- Chinese President Xi Jinping and US President Donald Trump set to meet on the sidelines of the Apec summit in Chile next month, a source says
- The two state leaders are expected to sign an interim trade deal ‘if everything goes smoothly’
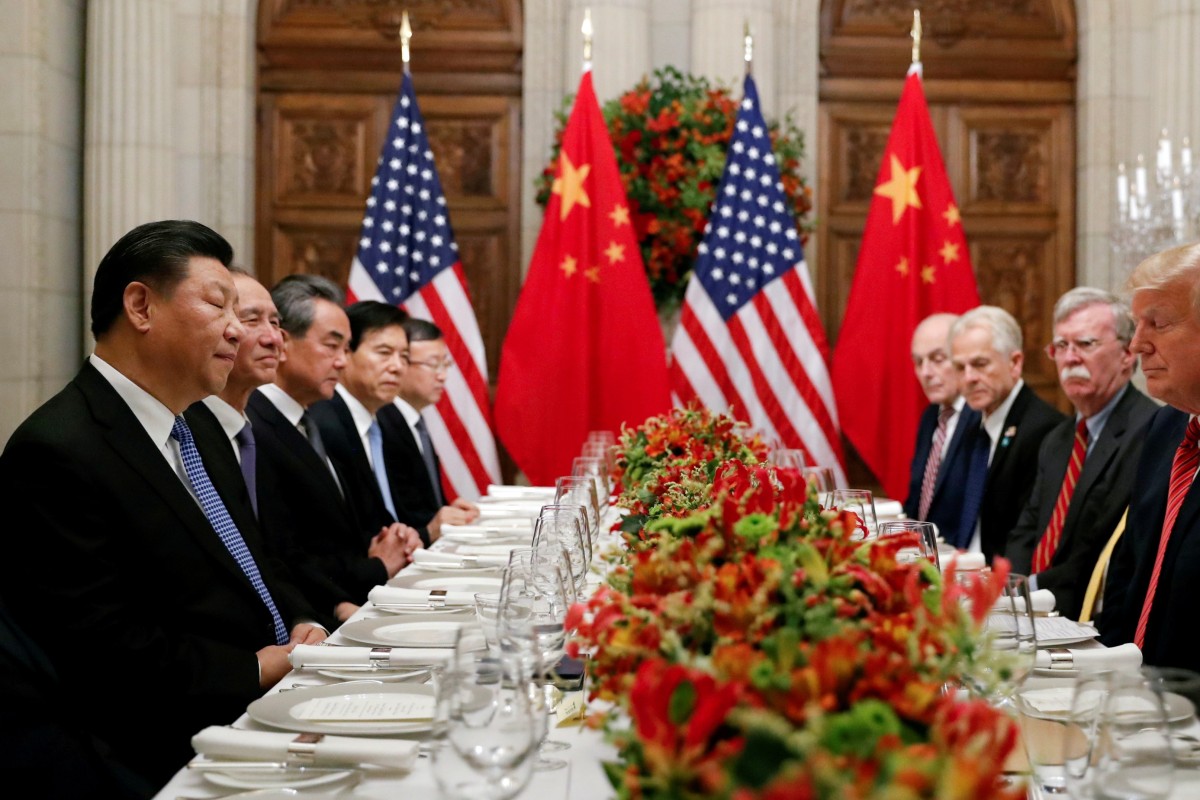
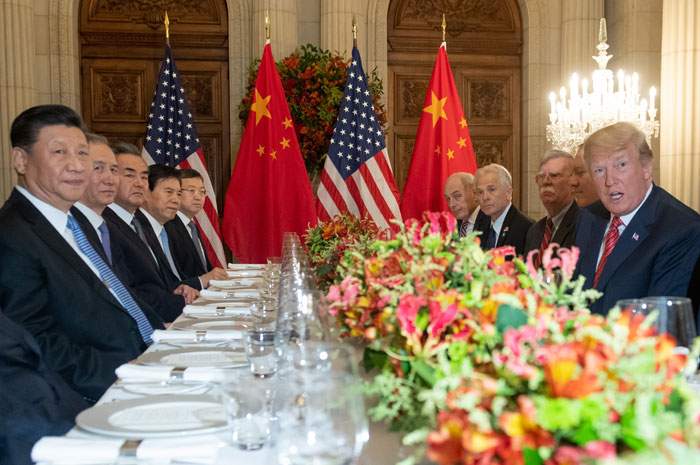
Chinese President Xi Jinping and US President Donald Trump are tentatively expected to meet on November 17 with the aim of signing an interim trade deal, a source briefed on the arrangements told the South China Morning Post.
The two leaders are expected to come face-to-face immediately after the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (Apec) summit in Santiago, Chile, with a trade truce signed “if everything goes smoothly”, said the person, who declined to be identified.
Trade envoys from Beijing and Washington are still finalising the text for the two leaders to sign, but both sides have expressed optimism that Trump’s so-called phase one trade deal can be completed in time for the meeting.
Trump said on Monday that negotiations on the interim deal were running “ahead of schedule”.
“We are looking probably to be ahead of schedule to sign a very big portion of the China deal, and we’ll call it phase one but it’s a very big portion,” Trump said. “That would take care of the farmers. It would take care of some of the other things. It will also take care of a lot of the banking needs.
“So we’re about, I would say, a little bit ahead of schedule, maybe a lot ahead of schedule,” the president said, adding the deal would “probably” be signed.
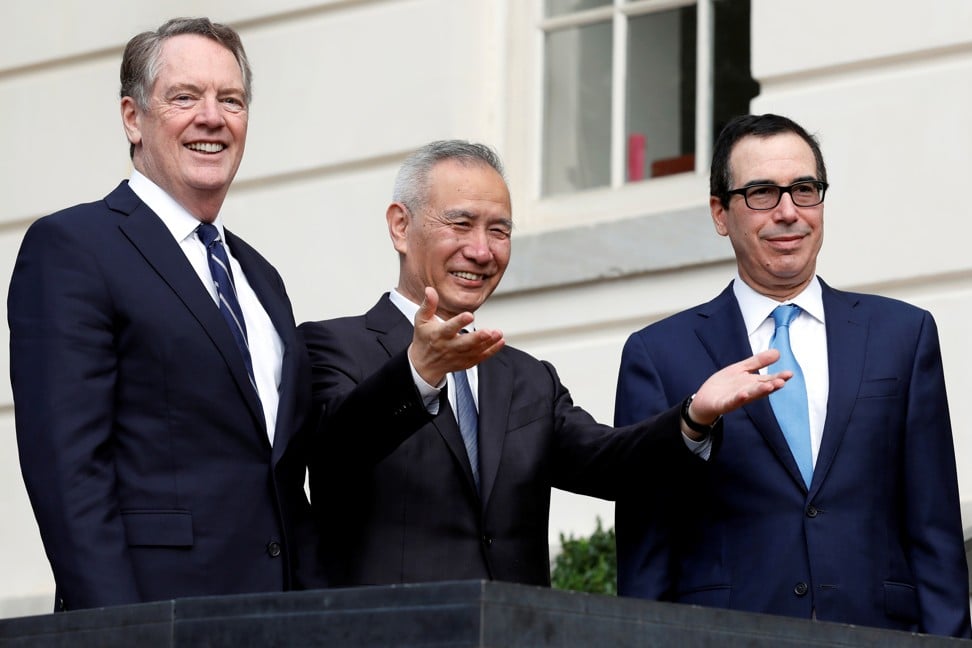
Top trade negotiators for the two countries – US Treasury Secretary Steven Mnuchin, US trade representative Robert Lighthizer and Chinese Vice-Premier Liu He – spoke by telephone last Friday. The Office of the US Trade Representative released a statement after the call saying that the two sides “made headway on specific issues” and “are close to finalising some sections of the agreement”.
China’s official Xinhua News Agency said on Saturday negotiators have “agreed to properly resolve core concerns of each other” and had “basically completed technical discussions about parts of the text”. In particular, China would lift the current ban on US poultry imports and recognise the American public health certification system for meat product imports, Xinhua said.
The top trade envoys are expected to hold another conference call in the near future.

Taoran Notes, an account on Chinese social media platform WeChat run by the official Economic Daily newspaper, wrote over the weekend that Beijing and Washington had moved a step closer to agreement on a “temporary deal”.
“According to past experiences and practises, the negotiation will enter the stage of translation and legal review after the technical completion of the text,” the account said.
Geng Shuang, a Chinese foreign ministry spokesman, said that technical negotiations about part of the deal were finished but deputy-level talks were ongoing. “China hopes both sides can find a trade solution based upon mutual respect and benefits,” Geng said at a regular press conference on Tuesday.
If it goes ahead as planned, the summit between Trump and Xi in Chile next month would be the third time the two leaders have sat down to talk about ending the nearly 16-month-long trade war.
Last December, the two leaders met on the sidelines of the G20 Leaders’ Summit in the Argentinian capital Buenos Aires and agreed to a three-month tariff truce to allow time for the countries’ trade envoys to work out a comprehensive deal. But the talks collapsed in early May with the US blaming China for reneging on promises it made in negotiations, while China blamed the US for attempting to infringe on its economic sovereignty.
The pair met again in late June in the Japanese city of Osaka, where they agreed to restart trade negotiations.
A minor ceasefire was reached in October when Beijing promised to buy US$40 billion to US$50 billion worth of American agricultural products in exchange for Washington postponing indefinitely a tariff increase on US$250 billion of Chinese goods to 30 per cent from 25 per cent on October 15.
Analysts expect fresh 15 per cent duties on about US$160 billion of Chinese imports – including popular products like smartphones and consumer electronics – that are due to go into effect mid-December will also be postponed if a deal is signed, though this has not been officially confirmed.
The interim deal is also expected to contain a provision on intellectual property protection, a key US demand. China has taken steps to improve IP protection, including setting up a system to punish and compensate instances of infringement, and improve settlement disputes. But how well these measures will be implemented remains in question.
China and the US would also agree to avoid allowing currency devaluations to gain trade advantages, codifying a commitment both countries made as part of a G20 agreement several years ago. A currency agreement – similar to provisions in the yet-to-be-ratified US-Mexico-Canada Agreement – could pave the way for the US to remove its designation of China as a “currency manipulator”.
The deal may include a new dispute resolution mechanism to ensure both sides live up to commitments. The system, which will give both sides equal standing, would replace a contentious US-proposed enforcement mechanism that was a key reason for trade talks breaking down in May after China felt the demands too intrusive and one-sided. It is unclear how effective the proposal would be, but the US has insisted since talks began that a similar mechanism be implemented to ensure China did not backslide on promises as it had in the past.
In addition to large purchases of farm products, the interim agreement may contain commitments by China to buy US-built aircraft and energy products, particularly liquefied natural gas.
China will also agree to lift foreign ownership limits on Chinese financial firms under the deal, changes which are already underway.
However, the interim deal will not address broader US complaints about China’s economic model, particularly allegations that foreign firms are treated unfairly and heavy government subsidies favour some domestic industries. Nor will it contain any break for telecommunications equipment maker Huawei and other Chinese tech companies that were blacklisted by the US on national security concerns.
Source: SCMP