30/07/2019
MANILA, July 29 (Xinhua) — The military-to-military relationship between China and the Philippines has become an important part of the bilateral relations, Chinese Ambassador to the Philippines Zhao Jianhua said on Monday.
“China-Philippines relations have achieved positive turnaround, consolidation and elevation over the past three years, and have entered a new stage of development,” Zhao said in a speech at a reception marking the 92nd anniversary of the founding of the People’s Liberation Army (PLA) of China.
“We have increased contacts and exchanges,” he said, referring to the series of recent military exchanges made by both countries.
In January 2019, the Chinese naval escort fleet, composed of three vessels, paid a five-day friendly visit to the Philippines, he said.
In April 2019, the Philippine Navy sent its amphibious warfare ship BRP Tarlac to participate in the international fleet review during the 70th anniversary celebration of PLA Navy in Qingdao, China, he added.
He further said that members of the Command and General Staff College students of the Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP) just concluded their educational and cultural tour in China recently.
“PLA stands ready to deepen the mutual understanding, mutual trust and mutual confidence with our Filipino counterparts, and to jointly safeguard regional peace and stability,” Zhao said.
As a result of the concerted efforts of China, the Philippines and other countries in the region, the situation in the South China Sea “has been stabilized in general, with growing momentum for cooperation and increasing positive factors,” Zhao said, adding that China stays committed to peace and stability in the South China Sea.
“China respects and upholds the freedom of navigation and overflight enjoyed by all states under international law in the South China Sea, and stays ready to work with other coastal states and the international community to ensure the safety of and the unimpeded access to the international shipping lanes in the South China Sea,” Zhao said.
For his part, Philippine Defense Secretary Delfin Lorenzana said at the reception that the Philippines is also “committed to the resolution of disputes through peaceful means.”
Lorenzana added that he is looking forward to “more shared endeavors, mutually productive and beneficial cooperation and partnership agreements” with China “to create understanding and friendship between our two nations.”
Source: Xinhua
Posted in amphibious warfare ship, Armed Forces of the Philippines (AFP), BRP Tarlac, China-Philippines ties, Chinese ambassador, Chinese naval escort fleet, Command and General Staff College, Filipino, important part, international shipping lanes, Military-to-military relationship, People's Liberation Army (PLA), Philippine Defense Secretary, Philippine Navy, pla navy, Qingdao, South China Sea, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
09/07/2019
- Ambassador to China Vikram Misri says they will be ‘meeting more and more in common waters’, and more exchanges are needed
- He also says preparations are under way for President Xi Jinping to visit India
The INS Kolkata arrives in Qingdao for PLA Navy 70th anniversary celebrations in April.
The Indian ambassador called for more communication between the two navies. Photo: Reuters
The Chinese and Indian navies should establish communication because they are increasingly operating within close proximity, according to India’s ambassador to China.
While the two nations’ militaries communicated extensively, it was mainly between their land forces, and that should be extended to the navies and air forces, Vikram Misri said.
“We need to talk about the two air forces and the two navies – especially the two navies – because we are operating in the same waters and increasingly in the coming years, we will be meeting more and more in common waters,” Misri said.
“I think it is important for us to develop those levels of understanding and communication,” he said. “There are some [navy and air force] exchanges now, but not as well developed as in the case of the land force.”
China and India have made efforts to repair their relations since a tense stand-off at the Doklam plateau two years ago, when communications between their forces along the border were seen as inadequate to contain the tension.
China and India have sought to repair relations after a tense stand-off at Doklam. Photo: AFP
Misri said the two nations had made incremental progress, and opened new points where “border personnel can meet and exchange information, or exchange views about any particular situation”.
The ambassador was visiting the Indian consulate in Hong Kong over the weekend, six months after taking up the post and six weeks after Prime Minister Narendra Modi was re-elected.
He said preparations were under way for Chinese President Xi Jinping to visit India, which was expected to happen in the fourth quarter, after they pledged earlier to strengthen cooperation.
Tensions between
have periodically flared along their 4,000km (2,485-mile) border, resulting in a brief war in 1962. Relations have also been strained by China’s ties with Pakistan, and India’s concern over China’s growing presence in the Indian Ocean.
India has also not signed on to China’s global trade and infrastructure strategy, the
, which has projects that run through the disputed Kashmir region.
“Our concerns with regards to this particular initiative are very clear, and we have continued to share them very, very frankly with our Chinese partners,” Misri said. “I think there is understanding on the part of our Chinese partners with regard to this.”
Indian ambassador to China Vikram Misri said New Delhi’s concerns on the Belt and Road Initiative were clear. Photo: Xiaomei Chen
But he said the two nations should not let their differences evolve into disputes, and they should focus on areas where they can cooperate.
One such area was maritime and investment cooperation in the Indo-Pacific region, including infrastructure and disaster response. The US in recent years has focused on the Indo-Pacific region, and has asked its allies to send naval vessels to the area as a counterbalance to Beijing.
“We have made the point that our vision of the Indo-Pacific is not a strategy, which sometimes is a concern on the part of some partners, aimed against any particular country,” Misri said. “It is definitely not a military alliance in any format.
“It is on the other hand a vision that aims at economic and development cooperation with our partners in the Indo-Pacific space,” he said, adding that India was discussing such cooperation with China.
He also said trilateral meetings between China, India and Russia would become more regular after their three leaders met on the sidelines of the
summit in Osaka, Japan last month, when they vowed to uphold multilateralism.
Those meetings would allow the nations to address challenges facing the international trading system and pushback against globalisation, but Misri said they should not be seen as a bid to counter the US, which is also involved in a trade battle with India.
India also had a trilateral meeting with Japan and the United States during the G20 summit.
“The fact that these countries seek us out also shows that they see value in engaging with India, and we have important issues to discuss in each of these settings,” he said. “None of our individual relationships is going to come at the cost of a relationship with any other partner.”
The ambassador said there could be a broader consensus on counterterrorism. Photo: AP
Misri also said there could be a broader consensus between China and India on counterterrorism. The two nations have clashed over Indian efforts to blacklist Masood Azhar, leader of the Pakistan-based terror group Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), at the United Nations, which China objected to for years – a move seen in India as being done at the behest of Islamabad.
Azhar was finally listed as a global terrorist by the UN in May, after JeM claimed responsibility for a deadly terror attack on Indian security forces in Pulwama in February, although the listing did not directly reference the attack.
“It could have happened earlier … but I’m glad that it did happen, and we hope to build on that – that should be taken as progress, and we hope to build on that in the coming years,” Misri said.
“Everybody is aware of the context in which the listing happened, and therefore, I don’t think it’s hidden from anybody as to what this was aimed at or who this was aimed at, or what the motivation for the action might have been.”
As for the tensions between India and Pakistan following the terror strike in Indian-controlled Kashmir, Misri said progress would be “largely dependent on Pakistan” and the actions it needed to take to address the “ecosystem of terror that prevails in different parts of that country”.
Source: SCMP
Posted in 70th anniversary, Ambassador Vikram Misri, Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), celebrations, Chinese navy, Chinese President Xi Jinping, communicate, counterterrorism, Doklam plateau, ecosystem of terror, Group of 20 (G20), Hong Kong, Indian ambassador to China, Indian consulate, indian navy, Indian-controlled Kashmir, INS Kolkata, Jaish-e-Mohammed (JeM), Japan, Masood Azhar, Osaka, pla navy, President Xi Jinping, Prime Minister Narendra Modi, Qingdao, Russia, Uncategorized, US, We need to talk |
Leave a Comment »
10/06/2019
- With a defence budget second only to the US, China is amassing a navy that can circle the globe and developing state-of-the-art autonomous drones
- The build-up is motivating surrounding countries to bolster their own armed forces, even if some big-ticket military equipment is of dubious necessity
Chinese President Xi Jinping reviews an honour guards before a naval parade in Qingdao. Photo: Xinhua
The Asia-Pacific region is one of the fastest-growing markets for arms dealers, with economic growth, territorial disputes and long-sought military modernisation propelling a 52 per cent increase in defence spending over the last decade to US$392 billion in 2018, according to the Stockholm International Peace Research Institute.
The region accounts for more than one-fifth of the global defence budget and is expected to grow. That was underscored last week by news of
’s bid to strike a
to purchase US tanks and missiles.
Taiwanese Soldiers on a CM11 battle tank, jointly developed with US arms manufacturer General Dynamics. Photo: EPA
The biggest driver in arms purchases, however, is
– responsible for 64 per cent of military
spending in the region. With a defence budget that is second only to the
, China is amassing a navy that can circle the globe and developing state-of-the-art autonomous drones. The build-up is motivating surrounding countries to bolster their armed forces too – good news for purveyors of submarines, unmanned vehicles and warplanes.
It is no coincidence that the recent
in
, a security conference attended by
chiefs, was sponsored by military contractors including Raytheon,
and
.
Opinion: How the Shangri-La Dialogue turned into a diplomatic coup for China
Kelvin Wong, a Singapore-based analyst for Jane’s, a trade publication that has been covering the defence industry for 121 years, has developed a niche in infiltrating China’s opaque defence industry by attending obscure trade shows that are rarely advertised outside the country.
He said the US is eager to train allies in Asia and sell them arms, while also stepping up its “freedom of navigation” naval operations in contested waters in the
and Taiwan Strait. It has lifted a ban on working with
’s special forces over atrocities committed in
. And it is considering restarting arms sales to the
.
In his speech at the Shangri-La Dialogue, acting US Defence Secretary Patrick Shanahan touted American advancements in technology “critical to deterring and defeating the threats of the future” and said any partner could choose to win access to that technology by joining the US defence network.
Wong said the message was clear: “Buy American.”
Analysts say Chinese soldiers have less training, motivation and lower morale than their Western counterparts. Photo: Reuters
The analyst said there is a growing admission among the Chinese leadership that the
has an Achilles’ heel: its own personnel.
He said one executive at a Chinese defence firm told him: “The individual Chinese soldier, in terms of morale, training, education and motivation, (cannot match) Western counterparts. So the only way to level up is through the use of unmanned platforms and
To that end, China has developed one of the world’s most sophisticated drone programmes, complete with custom-built weapon systems. By comparison, Wong said,
US drones rely on weapons originally developed for helicopters.
Wong got to see one of the Chinese drones in action two years ago after cultivating a relationship with its builder, the state-owned China Aerospace Science & Technology Corporation. He viewed a demonstration of a 28-foot-long CH-4 drone launching missiles at a target with uncanny ease and precision.
“Everyone knew they had this,” Wong said. “But how effective it was, nobody knew. I could personally vouch they got it down pat.”
China unveils its answer to US Reaper drone – how does it compare?
That is what Bernard Loo Fook Weng, a military expert at Singapore’s S. Rajaratnam School of International Studies, told the author Robert Kaplan for his 2014 book, Asia’s Cauldron, about simmering tensions in the South China Sea.
He was describing the competition for big-ticket military equipment of dubious necessity.
is littered with examples of such purchases.
owns an aircraft carrier without any aircraft. Indonesia dedicated about one-sixth of its military budget to the purchase of 11
Su-35 fighter jets. And
splurged on two
submarines it could not figure out how to submerge.
“It’s keeping up with the Joneses,” Wong said. “There’s an element of prestige to having these systems.”
Submarines remain one of the more debatable purchases, Wong said. The vessels aren’t ideal for the South China Sea, with its narrow shipping lanes hemmed in by shallow waters and coral reefs. Yet they provide smaller countries with a powerful deterrence by enabling sneak attacks on large ships.
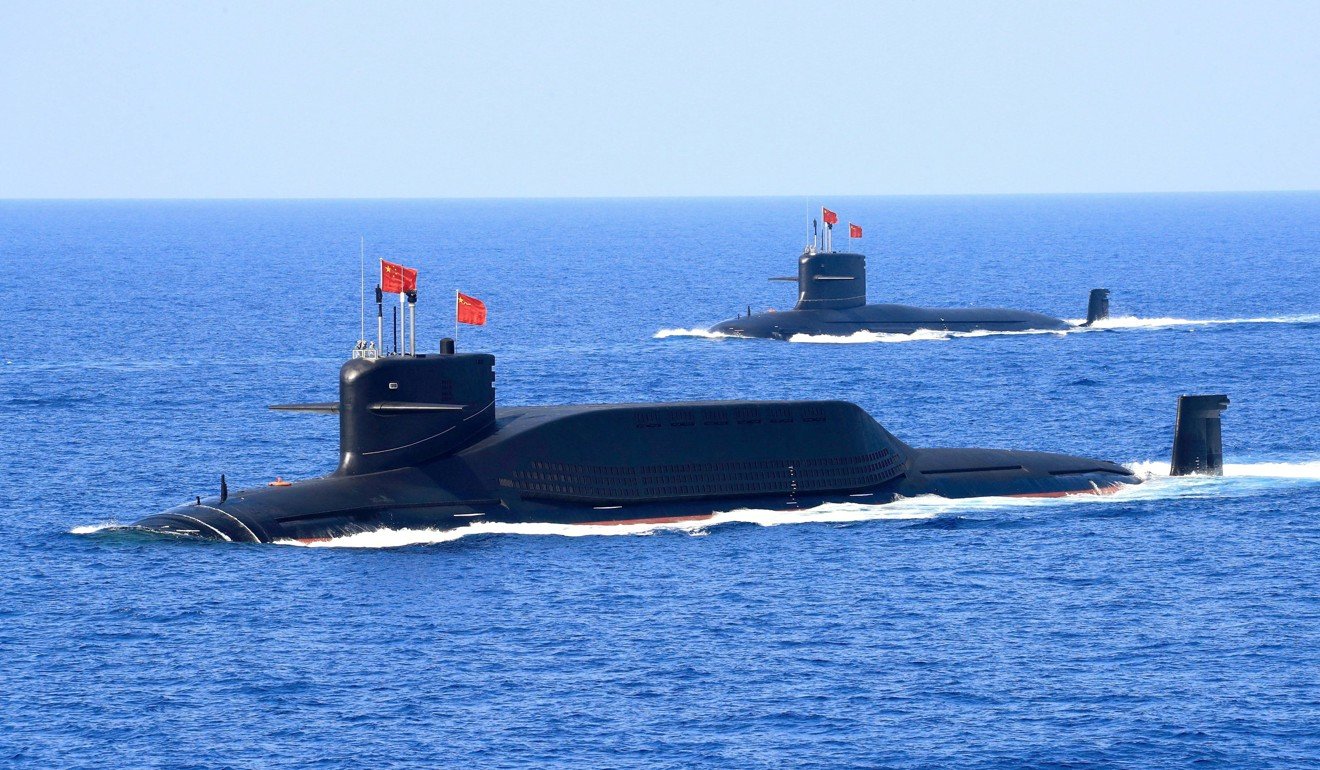
Nuclear-powered PLA Navy ballistic missile submarines in the South China Sea. Photo: Reuters
Asia and
are home to 245 submarines, or 45 per cent of the global fleet, according to the US-based naval market intelligence firm AMI International.
The Philippines remains one of the last coastal nations in the region without a sub – though it is in talks with Russian builders to acquire some.
Singapore recently received the first of four advanced
Type 218 submarines with propulsion systems that negate the need to surface more frequently. If the crew did not need to eat, the submarine could stay under water for prolonged periods. Wong said the craft were specially built for Asian crews.
“The older subs were designed for larger Europeans so the ergonomics were totally off,” he said.
Singapore, China deepen defence ties, plan larger military exercises
Tiny Singapore plays a crucial role securing the vital sea lanes linking the Strait of Malacca with the South China Sea. According to the
the country dedicates 3.3 per cent of its gross domestic product to defence, a rate higher than that of the United States.
State-of-the-art equipment defines the Singapore Armed Forces. Automation is now at the centre of the country’s military strategy, as available manpower is shrinking because of a rapidly ageing population.
Wong said Singapore is investing in autonomous systems and can operate frigates with 100 crew members – 50 fewer than they were originally designed for.
“We always have to punch above our weight,” he said.
Source: SCMP
Posted in artificial intelligence (AI), Asia, Asia-Pacific region, Australia, autonomous drones, BAE Systems, China Aerospace Science & Technology Corporation, East Timor, French, frigates, German, Indonesia, Lockheed Martin, Malaysia, military spending, naval parade, navy, People’s Liberation Army, President Xi Jinping, Qingdao, Raytheon Co, ripple effect, Russian, Shangri-La Dialogue, Singapore, Singapore Armed Forces, South China Sea, Southeast Asia, Stockholm International Peace Research Institute, Strait of Malacca, submarines, Taiwan Strait, Thailand, the Philippines, Uncategorized, unmanned vehicles, US Reaper drone, warplanes, World Bank |
Leave a Comment »
04/06/2019
- Unveiled in Shandong, prototype will be a first step towards ground-breaking high-speed travel that will rival passenger jets, project engineer says
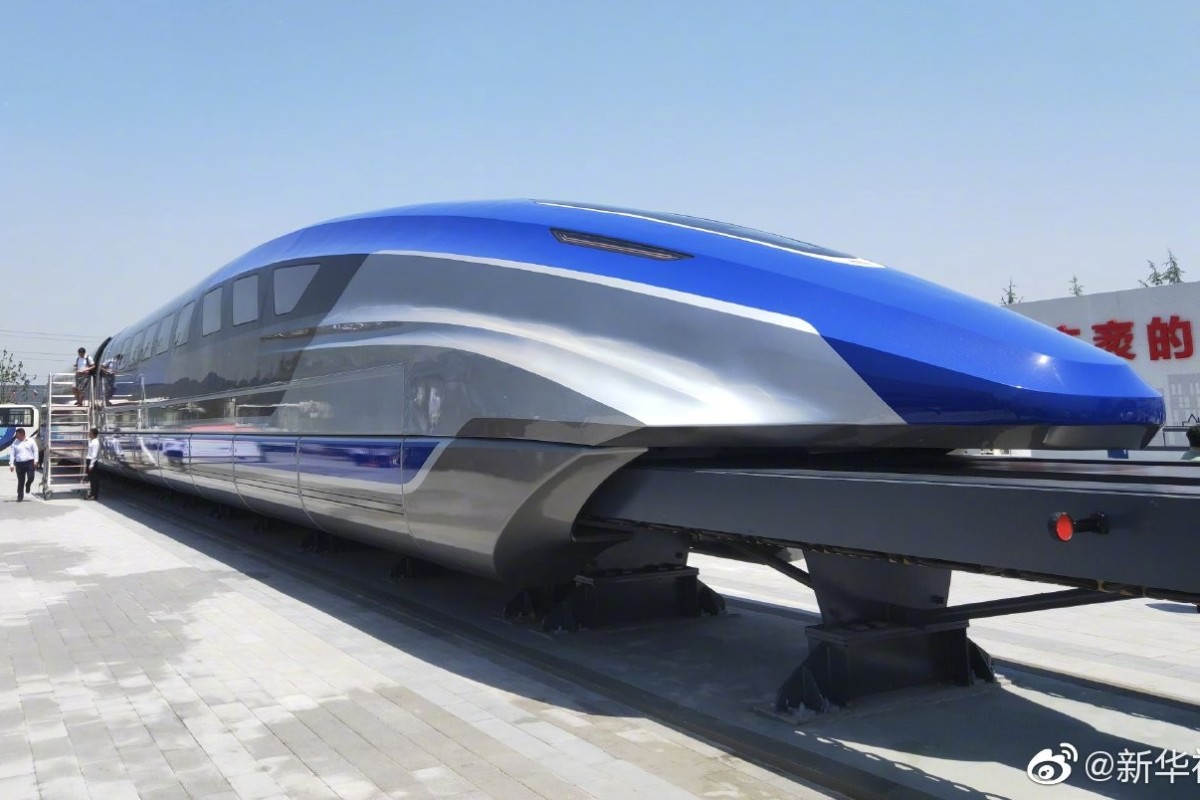
One possible future for rapid transport in China is unveiled in the form of a magnetic levitation train at Qingdao in Shandong province. Photo: Weibo
An experimental magnetic levitation train capable of travelling at 600km/h went on show at Qingdao in eastern Shandong province on Thursday, state media said.
Powerful electromagnets hold the Qingdao prototype at a thumb’s width from the rail, giving a quiet, smooth ride at speeds close to those involved in air travel, developers said.
While China operates the world’s fastest conventional train service, which can reach a speed of 350km/h, the Shanghai Maglev has been in commercial operation since the end of 2002 and can reach a top speed of 430km/h. It operates on one 30-kilometre (19-mile) line between two stations.
Ding Sansan, deputy chief engineer with developer the CRRC Sifang Corporation, said China achieved breakthroughs in maglev technology during the “three-year-battle” to build the new train that involved cooperation between more than 30 enterprises, universities and government research institutes.
The construction of a train body with ultra-lightweight, high-strength materials was a challenge, Ding said. Complex physical problems created by high speeds also needed to be solved in new ways if the Qingdao prototype was to reach peak performance.
China was a leader in technologies that included suspension, guidance, control and high-powered traction, Ding told Qingdao Daily.
“The test vehicle has been powered up and is in good order,” Ding was quoted by the newspaper as saying.
Chinese maglev train capable of travelling at 600km/h on track for 2020 test run as design completed
The prototype promised to eliminate the advantages jet passenger planes had over ground vehicles over a distance of 1,500km, he said.
Taking Beijing-to-Shanghai by plane as an example, Ding suggested: “It takes about four-and-a-half hours by plane including preparation time for the journey; about five-and-a-half hours by high-speed rail, and [would] only [take] about three-and-a-half hours by maglev.”
While earlier reports suggested the prototype was expected to begin full-scale testing by 2020, it was unclear what Thursday’s unveiling meant for this timetable.
China’s latest prototype high-speed maglev train factors the comfort of paying customers into its test operations. Photo: Weibo
More maglevs would join the development project in the coming months, the team leader was quoted as saying, while mass production of the technology was likely by 2021.
In contrast to the optimism of the team at Qingdao, Chen Peihong, professor of economics at Beijing Jiaotong University and a transport analyst, was more circumspect about the future of maglev trains.
“The market has to be bigger. Technology alone cannot make [the concept] a success,” she said.
Plane or train: as high-speed rail link connects Hong Kong to 44 mainland Chinese cities, what are cheapest and fastest ways to get where you are going?
Public transport relied heavily on economies of scale, Chen said. Chinese cities including Jinan, Hangzhou and Chongqing were considering maglev lines, but even the longest – from Jinan to Taian – would not exceed 50 kilometres.
Chen said that electromagnetic fields from maglevs were greater than those from the lines that powered high-speed trains, while environmental worries might keep maglevs out of densely-populated areas.
There was a debate in China in the early 2000s about the benefits of a developing a maglev compared to high-speed rail, researchers on that project said. Rail was preferred by the government because it was an established technology and one that was cheaper to realise.
By the end of last year, China’s high-speed rail network extended to most of the country at a distance in excess of 29,000 kilometres, according to government figures, twice as long as the rest of the world’s high-speed rail lines combined. Spain’s high-speed AVE network was the second-longest at 3,100km.
Elsewhere, researchers in Chengdu, Sichuan province, said a vehicle inside a vacuum tube powered by a superconductor coil from a maglev train – a hyperlink – was in development. They expected the vehicle to reach speeds in excess of 1,000km/h as air was pumped from the tube and resistance to the speeding object gradually eliminated.
Source: SCMP
Posted in air travellers, AVE network, Beijing Jiaotong University, Beijing-to-Shanghai, Chengdu, Chongqing, CRRC Sifang Corporation, down to earth, Hangzhou, High-speed rail, Hong Kong, Jinan, Jinan to Taian, maglev train, professor of economics, Qingdao, Qingdao Daily, shandong province, Shanghai Maglev, sichuan province, Spain, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
31/05/2019
BEIJING, May 30 (Xinhua) — Chinese and Russian military forces have maintained in-depth exchanges in 2019 to mark the 70th anniversary of the establishment of diplomatic ties between the two countries, the Ministry of National Defense said Thursday.
They have engaged in cooperation in high-level exchanges, real-combat training and military competitions, and had sound interaction and collaboration on international multilateral occasions, the ministry’s spokesperson Wu Qian said at a press conference.
Armies of the two countries have provided positive energy for safeguarding world peace and regional stability, Wu added.
Speaking of the joint naval exercise earlier this month in Qingdao, east China’s Shandong Province, Wu said the drill achieved a new high in making China-Russia joint naval exercises more real combat-oriented, information-based and standardized.
The two navies have also strengthened their capabilities of joint command and addressing maritime security threats, Wu said.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in China alert, China-Russia joint naval exercises, joint command, military exchanges, Ministry of National Defense, Qingdao, Russia, shandong province, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
18/05/2019
- Man hits glass with emergency hammer because ‘he had been drinking and felt ill’
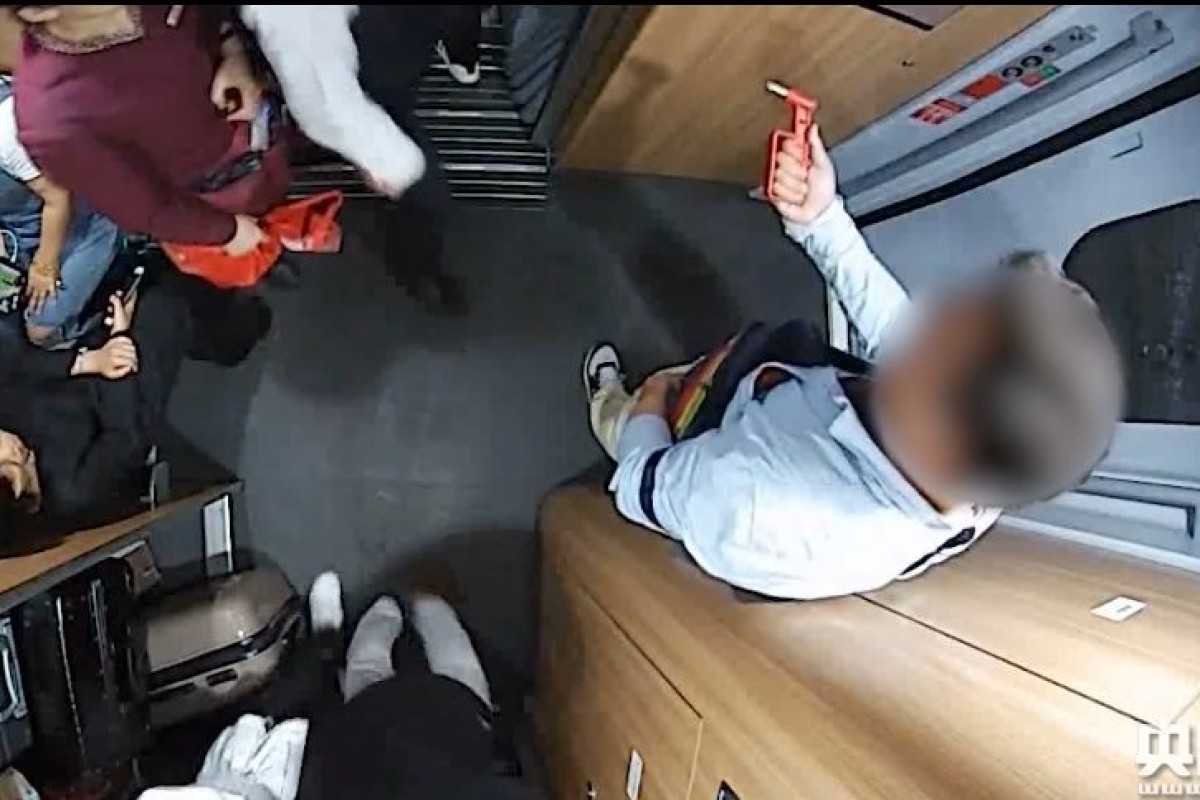
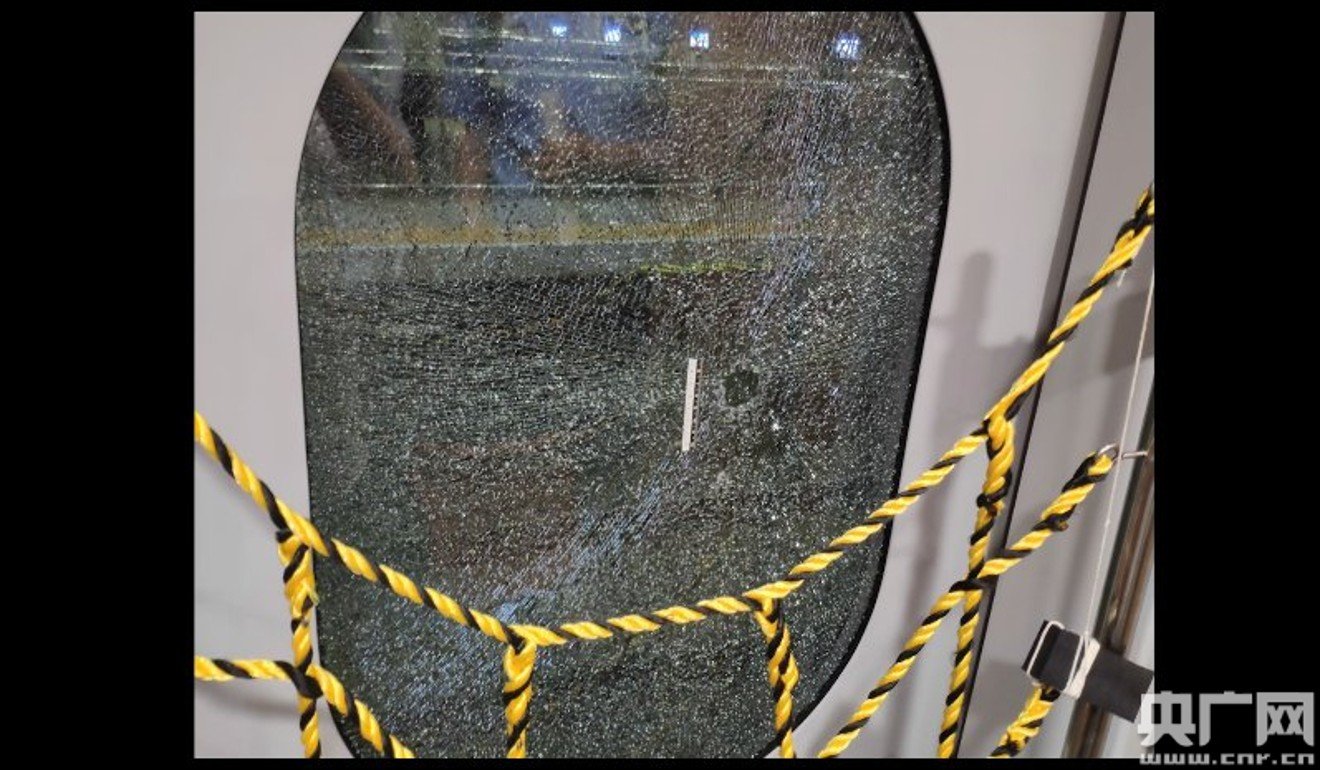
The train passenger tried to smash a hole in the door glass to let in some fresh air, according to Chinese media. Photo: CNR
Chinese railway police detained a passenger after he tried to smash the door window of a high-speed train to “get some fresh air” according to mainland media reports.
The 30-year-old man, identified only by his surname Xu, said he tried and failed to unlock the door and then decided to break the glass with an emergency hammer because he had been drinking and felt sick, China National Radio reported on Saturday.
Xu tried to smash the door after mechanical failure had forced the Beijing-bound train from Shanghai to stop at the main railway station in Jinan in Shandong province on Tuesday.
He said the train had been stranded for half an hour when he became impatient and wanted to have some fresh air, according to the report.
A Chinese train passenger attacked the door glass of a high-speed train as it was stranded in Jinan. Photo: CNR
Surveillance footage showed the man pulling on the door handle before hitting the glass with an emergency hammer mounted on a train wall.
Train staff quickly intervened and stopped Xu, who was taken into police custody after the train arrived in Beijing.
“I just smashed it once. I assumed this would allow air to come in, so I stopped,” Xu was quoted as saying.
“I felt unwell at that moment because I had been drinking at lunchtime. I did it on impulse.”
He was detained for allegedly intentionally damaging property, an offence that could lead to up to three years in jail.
The incident comes just a few months after a woman
to smash the window of a moving train on the way from Beijing to Qingdao.
The woman had been arguing with her boyfriend and hit the window in a fit of pique, according to media reports.
She was charged with criminal damage and sentenced to five days in detention.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Beijing, Beijing-bound train, China National Radio, Chinese passenger, criminal damage, detentions, emergency hammer, fit of pique, get some air, high-speed train window, Jinan, main railway station, Qingdao, shandong province, Shanghai, smash, Surveillance footage, Uncategorized |
Leave a Comment »
28/04/2019
- Police investigation finds nearly 40 people received the shots since January last year – before the drug was approved by the Chinese regulator
- Hainan hospital had rented out its medical cosmetics department to a beauty parlour, which authorities suspect administered the vaccinations
The Gardasil HPV vaccine has been in short supply in China since it was approved by the regulator last year. Photo: Shutterstock
A private hospital on Hainan Island has been closed down after it gave fake HPV vaccines to dozens of patients, including at least one who was pregnant, the local health authority said.
Police found 38 people had been given the fake shots at Boao Yinfeng Healthcare International Hospital, in the city of Boao, since January last year, the Health Commission of Hainan said in a statement on Sunday.
Some of the vaccines were found to have been smuggled in from overseas before the drug was approved in China, while others were illegally made in Jilin province.
The case is the latest in a series of scandals in recent years – including drug makers
and people including children being given fake, faulty or expired vaccines – that have rocked public confidence in the industry.
The hospital began administering the fake HPV shots three months before Merck’s Gardasil vaccine against human papillomavirus, which causes cervical cancer, was approved by the Chinese regulator in April last year. There has been a constant shortage of the vaccine since it was approved and a ballot system is used at some hospitals due to the huge demand and limited supply.
All of the Boao patients given fake shots had paid 9,000 yuan (US$1,300) to be immunised except for a hospital employee, who was vaccinated for free, the statement said.
The health commission said the hospital did not have approval to administer HPV vaccines and some of the shots were given before it officially opened in March last year.
Are Philippine children’s deaths linked to dengue vaccine?
It was also in breach of the hospital management regulation because it had rented out its medical cosmetics department to a beauty parlour from Qingdao, which authorities suspect administered the fake vaccinations.
Its medical institution business licence was revoked and the hospital was fined 8,000 yuan, while authorities have confiscated the illegal proceeds of the fake vaccinations. It was not known whether any arrests had been made in the case, and the investigation was continuing.
The scandal came to light in March when a man posted on the People’s Daily website his complaint to the health authority about his pregnant wife being told by police she was given a fake HPV shot.
Another patient, who identified herself as Wang Xi, wrote on microblog site Weibo last week that she was told the hospital could receive the vaccine before it was officially approved because it was located in a medical tourism pilot zone, giving it preferential access to treatments.
“As a victim, I’m constantly worried – what have they injected into my body?” Wang wrote.
Source: SCMP
Posted in ballot system, beauty parlour,, Boao, Boao Yinfeng Healthcare International Hospital, China alert, China-Pakistan Economic Corridor (CPEC), China-Pakistan relations, closed down, confiscated, dengue vaccine, dozens of patients, fake HPV vaccines, Gardasil HPV vaccine, Hainan hospital, human papillomavirus, illegal proceeds, investigation, medical cosmetics department, medical institution business licence, medical tourism pilot zone, Merck’s Gardasil vaccine, microblog site, People’s Daily, Philippine, pregnant woman, Private hospital, Qingdao, revoked, Uncategorized, Wang Xi, Weibo |
Leave a Comment »
21/04/2019
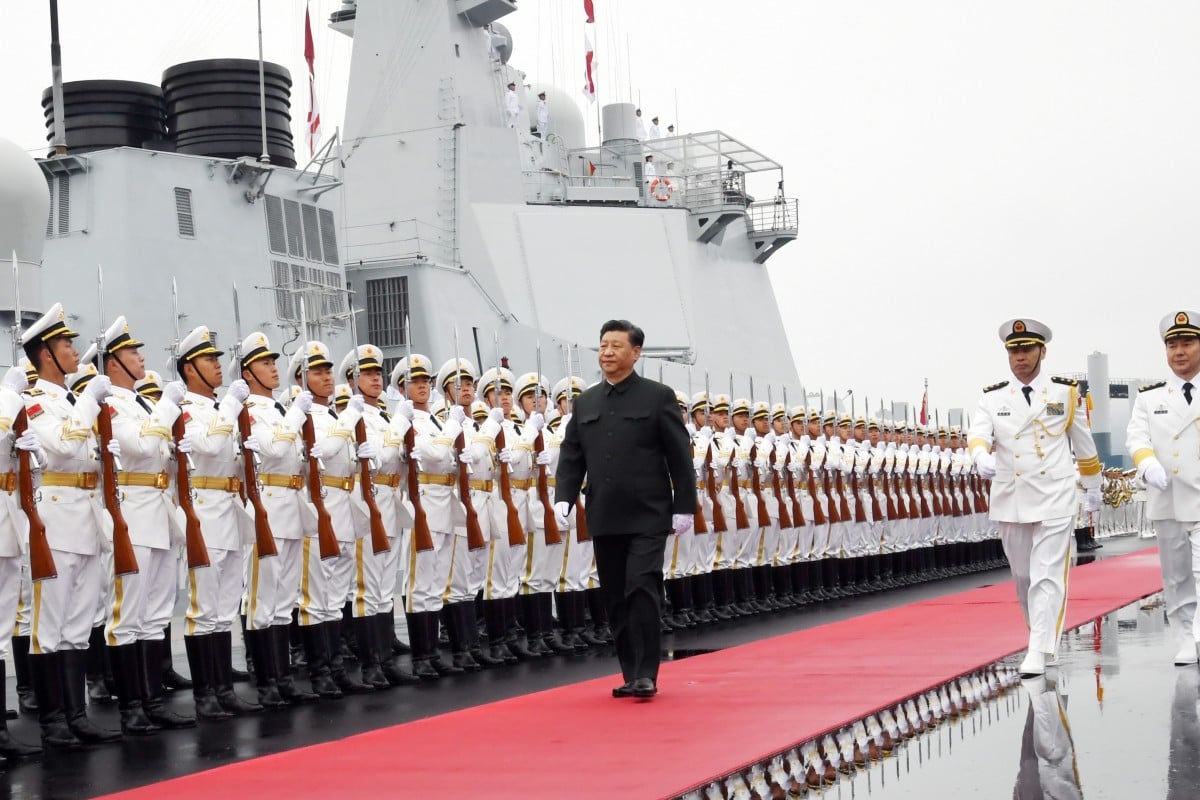
QINGDAO, China (Reuters) – Warships from India, Australia and several other nations arrived in the eastern Chinese port city of Qingdao on Sunday to attend a naval parade, part of a goodwill visit as China extends the hand of friendship despite regional tensions and suspicions.
China on Tuesday will mark 70 years since the founding of the People’s Liberation Army Navy, where it will show off new warships including nuclear submarines and destroyers at a major review in the waters off Qingdao.
China says warships from about a dozen nations are also taking part – one diplomatic source with direct knowledge said it was 13 countries in total – and the PLA is putting its best foot forward to welcome them.
India, which has been at odds with China over their disputed land border and Beijing’s support for India’s regional rival Pakistan, has sent stealth guided-missile destroyer the “INS Kolkata” to take part, along with a supply ship.
“We bring to you one of the best ships that we have made. It is the pride of the nation and the navy, and we are very happy to be here,” Captain Aditya Hara told reporters on the dockside after disembarking from the ship in Qingdao.
A source familiar with the situation told Reuters the “Kolkata” had sailed through the Taiwan Strait to get to Qingdao, a sensitive waterway that separates China from self-ruled Taiwan, claimed by Beijing as sacred Chinese territory.
“We headed on a direct route and we are very happy that we were facilitated by the PLA Navy and they ensured that we had a safe passage to Qingdao,” Hara said, when asked if they had sailed via the Taiwan Strait.
Australia, a close U.S. ally, has sent the “HMAS Melbourne” guided-missile frigate to Qingdao, though officials declined to make the captain available for interview.
China and Australia have sparred over Australian suspicions of Chinese interference in the country’s politics and Australia’s banning of China’s Huawei Technologies Co Ltd from supplying equipment for its planned 5G broadband network.
Japan has also sent a destroyer to Qingdao, in the first visit of a Japanese navy ship to China since 2011, according to Japanese media.
Ties between China and Japan, the world’s second and third-largest economies, have been plagued by a long-running territorial dispute over a cluster of East China Sea islets and suspicion in China about Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe’s efforts to amend Japan’s pacifist constitution.
But they have sought to improve relations more recently, with Abe visiting Beijing in October, when both countries pledged to forge closer ties and signed a broad range of agreements including a $30 billion currency swap pact.
The other countries taking part include China’s close friend Russia, and three countries which have sparred with China over competing claims in the disputed South China Sea: Vietnam, Malaysia and the Philippines.
Pakistan, a very close Chinese ally, is not on the list of countries officials have provided which are sending ships to the parade.
Source: Reuters
Posted in Australia, Beijing, Captain Aditya Hara, destroyers, East China Sea islets, guided-missile frigate, HMAS Melbourne, Huawei Technologies Co Ltd, India alert, INS Kolkata, Japan’s pacifist constitution, Japanese navy ship, Japanese Prime Minister Shinzo Abe, Malaysia, naval parade, nuclear submarines, Pakistan, People's Liberation Army Navy, pla navy, Qingdao, Russia, South China Sea, stealth guided-missile destroyer, Taiwan Strait, the Philippines, Uncategorized, Vietnam, warships |
Leave a Comment »
13/04/2019
- Shanghai Zhenhua Heavy Industries now exports quay cranes, gantry cranes to more than 300 ports in 100 countries, with 70 per cent of the global market
- China International Marine Containers Group (CIMC), took a little more than a decade to become the world’s largest maker of shipping containers
Quay cranes along a berth at the Yangshan deep-water port in Shanghai on September 14, 2011. Shanghai Zhenhua Heavy Machineries, established in 1992, has grown along with the explosive development of China’s ports to control 70 per cent of the global market for cranes, loaders and lifting equipment used in ports. Photo: Xinhua
The explosive growth of China’s container ports has turned one of the most important vendors in shipping into a best-in-class industry leader, whose cranes can now be found in 300 wharves in 100 countries, with 70 per cent of the global market share.
Shanghai Zhenhua Heavy Industries, a unit of China’s state-run construction behemoth China Communications Construction Company, makes quay cranes, gantry cranes, loaders and stackers used for loading and unloading shipping containers. It also developed the infrastructure for the automated berths in Phase IV of Shanghai’s Yangshan port, and in Qingdao.
Its net profit jumped 47.6 per cent last year to 443 million yuan, while sales was little changed at 21.8 billion yuan (US$3.25 billion).
“It is a major showcase of China’s manufacturing capability,” said Sun Can, a Chuancai Securities analyst. “The company has its own technologies and is a powerful player in the global port machinery industry.”
Why China now has six of the world’s 10 busiest container ports
Established in 1992, the company was formerly known as Zhenhua Port Machinery for its speciality in making lifting equipment on the harbourfront. Taking advantage of China’s low wages, Zhenhua quickly carved out a big chunk of the global market share by selling machines at lower prices than its competitors.
The company’s former chief executive Guan Tongxian, a confessed workaholic known for his hard-driving working ethic, retired at the age of 76 in 2009, the same year that the company renamed itself to reflect its forays into marine transport and installations, as well as the construction of special steel structures including the Las Vegas Ferris wheel, the San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge and Norway’s Hardangerfjord bridge.
Rows of gantry cranes standing along the Huangpu River in Shanghai on 26 June 2002. A consortium of Chinese domestic banks provided a 17 billion yuan (US$2 billion) credit line toward the construction of Shanghai’s Yangshan deep-sea container port. Photo: AFP
Share:
Listed on the Shanghai exchange in 1997, Zhenhua’s shares have risen 41 per cent in the past 12 months, ending 2.1 per cent lower at 4.46 yuan on Friday. All three analysts who cover the stock recommend their clients either “buy” or “accumulate” the stock, expecting Zhenhua to be a major winner in China’s megaplan to build infrastructure along the old Silk Road in its Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
Another major company that has emerged with China’s rising tide was China International Marine Containers (Group), or CIMC, a unit of the state-run conglomerate China Merchants Group. Established in 1980, the company took a little more than a decade to dominate the global industry, becoming the world’s largest maker of shipping containers since 1996.
Visitors look at rows of containers at the Yangshan deep water port in Shanghai on April 6, 2006. Photo: AP
Share:
Net profit jumped 34.7 per cent to 3.38 billion yuan last year, while sales rose 22.5 per cent to 93.5 billion yuan.
The company has also diversified into land transport and vehicles, boarding bridges used in 200 airports around the world and even the development of industrial parks.
Guosen Securities said in a research report that CIMC would face lower profit margin this year amid rising raw material costs and fiercer competition from global rivals.
Its shares have risen 43.7 per cent in the past 12 months on the Shenzhen exchange to 15.20 yuan as of Friday.
Source: SCMP
Posted in Belt and Road Initiative (BRI), building frenzy, Chief Executive, China alert, China International Marine Containers Group (CIMC), containers, cranes, gantry cranes, Guan Tongxian, Hardangerfjord bridge, Huangpu River, International Marine Containers (Group), Las Vegas Ferris wheel, Norway, ports, Qingdao, quay cranes, San Francisco-Oakland Bay Bridge, Shanghai, Shanghai Zhenhua Heavy Industries, Shenzhen exchange, shipping containers, Silk Road, trade boom, Uncategorized, wharves, workaholic, world market, Yangshan deep-water port, Yangshan port, Zhenhua Port Machinery |
Leave a Comment »
07/04/2019
HANGZHOU, April 6 (Xinhua) — The city of Ningbo in east China’s Zhejiang Province will launch direct flights to Tokyo and Seoul this year, the city’s Lishe International Airport said.
Sources with the airport said it would also increase flights to domestic cities like Beijing and Qingdao in 2019.
Ningbo has one of the busiest ports in the world.
The airport is expanding its terminal facilities amid a surging passenger volume. The airport handled 11.7 million passengers in 2018, a yearly increase of 24.8 percent.
Source: Xinhua
Posted in Beijing, direct flights, East China city, Ningbo, Qingdao, Seoul, Tokyo, Uncategorized, zhejiang province |
Leave a Comment »