NEW YORK/SAN FRANCISCO (Reuters) – Amazon.com Inc (AMZN.O) has bought cameras to take temperatures of workers during the coronavirus pandemic from a firm the United States blacklisted over allegations it helped China detain and monitor the Uighurs and other Muslim minorities, three people familiar with the matter told Reuters.
China’s Zhejiang Dahua Technology Co Ltd (002236.SZ) shipped 1,500 cameras to Amazon this month in a deal valued close to $10 million, one of the people said. At least 500 systems from Dahua – the blacklisted firm – are for Amazon’s use in the United States, another person said.
The Amazon procurement, which has not been previously reported, is legal because the rules control U.S. government contract awards and exports to blacklisted firms, but they do not stop sales to the private sector.
However, the United States “considers that transactions of any nature with listed entities carry a ‘red flag’ and recommends that U.S. companies proceed with caution,” according to the Bureau of Industry and Security’s website. Dahua has disputed the designation.
The deal comes as the U.S. Food and Drug Administration warned of a shortage of temperature-reading devices and said it wouldn’t halt certain pandemic uses of thermal cameras that lack the agency’s regulatory approval. Top U.S.-based maker FLIR Systems Inc (FLIR.O) has faced an up to weeks-long order backlog, forcing it to prioritize products for hospitals and other critical facilities.
Amazon declined to confirm its purchase from Dahua, but said its hardware complied with national, state and local law, and its temperature checks were to “support the health and safety of our employees, who continue to provide a critical service in our communities.”
The company added it was implementing thermal imagers from “multiple” manufacturers, which it declined to name. These vendors include Infrared Cameras Inc, which Reuters previously reported, and FLIR, according to employees at Amazon-owned Whole Foods who saw the deployment. FLIR declined to comment on its customers.
Dahua, one of the biggest surveillance camera manufacturers globally, said it does not discuss customer engagements and it adheres to applicable laws. Dahua is committed “to mitigate the spread of the COVID-19” through technology that detects “abnormal elevated skin temperature — with high accuracy,” it said in a statement.
The U.S. Department of Commerce, which maintains the blacklist, declined comment. The FDA said it would use discretion when enforcing regulations during the public health crisis as long as thermal systems lacking compliance posed no “undue risk” and secondary evaluations confirmed fevers.
Dahua’s thermal cameras have been used in hospitals, airports, train stations, government offices and factories during the pandemic. International Business Machines Corp (IBM.N) placed an order for 100 units, and the automaker Chrysler placed an order for 10, one of the sources said. In addition to selling thermal technology, Dahua makes white-label security cameras resold under dozens of other brands such as Honeywell, according to research and reporting firm IPVM.
Honeywell said some but not all its cameras are manufactured by Dahua, and it holds products to its cybersecurity and compliance standards. IBM and Chrysler’s parent Fiat Chrysler Automobiles NV (FCHA.MI) did not comment.
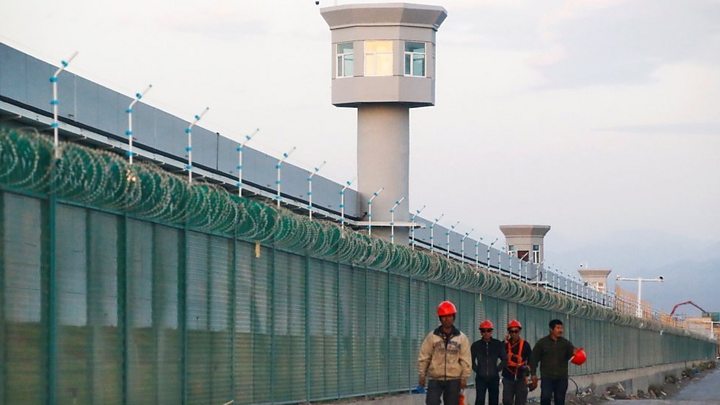
The Trump Administration added Dahua and seven other tech firms last year to the blacklist for acting against U.S. foreign policy interests, saying they were “implicated” in “China’s campaign of repression, mass arbitrary detention, and high-technology surveillance against Uighurs, Kazakhs, and other members of Muslim minority groups.”
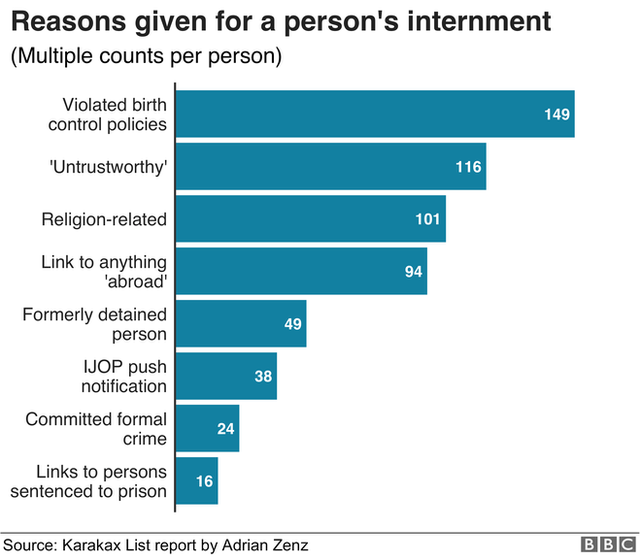
More than one million people have been sent to camps in the Xinjiang region as part of China’s campaign to root out terrorism, the United Nations has estimated.
Dahua has said the U.S. decision lacked “any factual basis.” Beijing has denied mistreatment of minorities in Xinjiang and urged the United States to remove the companies from the list.
A provision of U.S. law, which is scheduled to take effect in August, will also bar the federal government from starting or renewing contracts with a company using “any equipment, system, or service” from firms including Dahua “as a substantial or essential component of any system.”
Amazon’s cloud unit is a major contractor with the U.S. intelligence community, and it has been battling Microsoft Corp (MSFT.O) for an up to $10 billion deal with the Pentagon.
Top industry associations have asked Congress for a year-long delay because they say the law would reduce supplies to the government dramatically, and U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo said last week that policies clarifying the implementation of the law were forthcoming.
FACE DETECTION & PRIVACY
The coronavirus has infected staff from dozens of Amazon warehouses, ignited small protests over allegedly unsafe conditions and prompted unions to demand site closures. Temperature checks help Amazon stay operational, and the cameras – a faster, socially distant alternative to forehead thermometers – can speed up lines to enter its buildings. Amazon said the type of temperature reader it uses varies by building.
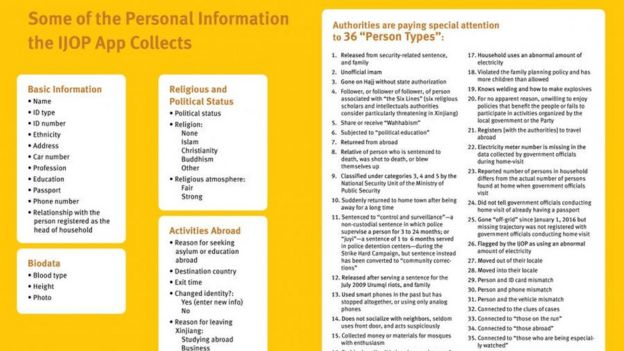
To see if someone has a fever, Dahua’s camera compares a person’s radiation to a separate infrared calibration device. It uses face detection technology to track subjects walking by and make sure it is looking for heat in the right place.
An additional recording device keeps snapshots of faces the camera has spotted and their temperatures, according to a demonstration of the technology in San Francisco. Optional facial recognition software can fetch images of the same subject across time to determine, for instance, who a virus patient may have been near in a line for temperature checks.
Amazon said it is not using facial recognition on any of its thermal cameras. Civil liberties groups have warned the software could strip people of privacy and lead to arbitrary apprehensions if relied on by police. U.S. authorities have also worried that equipment makers like Dahua could hide a technical “back door” to Chinese government agents seeking intelligence.
In response to questions about the thermal systems, Amazon said in a statement, “None of this equipment has network connectivity, and no personal identifiable information will be visible, collected, or stored.”
Dahua made the decision to market its technology in the United States before the FDA issued the guidance on thermal cameras in the pandemic. Its supply is attracting many U.S. customers not deterred by the blacklist, according to Evan Steiner, who sells surveillance equipment from a range of manufacturers in California through his firm EnterActive Networks LLC.
“You’re seeing a lot of companies doing everything that they possibly can preemptively to prepare for their workforce coming back,” he said.
Source: Reuters