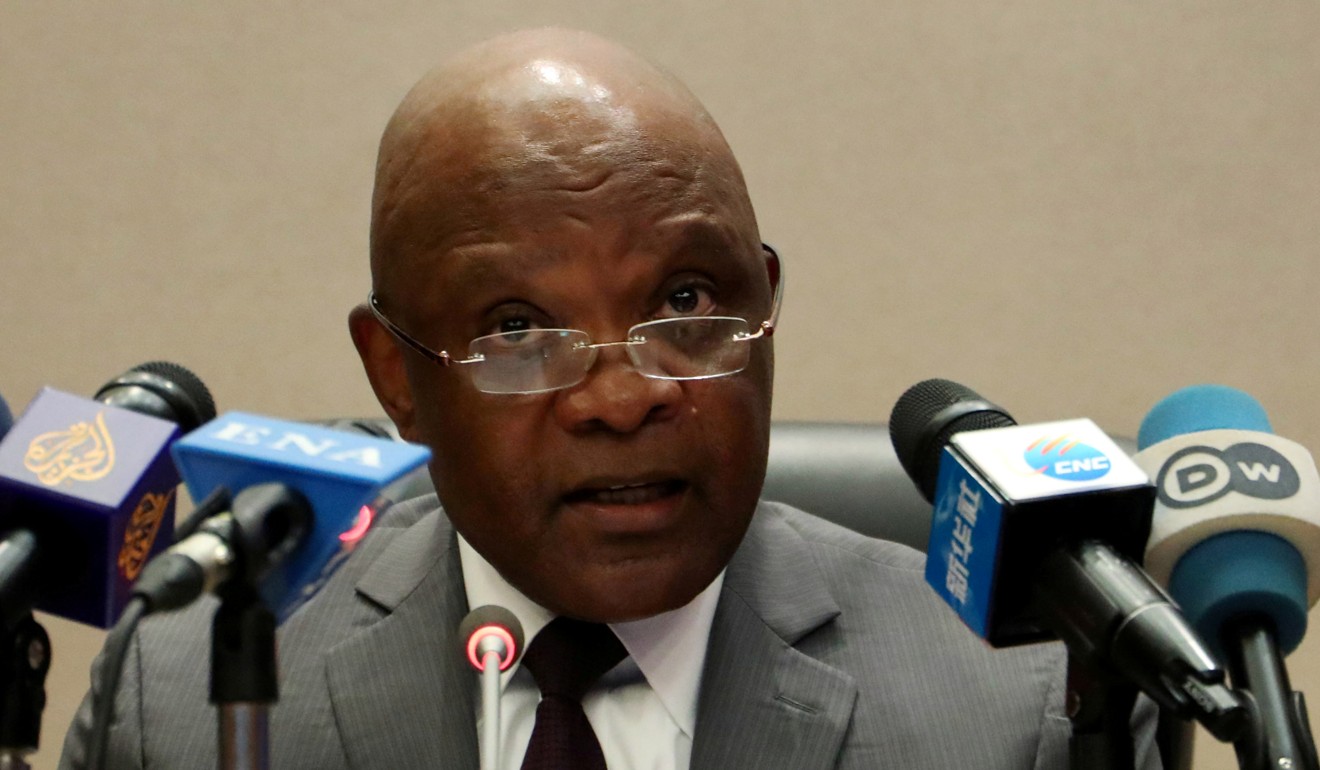

Africa CDC director John Nkengasong said it had been “investing in preparedness and response to the disease”. Photo: Reuters
John Nkengasong, director of the Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC), said it was working closely with the WHO and other partners to ensure that Egypt had the diagnostic tools it needed, and that the right actions were taken to contain the spread of the virus.
“We anticipated that the Covid-19 outbreak would inevitably impact Africa. That is why the Africa CDC has been working actively with African Union member states and partners in the past four weeks and investing in preparedness and response to the disease,” he said.
“[Last week in Dakar, Senegal] we conducted training and supplied test kits to 16 African laboratories, including from Egypt. Egypt also received additional test kits from the WHO,” Nkengasong said.
The Africa CDC would train 40 health workers from nine countries, including Egypt, in Nairobi this week, he said, on “enhancing detection and investigation of Covid-19 at points of entry”.
The Chinese medical workers on the front line of the coronavirus fight in Wuhan
On Monday, Ethiopia, home to one of the continent’s busiest airports, said it had received equipment and reagents for virus detection and control. “We are working hard day and night with the government to improve the critical measures needed to ensure that the country is ready to effectively respond to an outbreak of Covid-19,” said Boureima Hama Sambo, the WHO representative in Ethiopia.
despite pressure for it to suspend services to the country. Many countries on the continent have restricted travel to and from mainland China, while six out of eight African airlines with Chinese routes have halted flights until the virus is contained, including EgyptAir.
Egypt has suspended all flights to and from the mainland until the end of the month and has evacuated more than 300 Egyptians from Wuhan, the epicentre of the epidemic.
Source: SCMP
Posted in africa, Africa CDC, Africa Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC), African, airports, asymptomatic patient, Cameroon, Central African Republic, confirmed, coronavirus, coronavirus case, COVID-19, diagnose, Disease, Ebola virus, Egypt, EgyptAir, Egyptian health officials, Egyptians, epicentre, epidemic, Ethiopia, Ethiopian Airlines, evacuated, Forty countries, Gabon, Ghana, Ivory Coast, Kenya, mainland, monitoring, Morocco, nations, Nigeria, outbreak, Pasteur Institute, ports of entry, sends, Senegal, South Africa, Surveillance, Syria, test kits, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Tunisia, Uganda, Uncategorized, WHO, Wuhan, Zambia |
Leave a Comment »
18/08/2019
- Beijing will be watching as leaders of African nations and international organisations gather for development summit in Yokohama later this month
- Tokyo is expected to use the conference to articulate how its approach to aid and infrastructure is different from Chinese projects
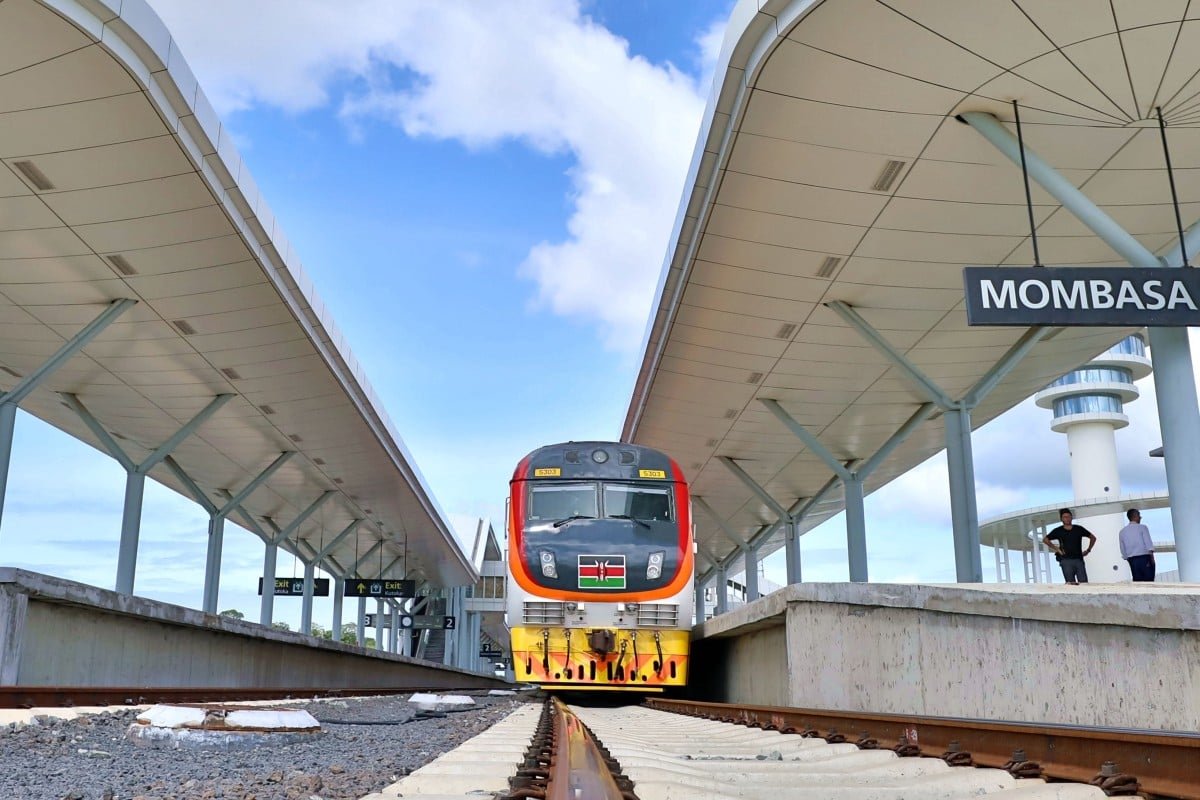
The Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway, funded by China, opened in 2017. Japan has criticised Chinese lending practices in Africa. Photo: Xinhua
The long rivalry between China and Japan is again playing out in Africa, with Tokyo planning to pour more aid into the continent and invest in infrastructure projects there.
Beijing – which has for decades funnelled money into the continent – will be watching as the leaders of 54 African countries and international organisations descend on Yokohama later this month for the seventh Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD).
Japan reportedly plans to pledge more than 300 billion yen (US$2.83 billion) in aid to Africa during the conference. While that might not be enough to alarm China – which in recent years has been on a spending spree in the continent – it will be paying close attention.
Japan has in the past used the meetings to criticise Chinese lending practices in Africa, saying it was worried about the “unrealistic” level of debt incurred by African countries – concerns that China has dismissed.
This year, analysts expect Tokyo will use the conference to articulate how its approach to African development is substantively different from that of the Chinese.
“So, look for the words ‘quality’, ‘transparency’ and ‘sustainability’ to be used a lot throughout the event,” said Eric Olander, managing editor of the non-partisan China Africa Project.
Japanese Foreign Minister Taro Kono gives a speech at the TICAD in Tokyo in October. Japan will reportedly pledge US$2.83 billion in aid to Africa this year. Photo: The Yomiuri Shimbun
Olander said Japan often sought to position its aid and development programmes as an alternative to China’s by emphasising more transparency in loan deals, higher-quality infrastructure projects and avoiding saddling countries with too much debt.
“In some ways, the Japanese position is very similar to that of the US where they express many of the same criticisms of China’s engagement strategy in Africa,” Olander said.
But the rivalry between China and Japan had little to do with Africa, according to Seifudein Adem, a professor at Doshisha University in Kyoto, Japan.
“It is a spillover effect of their contest for supremacy in East Asia,” said Adem, who is from Ethiopia.
“Japan’s trade with Africa, compared to China’s trade with Africa, is not only relatively small but it is even shrinking. It is a result of the acceleration of China’s engagement with Africa.”
Chinese President Xi Jinping attends a group photo session with African leaders during the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation in Beijing last year. Photo: AP
Japan launched the TICAD in 1993, to revive interest in the continent and find raw materials for its industries and markets for products. About a decade later, China began holding a rival event, the Forum on China-Africa Cooperation.
It is at heart an ideological rivalry unfolding on the continent, according to Martin Rupiya, head of innovation and training at the African Centre for the Constructive Resolution of Disputes in Durban, South Africa.
“China cast Japan as its former colonial interloper – and not necessarily master – until about 1949. Thereafter, China’s Mao [Zedong] developed close relations, mostly liberation linkages with several African nationalist movements,” Rupiya said.
Beijing had continued to invoke those traditional and historical ties, which Japan did not have, he said.
“Furthermore, Japan does not command the type of resources – call it largesse – that China has and occasionally makes available to Africa,” Rupiya said.
Although both Asian giants have made inroads in Africa, the scale is vastly different.
While Japan turned inward as it sought to rebuild its struggling economy amid a slowdown, China was ramping up trade with African countries at a time of rapid growth on the continent.
That saw trade between China and Africa growing twentyfold in the last two decades. The value of their trade reached US$204.2 billion last year, up 20 per cent from 2017, according to Chinese customs data. Exports from Africa to China stood at US$99 billion last year, the highest level since the 1990s. Meanwhile, through its Belt and Road Initiative that aims to revive the Silk Road to connect Asia with Europe and Africa, China is funding and building Kenya’s Standard Gauge Railway and the Addis Ababa-Djibouti Railway. Beijing is also building major infrastructure projects in Zambia, Angola and Nigeria.
Japan’s trade with Africa is just a small fraction of Africa’s trade with China. In 2017, Japan’s exports to the continent totalled US$7.8 billion, while imports were US$8.7 billion, according to trade data compiled by the Massachusetts Institute of Technology.
How speaking with one voice could help Africa get a better deal from China
But Japan now appears eager to get back in the game and expand its presence in Africa, and analysts say this year’s TICAD will be critical – both in terms of the amount of money Tokyo commits to African development and how it positions itself as an alternative to the Chinese model.
Ryo Hinata-Yamaguchi, a visiting professor at Pusan National University in South Korea, said the continent was “economically vital to Japan, both in trade and investments”.
“Moreover, Japan has established some strong links with African states through foreign aid,” Hinata-Yamaguchi said.
“Japan’s move is driven by both economic and political interests. Economically, Japan needs to secure and maintain its presence in, and linkages with, the African states while opening new markets and opportunities,” he said.
To counter China’s belt and road strategy, Japan has launched the Asia-Africa Growth Corridor project, an economic cooperation deal, with India and African countries.
Tokyo meanwhile pledged about US$30 billion in public-private development assistance to Africa over three years at the 2016 TICAD, in Nairobi. But China offered to double that amount last year, during its Forum on China-Africa Cooperation in Beijing.
Still, Japan continues to push forward infrastructure projects on the continent. It is building the Mombasa Port on the Kenyan coast, while Ngong Road, a major artery in Nairobi, is being converted into a dual carriageway with a grant from Tokyo.
Japan is also funding the construction of the Kampala Metropolitan transmission line, which draws power from Karuma dam in Uganda. In Tanzania, it provided funding for the Tanzania-Zambia Railway Authority (Tazara) flyover. And through the Japan International Cooperation Agency, Tokyo also helps African countries improve their rice yields using Japanese technology.
There are nearly 1,000 Japanese companies – including carmakers like Nissan and Toyota – operating in Africa, but that is just one-tenth the number of Chinese businesses on the continent.
Are Chinese loans putting Africa on the debt-trap express?
Olander said Japan’s construction companies were among the best in the world, albeit not necessarily the cheapest, and that Tokyo was pushing its message about “high-quality” construction.
XN Iraki, an associate professor at the University of Nairobi School of Business, said Japan wanted to change its approach to Africa on trade, which had long been dominated by cars and electronics.
“[It has] no big deals like China’s Standard Gauge Railway. But after China’s entry with a bang – including teaching Mandarin through Confucius Institutes – Japan has realised its market was under threat and hence the importance of the TICAD, which should remind us that Japan is also there.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Addis Ababa-Djibouti railway, africa, African Centre for the Constructive Resolution of Disputes, aid and infrastructure, alternative, Angola, Asia, Beijing, Belt and Road Initiative, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), best in the world, carmakers, cars, cheapest, China Africa Project, China alert, Chinese President Xi Jinping, Chinese projects, colonial interloper, Confucius Institutes, construction companies, continent, counter, debt-trap express, development summit, different, Doshisha University in Kyoto, dual carriageway, Durban, East Asia, Electronics, Ethiopia, Europe, flyover, Forum on China-Africa Cooperation, Forum on China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC), Forum on China–Africa Cooperation, high-quality development, ideological rivalry, Japan, Japanese Foreign Minister, Japanese technology, Kampala Metropolitan transmission line, Karuma dam, Kenya’s Standard Gauge Railway, Kenyan coast, largesse, leaders of African nations organisations, leaders of international organisations, Mandarin, Mao Zedong, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, master, Mombasa Port, Mombasa-Nairobi Standard Gauge Railway, Nairobi, Nigeria, Nissan, Pusan National University, quality, resources, rice yields, rivalry, seeks, Silk Road, South Africa, South Korea, Standard Gauge Railway, Sustainability, Tanzania, Tanzania-Zambia Railway Authority (Tazara), Taro Kono, TICAD, Tokyo, Tokyo International Conference on African Development (TICAD), Toyota, Transparency, Uganda, Uncategorized, University of Nairobi School of Business, watching, Yokohama, Yomiuri Shimbun, Zambia |
Leave a Comment »
17/08/2019
- Beijing has lent billions of dollars to countries on the continent to build railways, highways and airports but critics say the borrowings are unsustainable
- Chinese officials say the projects will pay off in the long run and host nations are well aware of their limits and needs
Illustration: Lau Kakuen
When Clement Mouamba went to Beijing last year, he had two main tasks.
The prime minister of the Republic of Congo needed to find out exactly how much his country owed to China, a number the struggling, oil-rich central African nation had until then not been able to provide the International Monetary Fund (IMF) to qualify for a bailout. He also needed to convince Beijing to restructure its debt to ensure sustainability.
The IMF had put talks for further loans on hold until Mouamba’s administration could say exactly how much it had to repay to the country’s external creditors, including China – the republic’s single largest bilateral lender – and oil multinationals such as Glencore and Trafigura.
The country, which heavily depends on oil revenue, turned to China and private oil majors for funding to run the government when in 2014 oil prices fell from a high of US$100 per barrel to as low as US$30.
The Republic of Congo has since restructured its borrowings from China, which holds about a third, or US$2.5 billion, of the Congolese debt, by extending the repayment period by an additional 15 years.
A number of other African countries struggling to service their loans from Beijing have also pursued concessions. Ethiopia has had part of its Chinese debt written off and terms relaxed for the US$3.3 billion loan it took to build its railway, while Zambia is seeking similar adjustments for its borrowings used to build airports and highways.
Critics say countries on the continent are being burdened with unrealistic levels of debt for inviable infrastructure backed and built by China without adequate transparency and scrutiny.
The biggest concern is that several African countries will be left with huge debts and grandiose infrastructure that they cannot maintain and run profitably. I liken it to borrowing money to buy a Tesla when you don’t have adequate access to electricity: Obert Hodzi of the University of Helsinki in Finland
But Chinese observers say the West must take some of the blame for the countries’ debt problems and that the support China offers will benefit the host countries in the long run.
In the early 1990s, when China began to embrace Africa again after years of isolation from the outside world, the aspiring manufacturer was at a serious disadvantage in the race for raw materials and markets for its industrial goods.
The former colonial powers of the West had already sewn up deals for many of the continent’s most lucrative and readily exploitable reserves, from fossil fuels to minerals.
China needed new strategies to convince African governments to allow it access raw materials for its industries and markets for its products to a largely unfamiliar partner.
China also wanted to challenge the dominance of the US in global trade and politics so it courted allies in Africa to help it push for political legitimacy in international institutions.
A Kenya Railways freight train leaves the port station on the Mombasa-Nairobi railway in Mombasa, Kenya, a huge project backed by China. Photo: Bloomberg
At the time, many African leaders were under fire to liberalise their economies. China’s approach was to promise not to meddle in individual country’s internal affairs and assure African countries that they could get billions in exchange for future delivery of minerals through resource-backed deals.
Beijing sold its policies that it had no conditions attached to its development finance. In the drive to drum up business, China promised affordable loans for African countries to build roads, bridges, highways, airports and power dams.
Is Kenya’s Chinese-built railway a massive white elephant?
But Beijing also pursued tied finance, ensuring that countries borrowing from China used Chinese contractors to implement the projects rather than open them up to outside bids.
In addition, many of the deals were built on weak financial, technical and environmental conditions, with Chinese state firms conducting the technical feasibility, environmental impact assessment and financial viability studies for free for projects that they also build.
For example, in Kenya, the China Road and Bridge Corporation conducted a free feasibility study that was used in the construction of the railway.
The same company was handed the contract to implement the project and is operating both the passenger and cargo train service for a fee.
Chinese companies were responsible for the construction of a rail line between Addis Ababa and Djibouti. Photo: AFP
In contrast, the World Bank and its partner institution, the IMF, demand that such studies be done by an independent consultant and not by the company that implements the project.
According to data compiled by the China-Africa Research Initiative, at the Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies, Beijing has advanced loans worth US$143 billion to African countries since 2000, levels that some critics say are unsustainable for the borrowers.
China meets resistance over Kenya coal plant, in test of its African ambitions
For many of China’s new African partners, these arrangements – from easy lending terms, to non-competitive bidding and opaque contract details – have led to new problems – problems that corrupt or poorly managed governments now share substantial responsibility.
Some critics, both in the West and in host countries, suggest there is a “debt-trap strategy” at the heart of Beijing’s push for international business and influence, but there is no evidence that China deliberately pushes other countries into debt to seize their assets or gain sway.
However, the drive for overseas contracts and big business has led some countries into difficulties with new debts, and there are question marks over the viability of many of the projects the money is funding.
Obert Hodzi, an international relations expert at the University of Helsinki in Finland, said the Addis Ababa-Djibouti railway and the Mombasa-Nairobi railway were good examples of huge projects that were financed by easy borrowing terms from China but were not sustainable and that had in turn forced the African partners to seek further Chinese help.
“The biggest concern is that several African countries will be left with huge debts and grandiose infrastructure that they cannot maintain and run profitably,” Hodzi said. “I liken it to borrowing money to buy a Tesla when you don’t have adequate access to electricity.”
Ken Opalo, a Kenyan scholar at Georgetown University in Washington, said the key issue was the inability of African countries to design projects that were actually needed for the local economies.
A road is not just a means of transport but an economic belt or corridor that will catalyse the development of the whole region: Huang Xueqing, spokeswoman for the Chinese embassy in Nairobi
“Most African countries have been willing to accept projects designed, financed, and implemented by Chinese firms,” Opalo said.
“It would be better to decouple the feasibility studies and design phases of projects from the financing. That way African governments can ensure that they are truly getting value for money.”
But Chinese officials said Beijing had invested in infrastructure largely at the request of the host countries, adding that it could take time to yield returns on the projects.
Huang Xueqing, spokeswoman for the Chinese embassy in Nairobi, said the projects were valid assets with value that would grow in time.
“So, in the long run, it is beneficial to the host countries. Just like when young people buy a house with a mortgage, they may take some debts, but they have a place to live in and have their own assets,” Huang said.
“Underdeveloped infrastructure is the bottleneck that has been holding back Africa’s development. Up to today, many African countries, although in the same continent, are not connected with direct flights, railways or even roads. You have to fly to Paris or Zurich in order to get to some African countries.
“A road is not just a means of transport but an economic belt or corridor that will catalyse the development of the whole region.”
Huang said Beijing had advised the countries to act within their means and not to overstretch themselves when they considered projects that might not be in line with local conditions.
“When making investment decisions, the Chinese side, along with the recipient countries, carry out rigorous feasibility studies and evaluations. We do things according to our ability,” she said.
China’s leadership has also said it is paying close attention to the fiscal and financial difficulties faced by some African countries.
“As a good friend and good brother … the Chinese side is willing to lend a helping hand when needed by the African people to help them overcome temporary difficulties,” State Councillor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi said in January while on a trip to Ethiopia, adding that the debt situation in Africa is also a legacy issue.
China must allay any debt-trap fears in its dealings with Africa
“The African debt issue does not come up today, still less is it caused by the Chinese side. The African people know who are the initiators of African debt.”
The West should take a lot of the blame for worsening debt problems in some African countries, according to Li Anshan, from Peking University’s Centre for African Studies.
He cited the cases of Liberia and the Democratic Republic of Congo, two countries that have had close relations with the West for many years but remain ravaged by war and poverty despite immense natural resources.
“China-Africa relations have been going on for quite some time. Is there any African country which has got poorer because of its deal with China?” Li said.
Gyude Moore, a former Liberian minister of public works whose department oversaw construction and maintenance of various public infrastructure funded and built by China, said it would be difficult to imagine that China would knowingly ensnare its partners in debt.
“China attempts to differentiate itself from Western donors by limiting non loan-related conditionality. China also practices non-interference, so how a country manages its resources, treats its people or deploy its finances were considered ‘internal’,” he said.
“So, Chinese loans are negotiated faster and place less emphasis on public financial management.”
Moore, now a visiting fellow at the Centre for Global Development, said there were trade-offs in such situations.
China focuses on sustainable projects to dismiss fears of African debt trap
“If the loans are going to be fast – the due diligence will not be as rigorous. Chinese project selection mixes political with economic considerations. So, while a project may not make as much economic sense, it may pay political dividends,” he said.
He said non-transparent processes would invite abuse, be they Chinese, Western or African.
Other observers say the question of opacity is more directly related to China’s own economic system.
Howard French, author of China’s Second Continent: How a Million Migrants are Building a New Empire in Africa, said China has very limited transparency and public accountability in its own domestic processes.
The Mombasa railway station is seen in Mombasa, Kenya, in 2018. Photo: Xinhua
“So it would be unusual to expect that China would introduce greater transparency and accountability in its dealings with African countries than it is used to at home – that is, unless African governments insist on it,” French said.
“And this is where African governance comes in. African states should insist on contract transparency but often don’t do so because that offers leaders plentiful opportunities for graft.”
David Shinn, professor of international relations at George Washington University in Washington, agreed that China’s lack of loan transparency was a huge problem and increased the risk of corruption on both the African and Chinese sides. But he also said that in some cases, African governments might have negotiated poorly.
“This is, however, the responsibility of the African government. I don’t think China is purposely trying to encourage African debts in order to gain leverage,” Shinn said.
“In fact, China is becoming more careful about its lending because it is concerned it has made too much credit available to some African countries.”
China ‘ready to talk’ about trade deal with East Africa bloc
Huang Hongxiang, director of China House, a Nairobi-based consultancy that helps Chinese in Africa integrate better, agreed, saying the Chinese government needs to communicate more about projects in Africa but African countries also have a bigger part to play in ensuring better deals.
“On commercial viability, accountability, transparency and governance, I believe the responsibility does not lie with China, the US or the West but in the hands of African countries,” he said.
Wherever the fault lies, one thing is clear when money is wasted on ill-designed projects that have little to no economic return, according to Opalo.
“The lack of planning and transparency creates default risks … [and] African taxpayers will be left holding the bag.”
This article is the third in a series examining the local impact of Chinese investment and infrastructure projects in Africa. Read part one here and part two
The next report will examine whether African countries can speak with one voice in relations with China.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Addis Ababa, Addis Ababa-Djibouti railway, africa, airports, bailout, Beijing, borrowings, bottleneck, build, cargo train service, Centre for Global Development, China House, China Road and Bridge Corporation, China-Africa relations, China-Africa Research Initiative, China’s Second Continent: How a Million Migrants are Building a New Empire in Africa, Chinese embassy, Chinese foreign minister Wang Yi, Chinese infrastructure loans, coal plant, Construction, continent, Contract, debt-trap express, direct flights, Djibouti, due diligence, East Africa bloc, economic belt or corridor, Ethiopia, Fee, Finland, freight train, George Washington University, Georgetown University, Glencore, good friend and good brother, Highways, IMF, International Monetary Fund (IMF), Johns Hopkins University, Kenya, Kenya Railways, lent, Liberian minister of public works, Mombasa, Mombasa railway station, Mombasa-Nairobi railway, Nairobi, oil revenue, Paris, passenger train service, planning, Prime minister, project, railways, Republic of Congo, roads, same continent, School of Advanced International Studies, situations, State Councillor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi, sustainable projects, taxpayers, trade-offs, Trafigura, Transparency, Transport, Uncategorized, Underdeveloped infrastructure, University of Helsinki, unsustainable, Wang Yi, Washington, West, Western donors, white elephant, World Bank, Zambia, Zurich |
Leave a Comment »
25/06/2019
Chinese State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi (R) meets with South African Foreign Minister Naledi Pandor in Beijing, capital of China, June 24, 2019. Naledi Pandor was here to attend the Coordinators’ Meeting on the Implementation of the Follow-up Actions of the Beijing Summit of the Forum on the China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC). (Xinhua/Zhai Jianlan)
BEIJING, June 24 (Xinhua) — Chinese State Councilor and Foreign Minister Wang Yi held respective meetings with foreign ministers from nine African countries on Monday, and they pledged efforts to strengthen cooperation and uphold multilateralism.
The foreign ministers are Naledi Pandor from South Africa, Palamagamba Kabudi from Tanzania, Ezechiel Nibigira from Burundi, Aurelien Agbenonci from Benin, Nhial Deng Nhial from South Sudan, Mamadou Tangara from Gambia, Joseph Malanji from Zambia, Luis Filipe Tavares from Cape Verde, and Gbehzohngar Findley from Liberia.
The African foreign ministers are in Beijing to attend the Coordinators’ Meeting on the Implementation of the Follow-up Actions of the Beijing Summit of the Forum on the China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC), with the aim of better implementing the outcomes of Beijing Summit in 2018.
While holding talks with Pandor, Wang hailed the solid mutual trust and deep-rooted traditional friendship between China and South Africa.
Wang said China and South Africa, both as major representatives of emerging markets and developing countries, should jointly safeguard the missions and principles of the United Nations Charter, champion multilateralism, uphold basic norms governing international relations, and oppose any form of unilateralism and bullying, to promote world peace, development and prosperity.
Pandor said South Africa and the whole African continent, as China’s partners for jointly resisting unilateralism and bullying practice, would stand together with China in safeguarding multilateralism and an open, inclusive global trade system.
In the meeting with Kabudi, Wang expressed China’s readiness to work with Tanzania to keep high-level exchanges, and avail the opportunity of jointly building the Belt and Road and the Coordinators’ Meeting to ensure better outcomes in bilateral cooperation.
Calling the Beijing Summit of the FOCAC a milestone, Kabudi said Tanzania is willing to facilitate cooperation in infrastructure construction, industrial capacity, and in cultural, educational sectors and other areas.
In respective meetings with Nibigira, Agbenonci, Nhial and Tangara, Wang said the current international situation is complex but China’s determination to strengthen its solidarity and friendship with African countries remains unchanged.
Nibigira said Burundi agreed with the Belt and Road Initiative and would continue to support China on issues concerning China’s core interests and major concerns.
Agbenonci said multilateralism was now the only correct choice. Only through multilateralism can the voice of small and medium-sized countries, especially African nations, be heard, he said.
Nhial said South Sudan thanked China for its help in various fields, especially its support and contributions to the peace process in South Sudan.
Tangara said since the resumption of diplomatic relations between China and Gambia, bilateral cooperation in various fields had developed fast, and Gambia can be trusted as a sincere partner of China.
When holding separate meetings with Malanji, Tavares and Findley, Wang said China would continue to uphold justice and pursue the shared principles of sincerity, results, affinity and good faith.
China’s cooperation with Africa is sincere and selfless, and has no geopolitical purposes, said Wang, adding that China had always followed the principle of non-interference, provided aid as Africa needed, carried out South-South cooperation, and helped achieve common development.
He said China-Africa cooperation was conducive to Africa’s infrastructure construction, economic and social benefits, and self-development.
“Africa offers a grand stage of cooperation between different countries, not an arena of major powers’ game,” said Wang, adding that “African friends will get a right conclusion on who truly attaches importance to, respect, and support Africa.”
Malanji said claims that Zambia-China cooperation had led to Zambia’s debt problem were inconsistent with the facts and China’s loans were used on the infrastructure that Zambia needs most, to promote Zambia’s economic development and bring social welfare.
Tavares said Cape Verde cherished relations with China and upheld the one-China principle. He said Cape Verde stood ready to fully implement consensus reached by leaders of the two countries, enhance strategic dialogue, and deepen cooperation, particularly marine economy cooperation, to push bilateral relations into a new era.
Findley said China is Liberia’s true friend which has helped fight Ebola alongside Liberia and played an important role in post-epidemic reconstruction. He said Liberia is ready to enhance mutually beneficial cooperation with China.
Also on Monday, Yang Jiechi, a member of the Political Bureau of the Central Committee of the Communist Party of China (CPC) and director of the Office of the Foreign Affairs Commission of the CPC Central Committee, met with all delegation heads here to attend the coordinators’ meeting.
The meeting will formally open Tuesday morning.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in African countries, Benin, Burundi, Cape Verde, China alert, Chinese State Councilor and Foreign Minister, cooperation, Forum on the China-Africa Cooperation (FOCAC), Gambia, Liberia, South Africa, South Sudan, Tanzania, to enhance, Uncategorized, United Nations Charter, vow, Wang Yi, Zambia |
Leave a Comment »
08/06/2019
BEIJING, June 8 (Xinhua) — China and African countries will see more intimate economic and trade ties as the first China-Africa Economic and Trade Expo will open on June 27 in Changsha, the capital city of Hunan Province.
A total of 53 African countries have confirmed to attend the expo, and international organizations including the United Nations Industrial Development Organization, the World Food Programme and the World Trade Organization will also send representatives to attend the event.
Here are some facts and figures revealing the growing vitality of trade between China and Africa as well as broader economic exchanges.
— China has been the largest trading partner of Africa for 10 consecutive years.
— In 2018, trade volume between China and Africa amounted to 204.2 billion U.S. dollars, up 20 percent year on year.
— China’s imports of non-resource products from Africa have increased significantly. In 2018, China’s imports from Africa went up 32 percent year on year, with the imports of agricultural products up 22 percent.
— China’s exports of mechanical, electrical and high-tech products accounted for 56 percent of its total exports to African countries.
— China has finished the negotiations of a free trade agreement with Mauritius.
— More than 3,700 Chinese enterprises have been set up in Africa by the end of 2018, with combined direct investment over 46 billion dollars.
— China’s financial institutions have established more than 10 branches in Africa.
— South Africa and seven other countries have included the Chinese currency renminbi (RMB), or the yuan, in their foreign exchange reserves.
— China has formed RMB clearing arrangements with Zambia and signed currency swap agreements with four African countries including Morocco.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in africa, Changsha, China alert, China-Africa Economic and Trade Expo, Hunan Province, Mauritius, Morocco, South Africa, Uncategorized, United Nations Industrial Development Organization, world food programme, World Trade Organization (WTO), Zambia |
Leave a Comment »
17/04/2019
NDOLA, Zambia, April 16 (Xinhua) — Chinese investments in Zambia’s agricultural sector will enhance technology adoption in the country’s farming industry, which will result in higher food productivity, a senior government official has said.
Minister of Agriculture Michael Katambo said in an interview with Xinhua early this week that Zambia is partnering with foreign investors, especially the Chinese in the farming industry to improve national food production.
“Our partnering with Chinese in agriculture sector will scale up investment in the farming industry in our country,” he said, adding the Chinese have shown an interest in investing in the country’s aquaculture sector.
Katambo said Zambia should be turned into a regional food basket in the next few years because of the anticipated increase in investment.
Agriculture sector is one of the major revenue generation contributors towards Zambia’s economic growth, he added.
The government, he said, has set aside 100,000 hectares of land across provinces to open up farming activities on a commercial basis.
“We are encouraging all our private partners to help develop the undeveloped farming blocks across the country. We want to be a food basket in the southern region,” he said.
This, he said, can only be achieved when the agriculture sector engages in modern agriculture technology to enhance farming activities.
According to him, the construction of multi-purpose dams such as Muwomboshi dam in Central province and Kafulafuta dam on the Copperbelt province will help harness water for improved irrigation activities.
“Farmers will benefit a lot to grow food all year round through enhanced irrigation system,” he said.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in China alert, Copperbelt province, Kafulafuta dam, Michael Katambo, Minister of Agriculture, multi-purpose dams, Muwomboshi dam, partnering with China, Uncategorized, Zambia, Zambian gov't |
Leave a Comment »