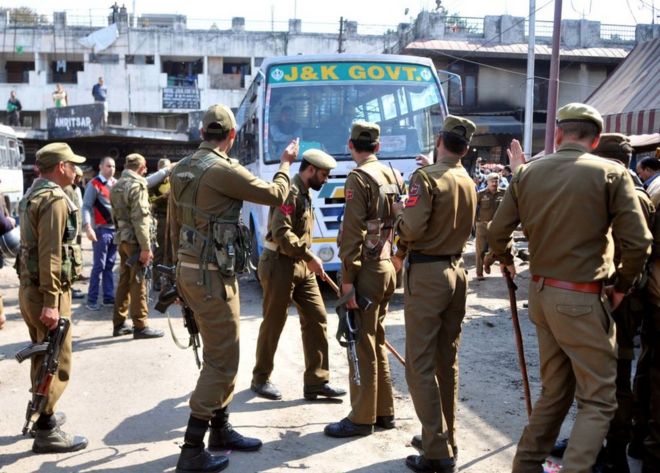
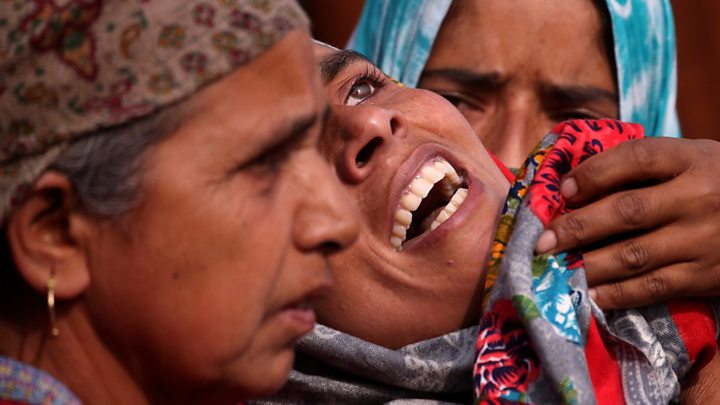
SRINAGAR/NEW DELHI (Reuters) – Authorities in Indian Kashmir have arrested nearly 4,000 people since the scrapping of its special status last month, government data shows, the most clear evidence yet of the scale of one of the disputed region’s biggest crackdowns.
Muslim-majority Kashmir, claimed by both India and Pakistan, has been in turmoil since India stripped its portion of the region of its autonomy and statehood on Aug. 5, leading to clashes between security forces and residents and inflaming tension with Pakistan.
India said the removal of the status that its part of Kashmir has held since independence from Britain in 1947 would help integrate it into the Indian economy, to the benefit of all.
In an attempt to stifle the protests that the reform sparked in Kashmir, India cut internet and mobile services and imposed curfew-like restrictions in many areas.
It has also arrested more than 3,800 people, according to a government report dated Sept. 6 and seen by Reuters, though about 2,600 have since been released.
A spokeswoman for India’s interior ministry did not respond to a request for comment. Neither did Jammu and Kashmir police.
It was not clear on what basis most of the people were being held but an Indian official said some were held under the Public Safety Act, a law in Jammu and Kashmir state that allows for detention for up to two years without charge.
The data for the first time shows the extent of the detentions, as well as indicating who was picked up and where.
More than 200 politicians, including two former chief ministers of the state were arrested, along with more than 100 leaders and activists from an umbrella organisation of pro-separatist political groups.
The bulk of those arrested – more than 3,000 – were listed as “stone pelters and other miscreants”. On Sunday, 85 detainees were shifted to a prison in Agra in northern India, a police source said.
Rights group Amnesty International said the crackdown was “distinct and unprecedented” in the recent history of the region and the detentions had contributed to “widespread fear and alienation”.
“The communication blackout, security clampdown and detention of the political leaders in the region has made it worse,” said Aakar Patel, head of Amnesty International India.
‘RIGHT TO LIFE’
India says the detentions are necessary to maintain order and prevent violence, and points to the relatively limited number of casualties compared with previous bouts of unrest.
The government says only one person is confirmed to have died compared with dozens in 2016, when the killing of a militant leader sparked widespread violence.
“The right to life is the most important human right,” India’s national security adviser Ajit Doval told reporters recently.
The report contains data from the 13 police districts that make up the Kashmir Valley, the most populous part of the Himalayan region where the main city of Srinagar is located.
The largest number of arrests have been in Srinagar, the data shows, at nearly 1,000. Earlier unrest often centred in rural areas.
Of the detained political leaders, more than 80 were from the People’s Democratic Party, formerly in coalition in Jammu and Kashmir state with the ruling Bharatiya Janata Party.
About 70 are from the National Conference, which has for years dominated politics in Indian Kashmir, and more than a dozen from India’s main opposition Congress party.
Police also arrested more than 150 people accused of association with militant groups fighting Indian rule.
An Indian official said it was likely that more than 1,200 people were still held, including all the high-profile politicians and separatists mentioned in the report, while dozens more are being arrested every day.
In the 24 hours before the report was compiled, more than two dozen people were arrested, mainly on suspicion of throwing stones at troops, the data showed.
The data did not include those under informal house arrest, nor people detained in a round-up of separatists that began in February after a bomb attack by a Pakistan-based militant group on Indian troops.
Days before India’s move to strip Kashmir of special status, one prominent separatist leader told Reuters that more than 250 people with links to the movement were already in detention.
Source: Reuters