27/12/2019
- As US financial support expires in 2023, Beijing could ‘loosen the screws’ on regional alliance with lucrative development deals
- Independence vote in Micronesia’s Chuuk state in March could raise the stakes, potentially allowing China access to strategically vital waters
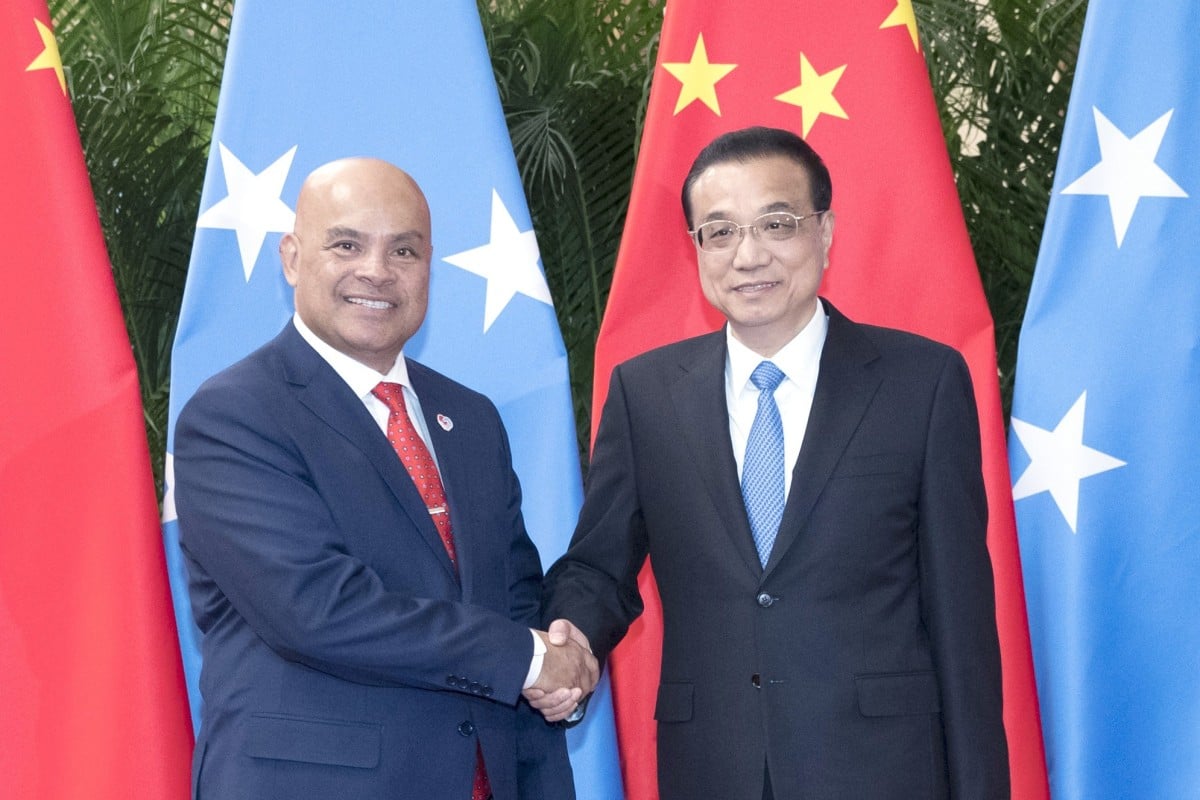
President of the Federated States of Micronesia David Panuelo shakes hands with Chinese Premier Li Keqiang at the Great Hall of the People in Beijing. Photo: Xinhua
In
China earlier this month, David Panuelo, the president of the Federated States of Micronesia, climbed the Badaling section of the Great Wall. And, according to Huang Zheng, Beijing’s ambassador to the
Pacific nation, the countries’ “great friendship rose to even greater heights” during Panuelo’s visit.
Chinese investment in Micronesia reached similarly lofty levels in conjunction with Panuelo’s trip, which marked three decades of diplomatic ties and included meetings with President Xi Jinping and Premier Li Keqiang. Beijing has committed US$72 million in economic development deals, almost as much as its total investment of the previous three decades.
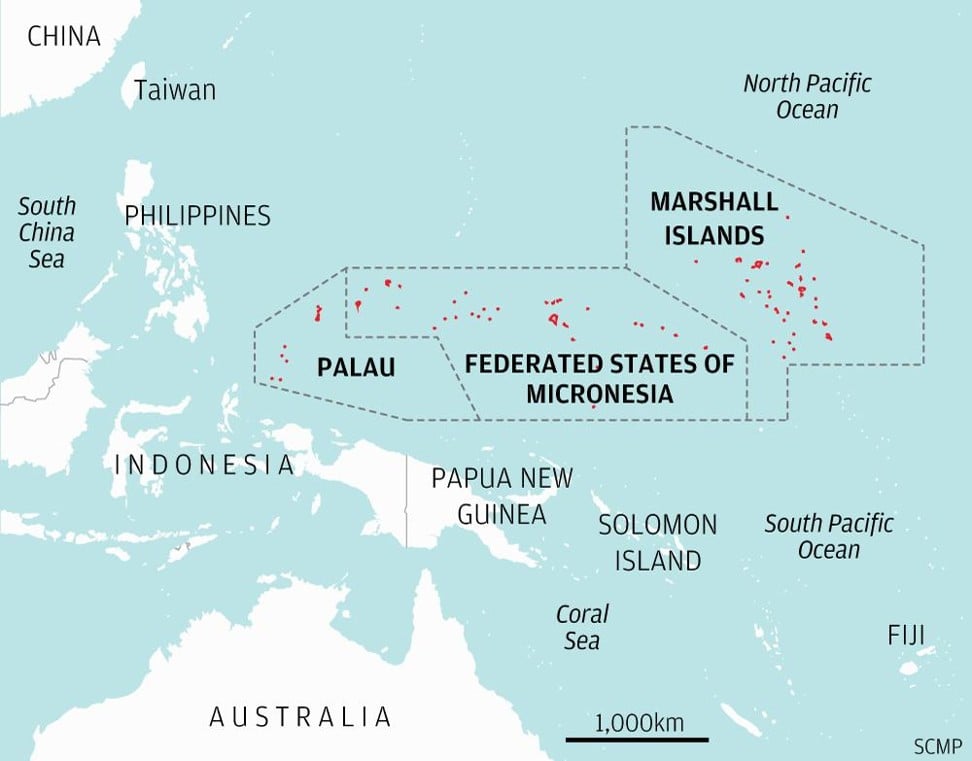
Micronesia is one of three Pacific nations with agreements with Washington, known as the Compact of Free Association (COFA), which allows their citizens to live and work in the US. In exchange, Micronesia, neighbouring Palau and the Marshall Islands grant the US exclusive military and defence access to their territorial waters – more than 2 million square miles of the Pacific that have been an essential element of Washington’s power projection in the region since World War II.
Much of China’s funding has been directed to Micronesia’s Chuuk state, which will in March vote in an independence referendum.
Although Chuuk is home to fewer than 50,000 people, its waters include one of the region’s deepest and most strategically appealing lagoons, creating extra incentive for Beijing and potential concern for Washington as the two countries
How China ‘loosens the screws’
With a population of just 113,000 people, Micronesia relies on remittances sent home by citizens working in the US as well as the financial support from Washington under COFA. That assistance is scheduled to expire in 2023, creating uncertainty about the future of the relationship and making
Chinese investment even more influential.
“Panuelo’s visit to China is a perfect example of how [the Chinese side] just needs to do a little to get a lot,” said Derek Grossman, senior analyst at Rand Corporation, a Washington think tank. “US$100 million is not very much for them and they can essentially loosen the screws [on COFA] with that.”
Micronesian President David Panuelo (second on left) and Chinese Premier Li Keqiang (right) during their talks in Beijing. Photo: EPA-EFE
The value of Micronesia’s bilateral trade with China has increased by nearly 30 per cent annually for the past five years, according to Micronesia’s Foreign Ministry. In 2017, the island nation signed onto President Xi’s signature Belt and Road Initiative which aims to build a vast network of strategic investment, trade routes and infrastructure projects across more than 150 countries.
US-China tech war’s new battleground: undersea internet cables14 Dec 2019
In recent years Chinese funding in Micronesia has built office and residential complexes for government officials, a showpiece new convention centre in the capital city Palikir, transport infrastructure and student exchanges, according to a recent report by Rand.
Jian Zhang, associate professor at UNSW Canberra at the Australian Defence Force Academy, said Beijing’s investment reflected a decision to cultivate broader, deeper ties.
Micronesian President David Panuelo during his meeting with Chinese officials in Beijing. Photo: EPA-EFE
“China’s interest in building the relationship with Micronesia is not just about its diplomatic rivalry with Taiwan or economic interests,” he said. “It has elevated the relationship to a comprehensive strategic partnership which encompasses all areas.”
During his recent visit, Panuelo described China as Micronesia’s top economic partner and the US as its top security partner. Pompeo’s visit to Micronesia highlights US anxiety about rising Chinese influence in Pacific 5 Aug 2019
Gerard Finin, professor of regional planning at Cornell University, who previously worked with the US Department of State in the Pacific, said: “China’s leadership consistently accords large ocean states the full protocol that is expected when a head of state visits.
“In contrast, Washington has only had a limited number of meetings and never hosted an official state visit to Washington for the leader of a Pacific Island nation,” said Finin.
US President
Donald Trump in May hosted the leaders of Micronesia, Palau and the Marshall Islands together at the White House. When
Mike Pompeo visited Micronesia
in August, he became the only sitting US secretary of state to have done so.
Pompeo said negotiations to update COFA had begun but no details have been made public. Micronesia has assembled a team to conduct the negotiations but the US has not, the Honolulu Civil Beat website reported.
US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo visited Micronesia in August. Photo: AFP
Breakaway vote could raise the stakes
Panuelo’s team met Micronesian students studying in China and representatives of state-owned China Railway Construction Corporation, which will build the roads in Chuuk, funded in part by US$50 million from Beijing. Construction of the Chuuk government complex was also funded by Beijing and the state’s governor joined Panuelo for his visit.
Should Chuuk vote to separate from Micronesia in March, it could also mean breaking from COFA, jeopardising the US work privileges of thousands of Chuukese and opening the state’s waters to other partners, particularly China.
Chuuk is home to one of the deepest lagoons in the Pacific, a geographic rarity of particular value in strategic military operations and submarine navigation.
US Coast Guard looks to bolster Pacific allegiances as Chinese clout grows
22 Oct 2019
Zhang said Beijing would explore any opportunity to build a port with potential military capability.
“China has a long-term need to gain a strategic foothold in the region,” Zhang said. “That is a key part of the Belt and Road Initiative. At the general level it’s an economic initiative but an important aspect of the maritime Silk Road is to develop a network of strategically located port facilities.”
Sabino Asor, chair of the public education committee for the Chuuk Political Status Commission, told Civil Beat seceding from Micronesia would be the best option for Chuuk’s future.
“There is no encouraging prospect if Chuuk remains within the Federation,” he said.
However, Patrick Buchan, at Washington think tank Centre for Strategic and International Studies, said Chuuk’s dependence on remittances from the US made breaking from COFA unlikely.
China courts Pacific island states in pursuit of ‘foothold’ as US risks losing influence
In the meantime, uncertainty over COFA negotiations persists, although there is a chance it will be renewed with few changes.
“There is circulation with people easily coming and going that provides a level of understanding and friendship that does not exist between too many other countries,” Finin said.
However, China’s most attractive feature may be its willingness to at least discuss the most pressing concern of Pacific Island nations: climate change.
“When the Trump administration talks about how it doesn’t believe in climate change, or can’t even say the words – that is really offensive for Pacific nations,” Grossman said. “China knows that, and is taking full advantage of it.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in Australian Defence Force Academy, ‘great friendship’, Beijing, Belt and Road Initiative, Centre for Strategic and International Studies, China Railway Construction Corporation, China’s, Chinese premier Li Keqiang, Compact of Free Association (COFA), David Panuelo, Great Hall of the People, Great Wall, grows, headache, Honolulu Civil Beat, leaving, Marshall Islands, Micronesia, Mike Pompeo, Pacific, Pompeo’s, President of the Federated States of Micronesia, President Xi Jinping, RAND Corporation, strategic, think tank, Uncategorized, UNSW Canberra, US, US Department of State, US President Donald Trump, warmer, Washington |
Leave a Comment »
12/12/2019
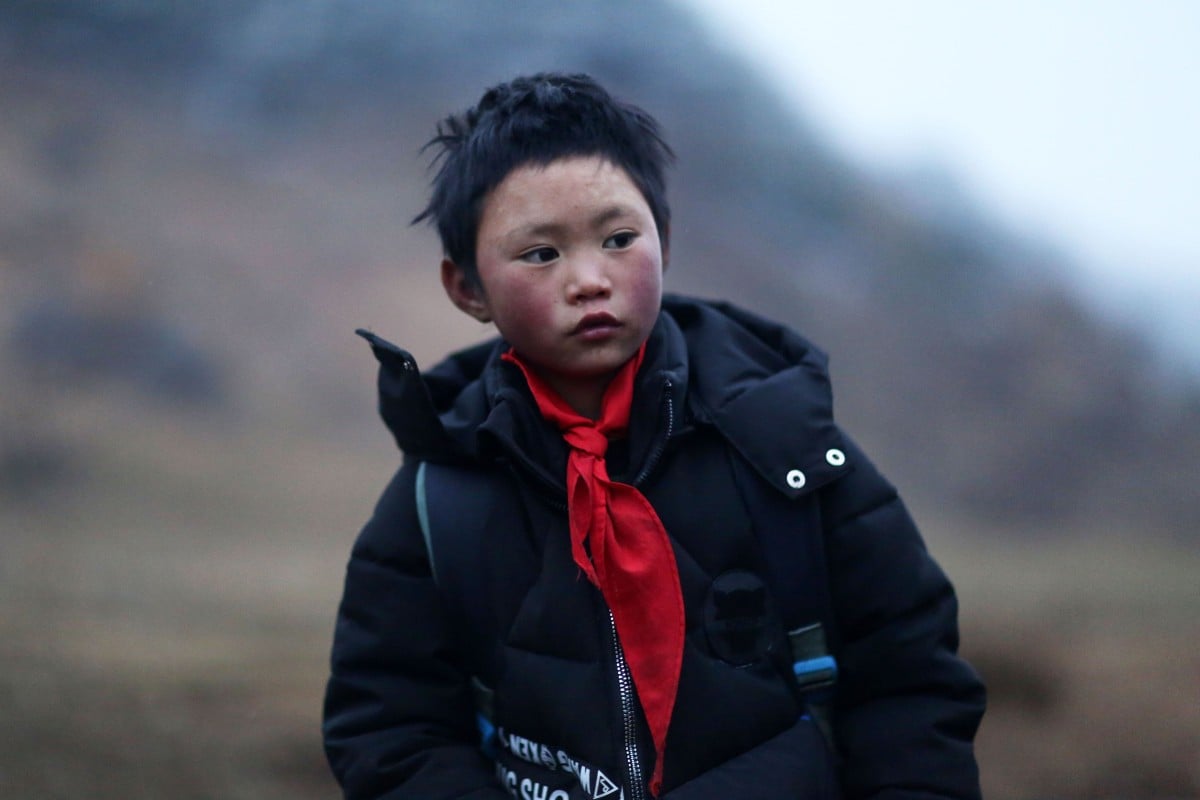
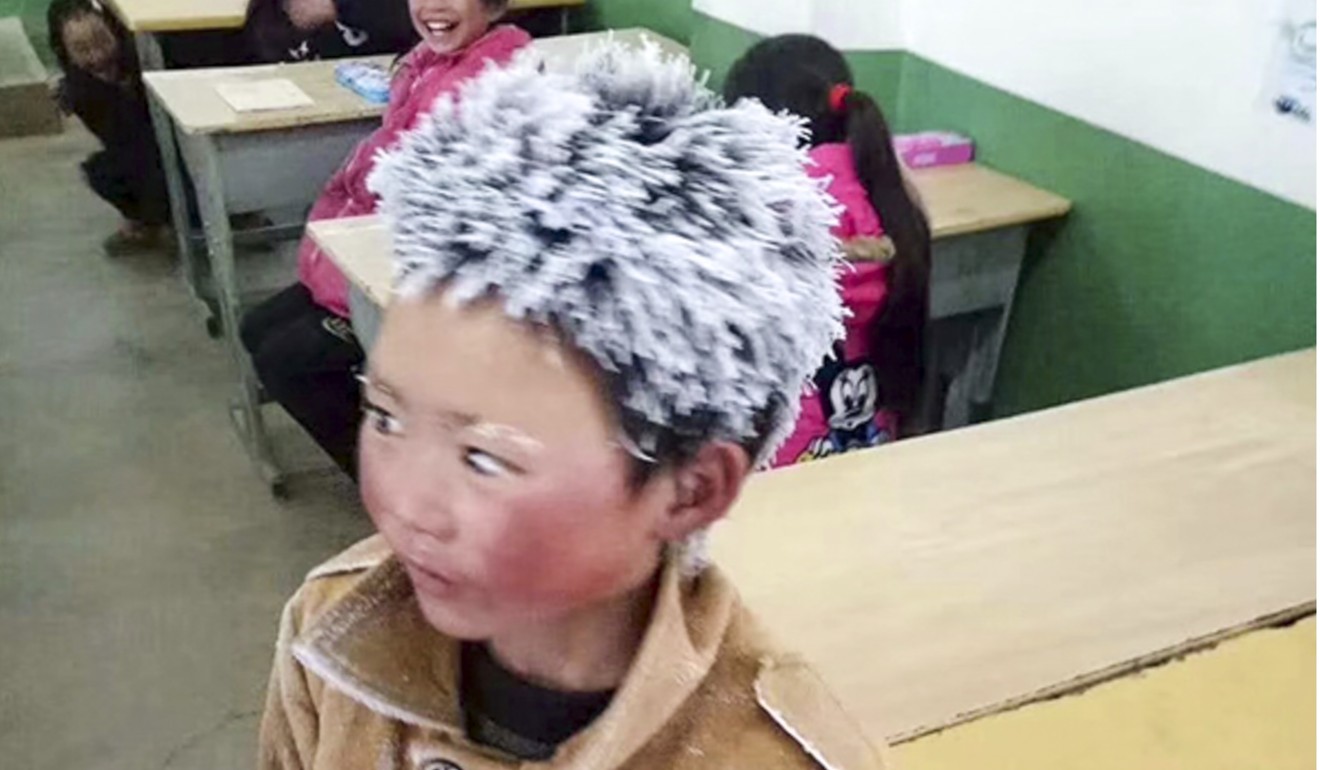
- Wang Fuman became an internet sensation after he was pictured with his head encrusted in ice after freezing trek to school
- Life has improved since then, but his dad says they are still struggling to make ends meet
Nine-year-old Wang Fuman’s family has now moved from their mud hut to a two-storey home. Photo: AFP
The father of the “Ice Boy” – who became an internet sensation after he was pictured with his head covered in icicles following a freezing trek to school in southwest China – has spoken out about being rejected for a poverty alleviation scheme.
Wang Gangkui’s son, Wang Fuman, was eight when a photo of him taken by a teacher went viral on social media in January last year. It showed the little boy with his hair and eyebrows covered in ice and his cheeks ruddy from the cold after he had walked for over an hour from his home in thin clothing and no hat along treacherous mountain paths.
The plight of the impoverished primary school pupil from Ludian county, a poor area in Zhaotong, Yunnan province, touched hearts across China, with many people expressing sympathy online for the hardships the boy, and other children like him, endured to get to school. Donations of money, warm clothes and heating flooded in.
The photo of Wang Fuman arriving at school with his hair and eyebrows covered in ice went viral last year. Photo: news.163.com
But according to his 30-year-old father, the family is still struggling to make ends meet. He said his application for the assistance scheme had been turned down for the past five years without a satisfactory explanation.
“It’s unfair and unjust that my application wasn’t approved,” Wang Gangkui said on Thursday. “There are allegations in media reports that I have various assets, and they’re just not true. And neither am I trying to take advantage of my son’s fame,” he said.
Families approved for the means-tested scheme, a nationwide programme that is administered at the local level, are given benefits ranging from subsidies to vocational training and job opportunities.
Geng Tao, the party secretary of Zhuanshanbao village, told China News Service on Monday that the Wang family did not meet the eligibility criteria for the programme, citing their two-storey house with a total area of 160 sq metres.
Wang was responding to criticism from internet users after he posted his complaint on social media app Jinri Toutiao on Sunday, a post he later deleted. Some accused him of taking advantage of his son’s fame to get access to government aid, claiming the family was being “greedy” as they were already doing better than others in the region because of the donations they received last year.
State media also weighed in, with Beijing News saying in an editorial on Tuesday that “the authorities should not be influenced by public sentiment towards the Ice Boy and should look at the family’s real situation when assessing if they are in need or not”.
Wang acknowledged that the media attention and subsequent donations from the public had eased the family’s situation, but said they only received a small share.
“There were a lot of donations, but most of them went to the school and were shared among all the pupils and their families here,” he said. “Our family only received a small amount of money.”
After Fuman’s photo went viral, the Ludian county education authorities said there were many “Ice Boys” in the area, and all donations received had been distributed to local families in need, according to China News Service.
A local charity organisation received more than 300,000 yuan (US$42,500) in donations from the public, and said the money was shared among pupils at the Zhuanshanbao primary school, with Fuman receiving just 500 yuan.
Life has improved for Fuman and his family since the photo was taken. He was a
– a term used to describe youngsters from poor families whose parents work in cities away from home, leaving them in the care of relatives. His parents have now returned to their hometown and his father works nearby at a construction site in Zhaotong, earning 3,000 yuan a month – a relatively high salary for the area. But he is the breadwinner for the family of five – his wife, Lu Dafeng, and their two children, Fuman and their 11-year-old daughter Wang Fumei, as well as his mother.
They moved out of their mud hut into the two-storey home, and with the donated funds, Fuman’s primary school was renovated and now has a dormitory equipped with heating. Fuman stays at the school during the week and returns to his home – a 20-minute walk away – on the weekend.
Wang Gangkui said his wife and mother could not apply for jobs designated as “public welfare” positions – such as a street cleaner post offering 500 yuan a month – because they were not recognised as a family in need under the scheme.
He also dismissed media reports that he had two cars, saying he had a second-hand van worth no more than 3,000 yuan. He said reports that his family also had cattle were not true.
Instead, he said he was paying off a loan of tens of thousands of yuan that he took out to build the family’s new house.
There were an estimated 16.6 million people living in poverty in rural China at the end of 2018, about 14 million fewer than a year earlier, according to official data. The ruling Communist Party set the ambitious target of eliminating extreme poverty in China by the end of 2020, and claims that more than 700 million people have already been lifted out of poverty over the past four decades.
Posted in ‘Ice Boy’, China News Service, China’s, Critics, donations, encrusted in ice, Family, father, flooded, freezing tre, head, heating, money, mud hut, poverty assistance scheme, responds, school, The Beijing News, two-storey home, Uncategorized, warm clothes, Yunnan Province |
Leave a Comment »
10/12/2019
- The Battle of Triangle Hill is known in China as a victory against foreign aggressors
- Film’s timing linked to deteriorating relations between Beijing and Washington on multiple fronts
A scene from the 1956 Chinese film Shang Gan Ling, about the Korean war Battle for Triangle Hill, subject of a new film which is about to go into production in China. Photo: Handout
One of the bloodiest battles of the Korean war is the subject of a film that will soon start production in China, in a move which is being linked to surging Chinese nationalism amid poor relations between Beijing and Washington.
The film, based on the Battle of Triangle Hill – also known as the Shang Gan Ling campaign in China – was given the green light by state regulator the China Film Administration in July, but was not reported by Chinese official media until last week.
Hou Jianwei, one of China’s best known war novelists, has been signed on as screenwriter for the film, to be produced by Ao Bo Film Zhejiang which confirmed on microblogging platform Weibo that production was already in “active preparation”.
“More than 100,000 people from the People’s Voluntary Army and forces from the US and South Korea took part in the 43-day fighting, and over 2.4 million shells of ammunition were fired. The battle was unprecedentedly fierce and 40,000 lives were lost,” the film company said in its most recent Weibo post.
“With a multitude of heroes, our army built up an impenetrable barrier in the East.”
China invokes Korean war talks as reason not to bow to US in trade dispute
News of the film has coincided with mounting confrontations between Beijing and Washington on multiple fronts ranging from trade and technology, to Hong Kong and Xinjiang.
Korean war-themed productions have long been a taboo subject for China’s heavily censored film industry, partly because of Beijing’s complicated relations with the US and North Korea.
But the 1950-53 war, in which China and North Korea battled Western forces led by the US, has increasingly become a tool to rally public opinion behind Beijing’s ongoing trade war with the US. Study Times, a Central Party School publication, for example, has directly likened the trade war to the end of the Korean conflict, saying China was determined to oppose US bullying as trade negotiations entered their 17th month.
While Beijing has never given an official account of its decision to join the Korean war, it is often portrayed as a necessary intervention to shield China from US aggression.
The Battle of Triangle Hill has often been presented in China’s official media as a victory by the “volunteers” of the People’s Liberation Army over foreign aggressors.
News of the production has raised avid discussion on Chinese social media, with many seeing the new film as part of China’s efforts to reinforce surging Chinese nationalism in the face of growing pressure from the West.
“Isn’t the approval [to make the film] a strong signal to the West that we are now a strong power?” one Weibo microblogger wrote.
Source: SCMP
Posted in against, Ao Bo Film, Beijing, boost, Central Party School publication, China Film Administration, China’s, foreign aggressors, Hong Kong, Korean, Korean War, Microblogging, nationalism, North Korea, People’s Voluntary Army, platform, poor relations, rare nod, seen, South Korea, Study Times, taboo subject, talks, The Battle of Triangle Hill, trade and technology, trade dispute, Uncategorized, US, victory, war film, Washington, Weibo, Xinjiang, Zhejiang |
Leave a Comment »
02/12/2019
- World’s largest coal consumer shows little sign of ending its dependency even though it is also the biggest market for renewable energy sources
- UN climate summit is meeting to discuss ways to limit future warming, but hopes are fading that China will commit to further curbs on emissions
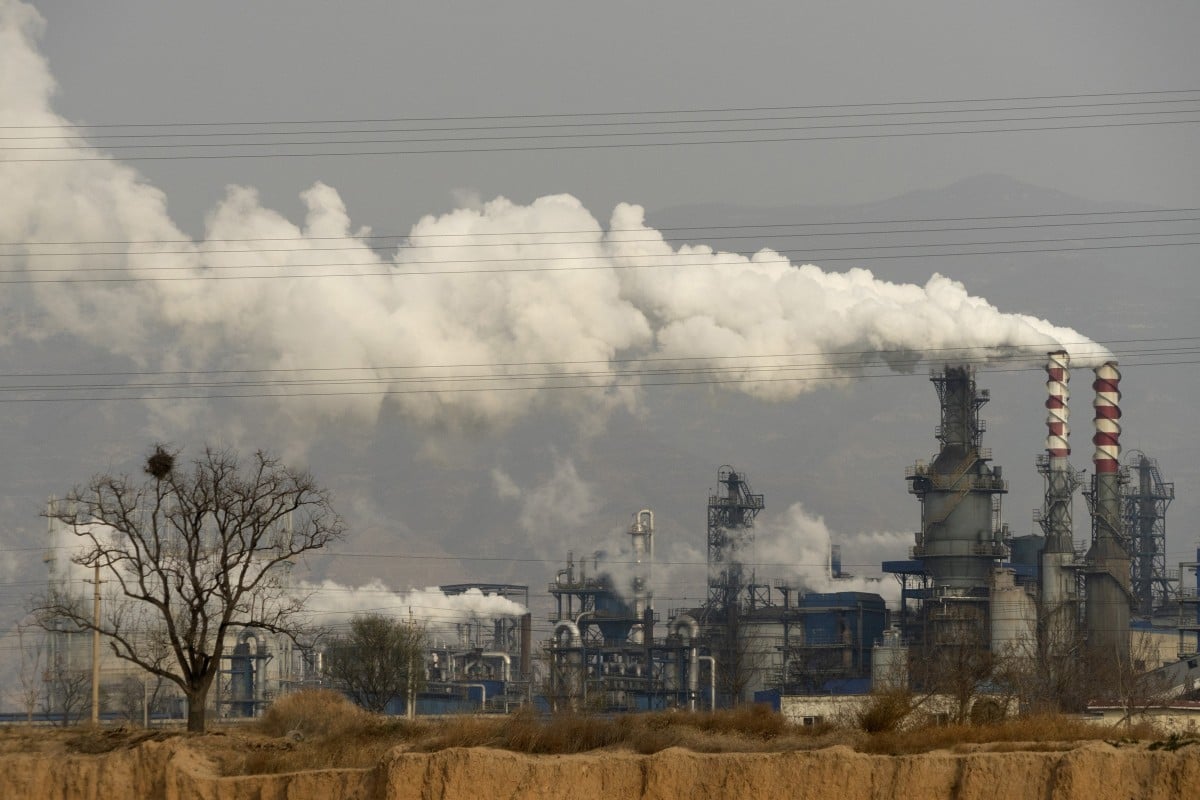
China now accounts for around 30 per cent of the world’s carbon emissions. Photo: AP
As world leaders gather in Spain to discuss how to slow the warming of the planet, the spotlight has fallen on China – the top emitter of greenhouse gases.
China burns about half the coal used globally each year. Between 2000 and 2018, its annual carbon emissions nearly tripled, and it now accounts for about 30 per cent of the world’s total.
Yet it is also the leading market for solar panels, wind turbines and electric vehicles, and it manufactures about two-thirds of solar cells installed worldwide.
“We are witnessing many contradictions in China’s energy development,” said Kevin Tu, a Beijing-based fellow with the Centre on Global Energy Policy at Columbia University. “It’s the largest coal market and the largest clean energy market in the world.”
That apparent paradox is possible because of the sheer scale of China’s energy demands.
Pollution alarm as tourism businesses contaminate home of China’s hairy crab
But as China’s economy slows to the lowest level in a quarter century – around 6 per cent growth, according to government statistics – policymakers are doubling down on support for coal and other heavy industries, the traditional backbones of China’s energy system and economy. At the same time, the country is reducing subsidies for renewable energy.
At the annual United Nations climate summit, this year in Madrid, government representatives will put the finishing touches on implementing the 2015 Paris Agreement, which set a goal to limit future warming to 1.5 to 2 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels.
Nations may decide for themselves how to achieve it.
China had previously committed to shifting its energy mix to 20 per cent renewables, including nuclear and hydroelectric energy.
Climate experts generally agree that the initial targets pledged in Paris will not be enough to reach the goal, and next year nations are required to articulate more ambitious targets.
Hopes that China would offer to do much more are fading.
Recent media reports and satellite images suggest that China is building or planning to complete new coal power plants with total capacity of 148 gigawatts – nearly equal to the entire coal-power capacity of the European Union within the next few years, according to an analysis by Global Energy Monitor, a San Francisco-based non-profit.
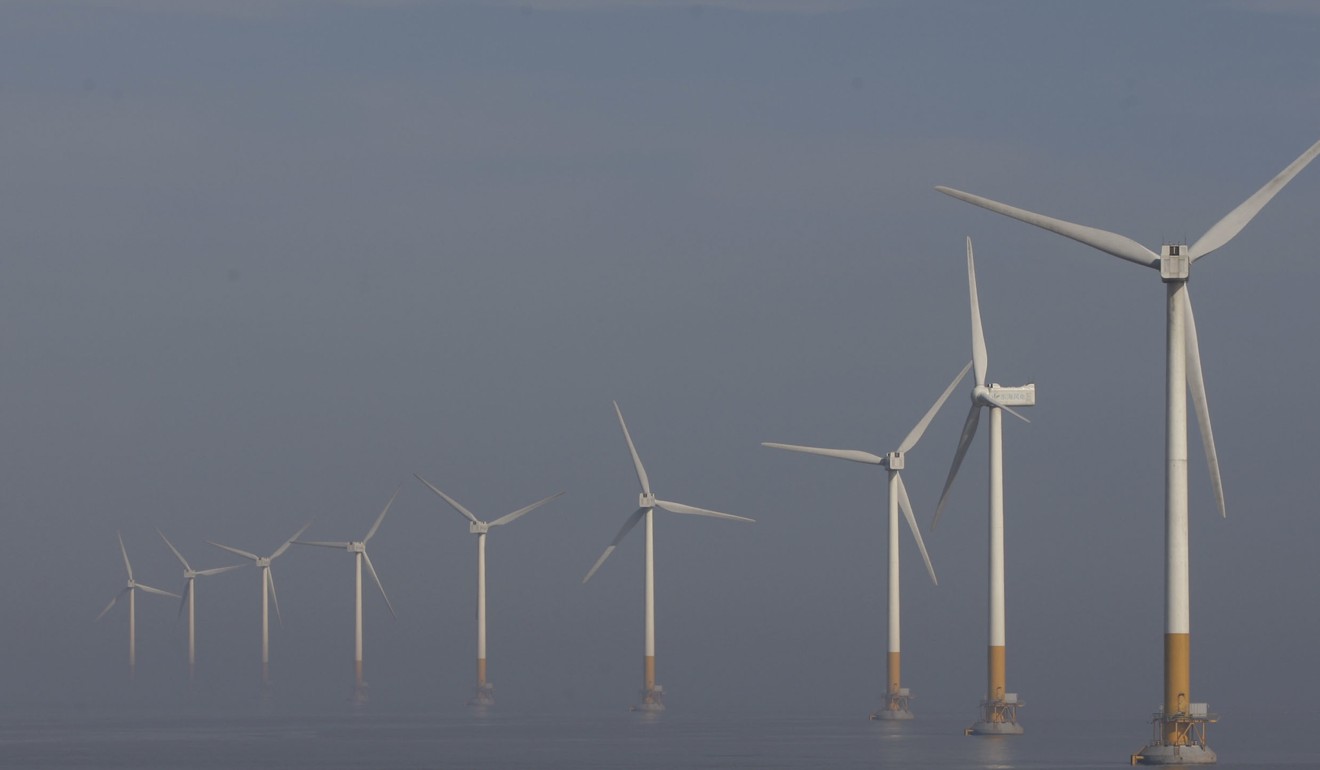

China is the world’s leading market for wind turbines and other renewables – but is still a major source of emissions. Photo: Chinatopix via AP
Meanwhile, investment in China’s renewable energy dropped almost 40 per cent in the first half of 2019 compared with the same period last year, according to Bloomberg New Energy Finance, a research organisation. The government slashed subsidies for solar energy.
Last week in Beijing, China’s vice-minister of ecology and environment told reporters that non-fossil-fuel sources already account for 14.3 per cent of the country’s energy mix. He did not indicate that China would embrace more stringent targets soon.
“We are still faced with challenges of developing our economy, improving people’s livelihood,” Zhao Yingmin said.
As a fast-growing economy, it was always inevitable that China’s energy demands would climb steeply. The only question was whether the country could power a sufficiently large portion of its economy with renewables to curb emissions growth.
Many observers took hope from a brief dip in China’s carbon emissions between 2014 and 2016. Today the country’s renewed focus on coal comes as a disappointment.
“Now there’s a sense that rather than being a leader, China is the one that is out of step,” said Lauri Myllyvirta, lead analyst at the Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air in Helsinki.
He notes that several developed countries – including Germany, South Korea and the United States – are rapidly reducing their reliance on coal power.
After climbing sharply for two decades, China’s emissions stalled around 2013 and then declined slightly in 2015 and 2016, according to Global Carbon Budget, which tracks emissions worldwide.
This dip came as Chinese leaders declared a “war on pollution” and suspended the construction of dozens of planned coal power plants, including some in Shanxi.
Pollution scandal near China nature reserve at Tengger desert’s edge
At the same time, the government required many existing coal operators to install new equipment in chimneys to remove sulphur dioxide, nitrous oxide and other hazardous substances. About 80 per cent of coal plants now have scrubbers, said Alvin Lin, Beijing-based China climate and energy policy director for the Natural Resources Defence Council, a non-profit.
As a result, the air quality in many Chinese cities, including Beijing, improved significantly between 2013 and 2017. Residents long accustomed to wearing face masks and running home air-filter machines enjoyed a reprieve of more “blue sky days,” as low-pollution days are known in China.
In the past three years, China’s carbon emissions have begun to rise again, according to Global Carbon Budget.
The coming winter in Beijing may see a return of prolonged smog, as authorities loosen environmental controls on heavy industry – in part to compensate for other slowing sectors in the economy.

The UN Climate Change Conference is taking place in Madrid this month. Photo: AFP
Permits for new coal plants proliferated after regulatory authority was briefly devolved from Beijing to provincial governments, which see construction projects and coal operations as boosts to local economies and tax bases, said Ted Nace, executive director of Global Energy Monitor.
“It’s as though a boa constrictor swallowed a giraffe, and now we’re watching that bulge move through the system,” said Nace. In China, it takes about three years to build a coal plant.
The world has already warmed by 1 degree Celsius. All scenarios envisioned by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change for holding planetary warming to around 1.5 degrees Celsius involve steep worldwide reductions in coal-power generation.
In that effort, other countries rely on Chinese manufacturing to hold down prices on solar panels. wind turbines and lithium-ion batteries.
“China has a really mixed record. On the one hand, it’s seen rapidly rising emissions over the past two decades,” said Jonas Nahm, an energy expert at Johns Hopkins University.
“On the other hand, it’s shown it’s able to innovate around manufacturing – and make new energy technologies available at scale, faster and cheaper.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in against, “blue sky days,, battle, Beijing, Bloomberg New Energy Finance, boa constrictor, boa constructor, Centre for Research on Energy and Clean Air, Centre on Global Energy Policy, China’s, coal, coal plants, Coal Power, Columbia University, Construction, demands, electric vehicles, emissions, energy, European Union, Germany, giraffe, global, Global Carbon Budget, Global Energy Monitor, global warming, greenhouse gases, heavy industry, Helsinki, Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change, Johns Hopkins University, leading market, Madrid, Natural Resources Defence Council, new, paradox, plans, plants, Reliance, renewables, Risk, Shanxi, Solar Energy, solar panels, source, South Korea, suspended, swallowed, Tengger desert, top emitter, UN Climate Change Conference, UN climate summit, Uncategorized, undermining, United States, war on pollution, warming, wind turbines |
Leave a Comment »
19/11/2019
- Every morning and night for the past four years, businessman Zhong Congrong has been on the streets of Chongqing to stop people dropping their litter
- Admired as a welfare champion, the 54-year-old says he has been beaten and insulted for his cause
Zhong Congrong is a familiar figure on the streets of his hometown. Photo: Handout
Zhong Congrong owns three businesses in southwestern China which together are worth more than 100 million yuan (US$14.3 million), but he prefers to risk being labelled as an environment “nut” who wants to clean up Chongqing.
Every morning after breakfast and each evening after supper, the entrepreneur pulls on an orange T-shirt, gets into his Mercedes-Benz SUV and heads downtown. For one or two hours, he walks the streets, picking scraps of rubbish off the road and talking to passers-by about littering.
“It is my mission to change people’s bad habits and to raise their awareness of protecting the environment,” said Zhong, who has been on this mission for four years. It has brought the 54-year-old civic rewards, earned him a bruising or two from people who do not want to listen to his message and it nearly cost him his marriage.
Throughout it all, he has remained a persistent voice for the environment in the city of more than 30 million people and, as some of them have learned, he refuses to give up.
Yang Zuhui (right) has come to admire Zhong Congrong’s dedication to his litter picking mission, but she fears for her husband’s safety. Photo: Weibo
On mainland China, cities have banned littering and some hit offenders with fines as high as 200 yuan. However, the rules are rarely obeyed and feebly enforced, and while there are plenty of dustbins in public places, litter is still a nuisance.
Zhong said his mission started in 2015 after he met a woman in her 70s in Sanya, the southern coastal city on the South China Sea island of Hainan. He was struck by how dedicated she and her husband were when they went litter picking each day.
“They are retired professors from a prestigious university in Beijing,” Zhong said. “I chatted a lot with her and I asked her, ‘What’s the point of collecting rubbish every day? You clean up the beach today, but tomorrow new rubbish appears’.”
The way to solve the problem was to teach people to not litter, she told him, but she said she “dared not” try to do that. Zhong said that encounter gave him his purpose and he would dare to change attitudes.
Shanghai recycling scheme slips up on 9,000 tonnes of waste
Back home, Zhong watched and learned – concluding that customers of restaurants and fast food businesses tended to be the people who dropped rubbish most.
“Perhaps it’s because when people dine in restaurants, they throw their rubbish wherever they like. Going outside, they keep on doing it,” he said.
“People in shopping malls are generally more civilised.”
Zhong says his mission began in 2015 during a holiday on the island of Hainan. Photo: Dickson Lee
While on patrol, Zhong makes himself easy to see in an orange T-shirt that bears his clean-up message. His tools include a metal pincer for picking up tissue paper, plastic bags, drinks bottles, nappies and other everyday detritus and putting it into bins.
He also carries a voice recorder that sends out an appeal to restaurant customers: “To protect our environment and not to affect our kids’ healthy growing up, dear friends, please don’t throw rubbish.”
Can China sort its household waste recycling problem by 2020?
Zhong said that at first he felt afraid and self-conscious when he stood in front of a crowd of diners with his green gospel. But time and practise taught him he had almost nothing to fear, he said.
One of the bigger challenges is getting through to the many people who do not listen to him and refuse to dispose of their rubbish the right way.
“It’s normal that our society has various kinds of people and I need to face this reality,” Zhong said. “I was prepared in my mind that I would be called ‘nut’ since this is such an arduous but fruitless cause.”
He tackles the problem with his usual persistence, so argument and persuasion is all part of the job. When Zhong insists the rule breakers take their rubbish and bin it, some ignore him and others walk away – but he is ready with an answer.
“I tell them, ‘If you don’t pick it up, I guarantee that you will lose face today. I will let passers-by see and hear what a humiliating thing you have done. Everybody will then condemn you and you will be embarrassed’,” he said.
When people tell him what they do is none of his business, Zhong replies that what he is doing is in the public interest.
Sometimes there is a heavier price. Zhong said he once watched several men in their 20s throw rubbish onto the road from their car. He set off after them in his SUV. He waylaid them and asked them to clean up after themselves – the men refused, swore at him and beat him up. Their day ended in a police station.
Zhong said he hoped his work would bring “positive energy” to the employees of his vehicle components and packaging materials companies, but his mission was not about business prestige.
However, last year, he was named as one of the top 10 public welfare figures of Chongqing by the municipal government, while his family was honoured as a Chinese good family by the semi-governmental All-China Women’s Federation, a women’s rights organisation established in 1949.
Street cleaner who found US$22,000 in rubbish refuses to accept a reward
There were trials for Zhong closer to home – his wife, Yang Zuhui, did not support his mission at first and threatened to divorce him.
“It’s OK that you picked up trash on the street and you were just another cleaner there,” she told him in an interview with Hunan Television in 2017. “But what worried me was that you tried to persuade others – physical violence [against him] was inevitable.”
She also said: “My husband is not very tall and, on many occasions, he was at a disadvantage and got beaten up. I am worried about his personal safety.”
Zhong impressed his daughter’s schoolfriends with an inspiring speech. Photo: Weibo
But two years ago, their 10-year-old daughter helped change Yang’s attitude towards her husband’s mission after a school outing.
After lunch that day, Zhong gave the adults and children who had left rubbish behind one of his lectures.
His daughter, who was embarrassed by Zhong’s speech, came to appreciate him when classmates told her: “Your father is awesome. He is like a hero who protects the Earth.”
Yang was won over because she knew her husband was a determined man and once he decided on a course of action would not change his mind.
Their son – who is in his 20s and has returned to Chongqing after studying in France – always stands by his father, Zhong said.
“My son told me that environmental voluntary work normal abroad and it is respected,” he said.
Going out to collect rubbish has become part of Zhong’s life, he said.
“In the evening, if I stay at home, my wife and daughter will ask me ‘Why don’t you go to pick up rubbish?’”
He said it was important to go litter picking every day because the more he did it the more people he could influence.
“By breaking the littering habit, Chinese people can stand tall when they travel abroad,” Zhong said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in abroad, Admired, All-China Women's Federation, beaten, Beijing, break, bruising, businessman, cause, China’s, Chinese people, Chongqing, civic rewards, civilised, concluding, customers, dirty job, downtown, dropping, Entrepreneur, Every morning and night, fast food, four years, France, habit, Hainan, Hunan Television, insulted, learned, litter, marriage, Mercedes-Benz SUV, millionaire, orange T-shirt, People, personal safety, prestigious university, professors, reputation, restaurants, retired, Risks, Sanya, Shanghai, shopping malls, South China Sea, stand tall, stop, streets, travel, Uncategorized, watched, welfare champion, Zhong Congrong |
Leave a Comment »
02/11/2019
- Chinese academics and young scientists join global scientific elite to explore frontiers of research
- International joint laboratory announced at Shanghai forum
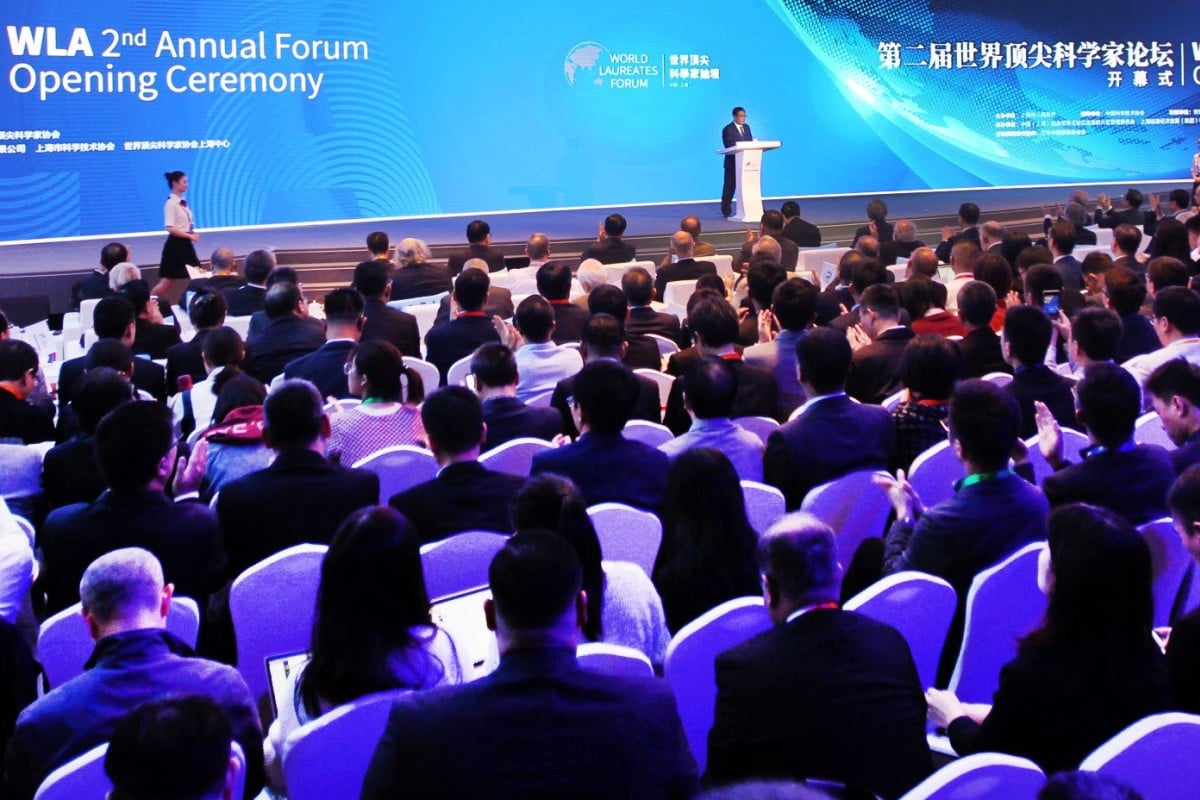
More than three dozen Nobel Prize winners for science were among the gathering in Shanghai for the second annual forum of the World Laureates Association. Photo: Xinhua
Shanghai hosted one of the largest gatherings of Nobel laureates in the world last week, with 44 Nobel Prize-winning scientists in the city for a government-sponsored forum with the lofty goal of discussing science and technology for the “common destiny of mankind”.
The four-day forum, which brought together young Chinese scientists and the cream of the international scientific crop, was a signal of China’s ambitions for its own researchers to take their place at the forefront of development and bring home their own prizes.
Experts agreed the event – the second in an annual “World Laureates Forum” – was hardly a public relations stunt, but a testament to China’s deep-seated, steadfast desire to learn from the world’s top scientists and join them, and their home countries, as leaders on the frontier of science and produce regular home-grown contenders for top prizes.
“The Nobel Prize is the holy grail for China, and it is still quite elusive for Chinese indigenous scientists to be awarded this prestigious recognition,” said Chengxin Pan, an associate professor of international relations at Australia’s Deakin University. “You could say China has a Nobel Prize complex.”
China says US tech ban is a barrier but will not halt scientific advance
Becoming a leader in the sciences was more than just an issue of driving economic expansion through technology and innovation, it was a matter of national preservation with deep roots in Chinese history, Pan said.
“China sees the lack of power, lack of scientific achievements and modern technology as largely responsible for the backwardness and humiliation it suffered during much of the 19th century and early 20th century,” he said.
“They need to make up for lagging behind by engaging with the top leading scientists in the world, wherever they are from.”
To that end, celebrated theoretical physicists, organic chemists, neuroscientists and biologists joined Chinese academics and youth scientists for the conference organised by the Shanghai city government and an association of top global scientists known as the World Laureates Association.
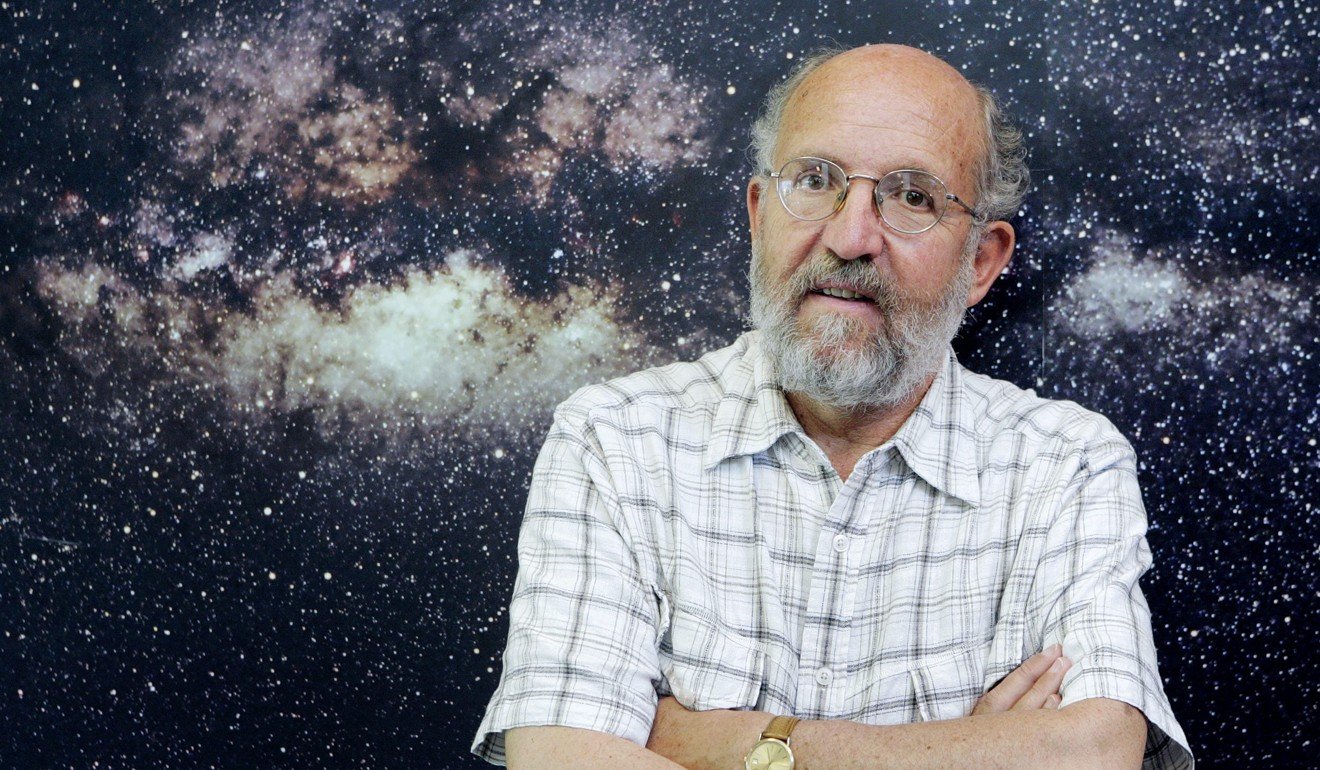
Among them were 2019 Nobel Prize for physics laureates Michel Mayor and Didier Queloz, as well as winners of other top prizes including the Wolf Prize, Lasker Award, and Fields Medal for mathematics. Discussions included the latest breakthroughs in disease prevention and drug development, sustainability and new energy, aerospace and black holes, as well as what drives their scientific curiosity.
Swiss professor Michel Mayor, astrophysicist and director of the Geneva Observatory, was one of the co-winners of the 2019 Nobel Prize in physics and among the attendees at the forum in Shanghai. Photo: EPA-EFE
The event, which culminated with the announcement of an international joint research laboratory for the world’s top scientists, to be established in Shanghai, was lauded by President Xi Jinping in an open letter to the attendees.
“China attaches great importance to the development of the frontier fields of science and technology,” Xi said, stressing China’s willingness to “work with all countries of the world” to “address the challenges of our age”.
The high calibre meeting was a rare opportunity for China to broadcast its message of commitment to scientific advancement, at a time when the reputation of its universities, academics and hi-tech companies have been taking a broad hit as part of a blowback from the US-China trade and tech wars, as well as suspicion among Western countries of China’s geopolitical aims.
In the past year, a number of major global Chinese tech companies, including Huawei and Hikvision, have been blacklisted in the US, while US tech giants like Google and Apple noticeably skipped out on China’s annual state-run World Internet Conference last month. Academic ties between Chinese and Western universities have also been called into question over suspicions of espionage, fraud, and intellectual property theft.
“China is saying we are still open for business and, at this juncture, we more warmly welcome foreign scientists and collaboration between countries in science and technology,” said Zhu Tian, an economics professor at the Chinese Europe International Business School in Shanghai.
60 science groups demand US end crackdown on foreign-born researchers
The past decade has seen China advance rapidly in the sciences. A surge in government funding, along with successive top level strategies to build up science and tech – including the Made in China 2025 innovation blueprint – and a significant uptick in international collaborations, have propelled the nation on to the global scientific stage.
Recent developments, like the first successful landing of a probe on the far side of the moon earlier this year, the dominance of the 5G network technology created by China’s Huawei, and the opening of the world’s largest radio telescope in Guizhou in 2017, have also raised the country’s profile in emerging tech and science.
But, so far, China’s rising visibility as a scientific powerhouse has been largely driven by scale. A June report by the journal Nature found researchers affiliated with the Chinese Academy of Sciences contributed the greatest number of “high-quality natural sciences research” to international journals compared with their peers at other institutions, while last month the journal found the top four “fastest rising” new universities for research output were all from mainland China.
“To some in the outside world, China is already a powerhouse in innovation … but in terms of the quality of innovations or scientific research, China still lags behind developed countries like the US, UK or Switzerland,” Zhu said.
Despite “making the fastest progress among all countries”, and significant leaps as a developing nation, “China is not at the frontier of technology or science yet,” he said, which is why international engagement, like the recent summit, is key to China’s growth.
“In order to catch up you have to know what is the frontier, you have to learn from those who are at the frontier.”
It is a point further underlined by the numerous blog posts and widely circulated articles in Chinese media about China’s meagre Nobel track record. Apart from one celebrated exception – 2015 Nobel laureate for medicine Tu Youyou – Chinese-born scientists who have won the prize did so for their work in overseas laboratories, or after changing citizenship.
Nobel Prize winner may have found solution to malaria drug resistance
Tu was the People’s Republic of China’s first Nobel Prize winner in the sciences and the country’s first woman to win the prize in any category.
Among China’s other Nobel laureates in the sciences are 1957 physics prizewinners Li Zhengdao and Yang Chen-ning, who won their award while in the US, having left China before the Communist Party takeover in 1949. Both later became US citizens. In 2017,
relinquishing his US citizenship to become a Chinese citizen.
China has worked hard to reverse the damage of brain drain, for example with its flagship “Thousand Talents” programme, a high-profile, state-backed recruitment drive set up in 2008 to attract overseas Chinese students and academics back to China with generous funding.
But reaching the frontiers of science, and making Nobel-worthy advancements, will also require China to do some reshuffling of its domestic priorities, which have been heavy on producing innovations in applied sciences and tech, but lighter on the basics – like physics, chemistry, and biology – whose mysteries are probed by the leading labs around the developed world.
Chinese scientists turn black coal by-product into gleaming white paper
“China in the past has been known as a place for incremental innovation, and not the place where really radical innovation and big breakthroughs have come from, but they don’t want to be tinkering at the margins, they want to be a major innovation powerhouse,” said Andrew Kennedy, an associate professor in the policy and governance programme at the Australian National University.
To change this, China has begun to raise investment in basic sciences, Kennedy said, pointing to National Bureau of Statistics figures which indicate an average spending increase of more than 20 per cent each year between 1995 to 2016. Even so, spending at the end of that period – some US$11.9 billion at market rates – still lagged well below the figure cited for the US in 2015, which rang up US$83.5 billion, he said.
Chinese scientists develop laser that could track submarines
The gathering of science laureates itself was further indication of that shift to place more emphasis on basic sciences, the kinds of disciplines the laureates lead, and could be a major boost to that agenda, according to Naubahar Sharif, associate professor of social science and public policy at Hong Kong University of Science and Technology.
“This [event] is a rocket-propelled, massive injection of scientific power into one place, and China has ambitions to gear up their own scientists to this level,” Sharif said, “and I’m sure the local Chinese scientists have been prepped to take advantage of it.”
While China has work to do in pushing back on criticism of questionable practices in intellectual property transfer, or the extent to which they share their own advances with others, collaboration with leading scientists is a crucial part of China’s “long-haul” vision in the sciences, Sharif said.
“If you rub shoulders with the most prestigious scientists of your era, your local scientists will learn something, and there’s going to be knowledge exchange and making linkages and a start to partnerships,” he said.
“This is the way that getting to that frontier can be achieved.”
Source: SCMP
Posted in 2019 Nobel Prize, Aerospace, Apple, astrophysicist, Australian National University, “Thousand Talents”, “World Laureates Forum”, biologists, black holes, blacklisted, Brain drain, China’s, Chinese academics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), Chinese Europe International Business School, Deakin University, disease prevention, Dozens, drug development, Fields Medal, Geneva Observatory, Google, Hikvision, holy grail, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology, Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (HKUST), Huawei, Lasker Award, meet, National Bureau of Statistics (NBS), neuroscientists, new energy, Nobel ambitions, Nobel Prize winner, on show, organic chemists, People's Republic of China's, physics, President Xi Jinping, science laureates, Shanghai, Sustainability, Switzerland, theoretical physicists, UK, Uncategorized, US, US tech giants, Wolf Prize, World Internet Conference, World Laureates Association, youth scientists |
Leave a Comment »
28/10/2019
- The president is set to become the first Russian leader to make a state visit to the Philippines for more than 40 years, according to a former envoy
- Moscow is aware of China’s entry into the Philippines, and could have its eye on some projects there, while the US is also watching developments
Russian President Vladimir Putin and Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte shake hands during a 2016 meeting in Peru. Photo: EPA
The timing of Moscow’s announcement over the weekend that
President Vladimir Putin
has accepted an invitation to visit Manila has raised eyebrows, as it comes on the eve of crucial bilateral talks between
the Philippines and China on joint oil exploration in the
.
In a statement immediately welcomed by the Philippine presidential palace, Igor Khovaev, Russia’s ambassador to the Philippines, on Saturday told reporters Putin had accepted Duterte’s invitation “with gratitude”.
No date has been set for the visit, with Khovaev only saying Moscow would “do our best to arrange this meeting as soon as possible”.
A steering committee with representatives from both Manila and Beijing is set to meet this week to discuss the joint oil exploration deal. China has proposed a 60 per cent-40 per cent split in favour of the Philippines, according to Hermogenes Esperon,
Courting Russia with South China Sea oil is a ‘dangerous gamble’ for Duterte
Neither side has clarified if the split refers to ownership or revenue, and no other details were disclosed.
After an August meeting with Duterte, Chinese President Xi Jinping said the countries could take a “bigger step” in jointly developing oil and gas resources if they could properly handle their sovereignty dispute in the South China Sea.
But defence and security analysts say the Philippine president took a “dangerous gamble” on a visit to
Russia last month, when he invited the Russian state oil company Rosneft to explore for oil in Philippine waters – which include parts of the South China Sea claimed by China.
The timing of Moscow’s announcement has not gone unnoticed.
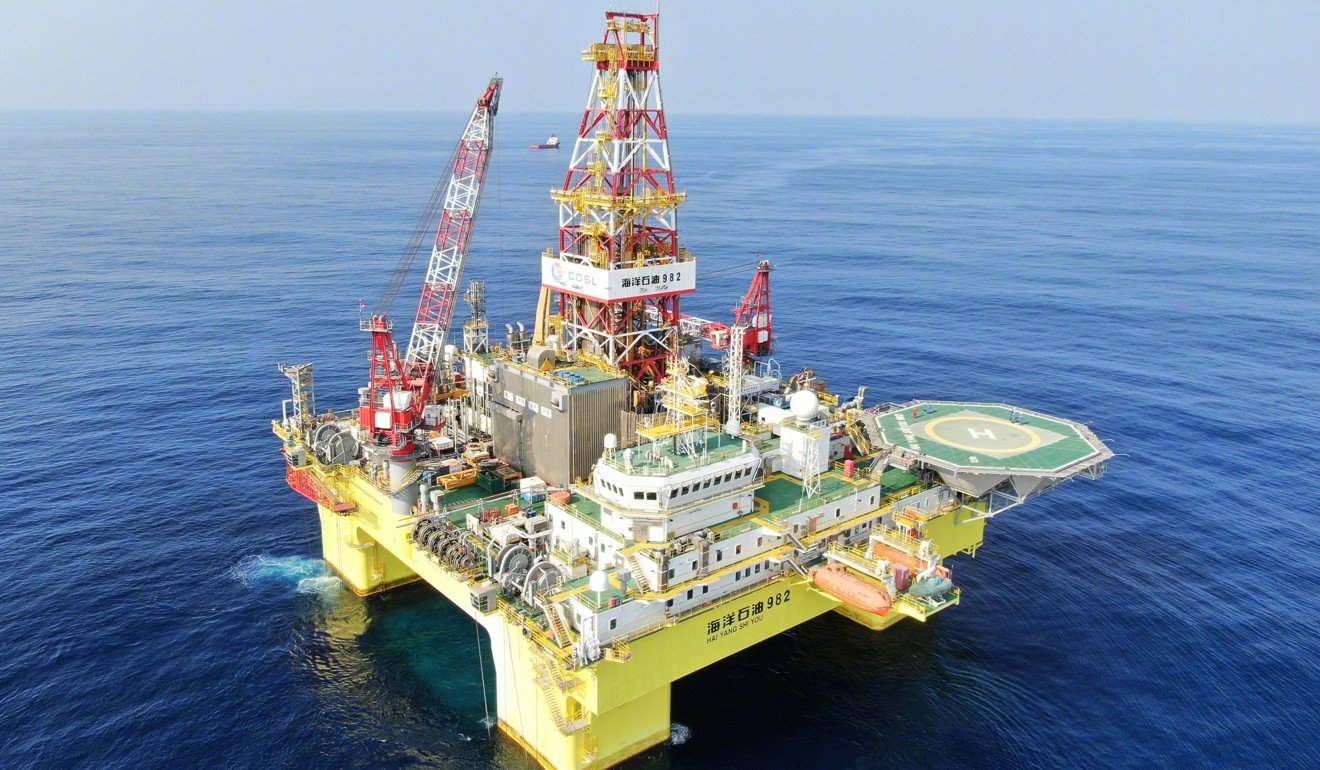
A Chinese deepwater oil rig in the South China Sea. Photo: Weibo
“It’s a welcome and historic development. Some wise guy in the Duterte government thought about timing [the invitation to Putin around the oil talks with Beijing],” said retired Philippine ambassador Lauro Baja, who once served as president of the United Nations Security Council.
Baja told the Post that no Russian president had visited the Philippines during his more than 40 years with the Department of Foreign Affairs.
“The Philippines then was almost a nonentity as far as Russia was concerned, [but] maybe now Russia recognises the strategic importance of the Philippines [in terms of] regional politics,” he said.
Baja said Moscow was aware of China’s entry into the Philippines, and could have its eye on some projects there.
“For all their so-called alliance, China and Russia are fierce competitors for influence and other benefits. And I think Russia has some objectives in mind like selling armaments and [forging] technological agreements,” he said, while cautioning that the situation remained “nebulous”.
New Philippines military chief sees no ‘shooting war’ in South China Sea despite disputes
“It’s a fascinating development but things are still early … For now, this is [just] an invitation extended by Duterte and accepted in principle by Putin.”
The United States will also be monitoring developments in the Philippines, according to Greg Poling, director of the Washington-based Centre for Strategic and International Studies’ Asia Maritime Transparency Initiative.
“Russia is eager to boost its influence in the region, and doubtless doing so with a long-standing US ally is seen as a bonus by Moscow,” he said. “There is nothing that prevents the Philippines from engaging in security cooperation with Russia, but the devil will be in the details.”
Poling added that the US would be concerned if Russia-Philippine cooperation involved acquiring military platforms that were incompatible with the shared platforms and doctrines used by Washington and Manila, as well as the latter’s other major security partners, namely Australia, Japan and South Korea.
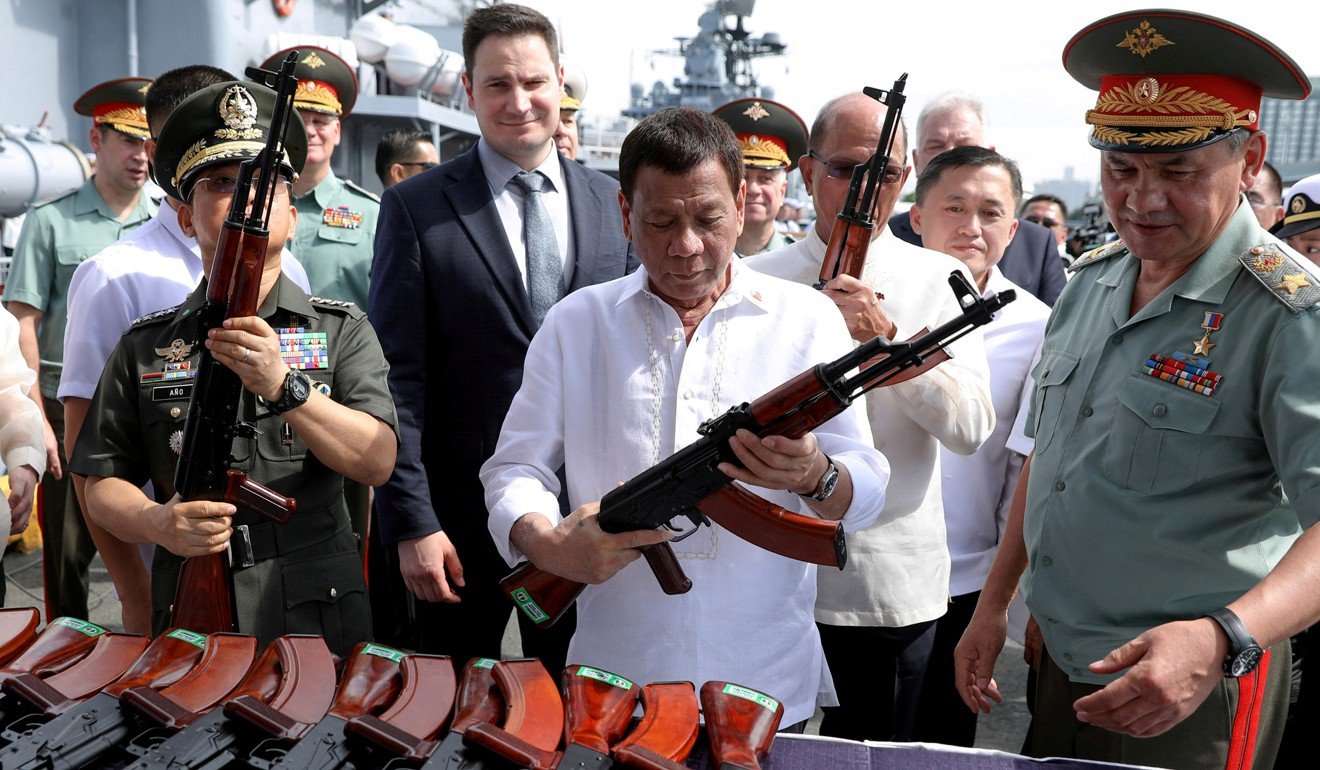
Philippine President Rodrigo Duterte inspects firearms donated by Russia in 2017. Photo: Reuters
“The US will also be concerned if any acquisitions or cooperation with Russia might threaten information security or intelligence cooperation between the US and the Philippines,” he said.
“And finally, any major platforms acquired from Russia would likely require the US to impose sanctions on the Philippines unless a waiver is granted, and the US government has been very stingy about awarding those waivers because they undermine the effectiveness of the sanctions regime.”
Moscow last week offered to help the Philippines produce its own arms for both domestic use and export with the help of Russian technology. Max Montero, an Australia-based Filipino security consultant, viewed that offer as “a swipe at the US”.
“Imagine a US stronghold and long-time ally and former colony becoming a manufacturing hub for Russian arms. And it makes it worse if [the Philippine armed forces] buys them too,” he said.
“Weakening the US alliances in Asia will benefit Russia [as it is] one of the US’ competitors in arms sales and geopolitics.”
Russia offers arms technology to the Philippines with ‘no conditions’ as US ties falter
The Philippines, Montero said, would benefit from such an arrangement since it is “a laggard in defence technology”. However, he pointed out that the country’s armed forces continue to buy weapons from the US and receive American arms as grants, potentially limiting the domestic market for Russian arms.
Navy cooperation has also been on the agenda, as Moscow and Manila discussed signing a new naval pact in March, while warships from each country have visited the other this year. Philippine naval vessels made their first-ever visit to Russia in October, while three Russian ships docked in the Philippines for a goodwill visit in January.
Russia is the top supplier of arms to Southeast Asia, and the No 2 global arms supplier, behind the US. Southeast Asia bought US$6.6 billion of Russian arms between 2010 and 2017, or more than 12 per cent of Russia’s sales, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, a Swedish think tank that publishes global arms tracking data.
Source: SCMP
Posted in acquisitions, agenda, arms sales, Australia, Beijing, Centre for Strategic and International Studies’ Asia Maritime Transparency Initiative, China’s, Chinese, Chinese President Xi Jinping, cooperation, deepwater oil rig, Department of Foreign Affairs, donated, entry, firearms, GeoPolitics, global arms supplier, global arms tracking data, inspects, invite, Japan, Manila, Manila-Beijing, Moscow, naval pact, Navy cooperation, nonentity, oil company, oil talks, Peru, Philippine President, Philippines, Putin, Rodrigo Duterte, Rosneft, Russia, Russian leader, Russian President, russian president vladimir putin, Russian state, Russian technology, South China Sea, South Korea, Southeast Asia, State visit, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, Swedish think tank, Uncategorized, United Nations Security Council, United Nations Security Council (UNSC), United States, US, Washington |
Leave a Comment »
26/10/2019
- After nearly 10 years of planning, the country’s two shipbuilders will be reunited with a combined revenue of US$141.5 billion
China’s two shipbuilding giants have built hundreds of military vessels over the past few years as the country’s navy seeks to modernise rapidly. Photo: Xinhua
China on Friday announced the merger of the country’s two largest state-owned shipbuilding giants, a step Beijing has been preparing for nearly a decade to strengthen the competitiveness of its shipbuilding industry.
The intention to merge the Shanghai-based China State Shipbuilding Corp (CSSC) and the China Shipbuilding Industry Co (CSIC), based in Dalian, Northern Liaoning province, was announced in a statement on the website of the state-owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council, China’s cabinet.
The merger would enable China to establish a shipbuilding giant with a combined revenue up to 1 trillion yuan (US$141.5 billion), capable of building vessels ranging from warships, like aircraft carriers, to civilian ships such as container ships and oil tankers, said a source familiar with the merger plan.
“This merger has been in the making since Hu Wenming, a former party leader of the state-owned aviation industry, was assigned to CSSC as party secretary in 2010,” the source said, requesting anonymity because of the sensitivity of the issue.
“The merger plan was put on the drawing board at a time when the world shipping industry had entered a golden period in 2009, and the business of CSSC and CSIC was at its peak, but [China’s] analysis indicated a decline was on the horizon, as has actually happened in recent years.”
Chinese shipbuilder touts warships in push to expand arms sales in region
CSIC and CSSC were part of the same group until 1999 when they were split into two separate entities. Since then, China has overtaken South Korea and Japan to become the world’s largest builder of merchant ships, a rise spurred by the boom in world trade and the country’s accession to the World Trade Organisation in 2001.
CSSC manages shipbuilding business in the east and south of China, while CSIC oversees activities in the northern and western parts of the country. Both are also primary contractors for PLA naval ships.
Commercial shipbuilding was the major source of revenue for both enterprises, given they were generally less technologically challenging and of lower cost to build, the source said.
“Developing and building warships for the PLA needs more manpower and more advanced technologies because naval ships, which are built for sea battles, take longer to build and require cutting-edge technologies, hence the higher costs,” the source said.
China tests new warships in live-fire drills near Vietnam
CSSC and CSIC have built hundreds of military vessels over the past few years as the Chinese navy seeks to modernise rapidly. These have included aircraft carriers, Type 055 destroyers, Type 075 amphibious assault ships and Type 094A nuclear submarines.
But, the source said, the two giants’ naval warship building mission would be cut back next year, as Beijing expected greater financial pressure as a result of slower economic growth. The merger would allow the two companies to pool their resources and enhance their competitiveness, especially in the development of mega vessels.
But the source said the two giants’ naval warships building missions would be cut back beginning next year as Beijing foresees greater financial pressure as a result of slower economic growth. The merger will allow the two companies to pool their resources and enhance their competitiveness, especially in areas of mega vessels.
“The merger is also part of China’s long-term maritime energy development plan to meet President Xi Jinping’s sustainable and clean energy goal, because China needs more giant vessels to help ship oil and gas from other countries,” the source said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in aircraft carriers, Assets Supervision and Administration Commission, Beijing, China Shipbuilding Industry Co (CSIC), China State Shipbuilding Corp (CSSC), China’s, China’s cabinet, Chinese State Council, civilian ships, competitiveness, container ships, Dalian, giants, green light, industry, Japan, Liaoning province, merchant ships, Merger, military vessels, oil tankers, PLA naval ships, Shanghai, shipbuilding, shipbuilding giants, South Korea, Uncategorized, Vietnam, warships, World Trade Organisation (WTO) |
Leave a Comment »
20/10/2019
BEIJING (Reuters) – China will launch test flights for the next two space rockets in its Smart Dragon series meant for commercial use in 2020 and 2021, the official Xinhua news agency reported on Sunday, as an expected boom in satellite deployment gathers pace.
The release of the flight schedule by China Rocket Co, a unit of state-owned China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp, comes two months after the firm’s first reusable rocket, the 23-tonne Smart Dragon-1, delivered three satellites into orbit.
China envisions constellations of commercial satellites that can offer services ranging from high-speed internet for aircraft to tracking coal shipments. Reusable designs will enable frequent rocket launches and help keep costs down.
The solid-propellant Smart Dragon-2, weighing about 60 tonnes and with a total length of 21 metres, will be capable of sending 500 kg payloads into orbit at an altitude of 500 km (310 miles), Xinhua said. It is expected to conduct a flight test next year.
At about 116 tonnes and with a length of 31 metres, the Smart Dragon-3, set for a test flight in 2021, will be capable of sending 1.5 tonne payloads into orbit, Xinhua added.
In July, Beijing-based iSpace became the first private Chinese firm to deliver a satellite into orbit on its rocket. Since late last year, two other startups have attempted to launch satellites but failed.
Source: Reuters
Posted in Aircraft, China Aerospace Science and Technology Corp, China Rocket Co, China’s, commercial rockets, high-speed internet, iSpace, next, satellite deployment, Smart Dragon-1, Smart Dragon-2, Smart Dragon-3, test flights, tracking coal shipments, Uncategorized, Xinhua |
Leave a Comment »
17/10/2019
- Fly-past will begin with helicopters and feature the country’s new generation warplanes
- A People’s Liberation Army Air Force officer will lead the squadron in a KJ-2000 and become the first serving commander to fly in a National Day parade
J-20 stealth fighter jets will be featured in Tuesday’s National Day parade in Beijing. Photo: AP
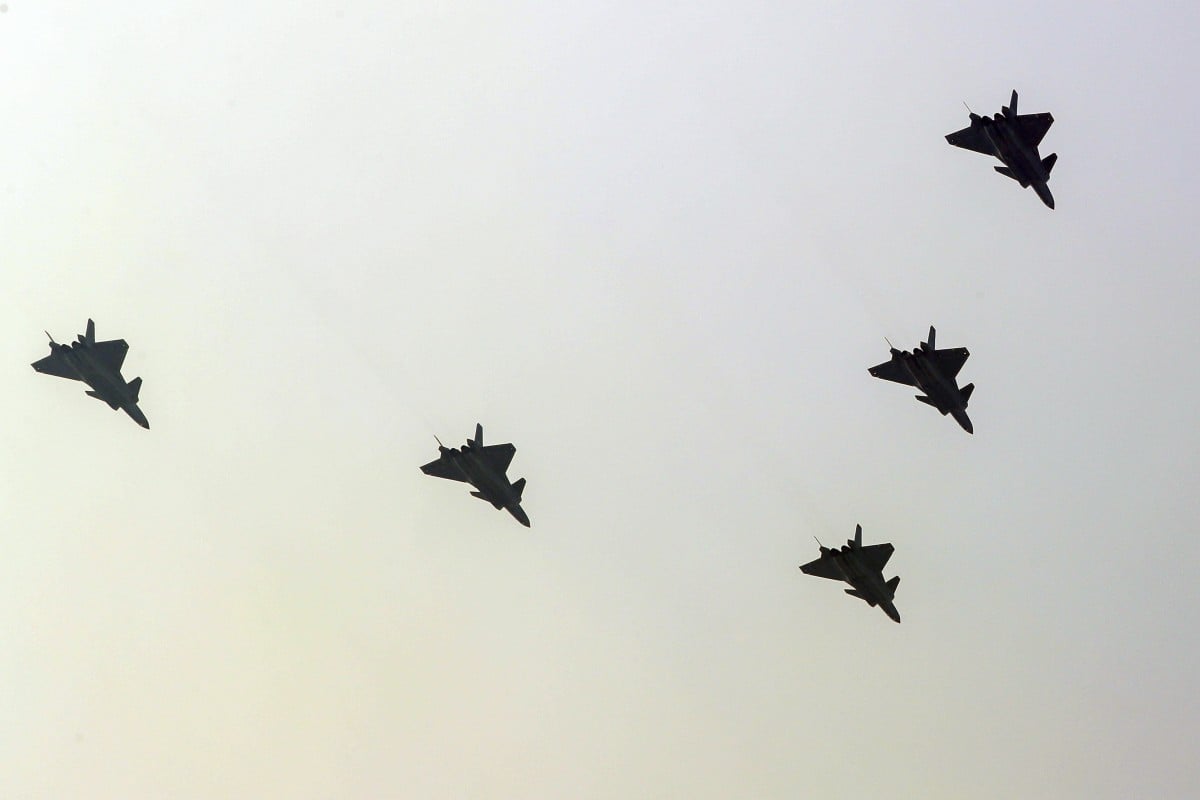
China will assemble the biggest squadron of its most advanced military aircraft for the National Day parade in the capital next week.
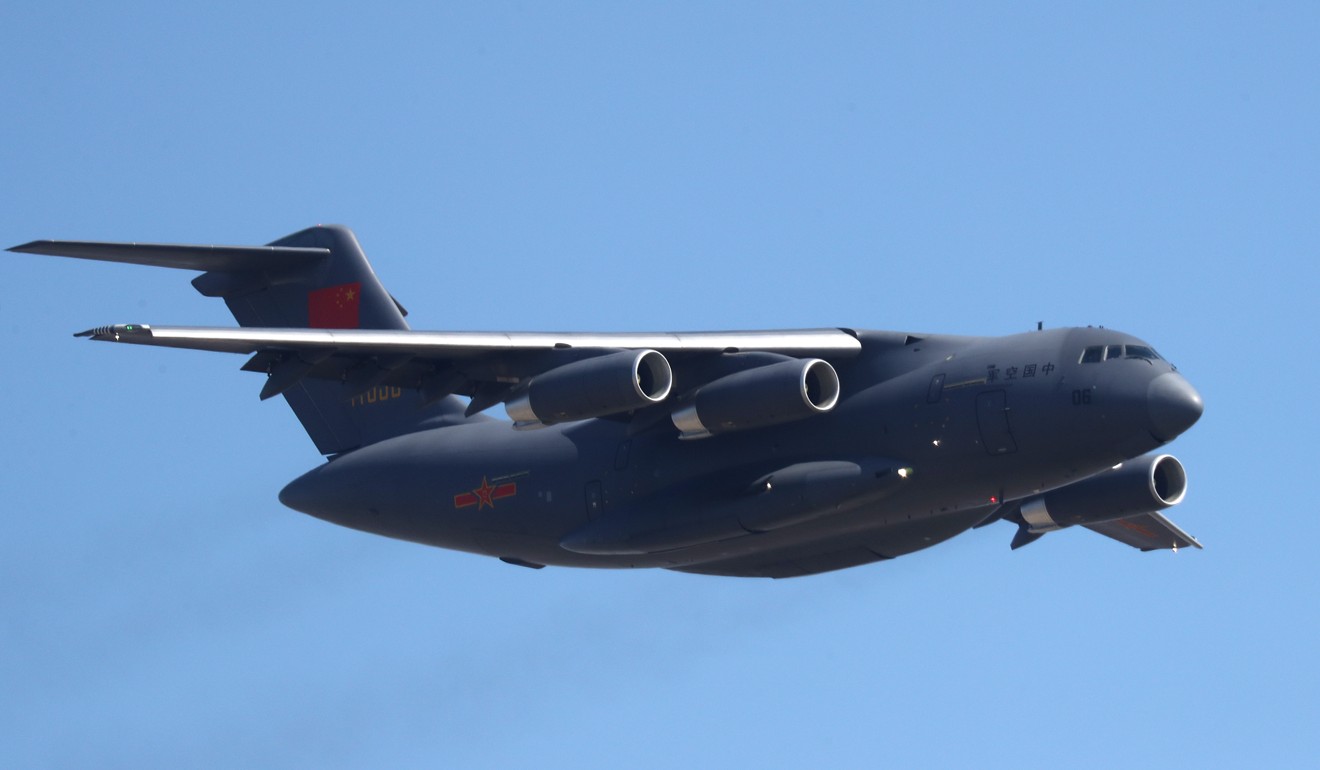
Three types of the new generation “20” series warplanes – five J-20 stealth fighter jets, three Y-20 transport planes and six Z-20 helicopters – will join airborne squadrons in the parade, according to a fly-past schedule obtained by the South China Morning Post.
“This year will be the biggest parade to have so many ‘20’ series advanced aircraft flying together,” a military insider said, referring to aircraft developed since 2000.
The J-20 is the country’s first stealth fighter; the Y-20 is China’s first heavy airlifter; and the Z-20 is a medium-lift utility helicopter comparable to the American Black Hawk.
The appearance of all three types of warplanes indicates that each one has entered production.
The H-20 subsonic stealth bomber, China’s answer to the US Air Force’s B-21 Raider, is also part of the “20” series will not make an appearance because it might need at least five more years of development.
The military insider involved in preparations for the parade, said People’s Liberation Army Air Force Commander Ding Laihang would lead the squadron in a KJ-2000 early warning aircraft.
Chinese fighter jets seen in skies over Beijing as preparations for National Day parade step up
“Ding will fly the KJ-2000 over Tiananmen Square for inspection by President Xi Jinping,” the source said, adding that Ding would be the first serving commander to fly in a National Day parade.
“The arrangement is similar to 2015 when [then] Russian Air Force commander Viktor Bondarev flew a Tu-160 strategic bomber over Moscow’s Red Square to mark the 70th anniversary of the end of the second world war.”
The KJ-2000 is the most advanced active early warning aircraft in the PLA Air Force, but it is based on the Russian Ilyushin aircraft.
The Y-20 transport aircraft will be among the new generation of planes taking part in the parade. Photo: Dickson Lee
According to the schedule, 167 aircraft will take part in the fly-past, starting with a helicopter carrying a national flag.
Eight Z-10 attack and 12 Z-19 reconnaissance helicopters will follow in formation, creating the number 70 in the sky to mark the 70th anniversary of the founding of the People’s Republic.
A source close to the navy said Z-8 multi-role and Z-19 reconnaissance helicopters be among the aircraft deployed to the Type 075 amphibious helicopter dock launched on Wednesday.
China says National Day military parade ‘won’t disappoint’ in scale or advanced weapons
A total of 44 fighter jets representing five key battle warplanes – the J-20, the J-16 fighter-bomber, the J-15 carrier-based fighter jet, the J-11 and the J-10 – will participate in the event.
But the J-8 fighter jet was not on the schedule, confirming that the first interceptor built in China has been formally retired.
Various H-6 series bombers will also make an appearance, including the H-6K and H-6N strategic bombers, as well as HU-6 refuelling plane based on the H-6 platform.
H-6K long-range bombers have been sent to the Taiwan Strait as part of “encirclement” patrols close to the self-ruled island in recent years.
Meanwhile the modified H-6N strategic bomber is designed to be armed with the Changjian-10 land-attack subsonic cruise missile, which has an operational range of more than 1,500km (932 miles).
Macau-based military observer Antony Wong Dong said that by adding more functions, the H-6 series of bombers was showing the world China had modified its combat capacity.
Wong also said the appearance of three types of training planes – the JL-8, JL-9 and JL-10 – was notable.
“It indicates that the Chinese air force had build up a systematic and comprehensive training system to train more pilots,” he said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 70th anniversary, 70th anniversary of the founding of the People's Republic of China (PRC), advanced, American Black Hawk, B-21 Raider, Beijing, biggest squadron, Changjian-10, China’s, early warning aircraft, Fly-past, fly-past schedule, H-20 subsonic stealth bomber, H-6N strategic bomber, helicopters, Ilyushin aircraft, J-20 stealth fighter jets, KJ-2000, Mass show, Military aircraft, Moscow, National Day, National Day parade, People’s Liberation Army Air Force, PLA Air Force, President Xi Jinping, Red Square, Russian, Russian Air Force, second world war, south china morning post, strategic bombers, Tiananmen Square, Tu-160, Uncategorized, US Air Force, Y-20 transport planes, Z-20 helicopters |
Leave a Comment »