22/05/2020
- The tech investment push is part of a fiscal package waiting to be signed off by the National People’s Congress, which convenes this week
- This initiative will reduce China’s dependence on foreign technology, echoing objectives set forth previously in the ‘Made in China 2025’ programme
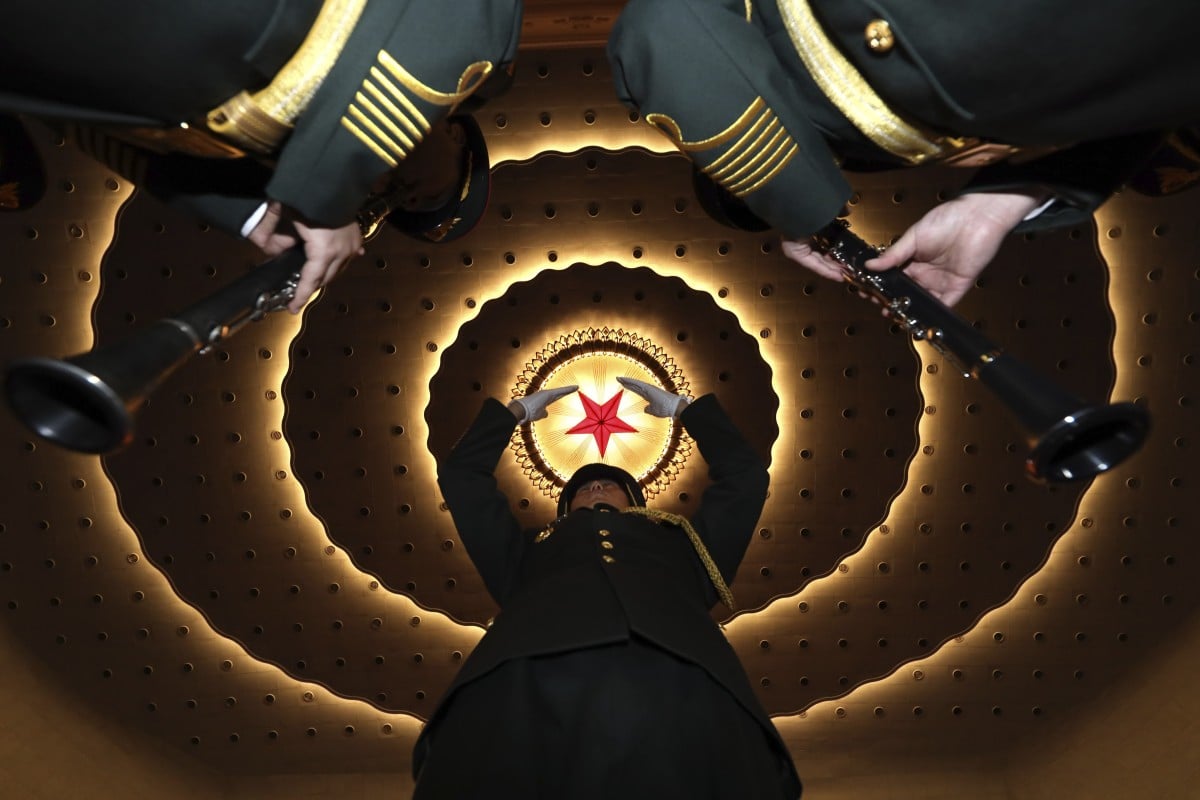
A conductor rehearses the military band on the sidelines of the National People’s Congress in Beijing’s Great Hall of the People in March of last year. China’s legislature is expected to sign off on a massive tech-led stimulus plan. Photo: AP
Beijing is accelerating its bid for global leadership in key technologies, planning to pump more than a trillion dollars into the economy through the roll-out of everything from next-generation wireless networks to artificial intelligence (AI).
In the master plan backed by President Xi Jinping himself, China will invest an estimated 10 trillion yuan (US$1.4 trillion) over six years to 2025, calling on urban governments and private hi-tech giants like Huawei Technologies to help lay 5G wireless networks, install cameras and sensors, and develop AI software that will underpin
to automated factories and mass surveillance.
The new infrastructure initiative is expected to drive mainly local giants, from
and Huawei to SenseTime Group at the expense of US companies.
As tech nationalism mounts, the investment drive will reduce China’s dependence on foreign technology, echoing objectives set forth previously in the “Made in China 2025”
programme. Such initiatives have already drawn fierce criticism from the Trump administration, resulting in moves to block the rise of Chinese tech companies such as Huawei.
How will China’s annual legislative meetings affect the stock investor? Five key industries to watch
“Nothing like this has happened before, this is China’s gambit to win the global tech race,” said Digital China Holdings chief operating officer Maria Kwok, as she sat in a Hong Kong office surrounded by facial recognition cameras and sensors. “Starting this year, we are really beginning to see the money flow through.”
The tech investment push is part of a fiscal package waiting to be signed off by China’s legislature, the
National People’s Congress, which convenes this week. The government is expected to announce infrastructure funding of as much as US$563 billion this year, against the backdrop of the country’s worst economic performance since the Mao era.
The nation’s biggest purveyors of cloud computing and data analysis Alibaba, the parent company of the
South China Morning Post, and
Tencent Holding will be linchpins of the upcoming endeavour. China has already entrusted Huawei, the world’s largest telecommunications equipment supplier, to help galvanise 5G. Tech leaders including Pony Ma Huateng and
Jack Ma are espousing the programme.
Maria Kwok’s company is a government-backed information technology systems integration provider, among many that are jumping at the chance. In the southern city of Guangzhou, Digital China is bringing half a million units of project housing online, including a complex three quarters the size of Central Park in New York City. To find a home, a user just has to log on to an app, scan their face and verify their identity. Leases can be signed digitally via smartphone and the renting authority is automatically flagged if a tenant’s payment is late.
China is no stranger to far-reaching plans with massive price tags that appear to achieve little. There is no guarantee this programme will deliver the economic rejuvenation its proponents promise. Unlike previous efforts to resuscitate the economy with “dumb” bridges and highways, this newly laid digital infrastructure will help national champions develop cutting-edge technologies.
“China’s new stimulus plan will likely lead to a consolidation of
industrial internet
providers, and could lead to the emergence of some larger companies able to compete with global leaders, such as GE and Siemens,” said Nannan Kou, head of research at BloombergNEF, in a report. “One bet is on industrial
internet-of-things (IoT) platforms, as China aims to cultivate three world leading companies in this area by 2025.”
China is not alone in pumping money into the technology sector as a way to get out of the post-coronavirus economic slump. Earlier this month, South Korea said AI and wireless communications would be at the core of it its “New Deal” to create jobs and boost growth.
Nothing like this has happened before, this is China’s gambit to win the global tech raceMaria Kwok, COO at Digital China Holdings
The 10 trillion yuan that China is estimated to spend from now until 2025 encompasses areas typically considered leading edge, such as AI and IoT, as well as items such as ultra-high voltage lines and high-speed rail, according to the government-backed China Centre for Information Industry Development. More than 20 of mainland China’s 31 provinces and regions have announced projects totaling over 1 trillion yuan with active participation from private capital, a state-backed newspaper reported on Wednesday.
Separate estimates by Morgan Stanley put new infrastructure at around US$180 billion each year for the next 11 years – or US$1.98 trillion in total. Those calculations also include power and rail lines. That annual figure would be almost double the past three-year average, the investment bank said in a March report that listed key stock beneficiaries including companies such as China Tower Corp, Alibaba, GDS Holdings, Quanta Computer and Advantech Co.
Beijing’s half-formed vision is already stirring a plethora of stocks, a big reason why five of China’s 10 best-performing stocks this year are tech plays like networking gear maker Dawning Information Industry and Apple supplier GoerTek. The bare outlines of the master plan were enough to drive pundits toward everything from satellite operators to broadband providers.
China’s telecoms carriers push to complete ‘political task’ of 5G network roll-out amid coronavirus crisis
It is unlikely that US companies will benefit much from the tech-led stimulus and in some cases they stand to lose existing business. Earlier this year, when the country’s largest telecoms carrier China Mobile awarded contracts worth 37 billion yuan for 5G base stations, the lion’s share went to Huawei and other Chinese companies. Sweden’s Ericsson got only a little over 10 per cent of the business in the first four months. In one of its projects, Digital China will help the northeastern city of Changchun swap out American cloud computing staples IBM, Oracle and EMC with home-grown technology.
It is in data centres that a considerable chunk of the new infrastructure development will take place. Over 20 provinces have launched policies to support enterprises using cloud computing services, according to a March research note from UBS Group.
Tony Yu, chief executive of Chinese server maker H3C, said that his company was seeing a significant increase in demand for data centre services from some of the country’s top internet companies. “Rapid growth in up-and-coming sectors will bring a new force to China’s economy after the pandemic passes,” he told Bloomberg News.
From there, more investment should flow. Bain Capital-backed data centre operator ChinData Group estimated that for every one dollar spent on data centres another US$5 to US$10 in investment in related sectors would take place, including in networking, power grid and advanced equipment manufacturing. “A whole host of
supply chain companies will benefit,” the company said in a statement.
There is concern about whether this long-term strategy provides much in the way of stimulus now, and where the money will come from. “It’s impossible to prop up China’s economy with new infrastructure alone,” said Zhu Tian, professor of economics at China Europe International Business School in Shanghai. “If you are worried about the government’s added debt levels and their debt servicing abilities right now, of course you wouldn’t do it. But it’s a necessary thing to do at a time of crisis.”
Digital China is confident that follow-up projects from its housing initiative in Guangzhou could generate 30 million yuan in revenue for the company. It is also hoping to replicate those efforts with local governments in the northeastern province of Jilin, where it has 3.3 billion yuan worth of projects approved. These include building a so-called city brain that will for the first time connect databases including traffic, schools and civil matters such as marriage registry. “The concept of smart cities has been touted for years but now we are finally seeing the investment,” said Kwok.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 5G network roll-out, 5G wireless networks, accelerating, Advantech Co, Alibaba Group Holding, American cloud computing, Apple, artificial intelligence (AI), automated factories, autonomous driving, ‘political task’, Bain Capital, Beijing, BloombergNEF, broadband providers, cameras and sensors, Central Park, Changchun, China, China Centre for Information Industry Development, China Europe International Business School, China Mobile, China Tower Corp, civil matters, conductor, coronavirus crisis, cutting-edge technologies, data centres, Dawning Information Industry, dependence, Digital China, Digital China Holdings, digital infrastructure, economic rejuvenation, EMC, Ericsson, everything, facial recognition cameras and sensors, foreign, GDS Holdings, GE, global leadership, GoerTek, Great Hall of the People, Guangzhou, H3C, High-speed rail, Huawei, huawei technologies, IBM, industrial internet, Infrastructure, install, internet-of-things (IoT), Jack Ma, Jilin, key technologies, linchpins, local governments, Made in China 2025, marriage registry, mass surveillance, master plan, military band, national champions, National People’s Congress, networking gear maker, New York City, next-generation wireless networks, northeastern province, Oracle, plan, planning, Pony Ma Huateng, President Xi Jinping, private hi-tech giants, pundits, Quanta Computer, rehearses, roll out, satellite operators, schools, SenseTime Group, Shanghai, Siemens, south china morning post, South Korea, tech crown, Technology, telecommunications equipment supplier, telecoms carriers, Tencent Holding, to pump, to seize, traffic, trillion dollars, UBS Group, ultra-high voltage lines, Uncategorized, urban governments, wireless communications, world’s |
Leave a Comment »
08/04/2020
- Wuhan, where the first cases of the novel coronavirus were detected, is ending a 76-day lockdown
- A day before the lockdown was fully lifted, Tencent announces a slew of initiatives focused on helping to revive the digital industry in the city
Passengers leaving Wuhan city are pictured at the Hankou Railway Station in Wuhan city, central China’s Hubei province, on Wednesday morning, April 08, 2020. Photo: SCMP/Simon Song
A day before China
lifted a months-long lockdown of Wuhan city, the initial epicentre of the coronavirus pandemic, Chinese internet giant
Tencent Holdings pledged to invest in digital government, online education and artificial intelligence (AI) in the city, among other fields.
“During the epidemic, Tencent has been supporting Hubei and Wuhan’s fight against the virus through funds and technology,” the company best known for its gaming business said in a statement posted on Tuesday on WeChat. “In the future, we will also fully support Wuhan’s post-pandemic reconstruction and continue to support the development of Wuhan’s digital industry.”
China’s major tech companies have played a big role in the fight against the coronavirus, and are now playing their part in the economic recovery of Wuhan and other areas that have suffered under extended travel restrictions and business closures.
Last week, China’s biggest e-commerce services providers Alibaba Group Holding,
and Pinduoduo each announced their own initiatives to help revive sales of farm goods from Hubei as the province emerges from its months-long lockdown.
Popular mobile payments app Alipay also created a dedicated section for Wuhan merchants to allow users to buy from merchants in the city, and offered loans to small local merchants in need of financial support, according to an Alipay statement. Alipay is operated by Ant Financial, an affiliate of Alibaba, which owns the South China Morning Post.
How tech has helped China in its public health battle with coronavirus
Wuhan, an industrial powerhouse for the steel, semiconductors and automotive sectors, is emerging from an unprecedented lockdown which began on January 23 and prevented people from moving in and out of the city.
Since restrictions began easing gradually in late March, business activity has shown signs of recovery: Tencent’s mobile payment platform WeChat Pay recorded a 162 per cent increase in offline transactions in a 10-day period from March 25, compared to the same period the previous month, according to a separate statement by Tencent on Wednesday.
Searches for “work resumption certificates” – which businesses need to submit to local authorities to prove their staff can safely restart work – also increased 320 per cent on Baidu, China’s biggest search engine, in the past month, Baidu said in a report on Wednesday.
Tencent declined to provide specific details regarding the size of its latest investment in Wuhan or a timeline for its implementation, but said in the statement that it will involve closer cooperation with city authorities in the areas of digital government, education, smart mobility, AI and cybersecurity to help the city with its digital industries.
Among these initiatives, it will push ahead with a plan to build a headquarters focusing on digital industries in Wuhan, specifically digitalisation for the government and smart city initiatives.
It will also establish a base in Wuhan for its online education initiatives, set up an AI lab and cybersecurity academy and build a school focusing on smart mobility in collaboration with Chinese carmaker Dongfeng Motor Corporation, the company said in the statement.
Source: SCMP
Posted in academy, AI, Alibaba, Alibaba Group Holding, Alipay, artificial intelligence (AI), automotive, “work resumption certificates”, Baidu, businesses, carmaker, City, coronavirus, Coronavirus pandemic, cybersecurity, digital government, digital industries, digitalisation, Dongfeng Motor Corporation, E-commerce, economic recovery, education, emerges, epicentre, financial support, Hankou Railway Station, headquarters, hubei province, Internet giant Tencent, invest, JD.com, loans, local authorities, lockdown, merchants, mobile payments app, online education, Pinduoduo, pledges, reconstruction, restart, school, search engine, sectors, Semiconductors, services providers, small local merchants, smart mobility, south china morning post, Steel, TENCENT, Uncategorized, WeChat, work, Wuhan |
Leave a Comment »
17/03/2020
- AutoNavi’s latest data shows increase in offline traffic and searches of major business districts
- Traffic data could signal that consumer activity in China has entered a recovery
AutoNavi’s mobile app users can search the names of malls and shops to see real-time traffic data. Photo: AP
Data from AutoNavi, the maps app operated by Alibaba Group Holding, shows that traffic in major shopping districts in China picked up by an average of 30 per cent over the past month, as consumer activity gradually returns to normal now that the coronavirus infection rate appears to have peaked in the country.
The early sign of increased consumer activity in China contrasts with the panic and economic uncertainty now engulfing Europe and the US, as the widening pandemic forces governments around the world to take lessons from China on how to tackle the spread of the disease with curfews and social distancing measures.
AutoNavi’s latest big data report, released on Monday, shows that traffic in and around shopping districts in several major cities in the country rose 30 per cent over the weekend of March 14-15 compared with the weekend of February 15-16, when the coronavirus in China was at its height and many areas in the country were under lockdown.
China’s Meituan Dianping to join maps service battle
15 Aug 2019
“Consumer confidence is starting to rebound as the coronavirus comes under control,” said Guo Ning, vice-president of AutoNavi. “We are seeing more and more people stepping out, with offline consumption slowly recovering.”
Alibaba is the owner of the South China Morning Post.
China’s nearly two-month lockdown has dealt a hammer blow to the economy, with retail sales – a key metric of consumption – down by 20.5 per cent across the combined two months of January and February, marking the first decline on record. The virus has however proved a boon for China’s e-commerce sector, as shoppers stuck at home buy even more online.
The new data appears to show that the country’s offline economy could now see a slow recovery. This does not mean that retail businesses can slack off on preventive measures – hand sanitiser, extra cleaning and temperature monitoring are likely to remain fixtures of everyday life in shopping malls.
AutoNavi’s mobile app users can search the names of malls and shops to see real-time traffic data – often used to avoid visiting malls at peak periods. AutoNavi said the average 30 per cent increase in traffic refers to the combined volume of people using the app to navigate the shopping destinations.
Alibaba’s AutoNavi crosses 100 million daily users
AutoNavi has more than 400 million monthly active users, according to company data. It was the first domestic travel platform to exceed 100 million daily active users.
Digital maps have become a key tool in China’s attempts to control the coronavirus pandemic, with competitor map apps from Baidu and Tencent also launching features to track population flows and provide information on clinics able to test for and treat the disease.
Covid-19, as the novel coronavirus is known, has now killed over 3,200 people in China and infected just over 80,000, of which around 68,000 have recovered. There are now around 87,000 confirmed cases outside China, according to the latest figures from health authorities.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Alibaba Group Holding, around, AutoNavi, Big data, China, coronavirus, Coronavirus pandemic, COVID-19, Data, Digital maps, e-commerce sector, economy, Fears, hammer blow, lockdown, maps, Meituan Dianping, novel coronavirus, recede, recovery, shopping areas, shows, south china morning post, traffic, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
06/03/2020
- A first batch of 72 bookstores are launching on food delivery platform Meituan “as soon as next week”
- Booksellers in China’s capital city have been struggling to stay afloat due to reduced footfall during the epidemic
For illustration: coffee and cake in front of a shelf of books at a bookstore. Photo: SCMP / Dickson Lee
Bookstores in Beijing, struggling to survive amid the coronavirus epidemic, are teaming up with a popular food delivery app to help get books into the hands of readers.
The initiative, co-launched by food delivery company Meituan Dianping and the municipal government of Beijing, will feature a first batch of 72 bookstores.
“Due to the epidemic, 80 per cent of physical bookstores are closed,” the publicity department of the Communist Party of China’s Beijing Municipal Committee told local media. “Although many of them try to launch online programmes to keep customers, it doesn’t make a substantial income for stores … companies want the government to coordinate more resources and platforms to help them.”
The bookstores will not have to pay a fee to join the programme, according to the Beijing publicity department.
Users will be able to purchase books on Meituan “as soon as next week”, the food delivery company said in a statement. “After the launch, we will support bookstores by charging them lower service fees, providing subsidies and launching reward plans to help them get on board quickly,” the company added.
China’s smartphone brands adapt to life under coronavirus restrictions
Bookstores in China’s capital city have been hit hard by the coronavirus outbreak. About 60 per cent of 248 stores in Beijing said they expected their revenues to drop more than 50 per cent year-on-year, while only 48 per cent said their cash flows were sufficient to support operations for another one to three months, according to a report by the Beijing Institute of Culture Innovation and Communication.
With fewer customers patronising physical stores and pressure from rent and employee salaries, more bookstores are looking toward online channels to increase sales. Among those interviewed by the Beijing Institute of Culture Innovation and Communication, 21.8 per cent said they were now selling books only via online channels, 48 per cent had tried advertising on social media platforms like WeChat and Weibo, while 16.9 per cent are promoting books on video-sharing platforms like Douyin and Kuaishou.
An interior view of a bookstore, Bookworm, at Sanlitun, Beijing. File photo: SCMP
Last week, Beijing-based bookstore chain OWSpace, which has 15 year history selling books and drinks, posted an appeal on its WeChat account for loyal customers to pay a 50 yuan to 8,000 yuan membership fee to help with its cash flow.
Among their four physical stores in China, only one in Beijing remains open and traffic is a tenth of what it was before the outbreak, it said.
“The store can only sell 15 books a day on average, and more than half are bought by our own staff. We expect our revenue in February to drop 80 per cent compared to other years,” OWSpace said in the post.
Wu Yanping, the general manager of OWSpace’s offline stores, said one of the chain’s stores in Beijing is joining Meituan’s book delivery platform. The store remains physically closed because it is located in an office park that prohibits anyone who travelled out of Beijing from entering before they complete the mandatory 14-day quarantine period.
“Our Dongfeng store is closed for now but even if it opens later, it will not have much traffic [because of the travel restrictions]. So we hope to sell books along with our coffee and drinks on the delivery platform even with the store closed,” Wu said.
Beijing has initiated a range of measures to help keep bookstores afloat, including subsidising their rent, rewarding stores that stay open during the epidemic and encouraging bookstores to expand their sales channels online.
Wu said that since OWSpace posted its appeal letter, it managed to reopen another store in Hangzhou, in the eastern province of Zhejiang, and traffic to both stores has been “gradually recovering to just under 50 per cent of a normal day [before the outbreak]”.
OWSpace also conducts live streams on Taobao three times a week to introduce books, encourage viewers to appreciate literature and sell the store’s peripheral products.
“Readers are quite enthusiastic about it. There were almost 10,000 people watching our last live stream” Wu said.
Taobao is an e-commerce platform operated by Alibaba Group Holding, which is the parent company of the Post.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Alibaba Group Holding, Beijing, Beijing Institute of Culture Innovation and Communication, Beijing Municipal Committee, Booksellers, bookstores, Bookworm, Capital city, Chinese, Communist Party of China’s, epidemic, food delivery app, Hangzhou, lunch, Meituan, order books, OWSpace, Post, quarantine period, Sanlitun, Taobao, Uncategorized, WeChat, Weibo, zhejiang province |
Leave a Comment »
13/10/2019
- The likes of Saudi Arabia also saw an upswing in travellers from the mainland after the release of its new visa programme
- But fewer Chinese tourists went abroad this year, with a 15 per cent drop from 2018 attributed to more opting to visit local historical sites
Chinese tourists take photos in front of the Imperial Palace in Tokyo, Japan. Photo: Reuters
Fewer Chinese travellers went overseas during
“golden week” this year – but for those who did, Japan, Thailand and Singapore were the top-ranked destinations as tourists from the mainland gave Hong Kong a miss, according to China’s largest travel company Ctrip.
Chinese government data showed only 6.07 million people travelled during the national holiday between October 1-6, a 15.1 per cent drop from the corresponding period last year. Analysts attributed this to Chinese tourists opting for a “staycation”, as 782 million people – a 7 per cent increase from last year – chose to celebrate the 70th anniversary of the People’s Republic of China by visiting local historical sites.
How a new wave of Indian travellers are transforming tourism in Southeast Asia
For those who did venture abroad, Japan, Thailand and Singapore ranked as the top three most-booked countries in Asia during the week, according to Chinese travel firm Ctrip, as tourists from the mainland skipped protest-hit Hong Kong for other destinations.
The city, now in its 19th week of anti-government protests, over the week saw a 50 per cent overall drop in tourism from last year, as well as a 47.8 per cent reduction in border crossings at the Luohu border checkpoint, according to government figures.
Japan remained the most popular destination for Chinese tourists. In the first half of 2019, the nation saw 4.5 million visitors from China, up 11.7 per cent from the same period in 2018. In order of popularity, the top-visited cities were Osaka, Tokyo, Kyoto, Sapporo and Nagoya, according to Japanese media.
Over the same week, Japan increased its sales tax from 8 to 10 per cent, but Chinese shoppers – who accounted for 37 per cent, or US$15.4 billion, of the spending by international visitors to the nation last year – were undeterred.
Japan saw the highest volume of overseas transactions over the week, according Alipay Mobile, the world’s largest mobile payment platform. The firm declined to share the exact amount Chinese tourists had spent in Japan, but reported average spending per international traveller during golden week had increased by 15 per cent to 2,500 yuan (US$350).
From Nissan sales to Tsushima tourism, trade spat with Korea hits Japan in the pocket
Alipay is operated by Ant Financial, an affiliate of Alibaba Group Holding, which owns the Post.
Japanese department stores such as Sogo and Seibu celebrated the Chinese national holiday by holding golden week events and sales at 15 different branches across the nation, with food and arts promotions targeting Chinese shoppers.
Chinese travellers to Japan want cultural experiences involving local customs such as temple tours, heritage sites and cultural events, according to Emily Guo, a researcher at Hong Kong-based marketing research firm Cherry Blossoms.
Chinese tourists visit Tiananmen Square in Beijing. Analysts say 782 million people opted for “staycations” at local historical sites over golden week this year. Photo: EPA
Experts say Thailand – the second-most booked country during golden week, according to Ctrip – saw many repeat travellers return to the country. The nation saw 1.03 million arrivals from China in August, up 19 per cent from 2018.
Guo said these travellers were more budget-conscious than those who travelled to Japan, and enjoyed the good value and picturesque scenery for sharing on social media.
“They have already travelled to Southeast Asia before, and are therefore looking for personalised and local experiences like interacting with Thai residents, jungle treks and food tours,” she said, adding that many are willing to spend extra on immersive experiences such as a hotel in the countryside, or on a room with a forest view.
Thailand’s tourism industry gets jitters after currency surges, visitor numbers from China fall
According to Alipay Mobile, the sale of “durian experience” packages for Chinese tourists looking to taste the spiky, pungent fruit at local farms increased by 60 per cent in Thailand and Malaysia from last year.
Shopping remained on the agenda, too. Thailand ranked second for the highest volume of overseas transactions during the week, according to data from Alipay Mobile. Most Chinese shoppers frequented duty-free shops, convenience stores and local malls, according to local press.
Singapore remained a destination of choice for tourists from the mainland. The city was among the most popular “traditional destinations” for them, according to China’s culture and tourism ministry, with others including Malaysia, Thailand, Japan, Australia, France, Italy, and Russia.
Chinese tourists visiting Singapore over golden week also seized the opportunity to check out property in the Lion City. Photo: AFP
July saw the Lion City break its record for the number of Chinese arrivals, at close to 390,000, an unprecedented 46 per cent jump from the previous month.
Analysts have attributed this to a diversion of tourists from Hong Kong, but property agents such as Clarence Foo, associate deputy group director at OrangeTee & Tie, said some of these Chinese tourists were using the golden week as a chance to eye Singaporean real estate.
“Compared to a normal week, there were probably 15 to 20 per cent more Chinese visitors who viewed property,” said Foo, who counts Singaporean and international buyers among his clients.” They are certainly more keen on Singapore [property] now as there isn’t another comparable investment destination in Asia.”
Meanwhile, the Middle East is emerging as a popular shopping destination for Chinese tourists. According to Ctrip, Dubai saw 501,000 travellers from the mainland in the first half of 2019, an 11 per cent increase from last year.
Saudi Arabia has also experienced a surge in Chinese tourists, with 7,931 heading to the country since it launched its new instant tourist visa programme on September 27. With the new visa, which can be obtained online or upon arrival, tourists can stay in the country for up to 90 days, and unwed foreign men and women can for the first time share hotel rooms.
“Saudi Arabia has the potential to become very popular with Chinese tourists,” said Guo from Cherry Blossoms, adding that travellers from the mainland are increasingly looking for exciting new adventures. “It’s a status symbol for them to visit a country others haven’t visited before.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in 70th anniversary, Alibaba Group Holding, Alipay Mobile, Australia, ‘golden week’, “staycation”, “staycations”, Beijing, benefit, celebrated, Chinese national holiday, chinese tourists, Ctrip, cultural events, cultural experiences, Dubai, durian experience, France, golden week, heritage sites, Hong Kong, Imperial Palace, Italy, Japan, Korea, Kyoto, Lion City, Luohu border checkpoint, mainland, Malaysia, Middle East, Nagoya, nation, Nissan, People’s Republic of China, Post, Russia, Sapporo, Saudi Arabia, Seibu, Singapore, Singaporean real estate, skip, Sogo, Southeast Asia, spiky, pungent fruit, temple tours, Thailand, Tiananmen Square, Tokyo, traditional destinations, travellers, Tsushima tourism, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
05/09/2019
- Doctor who helped 13-year-old girl recover says demands on her to do well at school induced condition
- Weibo poll reveals that 68 per cent of participants had hair loss in school
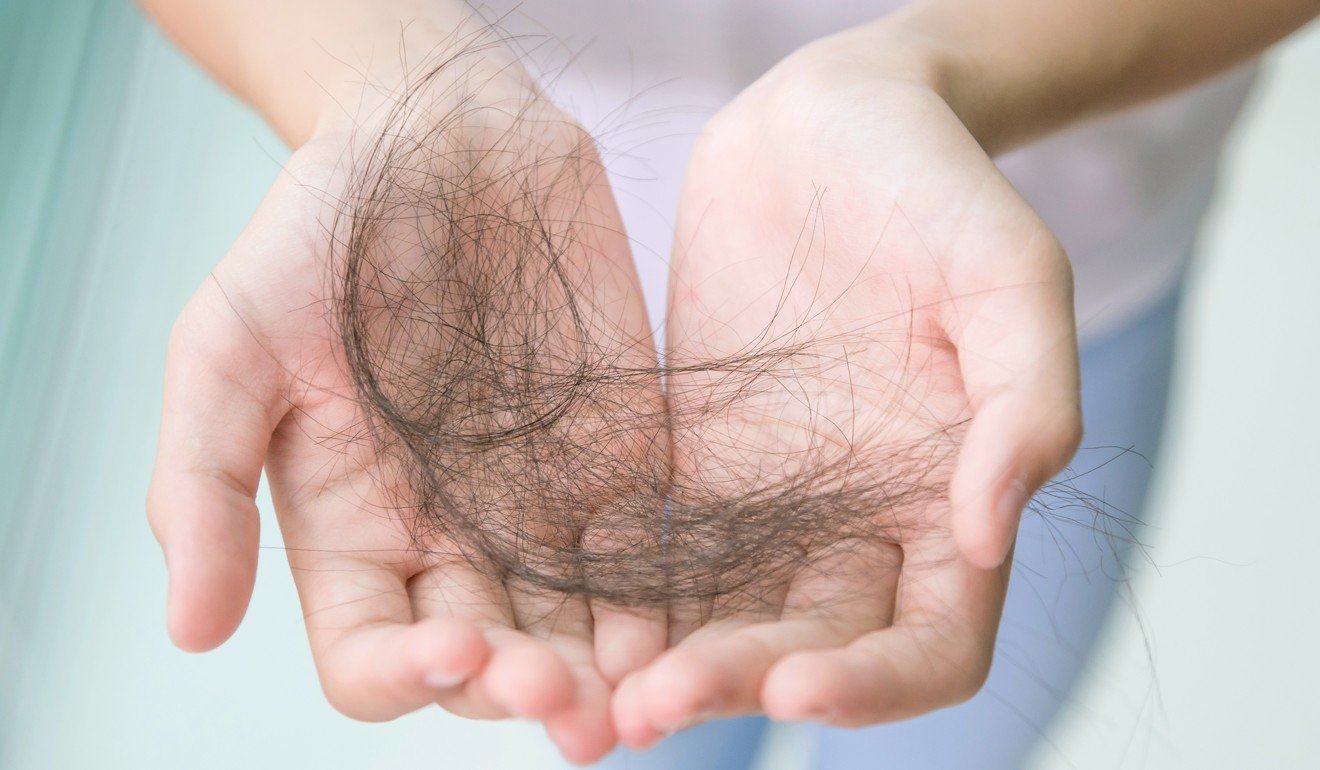
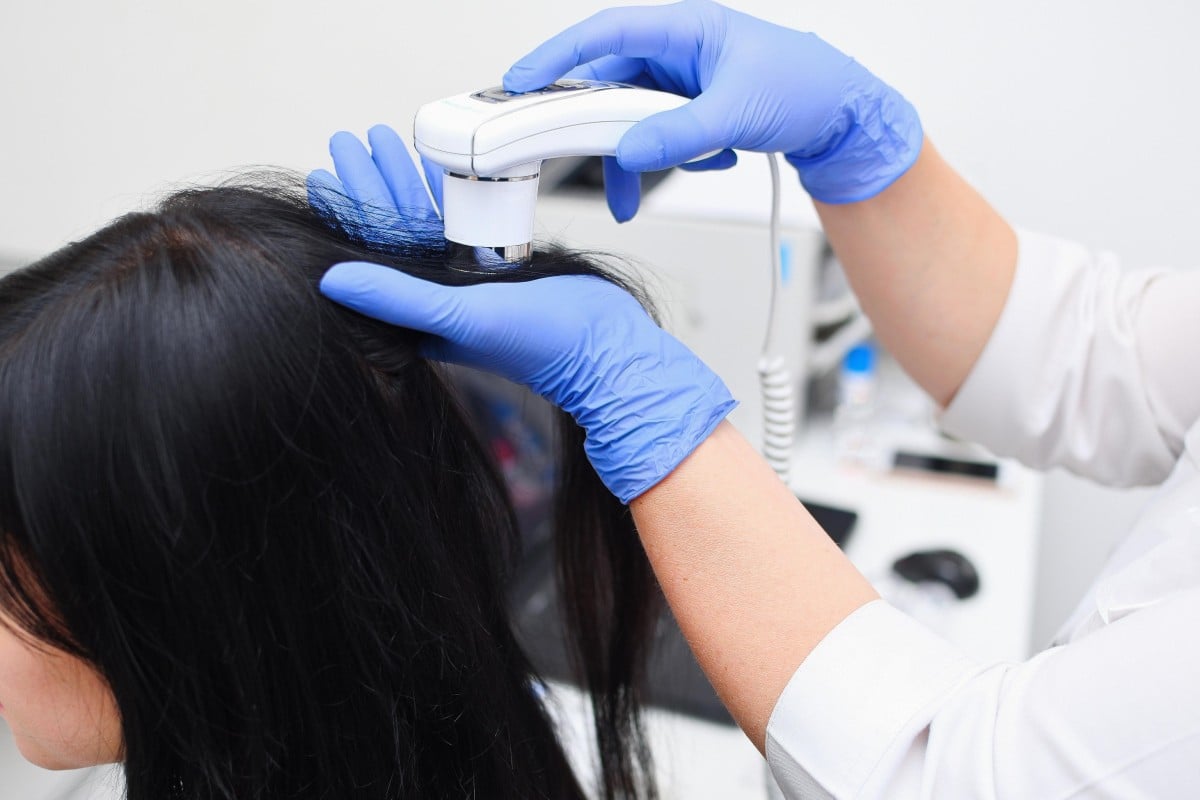
Studies and polls suggest stress leading to hair loss is a big health concern in China. Photo: Alamy
When the 13-year-old girl walked into the hospital in southern China around eight months ago, she was almost completely bald, and her eyebrows and eyelashes had gone.
“The patient came with a hat on and did not look very confident,” Shi Ge, a dermatologist at the Sixth Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou, told the Pear Video news portal.
The girl had done well in primary school but her grades dropped in middle school, Shi said.
Under parental pressure to do well, the girl pushed herself harder, but the stress resulted in severe hair loss.
With time and medical treatment, the teen’s hair grew back but her story left a lasting impression, raising awareness of the increasing number of young people in China seeking treatment for stress-induced hair loss, according to Chinese media reports.
Jia Lijun, a doctor at Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, told state-run Xinhua News Agency in May that aside from genetics, factors such as stress in work, study and life would result in endocrine imbalances which affected the cycle of hair growth.
And in January, a survey of 1,900 people by China Youth Daily found that 64.1 per cent of people aged between 18 and 35 said they had hair loss resulting from long and irregular working hours, insomnia, and mental stress.
Hits and myths: stress and hair loss
Shi said that an increasing number of young people had come to her for treatment of hair loss in recent years, and those working in information technology and white-collar jobs were the two biggest groups.
“They usually could not sleep well at night due to high pressure or had an irregular diet because of frequent business trips,” Shi said.
A Weibo poll on Wednesday revealed that 68 per cent out of 47,000 respondents said they had had serious hair loss when they were in school. About 22 per cent said they noticed after starting their careers, while only 5 per cent said it happened after they entered middle age.
More than half of the Chinese students who took part in a China Youth Daily survey said they had hair loss. Photo Shutterstock
Research published in 2017 by AliHealth, the health and medical unit of the Alibaba Group, found that 36.1 per cent of Chinese people born in the 1990s had hair loss, compared to the 38.5 per cent born in the 1980s. Alibaba is the parent company of the South China Morning Post.
The teenager’s experience sparked a heated discussion on Weibo, with users recounting similar cases and some voicing their panic.
“My niece’s hair was gone while she was in high school and has not recovered, even after she graduated from university. This makes her feel more and more inferior,” one user said.
Hong Kong’s schoolchildren are stressed out – and their parents are making matters worse
Another said: “I lost a small portion of my hair during the high school entrance exam, but that is already scary enough for a girl in her adolescence.”
“I had to quit my job and seek treatment,” said a third, who adding that he also suffered from very serious hair loss a few months ago because of high pressure.
Source: SCMP
Posted in adolescence, Alibaba Group, Alibaba Group Holding, AliHealth, at school, business trips, careers, chasing grades, China Youth Daily, Chinese people, Chinese teenager, condition, debate, demands, dermatologist, do well, doctor, entrance exam, frequent, Guangzhou, hair loss, health and medical unit, her hair, high pressure, High school, induced, inferior, Information technology, irregular diet, job, lost, middle age, middle school, myths, pressure, primary school, quit, recover, school, Shenzhen Traditional Chinese Medicine Hospital, Sixth Affiliated Hospital, south china morning post, sparks, stress, Sun Yat-Sen University, treatment, Uncategorized, university, Weibo, white-collar jobs, Xinhua News Agency, young people |
Leave a Comment »
16/08/2019
BEIJING/HONG KONG (Reuters) – Segway-Ninebot Group, a Beijing-based electric scooter maker, on Friday unveiled a scooter that can return itself to charging stations without a driver, a potential boon for the burgeoning scooter-sharing industry.
Ninebot said Uber and Lyft, the ride-hailing giants that are expanding into scooter-sharing, would be among the customers for the new semi-autonomous vehicles that are expected to hit roads early next year.
Gao Lufeng, Ninebot chairman and chief executive, told Reuters in an interview that AI-driven scooters, controlled remotely from the cloud, could radically improve the economics of scooter-sharing.
“The pain point for scooter operators is to better maintain the scooters at a lower cost,” he said. Currently, operators of scooter sharing fleets have to collect the machines manually for re-charging.
Formed by the 2015 combination of China’s Ninebot and U.S. transportation pioneer Segway, the company has quietly become the largest supplier for scooter-sharing companies such as Bird and Lime.
“I believe scooters will replace bicycles as the prime solution for micro-mobility,” Gao said. “It’s human nature to save energy when commuting.”
The scooter-sharing fad was triggered two years ago with the launch of Bird in California. Venture-capital investors have since poured hundreds of millions of dollars into the sector, and fleets of electric-powered scooters now operate in cities across the U.S. and Europe.
Segway-Ninebot Group has applied to list its shares on the China’s new Nasdaq-style board for homegrown tech firms, the STAR Market. The company sold 1.6 million scooters in 2018, according to a prospectus filed in April.
Lyft and Uber did not immediately respond to emailed requests for comment.
The new scooters will be priced at close to 10,000 yuan ($1,420), more than the company’s traditional scooters, which it sells to scooter companies for $100-$300.
The new machines will start road testing next month and will be largely commercialized in the first quarter of 2020.
The company also launched two self-driving delivery robots — one for outdoor delivery, the other for indoor services.
Ninebot said the unmanned delivery robots will initially serve the food delivery industry in China.
The company is in talks with food delivery operators, including Meituan Dianping and Alibaba Group’s Ele.me, to begin service by the first half of next year.
Source: Reuters
Posted in AI-driven scooters, Alibaba Group Holding, Beijing, bicycles, Bird, California, charging stations, cloud, delivery robots, drive, Ele.me, electric scooter, electric-powered scooters, Europe, indoor services, Lime, Lyft, maker, Meituan Dianping, micro-mobility, Nasdaq-style board, Ninebot, outdoor, scooters, Segway, Segway-Ninebot Group, self-driving, semi-autonomous vehicles, STAR Market, U.S., Uber, Uncategorized, unveils, vehicles |
Leave a Comment »
29/07/2019
- China last year poured US$2.5 billion into firms in India, which is a healthy breeding ground for up-and-coming tech outfits
- Active cooperation between these investors and entrepreneurs holds a multitude of benefits for both sides, according to industry pundits
Chinese venture capitalists are injecting funds into a variety of cash-hungry Indian businesses. Photo: Shutterstock
C
hinese President Xi Jinping and
look set for another informal summit in October, and a key item on the agenda will be
.
Indian start-ups have become a major target for
, who have been looking to emulate their United States counterparts such as Tiger Global and Sequoia Capital that dominate the sector.
On top of this, a slowdown in start-up deals in China has nudged the country’s investors to look beyond their borders, and
’s affordable labour market and strong economic growth provide a healthy breeding ground for young tech outfits.
Can Bollywood be the bridge that binds India and China?
Led by heavyweights such as Shunwei Capital, Fosun International, Tencent Holdings, Xiaomi and Alibaba Group Holding – which owns the
South China Morning Post –
have been injecting funds into a variety of cash-hungry Indian businesses.
For many of these start-ups, the knowledge and technology of Chinese investors act as the backbone of their business Ntasha B, Venture Gurukool
Beneficiaries have included advertising firm Media.net, e-commerce operator Snapdeal, digital payment provider Paytm, online travel firm MakeMyTrip, messaging platform Hike, health tech start-up Practo and news aggregator Dailyhunt.
“For many of these
, the knowledge and technology of Chinese investors act as the backbone of their business, along with the operational expertise of Indians in the domestic market,” said Ntasha B, co-founder of Venture Gurukool, a mentoring platform for start-ups which works closely with Indian diplomatic missions in China.
Chinese President Xi Jinping and Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi are set to meet again in October. Photo: Xinhua
She added that Chinese investors usually had a hands-on approach and were a bit inflexible, unlike their American counterparts, who gave some elbow room in hiring local teams.
A senior executive with an Indian start-up, who did not wish to be identified, said it was sometimes straightforward to convince Chinese investors as they could relate to Indian business models and requirements that were dissimilar to those from the Western world.
The world’s second-largest economy invested nearly US$2.5 billion in Indian start-ups last year, a figure that has touched almost US$1 billion so far this year, according to finance research firm Venture Intelligence. The number of such deals jumped from just one in 2013 to 27 last year.
What does Amazon’s China departure mean for its Indian e-commerce battle?
Indian start-ups are estimated to have raised US$3.9 billion from around the globe in the first six months of this year, and the inflow from Chinese behemoths played a key role in pushing them to turn east to source funding.
“What’s more interesting about [Chinese investors’] strategy is that they’re paying more attention to rural India. If you look at the companies they’ve invested in, a fair amount of their businesses target the rural segment,” said Sandeep Murthy, managing partner at venture capital firm Lightbox Ventures, which keeps a close watch on Chinese investments. He said the brisk economic activities in India’s tier two and tier three towns are more attractive to Chinese investors than India’s urban centres.
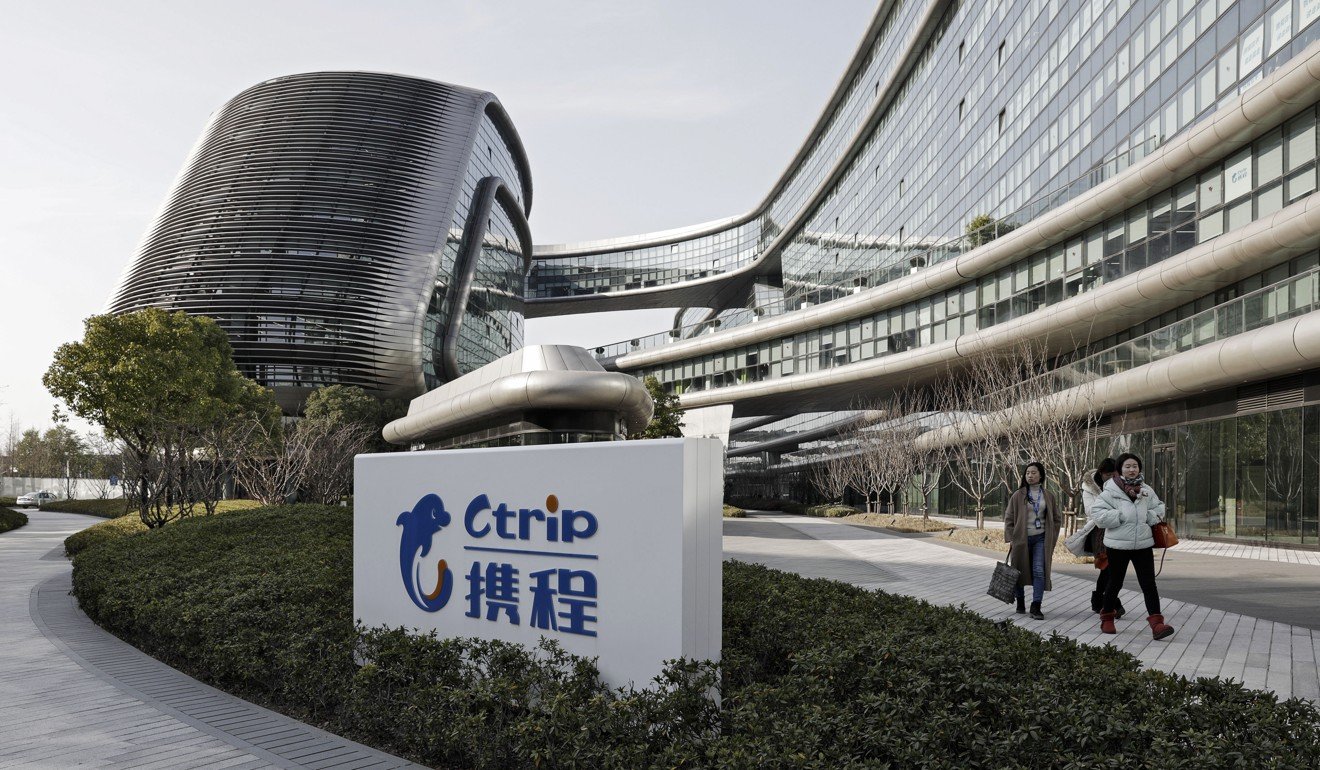
Ctrip, China’s largest online travel agency, is drawn to the size and rapid advancement of the Indian market. Photo: Bloomberg
For Ctrip – China’s largest online travel agency, which in April took a 49 per cent stake in MakeMyTrip – the appeal of India was its whirlwind technological advancement and the disposable income of its massive young population.
“[MakeMyTrip has] achieved fast growth in the online travel market and is becoming well recognised in the Indian market. Their comprehensive products and services, management team and the opportunities in India result in our confidence that they will continue to succeed,” said Wei Yuan Min, a member of Ctrip’s global team. Behind the US and China, India houses the world’s third-largest start-up ecosystem in terms of the number of companies. As for the number of unicorns – start-ups valued at over US$1 billion – India ranks third, offering a vibrant habitat for entrepreneurial ventures. The country is home to 32 such firms, with the addition of nearly half a dozen so far this year and 15 last year.
In India, one man took on Chinese firm ByteDance to shut down TikTok – and he wants to do it again
New Delhi expects there to be 12,000 tech start-ups in the country by next year, up from 7,200 last year. There were 1,200 new tech firms in the sector last year, according to industry body Nasscom.
One of those capitalising on this opportunity is the Beijing-headquartered technology company Xiaomi, which last year promised to pump US$1 billion into 100 Indian start-ups over the next five years. Most of these Indian firms are involved in businesses that are ancillary to Xiaomi’s key operations.
Chinese firm Xiaomi is banking on Indian start-ups to strengthen its own products. Photo: Reuters
“These start-ups help us in building a stronger product offering,” a Xiaomi spokesperson said. “The idea is to invest in start-ups which can further boost the mobile ecosystem in India. They could be into mobile gaming, service providers, value-added services or servicing the mobile industry.”
Xiaomi has been rapidly expanding its businesses in India, selling smartphones, television sets, security cameras, speakers, power banks, and more. India was the first market outside China where Xiaomi introduced its television sets.
Asked which sector would be Xiaomi’s focus for investment in the coming years, the spokesperson said the company was looking to focus on hardware-related start-ups in the ecosystem which could offer “robust solutions” to its Indian requirements.
Amazon, Uber and Google struggled in China, but Indian hotel chain Oyo is succeeding.
Here’s why
While hopes for India’s start-up sector are high, there have been some disappointments. There were reports this month that Alibaba, a major shareholder in Paytm, was unhappy with the Indian firm’s performance, pressuring it to realign its strategies and looking unlikely to provide fresh capital.
Paytm, a digital-payment-system unicorn, launched its own e-commerce Paytm Mall in 2016 when Walmart-backed Flipkart and Amazon were dominating the market.
However, the venture has yet to take off and is burning through cash.
Paytm refused to comment on the matter.
Paytm has attracted investment from Alibaba, but its Paytm Mall venture is struggling. Photo: Bloomberg
Chinese firms’ coordinated effort to enter the Indian start-up scene has made it easy for Indian ventures to access new sources of revenue. For instance, the state-run Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), the country’s largest lender, launched an India-specific investment fund for Chinese investors in May last year.
Several Chinese venture capitalists are also providing platforms for entrepreneurs through fellowship schemes. Four Indian ventures – Zefo, Healthy Buddha, NowFloats and Grozip – took part in one such fellowship initiative run by Alibaba last year.
Gold, jewels, ‘Islamic’ finance: how India’s I Monetary Advisory built a US$365 million Ponzi scheme
India has warmly welcomed these initiatives. Amitabh Kant, chief executive of state-backed policy think tank Niti Aayog and a close aide of Modi, has publicly said China should become the topmost investor in its neighbour.
Vikram Misri, India’s ambassador to China, has also been pushing for increased economic cooperation and Chinese investment since he took charge in January, despite expressing concerns over New Delhi’s widening trade deficit with Beijing.
Vikram Misri, India’s ambassador to China, is looking for more economic cooperation between the two countries. Photo: Xiaomei Chen
The increased Chinese investment in Indian ventures has coincided with the Modi administration’s 2015 launch of the Startup India initiative, an umbrella scheme aimed at easing related activities through measures such as tax exemptions and simplified paperwork.
Industry pundits say active cooperation between Chinese investors and Indian entrepreneurs holds a multitude of benefits for both sides.
“The cooperation gives Chinese investors global scale and opportunity to diversify their investments,” said Neil Shah, partner and research director at the technology market research firm Counterpoint.
The cooperation gives Chinese investors global scale and opportunity to diversify their investmentsNeil Shah, Counterpoint
“For Indian start-ups, this gives cross-border learning, guidance from their global investors on dos and don’ts, tactical and long-term strategy, how to create value, run operations efficiently as well as expand beyond India.”
Nilaya Varma, partner and leader of markets enablement at KPMG India, said there was a cultural shift happening in the country where young Indians brimming with ideas wanted to pursue their dreams rather than work for someone else. This brought out the entrepreneurial spirit of this generation, he said.
“The knowledge, concepts, ideas and innovations of the small start-ups in India will have a global appeal. So it makes a lot of sense for Chinese big players to invest here,” he said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Alibaba Group Holding, Amazon, Beijing, Bollywood, Bytedance, Chinese money, Chinese President Xi Jinping, Counterpoint Research, E-commerce, Flipkart, Fosun International, Google, Grozip, Healthy Buddha, I Monetary Advisory, India’s ambassador to China, Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Indian start-ups, Industrial and Commercial Bank of China (ICBC), KPMG India, MakeMyTrip, Nasscom, New Delhi, NowFloats, online travel agency Ctrip, OYO, Paytm, Paytm Mall, Ponzi, powering, Sequoia Capital, Shunwei Capital, south china morning post, Tencent Holdings Ltd, Tiger Global, TikTok, Travel agency Ctrip, Uber, Uncategorized, unicorn, United States, Vikram Misri, Walmart, Xiaomi, Zefo |
Leave a Comment »