The African Union headquarters in Addis Ababa is a shiny spaceship-like structure that glistens in the afternoon sun.
With its accompanying skyscraper, it stands out in the Ethiopian capital.
Greetings in Mandarin welcome visitors as they enter the lifts, and the plastic palm trees bear the logos of the China Development Bank.
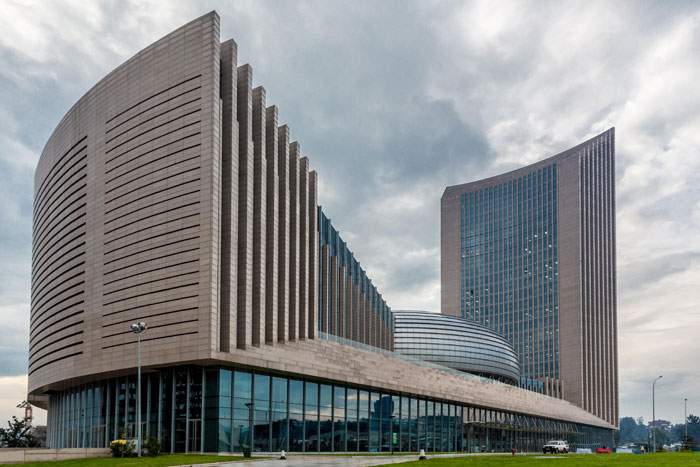

African Union HQ, Addis Ababa
Everywhere, there are small indications that the building was made possible through Chinese financial aid.
In 2006, Beijing pledged $200m to build the headquarters. Completed in 2012, everything was custom-built by the Chinese – including a state-of-the-art computer system.
For several years, the building stood as a proud testament to ever-closer ties between China and Africa. Trade has rocketed over the past two decades, growing by about 20% a year, according to international consultancy McKinsey. China is Africa’s largest economic partner.

But in January 2018, French newspaper Le Monde Afrique dropped a bombshell.
It reported that the AU’s computer system had been compromised.
The newspaper, citing multiple sources, said that for five years, between the hours of midnight and 0200, data from the AU’s servers was transferred more than 8,000km away – to servers in Shanghai.
This had allegedly continued for 1,825 days in a row.
Le Monde Afrique reported that it had come to light in 2017, when a conscientious scientist working for the AU recorded an unusually high amount of computer activity on its servers during hours when the offices would have been deserted.
It was also reported that microphones and listening devices had been discovered in the walls and desks of the building, following a sweep for bugs.
The reaction was swift.
Both AU and Chinese officials publicly condemned the report as false and sensationalist – an attempt by the Western media to damage relations between a more assertive China and an increasingly independent Africa.
But Le Monde Afrique said that AU officials had privately expressed concerns about just how dependent they were on Chinese aid – and what the consequences of that could be.
In the midst of all of this, one fact remained largely unreported.
The main supplier of information and communication technology systems to the AU headquarters was China’s best-known telecoms equipment company – Huawei.

The company says it had “nothing” to do with any alleged breach.
Huawei “served as the key ICT provider inside the AU’s headquarters”, said Danielle Cave of the Australian Strategic Policy Institute, in a review of the alleged incident.
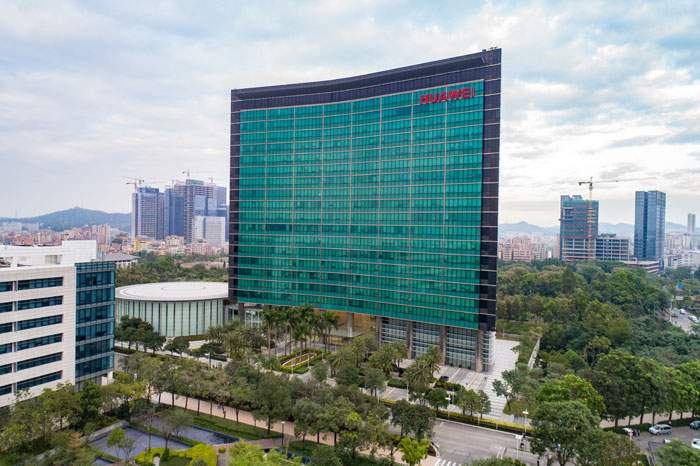

Huawei headquarters in Shenzhen, China
“This doesn’t mean the company was complicit in any theft of data. But… it’s hard to see how – given Huawei’s role in providing equipment and key ICT services to the AU building and specifically to the AU’s data centre – the company could have remained completely unaware of the apparent theft of large amounts of data, every day, for five years.”
There is no evidence to indicate that Huawei’s telecoms network equipment was ever used by the Chinese government – or anyone else – to gain access to the data of their customers.
Indeed, no-one has ever gone on record to confirm that the AU system was compromised in the first place.
But these reports played into years of suspicions about Huawei – that a large Chinese company might find itself unduly influenced by the Chinese government.
“When I first started out 30 years ago… we didn’t really have any telephones. The only phones we had were those hand-cranked phones that you see in old World War II films. We were pretty undeveloped then.”
Huawei’s founder and chairman Ren Zhengfei is reminiscing to the BBC about the origins of the world’s second-biggest smartphone firm, while sitting in the Huawei headquarters in Shenzhen – a symbol of the success that he’s worked his whole lifetime for.
A long marbled staircase, covered in plush red carpet, greets you as you first walk in.
At the top of the stairs, a giant painting depicts a traditional Chinese New Year scene.

Inside Huawei’s Shenzhen HQ
A few kilometres away in Dongguan, Huawei’s latest campus is even more eye-catching.
The site – designed to accommodate the company’s 25,000 R&D staff – comprises 12 “villages”, each of which recreates the architecture of a different European city, among them Paris, Bologna and Granada.
It’s as if Silicon Valley had been re-imagined by Walt Disney. Long corridors of Roman pillars and picturesque French cafes adorn the campus, with a train connecting the different areas, running through manicured gardens and past an artificial lake.
It’s a world away from the environment that Mr Ren found himself in when he first started the company in 1987. “I founded Huawei when China began to implement its reform and opening up policy,” he says. “At that time, China was shifting from a planned economy to a market economy. Not only people like myself, but even the most senior government officials, did not have the vaguest idea of what a market economy was. It seemed it was hard to survive.”
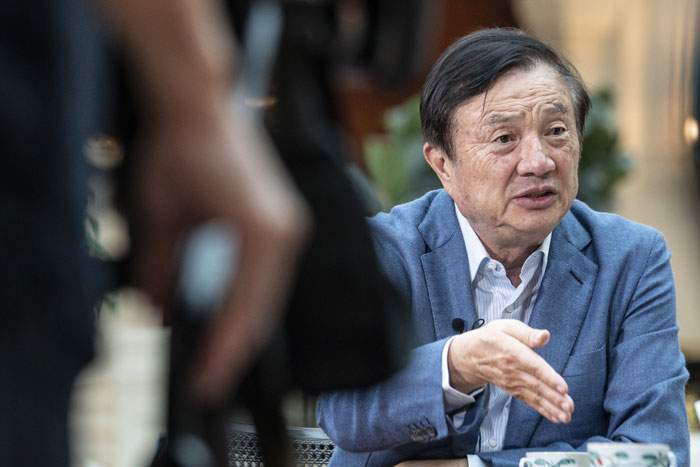

Ren was born in 1944 in Southern China – a tumultuous, chaotic place, one of the poorest regions in an already destitute country.
For a long time, hardship was all he ever knew.
He was from a family of seven children. “They were very poor,” says David De Cremer, who has co-written a book on Ren and Huawei.
“I think hardship is something that you can see throughout his life, and which he keeps emphasising himself.”
To escape that life of poverty and drudgery, Ren did what many young Chinese men of that era did. He joined the army.
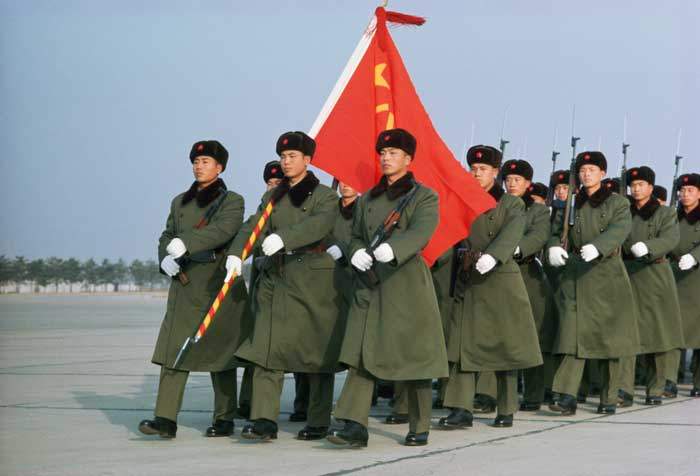

Soldiers from the People’s Liberation Army, 1972
“I was a very low-ranking officer in the People’s Liberation Army,” he says. “I served in an ordinary construction project, not a field unit. At the time, I was a technician of a company in the military, and then I became an engineer.”
He left the military in 1983 when China began to downsize its forces, and went into the electronics business.
By his own admission, he wasn’t a great businessman at first.
“I was someone who had been in the military all my life at the time, used to doing what I was told,” he says. “Suddenly, I began to work in a market economy. I was at a total loss. So I too suffered losses, I too was deceived, and I was cheated.”

But he was quick to learn, and was a keen student of Western business practices and European history.
“I did research on what exactly a market economy was all about,” he says. “I read books on laws, including those about European and US laws. At that time, there were very few books on Chinese laws, and I had to read those on European and US laws.”
Five years later, he founded Huawei – the name can be translated as “splendid achievement” or “China is able” – to sell simple telecoms equipment to the rural Chinese market. Within a few years, Huawei was developing and producing the equipment itself.
Sometime in the early 90s, Huawei won a government contract to provide telecoms equipment for the People’s Liberation Army.
By 1995, the company was generating sales of around US$220,000, mainly from selling to the rural market.
The following year Huawei was given the status of a Chinese “national champion”. In practice, this meant the government closed the market to foreign competition.
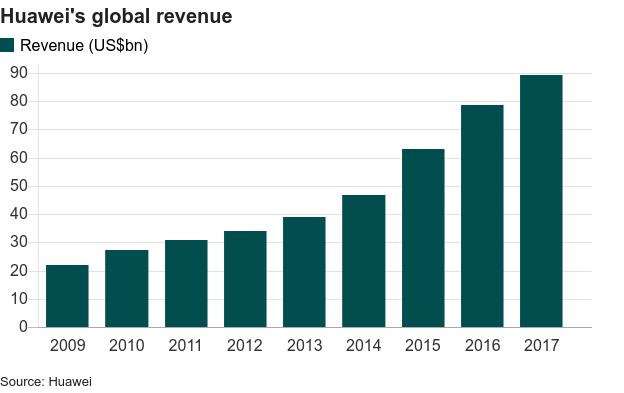
At a time when China’s economy was growing by an average of 10% per year, this was no small advantage. But it was only when Huawei started to expand overseas in 2000, that it really saw its sales soar.
In 2002, Huawei made US$552m from its international market sales. By 2005 its international market contracts exceeded its domestic business for the first time.
Ren’s early days in business instilled in him a desire to protect his company from the whims and fancies of the stock market. Huawei is privately held and employee-owned. This gave Ren the power to plough more money back into research and development. Each year, Huawei spends US$20bn on R&D – one of the biggest such budgets in the world.
“Publicly listed companies have to pay a lot of attention to their balance sheets,” he says. “They can’t invest too much, otherwise profits will drop and so will their share prices. At Huawei, we fight for our ideals. We know that if we fertilise our ‘soil’ it will become more bountiful. That’s how we’ve managed to pull ahead and succeed.”
One story from the early days of the company tells how Ren was cooking for his staff (he loves to cook, or so the story goes). Suddenly he rushed out of the kitchen and announced to the room: “Huawei will be a top three player in the global communications market 20 years from now!”
And that’s exactly what happened. In fact, those ambitions were surpassed.
Today, Huawei is the world’s biggest seller of network telecommunications equipment.
From aspiring to be a company like Apple, it now sells more smartphones than Apple.
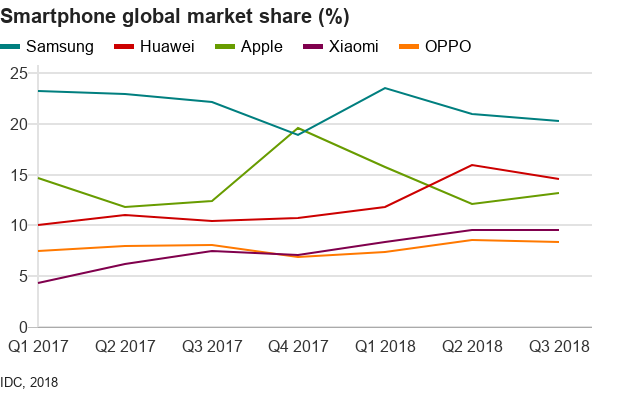
But shadows have continued to loom over Huawei’s international success.
Ren and Huawei’s links to the Chinese Communist Party have raised suspicions that the company owes its meteoric rise to its powerful political connections in China. The US has accused Huawei of being a tool of the Chinese government.
It’s an accusation which Ren denies. “Please don’t think that Huawei has become what it is today because we have special connections,” he says. “Even 100% state-owned companies have failed. Do good connections mean you will succeed then? Huawei’s success is still very much due to our hard work.”
It was 1 December 2018. US President Donald Trump and China’s President Xi Jinping were dining on grilled sirloin followed by caramel rolled pancakes at the G20 summit in Buenos Aires.
They had a lot to discuss. The US and China were in the middle of a trade war – imposing tariffs on each other’s goods – and growth forecasts for both countries had recently been cut as a result. This was adding to the fear of a slowing global economy.
In the event, the two leaders agreed a truce in the trade war, with Donald Trump tweeting that “Relations with China have taken a BIG leap forward!”
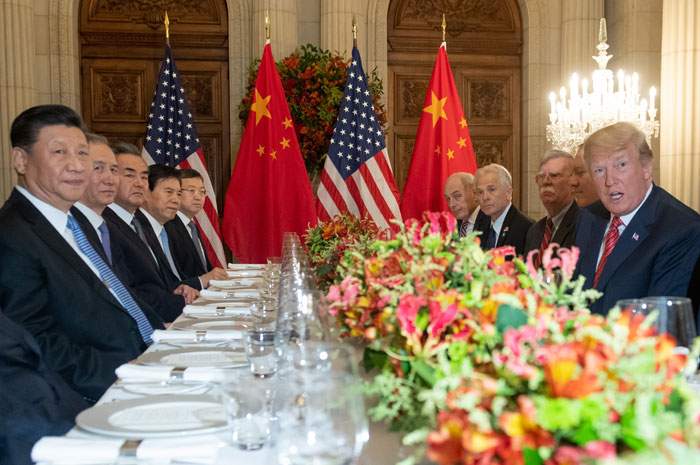

Xi Jinping and Donald Trump at dinner, December 2018
But thousands of kilometres north in Canada, an arrest was taking place that would throw doubt on this rapprochement.
Meng Wanzhou, Huawei’s chief financial officer and Ren Zhengfei’s eldest daughter, had been detained by Canadian officials while transferring between flights at Vancouver airport.
The arrest had come at the request of the US, who accused her of breaking sanctions against Iran.
“When she was detained, as her father, my heart broke,” says Ren, visibly emotional. “How could I watch my child suffer like this? But what happened, has happened. We can only depend on the law to solve this problem.”

Meng Wanzhou being driven to court in Canada
Huawei’s problems were just beginning. Nearly two months later, the US Department of Justice filed two indictments against Huawei and Ms Meng.
Under the first indictment, Huawei and Ms Meng were charged with misleading banks and the US government about their business in Iran.
The second indictment – against Huawei – involved criminal charges including obstruction of justice and the attempted theft of trade secrets.
Both Huawei and Ms Meng deny the charges.

January 2019: Acting US attorney general Matthew Whittaker announces charges against Huawei and Meng Wanzhou
The charge of stealing trade secrets centres on a robotic tool – developed by T-Mobile – known as Tappy.
According to legal documents, Huawei had tried to buy Tappy, a device which mimicked human fingers by tapping mobile phone screens rapidly to test responsiveness.
T-Mobile was in partnership with Huawei at the time, but it rebuffed the Chinese firm’s offers, fearing it would use the technology to make phones for T-Mobile’s competitors.

It’s alleged that one of Huawei’s US employees then smuggled Tappy’s robotic arm into his satchel so that he could send its details to colleagues in China.
After the alleged theft was discovered, the Huawei employee claimed that the arm had mistakenly fallen into his bag.
Huawei claimed that the employee had been acting alone, and the case was settled out of court in 2014. But the latest case is built on email trails between managers in China and the company’s US employees, linking Huawei management to the alleged theft.
The indictment also details evidence of a bonus scheme from 2013, offering Huawei employees financial rewards for stealing confidential information from competitors.
Huawei has denied any such scheme exists.

Meng Wanzhou, photographed in 2014
This is not the first time that Huawei has been accused of stealing trade secrets. Over the years companies like Cisco, Nortel and Motorola have all pointed the finger at the Chinese firm.
But US fears about Huawei are about much more than industrial espionage. For more than a decade, the US government has seen the company as little more than an arm of the Chinese Communist Party.
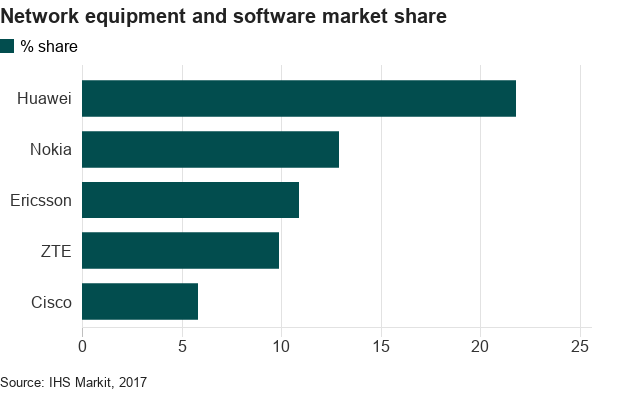
These concerns have been brought to the fore with the advent of “fifth generation” or 5G mobile internet, which promises download speeds 10 or 20 times faster than at present, and much greater connectivity between devices.
As the world’s biggest telecoms infrastructure provider, Huawei is one of the companies best placed to build new 5G networks. But the US has warned its intelligence partners that awarding contracts to Huawei would be tantamount to allowing the Chinese spy on them.
US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo recently cautioned against Huawei, saying, “If a country adopts this and puts it in some of their critical information systems, we won’t be able to share information with them.”

US Secretary of State Mike Pompeo
The UK, Germany and Canada are reviewing whether Huawei’s products pose a security threat.
Zhou Daiqi is Huawei’s chief ethics and compliance officer.
He’s been with the company for nearly 25 years, in a number of different positions – chief engineer, director of the hardware department, head of the research centre in Xi’an, according to his biography on the company’s website. He is also understood to combine his high-ranking executive duties with another role – party secretary of Huawei’s Communist Party committee.
All companies in China are required by law to have a Communist Party committee.
Zhou Daiqi’s profile on Huawei’s website
The official line is that they exist to ensure that employees uphold the country’s moral and social values. Representatives of the committee are also often tasked with helping workers with financial problems.
But critics of China’s one-party system argue that they allow the state to exert control on corporate China. And they say the level of this control has increased in recent years.
“[President] Xi Jinping is exerting greater control over the business community in China,” says Elliott Zaagman, who regularly advises Chinese companies on their PR strategy. “As these companies gain power and influence overseas, the party doesn’t want to lose control over them.”
Ren, however, argues that the role of Huawei’s Communist Party committee is far less important than many in the West believe.
“[It] serves only to educate its employees,” he says. “It is not involved in any business decisions.”
In China, most chief executives are Communist Party members.
Every year, they dutifully turn up to the National People’s Congress along with local and national party chiefs, officials and chief executives.
It’s where the big economic decisions are voted on – although no proposal is put forward which hasn’t already been agreed upon.
Still, big CEOs come to show their commitment to the party, and to contribute to working papers that are meant to help the government understand the concerns of the business community.
Being a member of the party is very much a networking opportunity – in the way one would join a business association.
Elliott Zaagman argues that this is a system that demands loyalty.
“There is no separation from the party and the state,” he says.
“The system in China encourages the lack of transparency in companies like Huawei.”

The worry is that these close links mean that if the Communist Party asked a company to do something, they would have no choice but to comply.
And if that company is one that is involved in sensitive global telecoms infrastructure projects, it’s easy to see why Western observers would be worried.
There is no evidence to indicate that Huawei is in any way under the orders of the Chinese government, or that Beijing has any plans to dictate business plans and strategy at Huawei – particularly when it comes to spying.
But the way in which the Chinese Communist Party has robustly defended Huawei has raised questions about how independent the company is of its influence.
For example, Beijing stated that Ms Meng’s detention was a rights abuse .
And while her extradition case to the US was moving forward, China detained two Canadian citizens and accused them of stealing state secrets. Critics say the detentions are linked to Ms Meng’s arrest.

December 2018: Chinese police patrol outside Canada’s embassy in Beijing
While not commenting on the arrest of the Canadians, Ren says China’s defence of Huawei is understandable.
“It is the Chinese government’s duty to protect its people,” he says. “If the US attempts to gain competitive edge by undermining China’s most outstanding hi-tech talent, then it is understandable if the Chinese government, in turn, protects its hi-tech companies.”
Over the past few years, there have been signs of a bigger push by the government to get private companies, and in particular tech firms, to cooperate with party rules – even when they are firmly resistant.

A Didi Chuxing logo adorns a building in Hangzhou, China
China’s ride-hailing giant Didi Chuxing’s troubles are an example of the struggles Chinese firms face when they try to uphold their independence in the face of government pressure.
Chinese attitudes to data collection and data privacy are different to those in the West – many people don’t care if businesses have access to their data, arguing that it adds to the convenience of life and work.
Government access to data in China is not the free-for-all that many outside of China assume it to be
So it wasn’t unusual when, after the murders of two of its passengers by Didi drivers, regulators used the scandal to force Didi to share more corporate data with the government. But Didi resisted – citing customer privacy. Under Chinese law, it had no choice but to comply.
When it did, it handed over “three boxes of data printed on paper, including 95 hard copies for authorities to review”.
According to Samm Sacks of the Center for Strategic and International Studies (CSIS), the case demonstrates that “government access to data in China is not the free-for-all that many outside China assume it to be”.
She says this indicates that there appears to be “a kind of tug of war between the government and companies over data”.
How this plays out will determine how Chinese companies are viewed by foreign governments when they do business overseas.
Companies like Huawei have grown up in a system where to survive and thrive they needed strong links to the Chinese government – there was and is no other choice. But these links could harm their reputation abroad.
“It’s two different systems,” says Zaagman. “Think of it like an electrical outlet. China’s plug doesn’t fit in to the outlets we have in the West.”
“Basically you want to connect to everything that can be connected.”
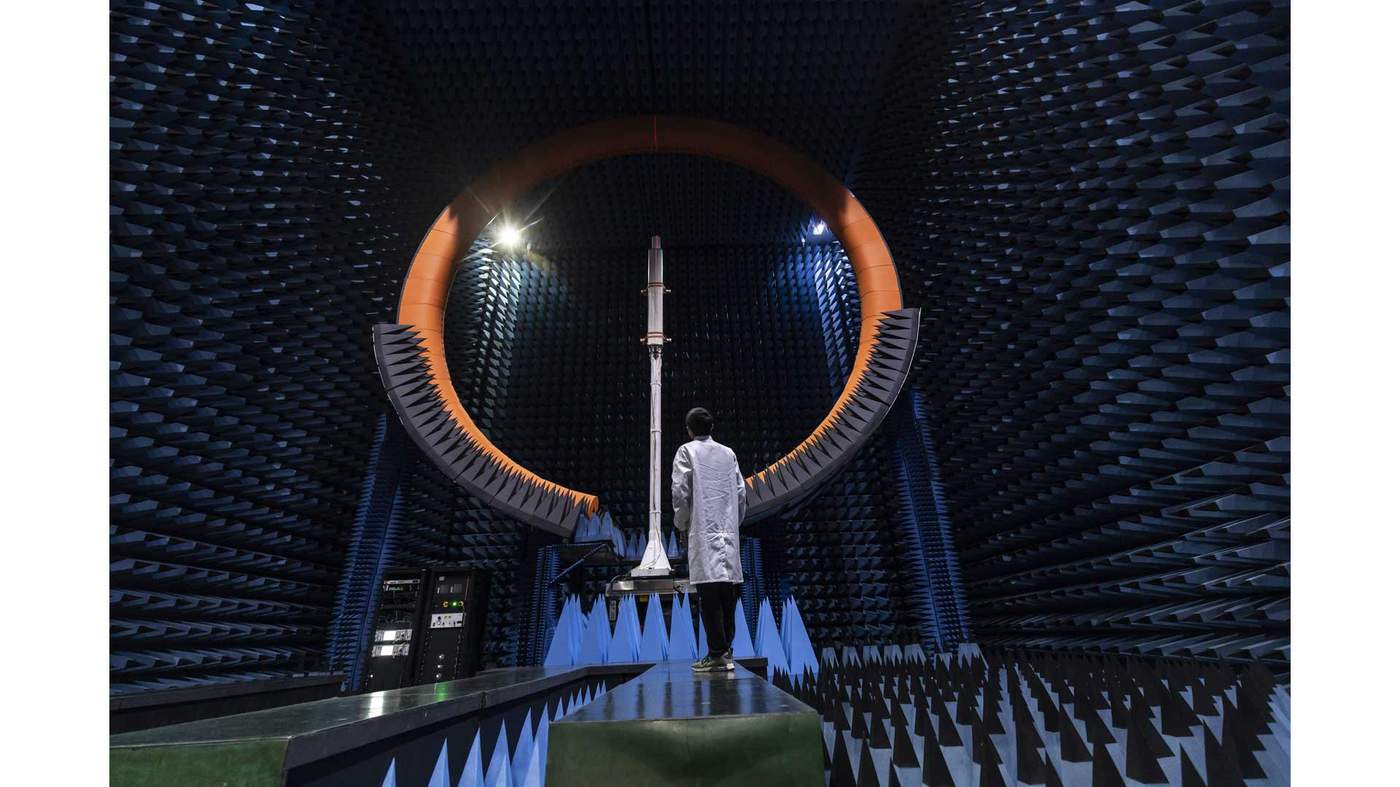
Zhu Peiying, head of Huawei’s 5G wireless labs, is showing off devices that can connect to the new technology. From a smart toothbrush that collects data about how well you brush your teeth, to a smart cup that reminds you when you should drink some water, this is a world where everything you can think of is being measured and analysed.
At its most sophisticated, everything in entire cities would be connected – driverless cars, the temperature of buildings, the speed of public transport – the list is endless.
Huawei is thought to be a year ahead of its competitors in terms of its technological expertise and what it can offer customers, according to industry sources.

It’s also thought that the company can offer prices that are about 10% cheaper than its competitors, although critics claim this is because of state support.
Ren dismisses this, saying that Huawei doesn’t receive government subsidies.
He says the real reason behind the US resistance to Huawei is its superior technology.
“There’s no way the US can crush us,” he says. “The world needs Huawei because we are more advanced. Even if they persuade more countries not to use us temporarily we could just scale things down a bit.”

Ren is sanguine about such concerns.
“For countries who believe in them [suspicions about Huawei] we will hold off,” he says. “For countries who feel Huawei is trustworthy, we may move a little faster. The world is so big. We can’t walk across every corner of it.”
But this is about more than just one company or one CEO and his family.
Increasingly, this is perceived as a battle between two world orders, and which one is the future.
In the early days of China opening up, US presidents like George HW Bush espoused the merits of engagement.
“No nation on Earth has discovered a way to import the world’s goods and services while stopping foreign ideas at the border,” he said in a 1991 speech. “Just as the democratic idea has transformed nations on every continent, so, too, change will inevitably come to China.”
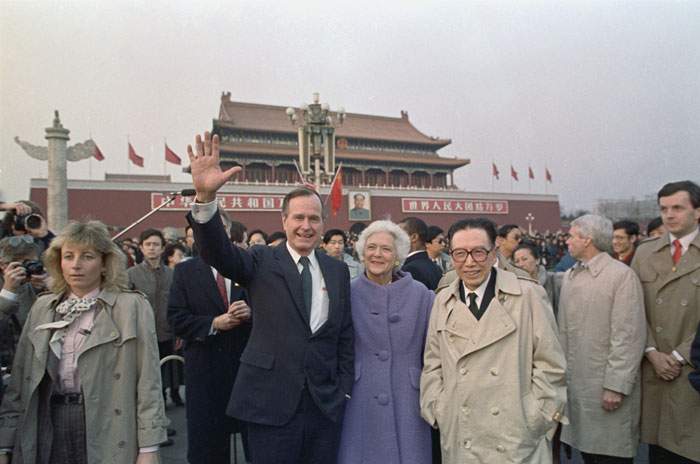

1989: George HW Bush in Beijing – he encouraged economic engagement with China
Previous US administrations believed that economic engagement in China would lead to China following a freer, more “liberal” path.
There’s no denying China has made remarkable strides in the past 40 years. The economy grew by an annual average of 10% for three decades, helping to lift 800 million people out of poverty. It is now the second-largest economy in the world, only surpassed by the US.
Some estimates put China’s economy ahead of America’s by 2030.
It achieved this while maintaining one-party rule and the supremacy of the Communist Party.
But its success has raised concerns that it is only possible with a huge amount of government control over the country’s companies. The fear is that control could be used to achieve the Communist Party’s goals – which are at this point unclear.
“It’s a double-edged sword for China,” says Danielle Cave. “[Because of its laws] the Chinese Communist Party has made it virtually impossible for Chinese companies to expand without attracting understandable and legitimate suspicion.”
Added to this, China has become more authoritarian under Xi Jinping’s rule.

President Xi Jinping
“Xi is systematically undermining virtually every feature that made China so distinct and helped it work so well in the past,” writes Jonathan Tepperman, editor in chief of Foreign Policy.
“His efforts may boost his own power and prestige in the short term and reduce some forms of corruption. On balance, however, Xi’s campaign will have disastrous long-term consequences for his country and the world.”
But Ren dismisses this, insisting that China is more open than ever before.
“If this meeting took place 30 years ago,” he says of our interview, “it would have been very dangerous for me. Today, I can be straightforward when answering difficult questions. This shows that China has a more open political environment.”
Still, Ren is hopeful of the direction China will take in the future.
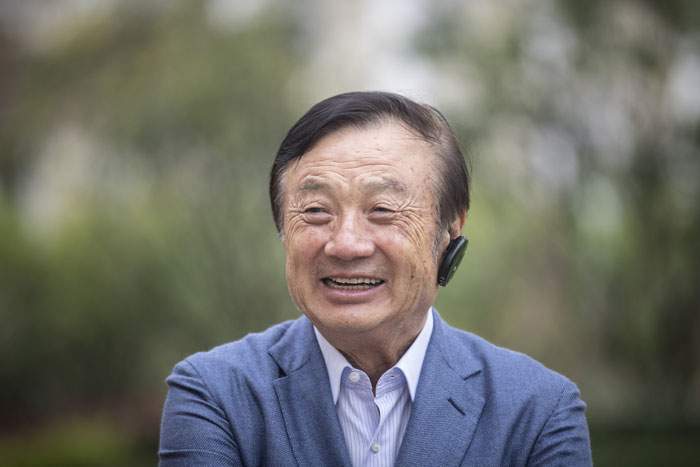

“China has more or less tried to close itself off from the outside world for 5,000 years,” he says. “Yet we had found ourselves poor, lagging behind other nations. It was only in the past 30 years since Deng Xiaoping opened China’s doors to the world that China has become more prosperous. Therefore, China must continue to move forward on the path of reform and opening-up.”
In one of Huawei’s vast campus sites across Shenzen, lies a man-made lake. Swimming in these serene waters are two black swans.
There is a story that Ren put the birds here to remind employees of “black swan” events – unpredictable and catastrophic financial eventualities that are impossible to prepare for. He dismisses this as an urban myth, but it’s hard not to read something into it.
For Huawei, and Ren, these are highly uncertain times with no way of telling what lies ahead.
Source: The BBC





