Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
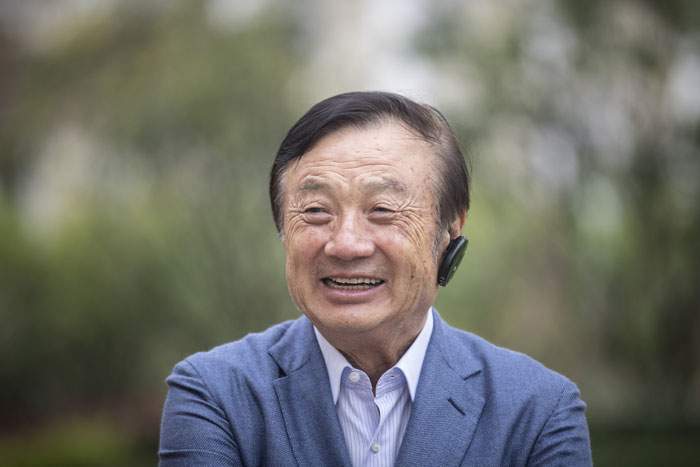
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESWhen I spoke to him on the phone, he had just returned home to his village in the northern state of Rajasthan from neighbouring Gujarat, where he worked as a mason.
In the rising heat, Goutam Lal Meena had walked on macadam in his sandals. He said he had survived on water and biscuits.
In Gujarat, Mr Meena earned up to 400 rupees ($5.34; £4.29) a day and sent most of his earnings home. Work and wages dried up after India declared a 21-day lockdown with four hours notice on the midnight of 24 March to prevent the spread of coronavirus. (India has reported more than 1,000 Covid-19 cases and 27 deaths so far.) The shutting down of all transport meant that he was forced to travel on foot.
“I walked through the day and I walked through the night. What option did I have? I had little money and almost no food,” Mr Meena told me, his voice raspy and strained.
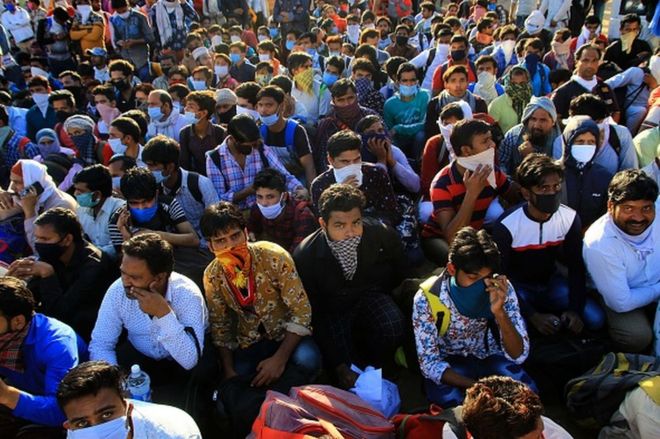
He was not alone. All over India, millions of migrant workers are fleeing its shuttered cities and trekking home to their villages.
These informal workers are the backbone of the big city economy, constructing houses, cooking food, serving in eateries, delivering takeaways, cutting hair in salons, making automobiles, plumbing toilets and delivering newspapers, among other things. Escaping poverty in their villages, most of the estimated 100 million of them live in squalid housing in congested urban ghettos and aspire for upward mobility.
 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESLast week’s lockdown turned them into refugees overnight. Their workplaces were shut, and most employees and contractors who paid them vanished.
Sprawled together, men, women and children began their journeys at all hours of the day last week. They carried their paltry belongings – usually food, water and clothes – in cheap rexine and cloth bags. The young men carried tatty backpacks. When the children were too tired to walk, their parents carried them on their shoulders.
They walked under the sun and they walked under the stars. Most said they had run out of money and were afraid they would starve. “India is walking home,” headlined The Indian Express newspaper.
The staggering exodus was reminiscent of the flight of refugees during the bloody partition in 1947. Millions of bedraggled refugees had then trekked to east and west Pakistan, in a migration that displaced 15 million people.
 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESThis time, hundreds of thousands of migrant workers are desperately trying to return home in their own country. Battling hunger and fatigue, they are bound by a collective will to somehow get back to where they belong. Home in the village ensures food and the comfort of the family, they say.
Clearly, a lockdown to stave off a pandemic is turning into a humanitarian crisis.
Among the teeming refugees of the lockdown was a 90-year-old woman, whose family sold cheap toys at traffic lights in a suburb outside Delhi.
Kajodi was walking with her family to their native Rajasthan, some 100km (62 miles) away. They were eating biscuits and smoking beedis, – traditional hand-rolled cigarettes – to kill hunger. Leaning on a stick, she had been walking for three hours when journalist Salik Ahmed met her. The humiliating flight from the city had not robbed her off her pride. “She said she would have bought a ticket to go home if transport was available,” Mr Ahmed told me.
- What India can learn from 1918 flu to fight Covid-19
- India gambles on lockdown to save millions
- Coronavirus: Why is India testing so little?
Others on the road included a five-year-old boy who was on a 700km (434 miles) journey by foot with his father, a construction worker, from Delhi to their home in Madhya Pradesh state in central India. “When the sun sets we will stop and sleep,” the father told journalist Barkha Dutt. Another woman walked with her husband and two-and-a-half year old daughter, her bag stuffed with food, clothes and water. “We had a place to stay but no money to buy food,” she said.
Then there was Rajneesh, a 26-year-old automobile worker who walking 250km (155 miles) to his village in neighbouring Uttar Pradesh. It would take him four days, he reckoned. “We will die walking before coronavirus hits us,” the man told Ms Dutt.
He was not exaggerating. Last week, a 39-year-old man on a 300km (186 miles) trek from Delhi to Madhya Pradesh complained of chest pain and exhaustion and died; and a 62-year-old man, returning from a hospital by foot in Gujarat, collapsed outside his house and died. Four other migrants, turned away at the borders on their way to Rajasthan from Gujarat, were mowed down by a truck on a dark highway.
As the crisis worsened, state governments scrambled to arrange transport, shelter and food.
 Image copyright SALIK AHMED/OUTLOOK
Image copyright SALIK AHMED/OUTLOOKBut trying to transport them to their villages quickly turned into another nightmare. Hundreds of thousands of workers were pressed against each other at a major bus terminal in Delhi as buses rolled in to pick them up.
Delhi chief minister Arvind Kejriwal implored the workers not to leave the capital. He asked them to “stay wherever you are, because in large gatherings, you are also at risk of being infected with the coronavirus.” He said his government would pay their rent, and announced the opening of 568 food distribution centres in the capital. Prime Minister Narendra Modi apologised for the lockdown “which has caused difficulties in your lives, especially the poor people”, adding these “tough measures were needed to win this battle.”
Whatever the reason, Mr Modi and state governments appeared to have bungled in not anticipating this exodus.
Mr Modi has been extremely responsive to the plight of Indian migrant workers stranded abroad: hundreds of them have been brought back home in special flights. But the plight of workers at home struck a jarring note.
“Wanting to go home in a crisis is natural. If Indian students, tourists, pilgrims stranded overseas want to return, so do labourers in big cities. They want to go home to their villages. We can’t be sending planes to bring home one lot, but leave the other to walk back home,” tweeted Shekhar Gupta, founder and editor of The Print.
 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESThe city, says Chinmay Tumbe, author of India Moving: A History of Migration, offers economic security to the poor migrant, but their social security lies in their villages, where they have assured food and accommodation. “With work coming to a halt and jobs gone, they are now looking for social security and trying to return home,” he told me.
Also there’s plenty of precedent for the flight of migrant workers during a crisis – the 2005 floods in Mumbai witnessed many workers fleeing the city. Half of the city’s population, mostly migrants, had also fled the city – then Bombay – in the wake of the 1918 Spanish flu.
When plague broke out in western India in 1994 there was an “almost biblical exodus of hundreds of thousands of people from the industrial city of Surat [in Gujarat]”, recounts historian Frank Snowden in his book Epidemics and Society.
Half of Bombay’s population deserted the city, during a previous plague epidemic in 1896. The draconian anti-plague measures imposed by the British rulers, writes Dr Snowden, turned out to be a “blunt sledgehammer rather than a surgical instrument of precision”. They had helped Bombay to survive the epidemic, but “the fleeing residents carried the disease with them, thereby spreading it.”
More than a century later, that same fear haunts India today. Hundreds of thousands of the migrants will eventually reach home, either by foot, or in packed buses. There they will move into their joint family homes, often with ageing parents. Some 56 districts in nine Indian states account for half of inter-state migration of male workers, according to a government report. These could turn out to be potential hotspots as thousands of migrants return home.
 Image copyright GETTY IMAGES
Image copyright GETTY IMAGESPartha Mukhopadhyay, a senior fellow at Delhi’s Centre for Policy Research, suggests that 35,000 village councils in these 56 potentially sensitive districts should be involved to test returning workers for the virus, and isolate infected people in local facilities.
In the end, India is facing daunting and predictable challenges in enforcing the lockdown and also making sure the poor and homeless are not fatally hurt. Much of it, Dr Snowden told me, will depend on whether the economic and living consequences of the lockdown strategy are carefully managed, and the consent of the people is won. “If not, there is a potential for very serious hardship, social tension and resistance.” India has already announced a $22bn relief package for those affected by the lockdown.
The next few days will determine whether the states are able to transport the workers home or keep them in the cities and provide them with food and money. “People are forgetting the big stakes amid the drama of the consequences of the lockdown: the risk of millions of people dying,” says Nitin Pai of Takshashila Institution, a prominent think tank.
“There too, likely the worst affected will be the poor.”
Source: The BBC